Aegean / Greek / Etruscan / Roman Civilization
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms


Tholos tomb
A beehive-shaped burial structure with a false dome created by corbelling
Independent city-states which composed Greece
Period relating to King Minos


Greek word for 'male youth.' An Archaic Greek statue of a standing, nude youth.

Greek statue of a young woman, standing and clothed in long loose robes.
A style of sculpture characterized by movement; towards increasing naturalness and freedom of form; use of lost wax method and bronze casting.
Contrapposto
a pose in which a figure's weight is shifted to one leg, creating an S-shaped curve.
Hellenic Art
Pertaining to ancient Greek history, culture and art before the time of Alexander the Great
Style of Greek pottery characterized by rectilinear meander patterns.
Style of Greek pottery characterized by assimilation of Eastern iconography.

Black-figure pottery
A style during Archaic period; characterized by black silhouettes of figures and designs painted on clay vessels; a black slip was applied to the clay, which turned black during firing
Black and red figure techniques
A style or technique of ancient Greek to decorate fine pottery

White-ground technique
A style during Classical period; refers to the application of a white clay slip on the surface of a vessel before adding figure decoration
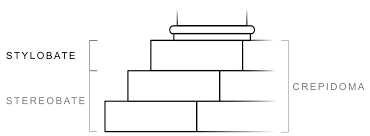
Column itself composed of individual sections (drums) and concave groove (flutes), with a base and capital.

Flat, curved element like a plate with rounded sides

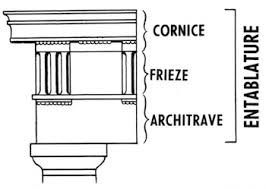
Part of entablature; plain, horizontal member above a capital
Part of entablature; a band above the architrave consisting of metopes and triglyphs
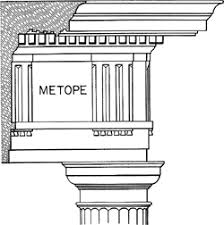
Part of frieze; Slabs of stone either plane or with relief sculpture on an entablature
Part of frieze; short band under the triglyph
Part of entablature; projects above the frieze to protect it from weather

type of cornice that is low and slanting
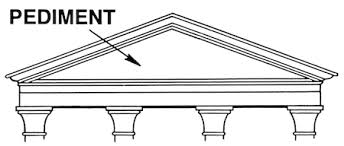
a triangular gable with raked cornices on each side
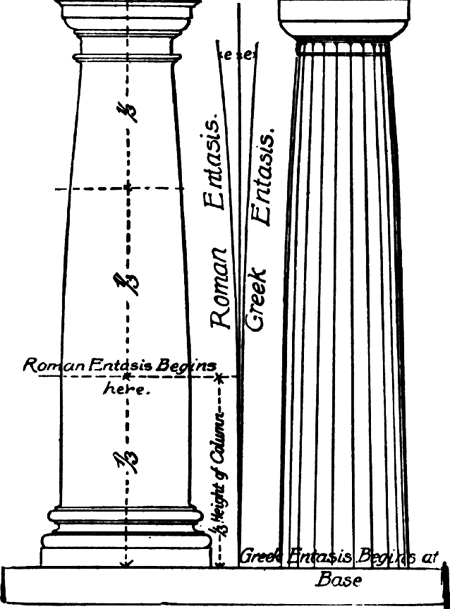
Technique applied on columns which do not taper in a straight line but bulge outward

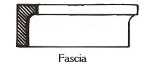
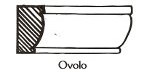
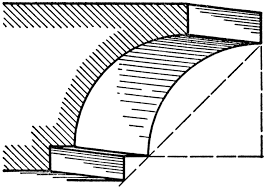
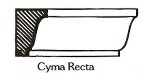
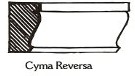
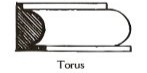
(Moulding) Convex surface; semi-circle; with guilloche

Telamon
Male figure as columns; also called an atlas
Agora

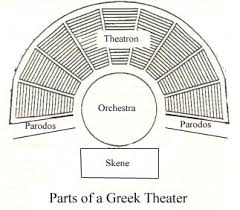
(Greek architecture) For plays and performances; consist of stone seat wrapped around the orchestra and face the skene (stage building)
(Part of Greek Theater) a structure serving as backdrop or dressing room
(Part of Greek Theater) Entrance or Exit (exodus) on each side of the orchestra
(Greek architecture) Senate house for elected officials
(Greek architecture) Council house; covered meeting place for elected officials



(Roman art) good or true fresco; painting on wet plaster
(Roman art) Dry fresco
A Roman architect who established certain rules for standardizing Greek orders for architecture

(Forms of Roman architecture) Counterpart of the agora composed of temples, triumphal arches, pillars of victories, basilica, senate and shops
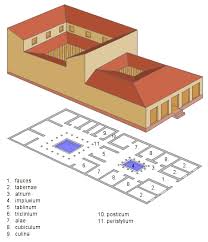
(Roman architecture) Middle class house

(Roman architecture) Blocks of flats used as a shop and apartment.

(Roman architecture) Upper class house
(Roman architecture) Smaller than a colosseum

(Roman architecture) Large reservoir for lead pipes to transport water to towns
(Roman architecture) Roman law court which eventually became a hall of justice and commercial exchange
(Roman architecture) Public bath. Example: Baths of Caracalla
(Part of a thermae) hot room
(Part of a thermae) warm room
(Part of a thermae) cold room
(Part of a thermae) dry sweating room
(Part of a thermae) oiling and shampooing
(Part of a thermae) dressing room

(Roman architecture) Also called a Flavian amphitheater built for games.

(Roman architecture) a large, free-standing archway built to commemorate military triumphs designed with relief

(Roman architecture) a monument in the form of column erected in memory of a victorious battle

(Roman architecture) Great marble monument during the reign of Augustus
A large vessel with two handles for mixing wine and water.