Lecture 7 BCH 3120 - ATP Synthesis + Oxidative Phosphorylation uncoupling
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
ATP synthase
Complex V, converts energy from proton gradient into ATP
ATP Synthase Structure
F0F1 complex
F0 unit of ATP synthase
portion of ATP synthase embedded in the membrane. Proton turbine
- 8-15 c subunits (c-ring)
- a subunit (channel)
- 2 b subunits
F1 unit of ATP synthase
Subunits not bound to the membrane. ATP synthase activity
- (𝛼β)3 (3 dimers)
- 𝛾
- 𝛿
- ε
Binding change model of ATP synthase
Since the 𝛾 subunit is asymmetric, when it turns it will make different contacts with 𝛼β subunits, causing the three dimers to be in different conformation depending on the rotation of 𝛾
Rotor - ATP synthase
moving units
- c-ring
- 𝛿
- ε
- 𝛾
Stator
Stationary units
- a
- b
- the 3 𝛼β dimers
Flow of protons through ATP synthase
- protons enter through the channel (subunit a)
- proton binds 1 c subunit
- this causes the c-ring to turn
- when the proton makes a full turn it exits the a channel into the matrix
Each c subunit can bind --- proton(s)?
one
αβ dimer conformations
Open → Loose → Tight
O conformation
open site, releases ATP
L conformation
loose binding to ADP
T conformation
tight binding to ATP
ATP is formed in which conformation?
T conformation
Proton to ATP ratio
4 protons are needed to generate 1 ATP
- (1 used to transport Pi into the matrix and 3 to drive the ATP synthase)
NADH ATP yield
2.5 ATP
FADH2 ATP yield
1.5 ATP
Why does NADH need a shuttle?
The inner mitochondrial membrane is not permeable to NADH
2 NADH shuttles
1. Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle
2. Malate-Aspartate shuttle
Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle is used where in the body?
muscles and brain
malate-aspartate shuttle is used where in the body?
liver, kidney, and heart
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 1
Reduction of OAA into malate by malate dehyrogenase using NADH
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 2
Transport of malate into mitochondrial matrix by the malate-𝛼-ketoglutarate transporter
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 3
oxidation of malate into OAA by malate dehydrogenase using NAD+
(NADH now in the mitochondria)
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 4
transamination of OAA into asp by the aspartate aminotransferase (transaminase)
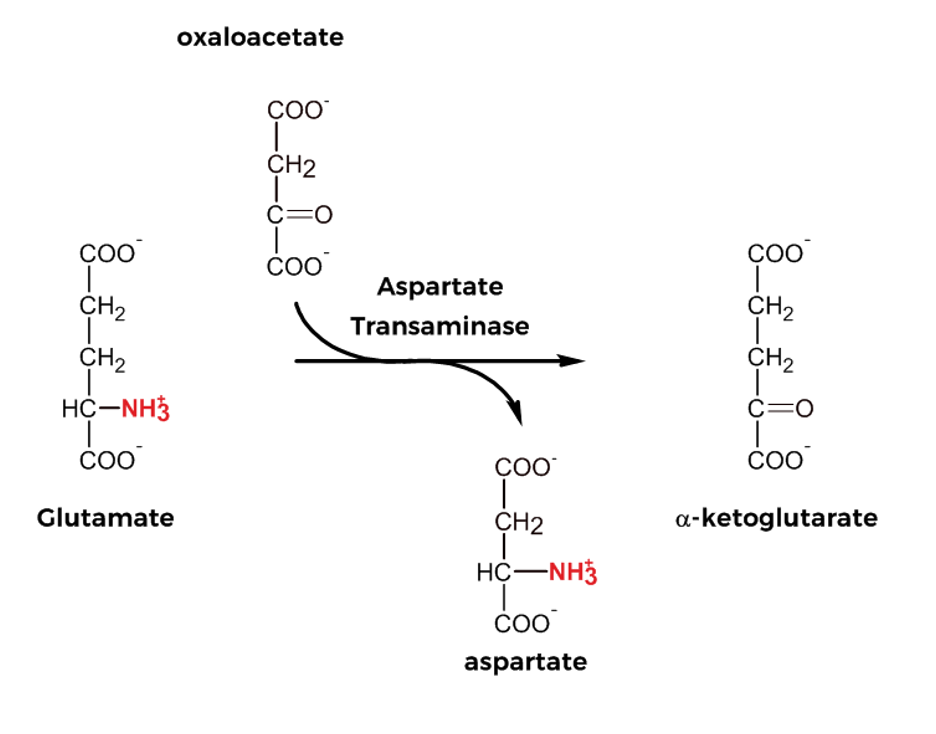
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 5
transport of asp outside the mitochondria by the glutamate-aspartate transporter
Malate-Aspartate shuttle - step 6
transamination of asp into OAA into asp by transaminase
Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle - step 1
DHAP is reduced to glycerol 3-phosphate by the cytosolic glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase using electrons from NADH
Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle - step 2
glycerol 3-phosphate enters the intermembrane space
Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle - step 3
Glycerol 3-phosphate is re-oxidized into DHAP by the mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Where are electrons from the Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle stored?
On FAD to form FADH2
What complexes of the ETC does the Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle bybass?
Complex I, and II
Oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling
when protons are returned to the matrix by other means then the ATP synthase
What are the 2 types of oxidative phosphorylation uncouplers?
Chemical uncouplers
Endogenous uncoupling proteins
Thermogenin (UCP1)
endogenous uncoupling protein
- found in inner mitochondrial membrane
Where is thermogenin expressed?
Brown adipose tissue
What does thermogenin allow?
Production of heat through proton dissipation
- non-shivering heat production
2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP)
chemical uncoupler
- transports protons across the membrane; able to cross it easily
DNP allows for?
heat production
DNP side effects
blindness, hyperthermia, death
Complex I inhibitor
Rotenone
Rotenone use
pesticide, insecticide, etc.
Complex III inhibitor
Antimycin A
Complex IV inhibitor
cyanide and carbon monoxide