Oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons.
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gnbuTl2ariI&list=PL9IouNCPbCxXDlRtCQEG0cGehBvJ7t9Pf&index=4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Whats the other definitions for oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation is the loss of electrons
Reduction is the gain of electrons.
Heres an example:
Mg → Mg+2 + 2e-
Magnesium atom produced magnesium ion and 2 electrons.
The magnesium atom has been oxidised as it has lost electrons.
S + 2e- → S2-
Sulfr atom reacts with 2 electrons to produce a sulfide ion.
The sulfur atom has been reduced as it has gained electrons.
Whats easy way to remember oxidation / reduction
O I L = Oxidation is Loss
R I G= Reduction is Gain.
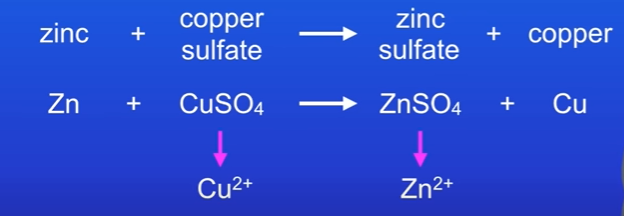
Identify in the reaction below which element has been oxidised and which has been reduced
We start with Zn, and end with Zn+2, and in order for this to happen, the zinc atom must have lost 2 electrons like this : Zn → Zn2+ + 2e- and therefore zinc atom was oxidised.
Looking at the copper, we start with Cu2+ and make copper atom Cu. For this to happen, copper must have gained 2 electrons, in other words it was reduced. Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
a
a