Cells and Systems Grade 8
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
All living things
-are made of cell
-need energy
-can reproduce
-adapt to their environment
-grow and develop
-respond to their environment

Cell
basic unit of life
Energy
the ability to make things move or change
Nutrients
substances that provide the energy and material organisms need to grow
Metabolism
the sum of all life processes that take place in to cell
Stimulus
any change in an organisms environment
Response
an organism's reaction to a stimulus
Reproduction
the process by which all living things come from other living lines
Adaptations
physical characteristics or behaviours of a species that increase the chance of survival
Structure
parts of an organism that performs a certain task
Function
the purpose or task of a structure
Organ
a group of tissues that work together to perform a function
Organ System
a group of organs that work together to perform a certain task
Mycoplasma
type of microscopic organism, smallest know to man
Multicellular
made of more than one cell
Unicellular
made of one cell
Diffusion
the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
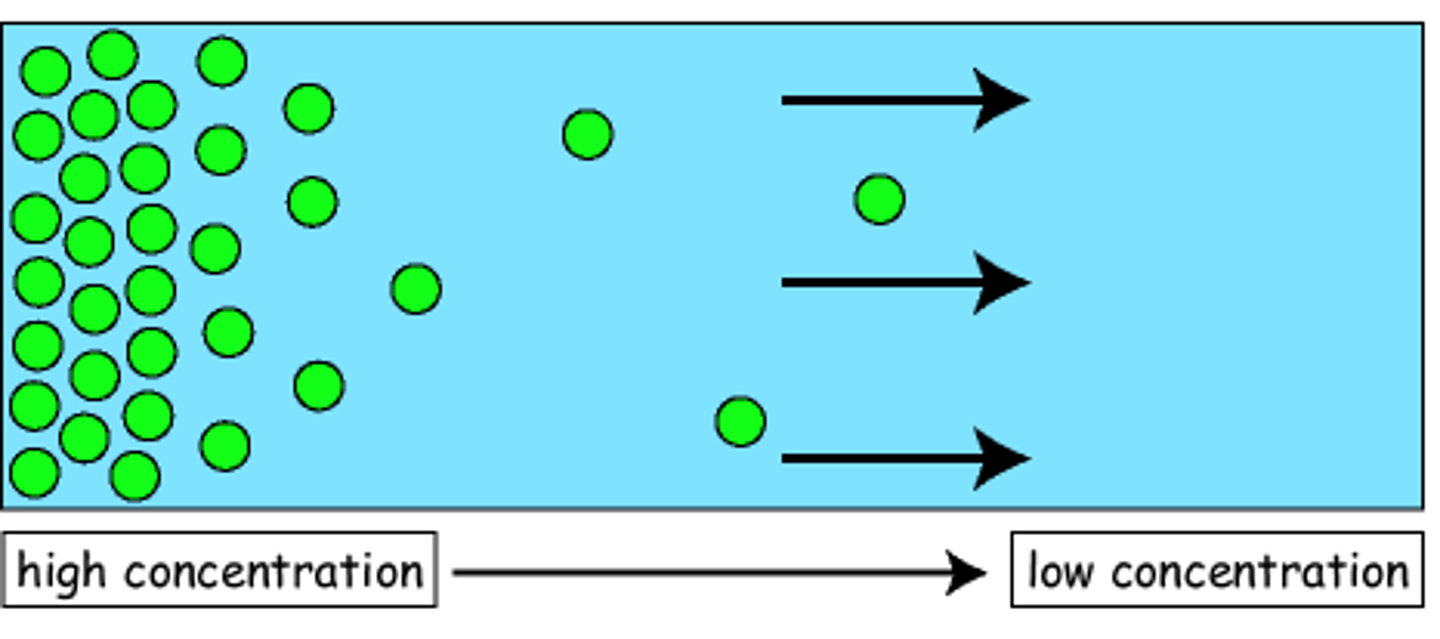
Osmosis
a type of diffusion through a selectively permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane
describes a type of membrane that only allows certain particle through
Specialized Cells
cells that have specific structures to help them perform certain tasks
Connective Tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts; blood, fat, cartilage, bones, tendons
Epitherial Tissue
covers the surface of the body and internal organ and lines inside or some organs (intestine)
Nervous Tissue
tissue of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Muscle Tissue
allows for movement
Striated Muscle Tissue
type of muscle tissue that allow movement
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
type of muscle tissue that pumps blood through the heart
Smooth Muscle Tissue
moves food along your intestine
Mechanical Digestion
physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces

Chemical Digestion
breakdown of large food particles into smaller particle by enzymes
Villi
small fingerlike projections on the walls of the small intestines that absorb nutrients
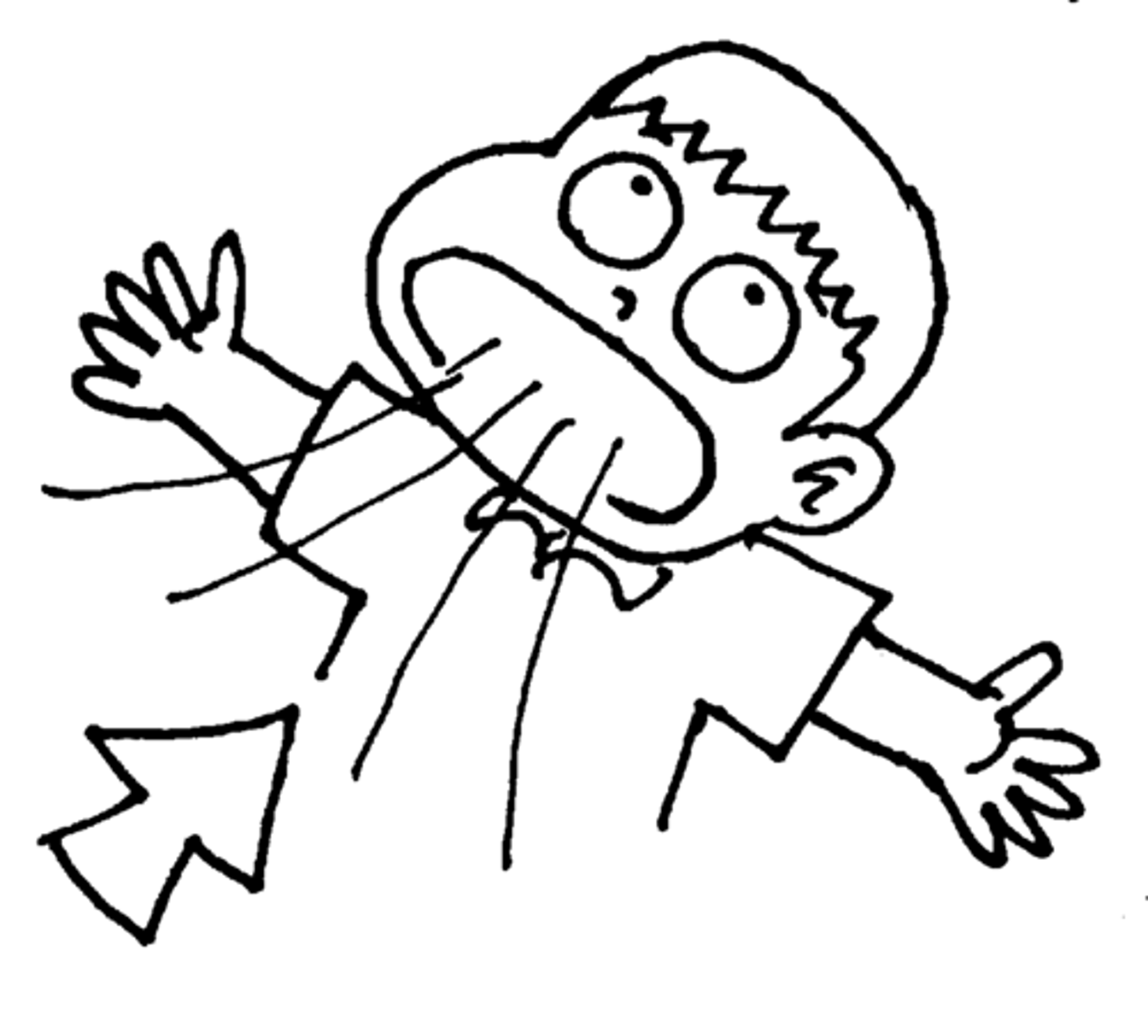
Inhalation
-ribs and diaphragm contract
-ribs pull up
-diaphragm moves downward
-chest and lung size increase

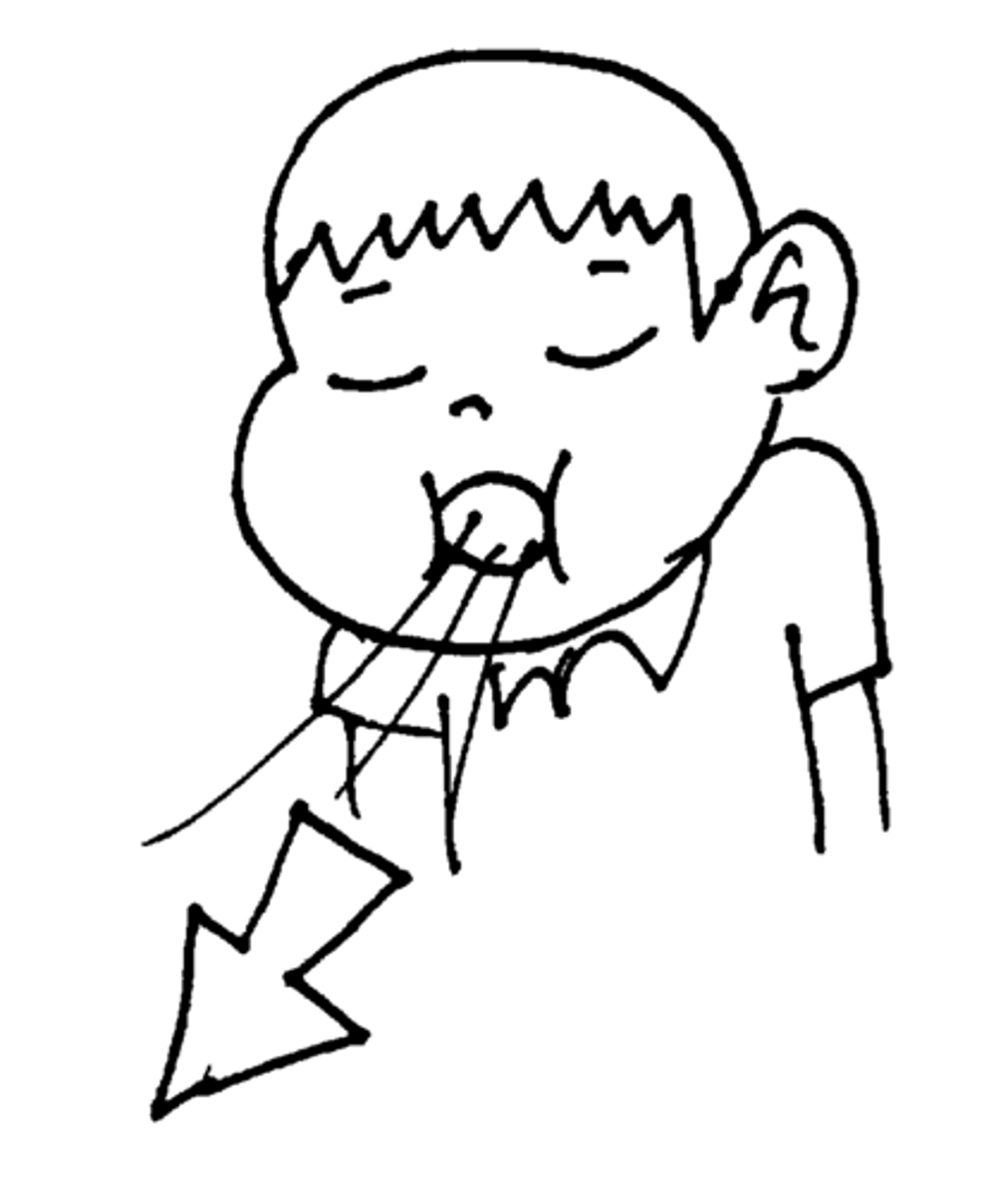
Exhalation
-ribs and diaphragm relax
-ribs move downward
-diaphragm moves up
-chest and lung size decrease

Red Blood Cells
small, pliable cells that have no nucleus and are specialized for carrying oxygen
White Blood Cells
blood cells specialized to fight infection
Platelets
cell fragments in the blood that helps stop bleeding from cuts
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease that produced rash and causes high fever and can cause blindness or death
Who was Galen?
the first person to observe internal body structures and how they worked
What did Galen map in the body?
major nerves
What did Galen believe about the liver?
he thought the liver was responsible for heating the body because of its size and amount of nerves
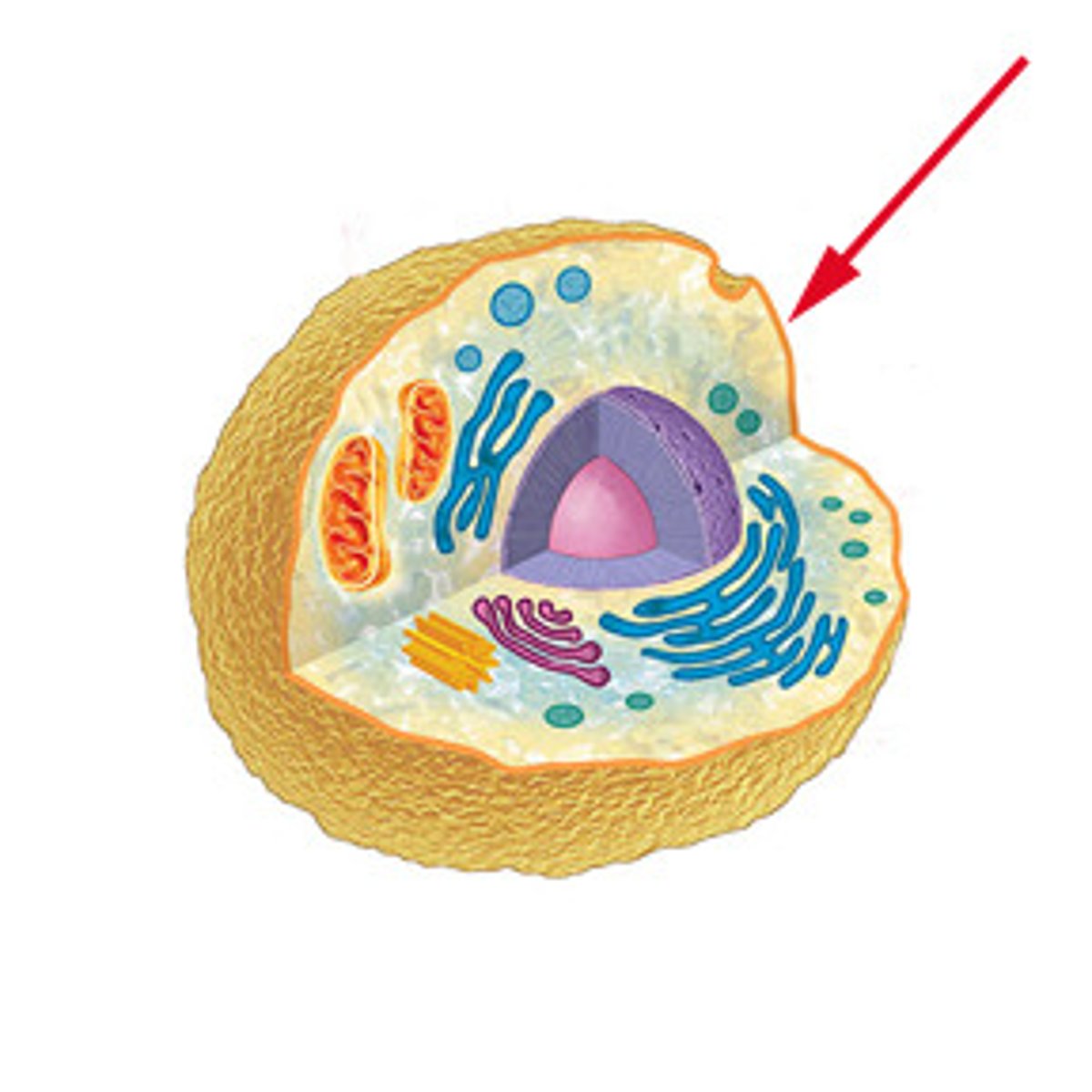
Cell Membrane
surround and protects the cell (controlled gateway)
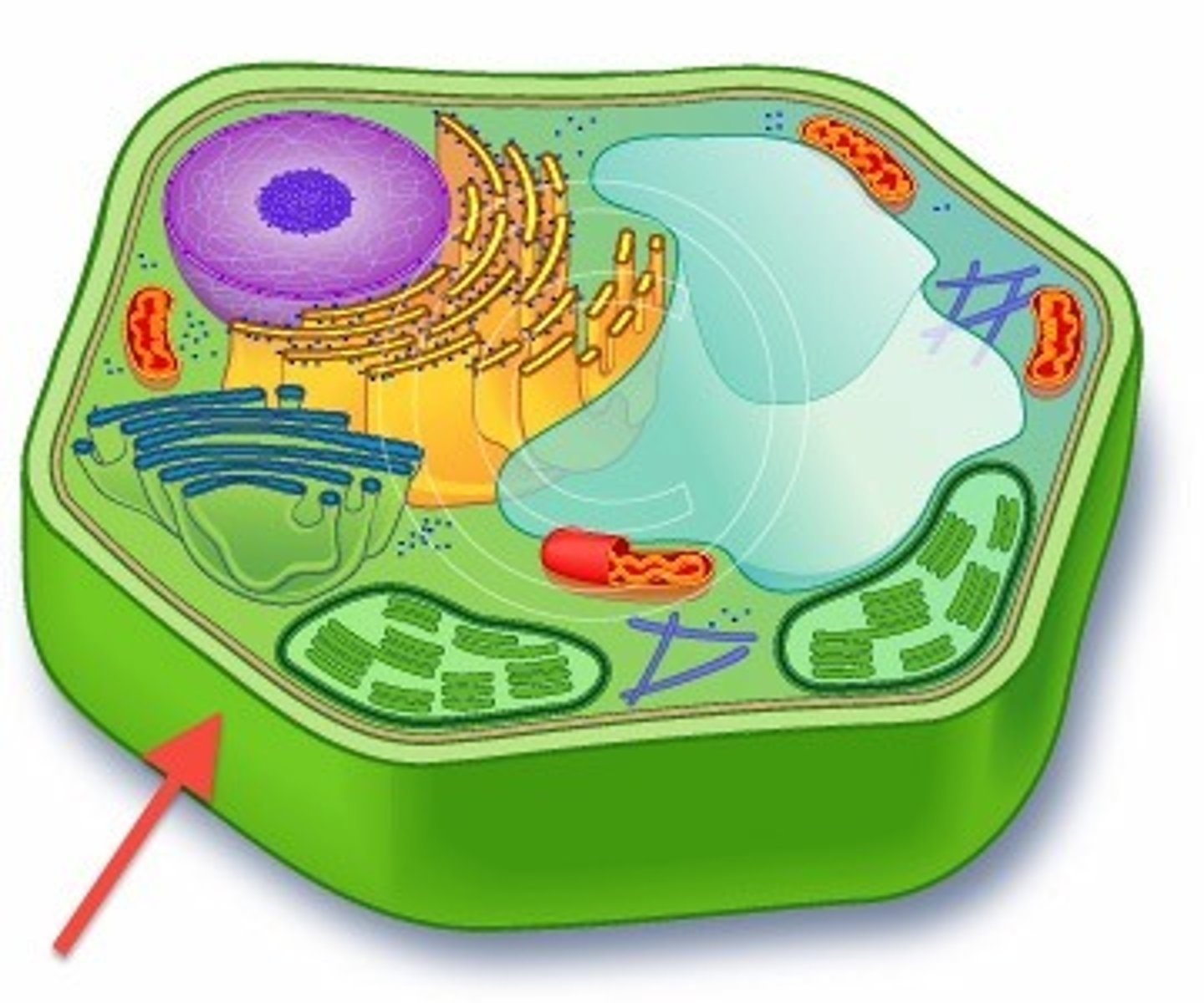
Cell Wall
very rigid and provides support for plant/fungi cells (rigid covering)
- plant cell ONLY
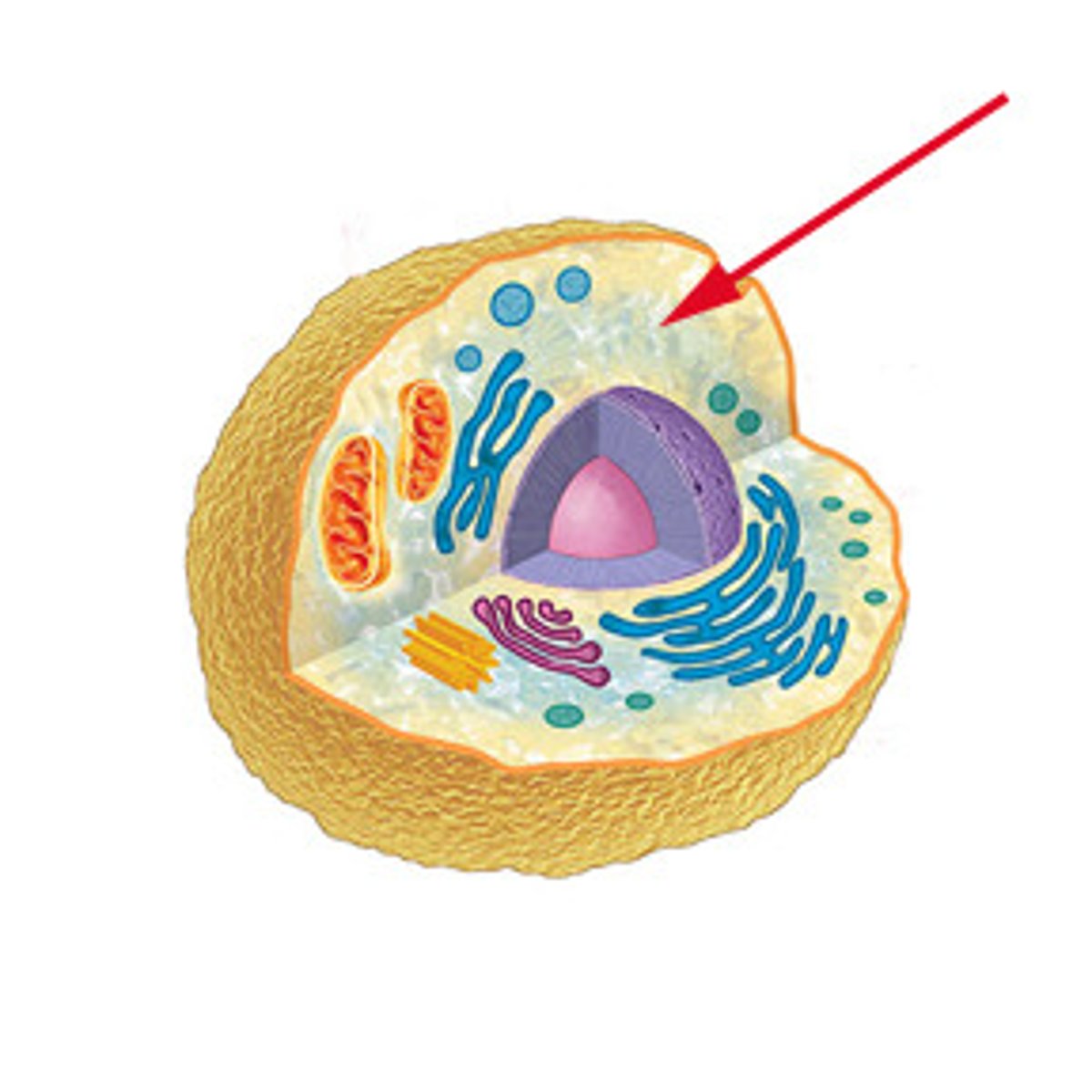
Cytoplasm
holds organelles in place
Nuclueus
controls all cell activities (brain)
Vacuoles
membrane bound sac - acts as storage for waste or surplus (storage)
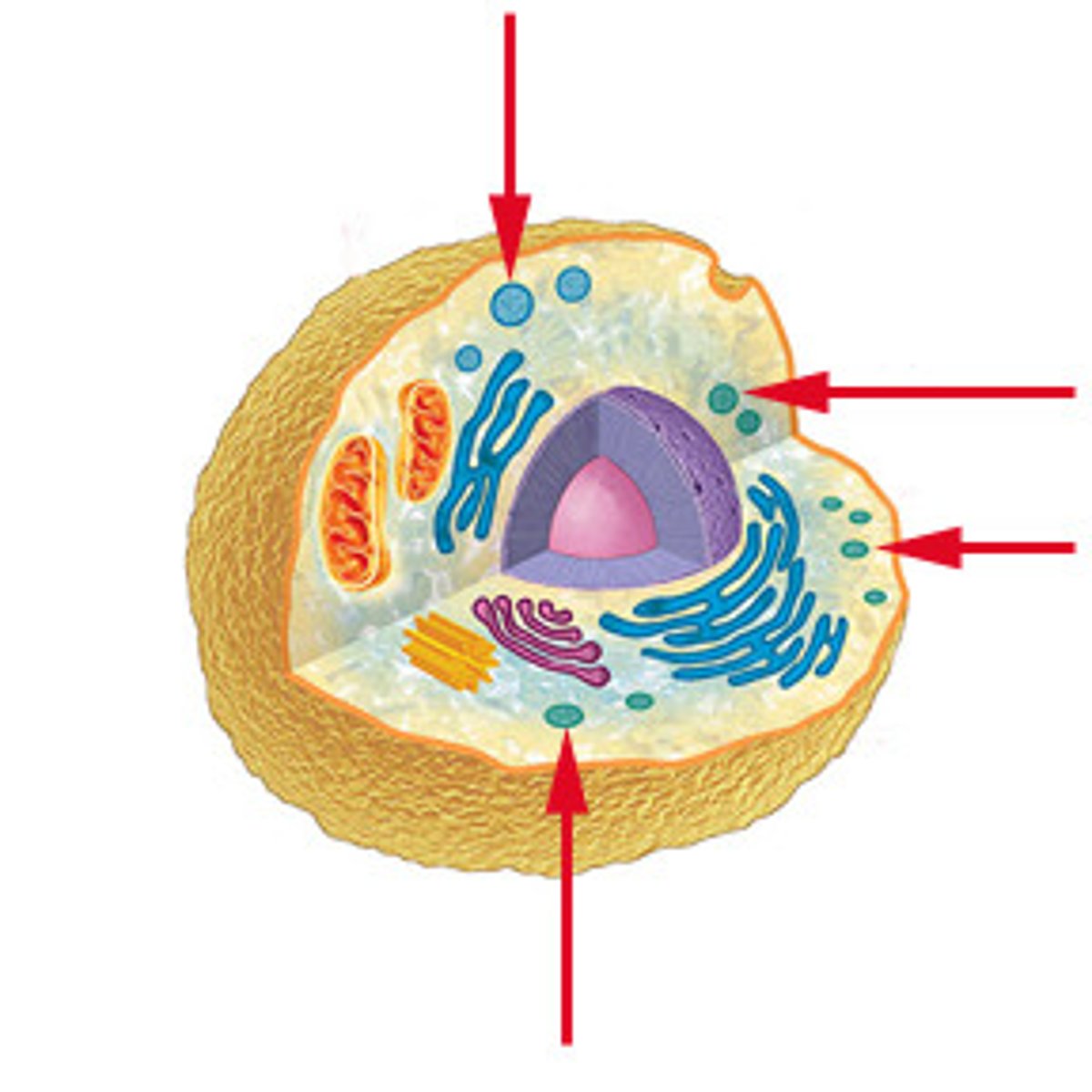
Chloroplast
where photosynthesis occurs (solar panels)
- plants ONLY
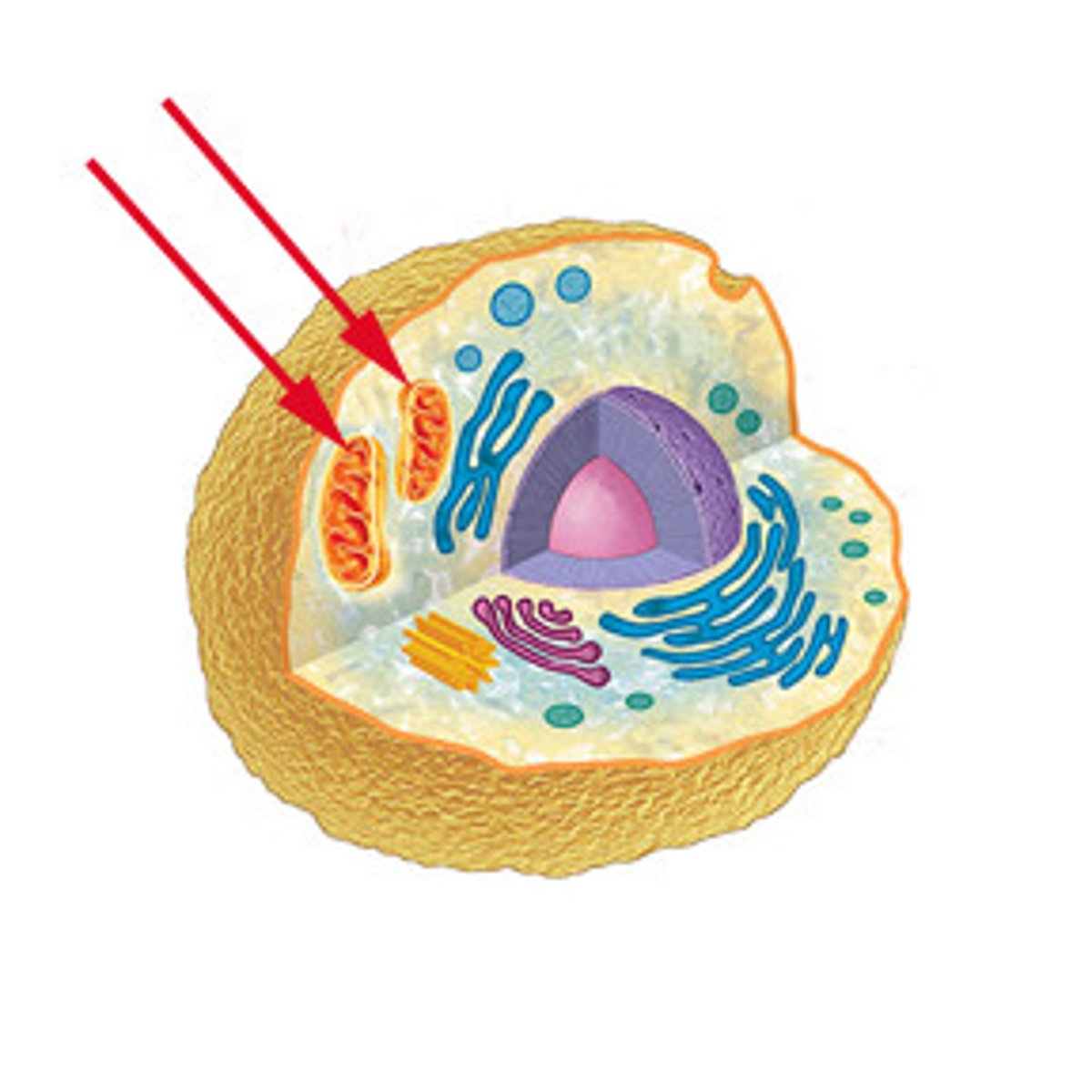
Mitocondria
chemical reaction occur to convert glucose into energy (powerhouse)
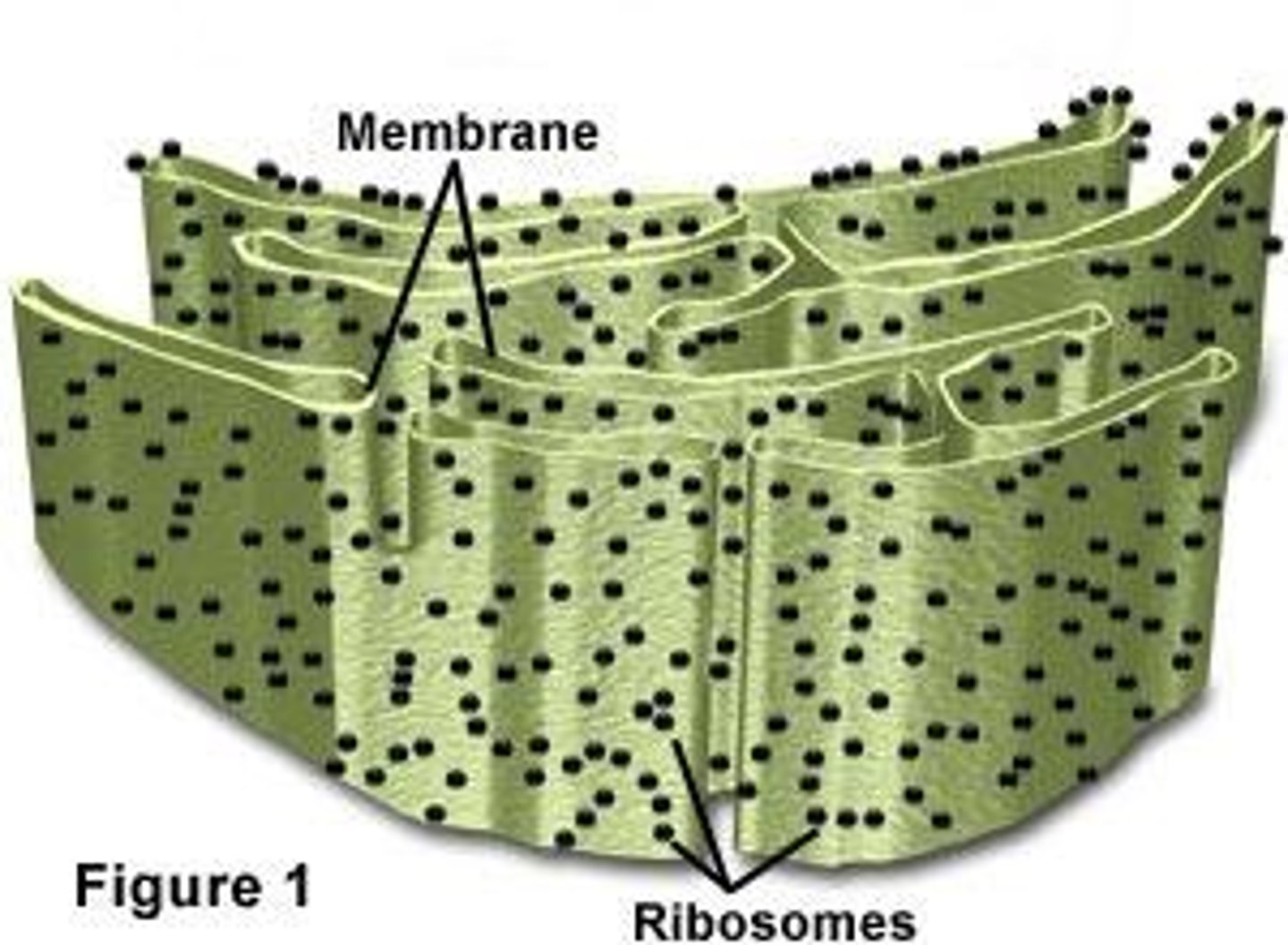
Ribosomes
provides proteins
Smooth ER
synthesis of lipids
Rough ER
folding/synthesizing proteins
- has ribosomes on it
Golgi Body
process/package lipids/proteins for export (post office)
Lysosomes
breaks down all cell material (digestive system)
Centrosome
organizes microtubules for proper cell division
Microscope
an optical device used for viewing very small object
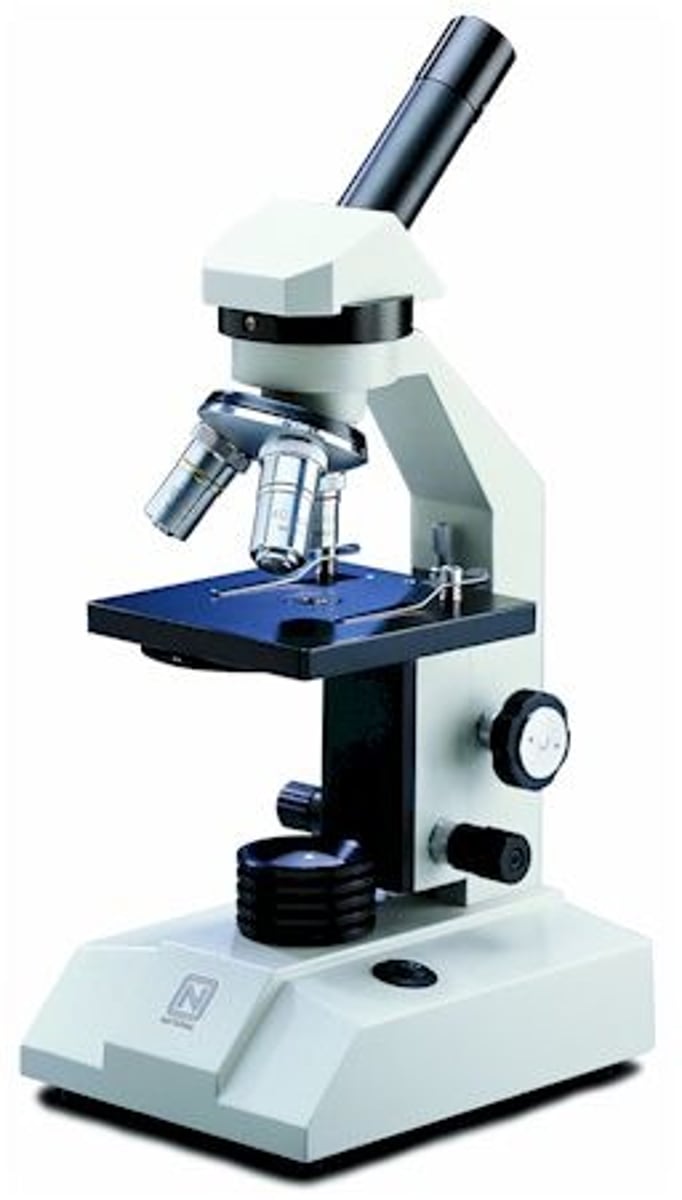

Compound Light Microscope
microscope that has 2 or more lenses and a light source
Eyepiece
contains the lens that magnifies
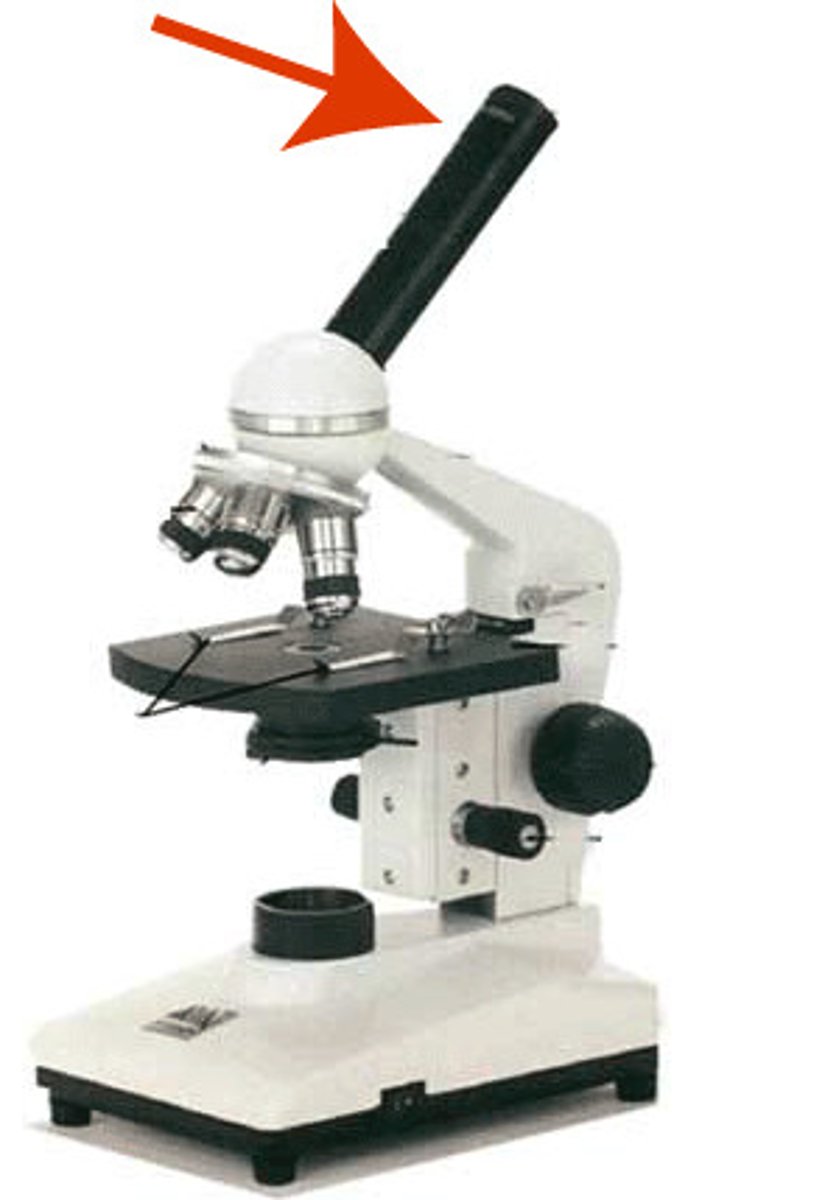
Coarse Adjustment Knob
moves the stage up and down for focusing
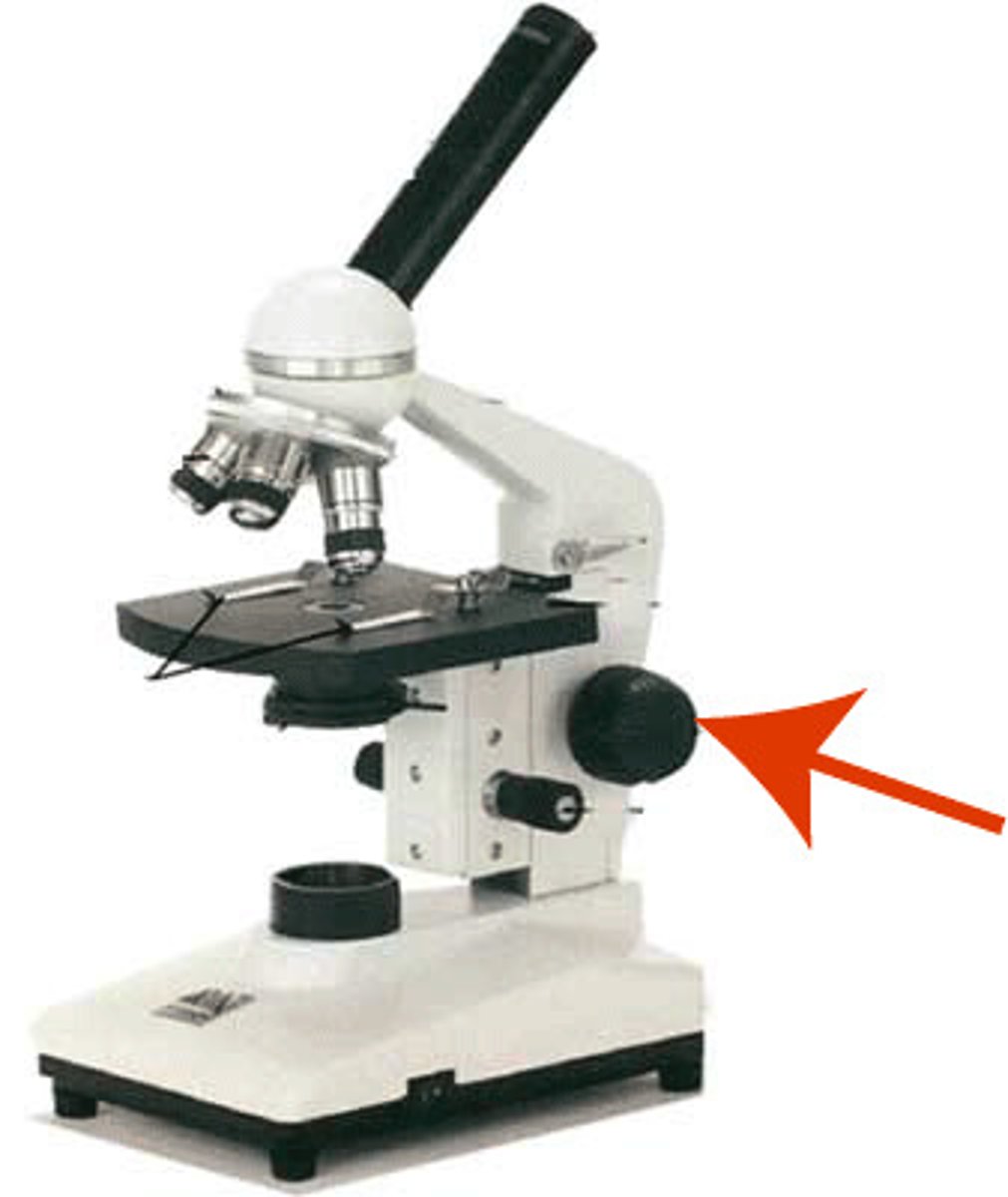

Fine Adjustment Knob
brings the object into sharper focus
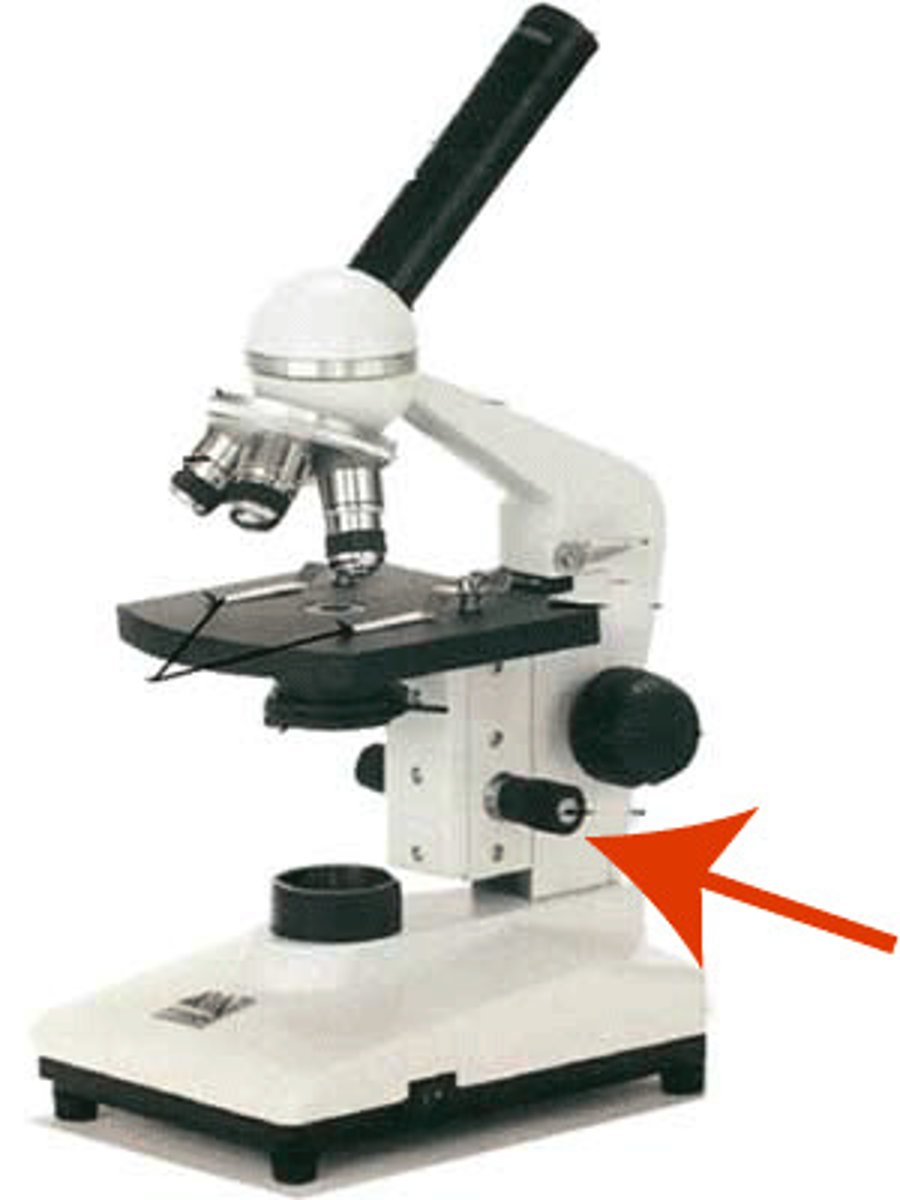
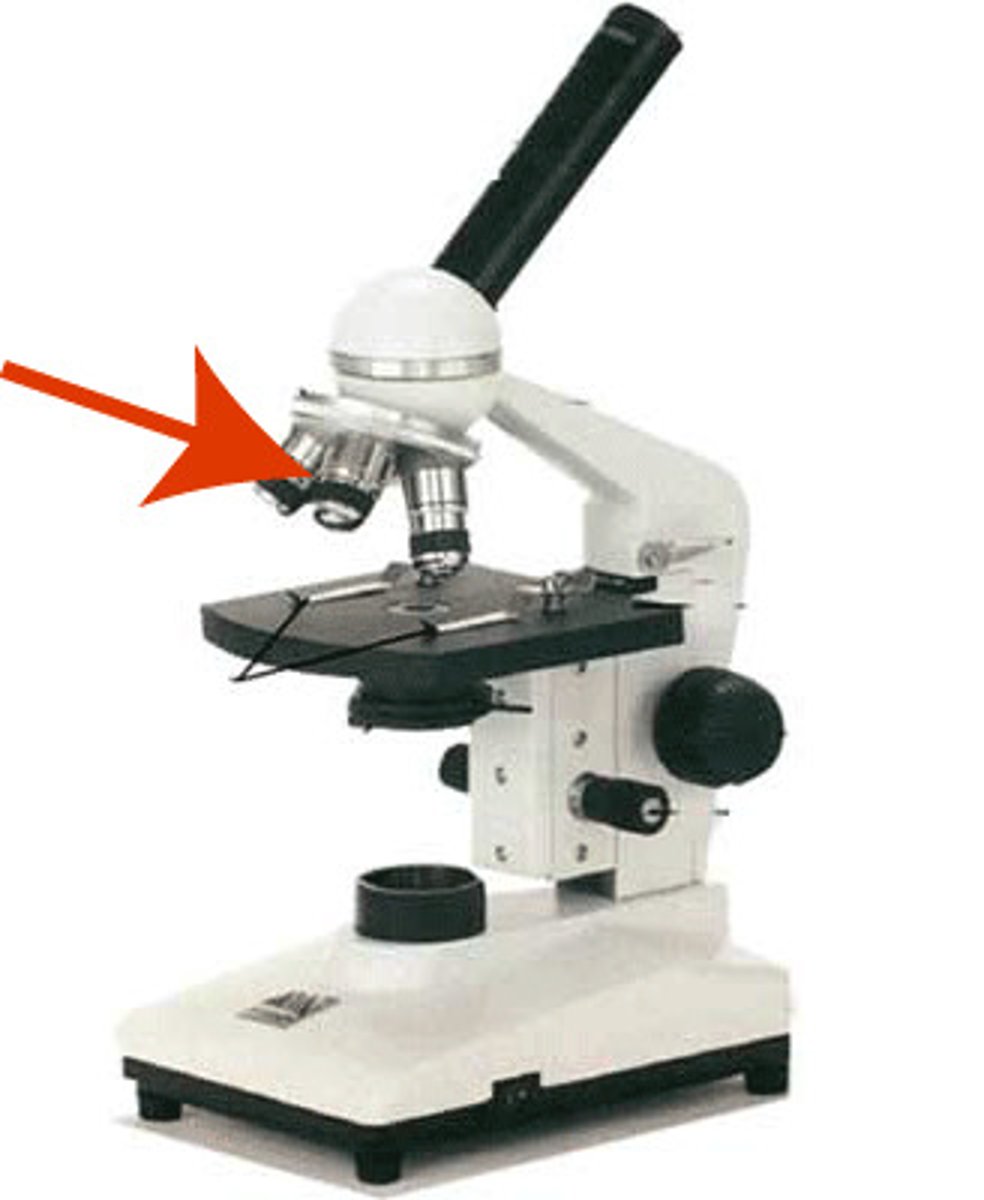
Revolving Nosepiece
holds 3 objective lens
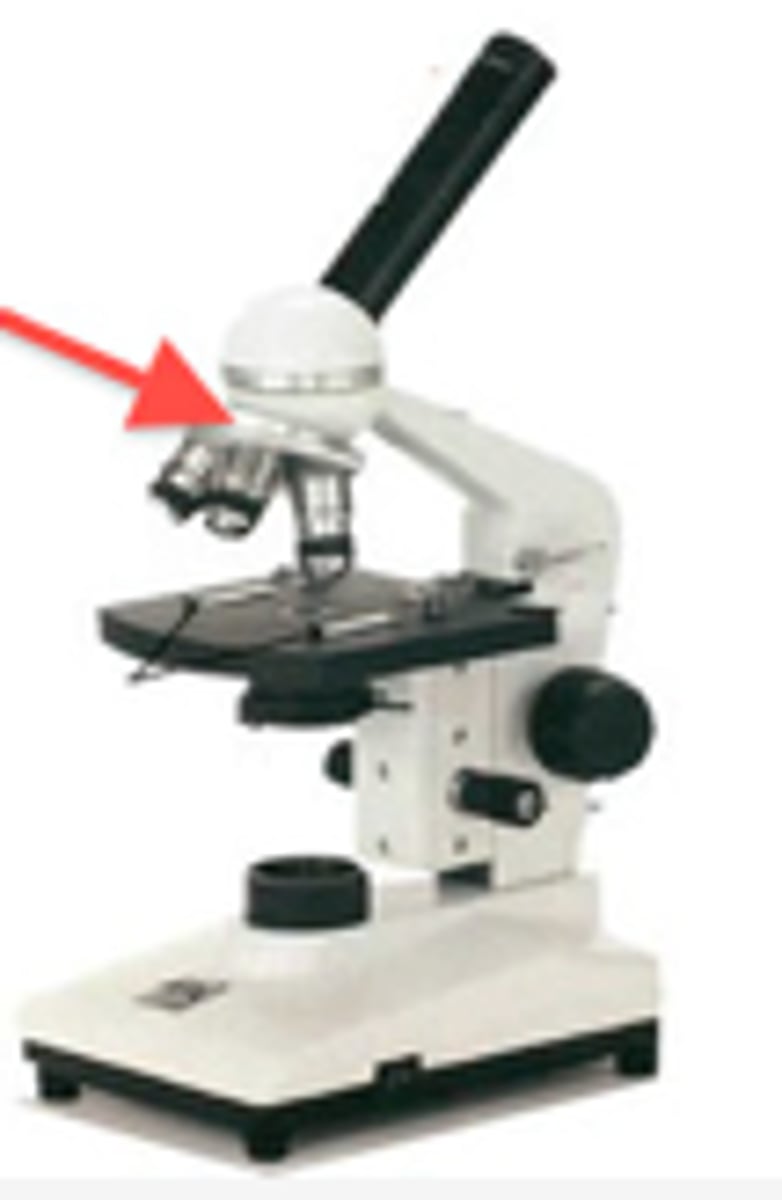
Objective Lens
provided different strengths of magnification

Stage
supports the slide that holds the object being viewed
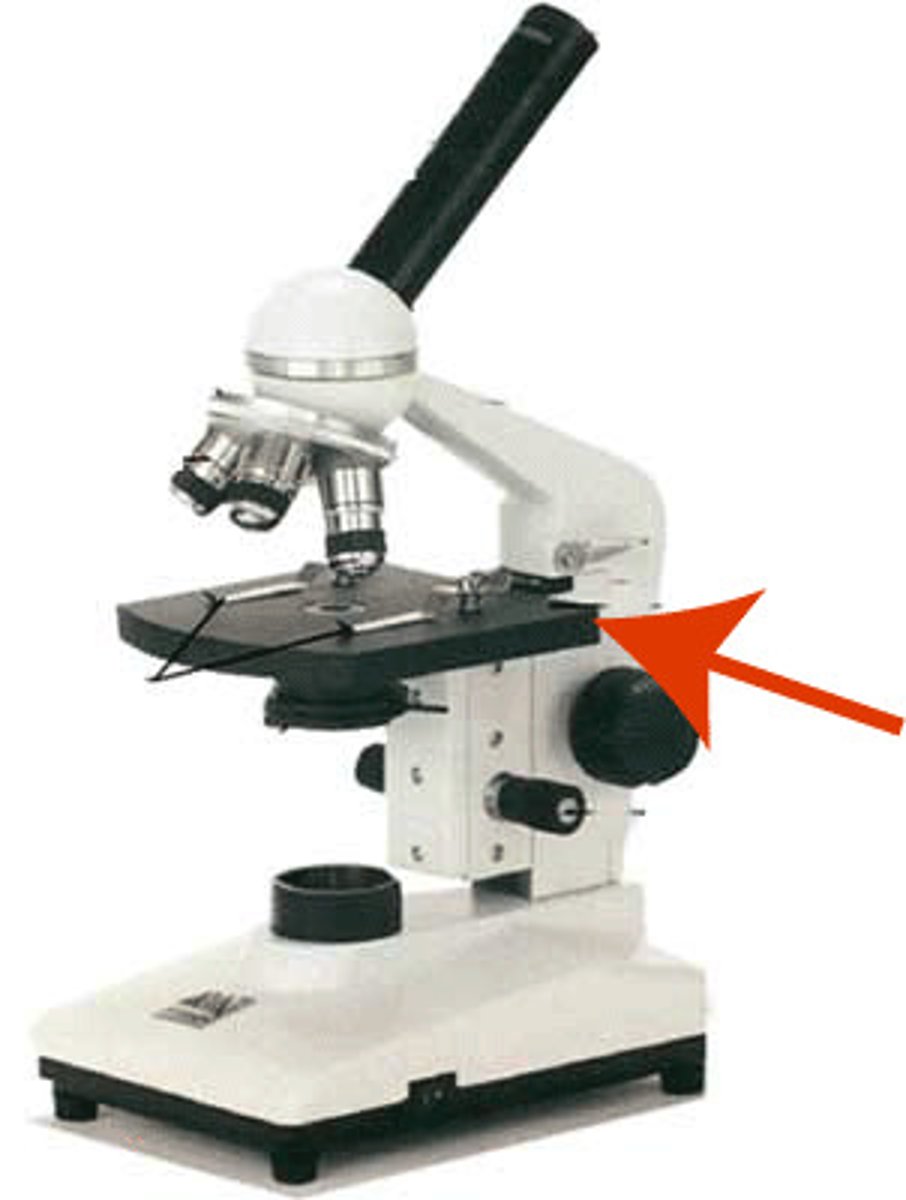
Stage Clips
holds the slide firmly on the stage
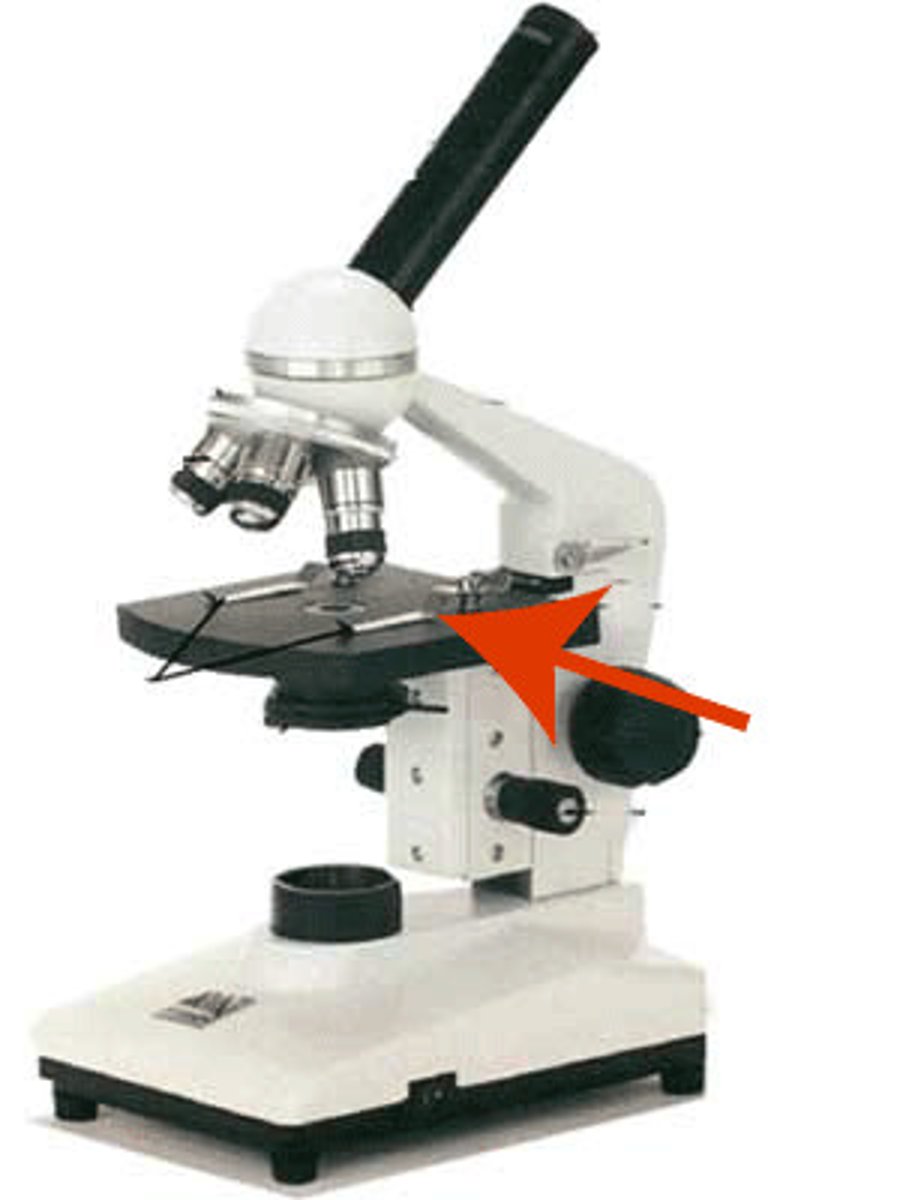
Diaphragm
has different sizes of holes to let in different amounts of light
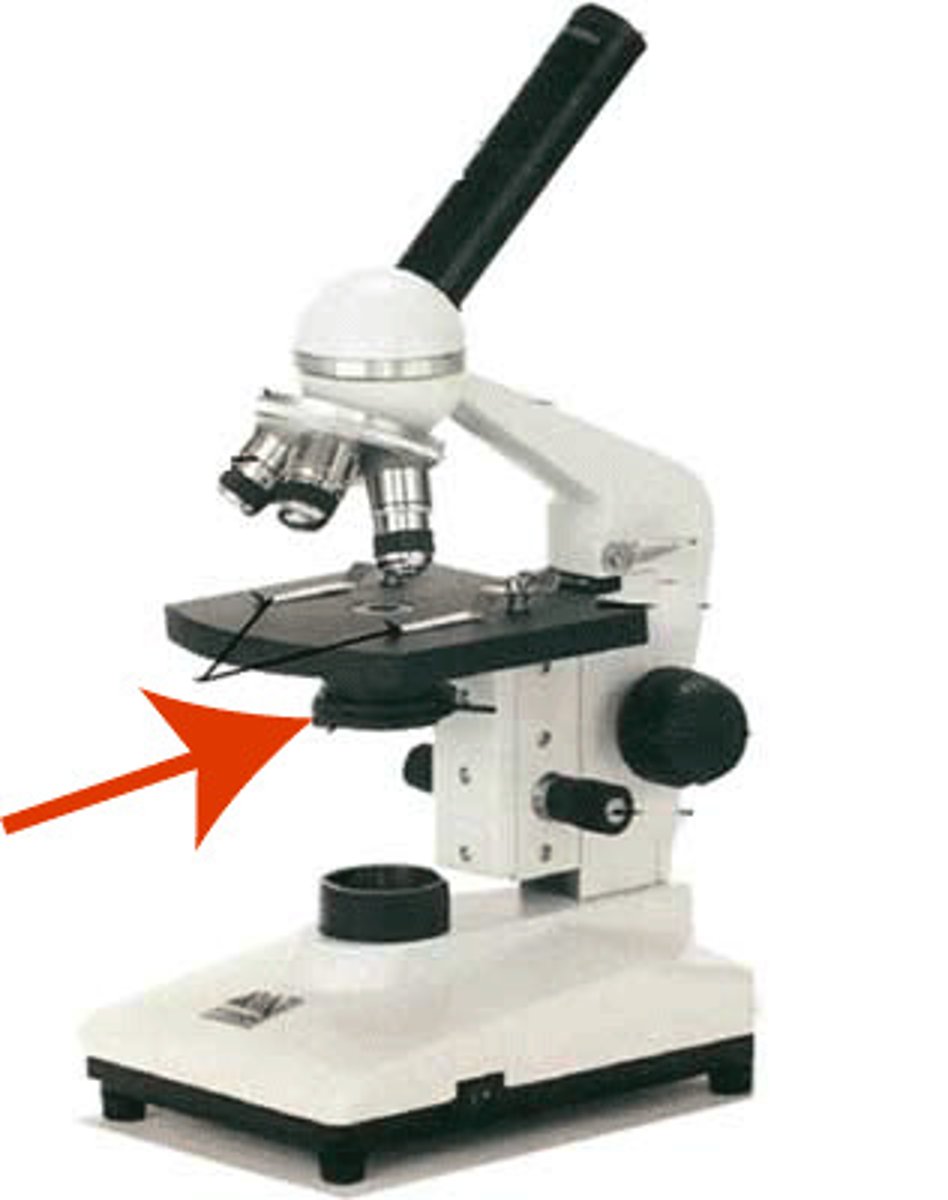
Lamp
supplies that light that passes through the object you are viewing

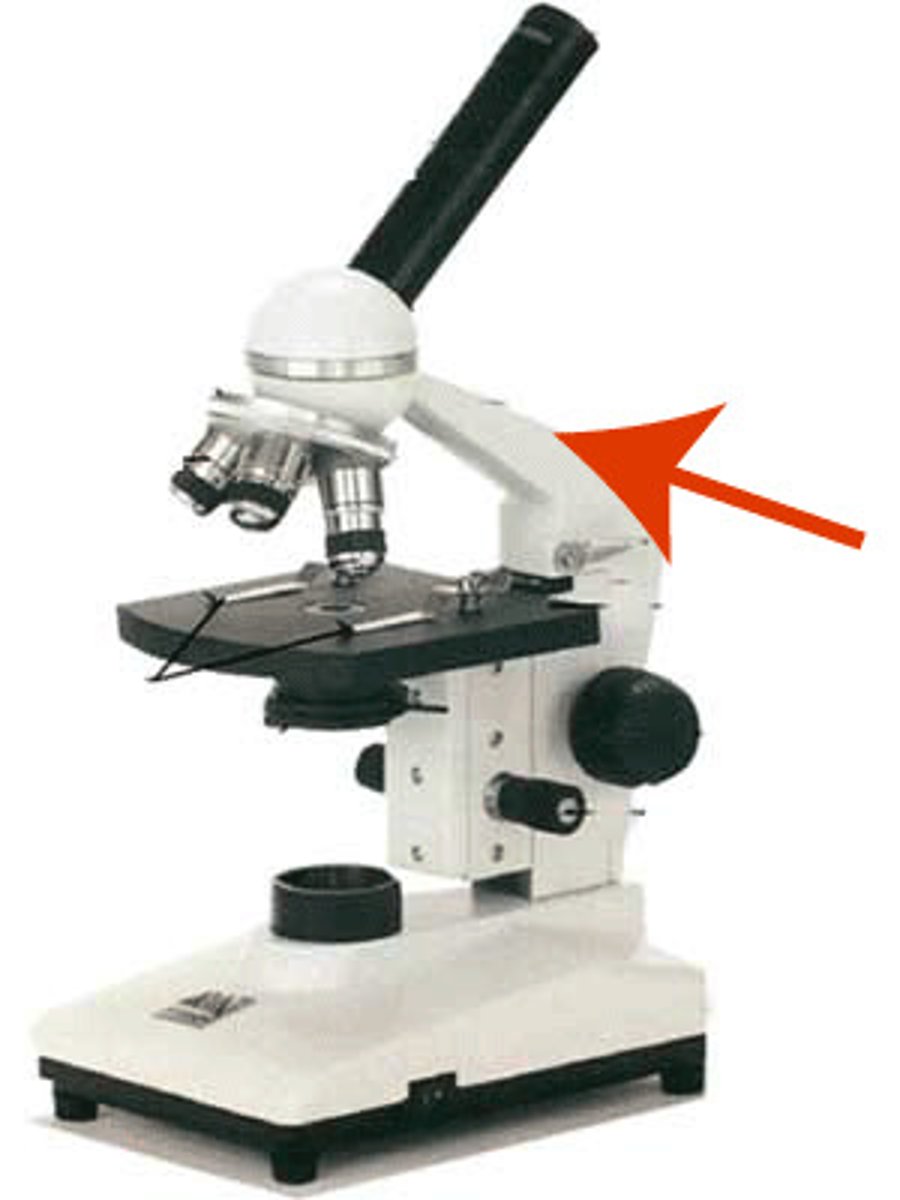
Arm
allows you to carry the microscope
Base
serves as the foundation for the rest of the microscope
