BE300: Articular Cartilage
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Where do you find articular cartilage in terms of bones?
On the ends of long bones (articulating surfaces in joints)
2
New cards
What type of joint is articular cartilage present in?
Synovial
3
New cards
Why is there limited capacity for healing and repair of articular cartilage?
* There are no blood vessels, lymphatic vessels or nerves
* Nutrients are delivered by diffusion from synovial fluid
* Nutrients are delivered by diffusion from synovial fluid
4
New cards
What is articular cartilage?
Load bearing cartilage found where bones come together to form joints
5
New cards
What are the functions of articular cartilage?
* distribute load over wider area to reduce contact stresses
* allow relative movement of 2 surfaces with minimal friction (AC on AC = one of lowest known frictionless surface frictions)
* allow relative movement of 2 surfaces with minimal friction (AC on AC = one of lowest known frictionless surface frictions)
6
New cards
What is the friction coefficient of articular cartilage?
µ = 0.02
7
New cards
What are articular cartilage cells called?
Chondrocytes
8
New cards
What is the ECM?
Anything that is not cells
9
New cards
What makes up the ECM of AC?
* Type II collagen (15-20% by wet weight)
* Proteoglycans (4-7% by wet weight)
* Water (60-85% by wet weight)
* Proteoglycans (4-7% by wet weight)
* Water (60-85% by wet weight)
10
New cards
What is sub-chondral bone?
The bone beneath articular cartilage
11
New cards
Draw diagram of AC in trabecular bone, highlighting the different zones
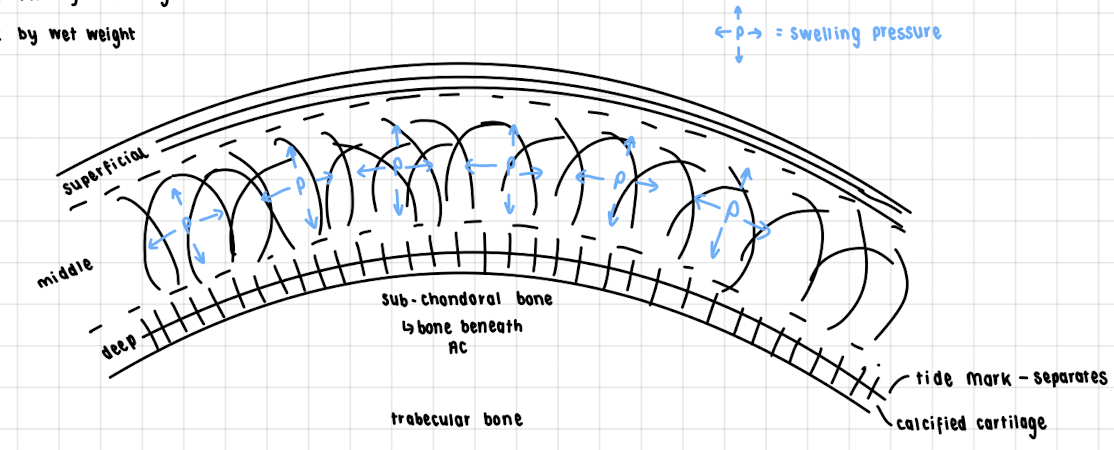
12
New cards
What are the 3 zones of AC?
* superficial - collagen fibres parallel to articulating surfaces, smooth surface, resistance on tension, low concentration of proteoglycans
* deep - collagen fibres are perpendicular to surface, this anchors AC to the sub-chondral bone, high concentration of proteoglycans
* middle - transitions collagen fibre orientation, medium concentration of proteoglycans
* deep - collagen fibres are perpendicular to surface, this anchors AC to the sub-chondral bone, high concentration of proteoglycans
* middle - transitions collagen fibre orientation, medium concentration of proteoglycans
13
New cards
What is the core protein of proteoglycans?
Hyaluranon
14
New cards
What are the side chains of proteoglycans called?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
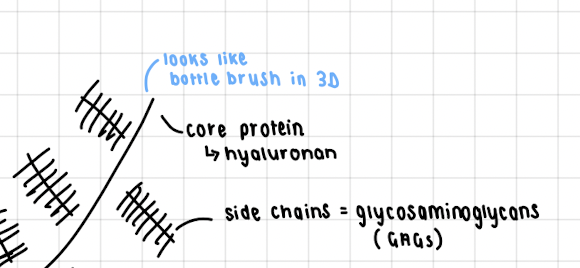
15
New cards
What are the 2 types of GAGs in proteoglycans?
* chondroitin sulphite
* keratin sulphite
* keratin sulphite
16
New cards
What type of charge do sulphites have?
negative (SO₃−)
17
New cards
How is the ECM created by GAGs and collagen fibres?
The GAGs become entangled and entwined with the collagen fibres (-ve charges can’t move as they are fixed in place)
18
New cards
What is the amount of charge by unit volume called?
Fixed charge density (FCD)
19
New cards
Describe the Donnan Osmotic Pressure
Semipermeable membrane separates 2 solutions with different electrolytes - allows passage of water molecules but restricts movement of electrolytes. Donnan osmotic pressure important in AC for maintaining hydration and mechanical properties of tissue.
20
New cards
What % of stiffness do electrical effects account for?
\~ 60%, compression increases charge-charge repulsion forces
21
New cards
What % of stiffness do proteoglycans account for?
\~ 98% (PG volume = 38%)