Micro Lecture 23 - Enterobacter spp., Serratia marcescens, Bordetella pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Enterobacter spp. biochemical identification
-Oxidase negative
-Indole negative
-Catalase positive
-Citrate positive
-High levels of drug resistance – carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter or CRE
-cause of nosocomial infections
Serratia marcescens
-S. marcescens most common member of genus
-Environmental source (water, soil, plants, insects)
-Motile, often producing red pigment
Serratia marcescens virulence
-Extracellular enzymes (elastase, lecithinase, caseinase)
-LPS
-Biofilm formation
-Some incidence of drug resistance
Serratia marcescens disease
Often healthcare-associated infections with spread being on hands of hospital staff
Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough)
-Causes severe cough in children
-Morphology and structure: Small rods. Aerobe, Non-motile, Fastidious (requires enriched medium)
Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough) disease
-Transmitted by inhalation of aerosol and highly infectious
-Emerging disease!!
-Occurs in the vaccinated individuals when immunity wanes
Bordetella pertussis
-Whooping cough (pertussis)
Bordetella pertussis: Catarrhal stage
Mild upper respiratory tract infection, sneezing, slight cough, low fever, runny nose.
Bordetella pertussis: Paroxysmal stage
Lower respiratory tract. Severe cough (5 to 20 forced hacking coughs per 20 seconds).
Bordetella pertussis: Convalescent stage
Less severe but persistent cough.
Bordetella pertussis: adherence
-Filamentous Hemagglutinin (FHA), pertactin, and pili
-Allows bacterium to bind to ciliated respiratory epithelium
-Initiates phagocytosis by binding PMNs (survives intracellularly)
Bordetella pertussis: Pertussis Toxin
-An A/B toxin
-The active portion is ADP ribosyl transferase
-dysregulates cAMP -> increase cAMP and increase respiratory secretions and inhibiting neutrophil functioning
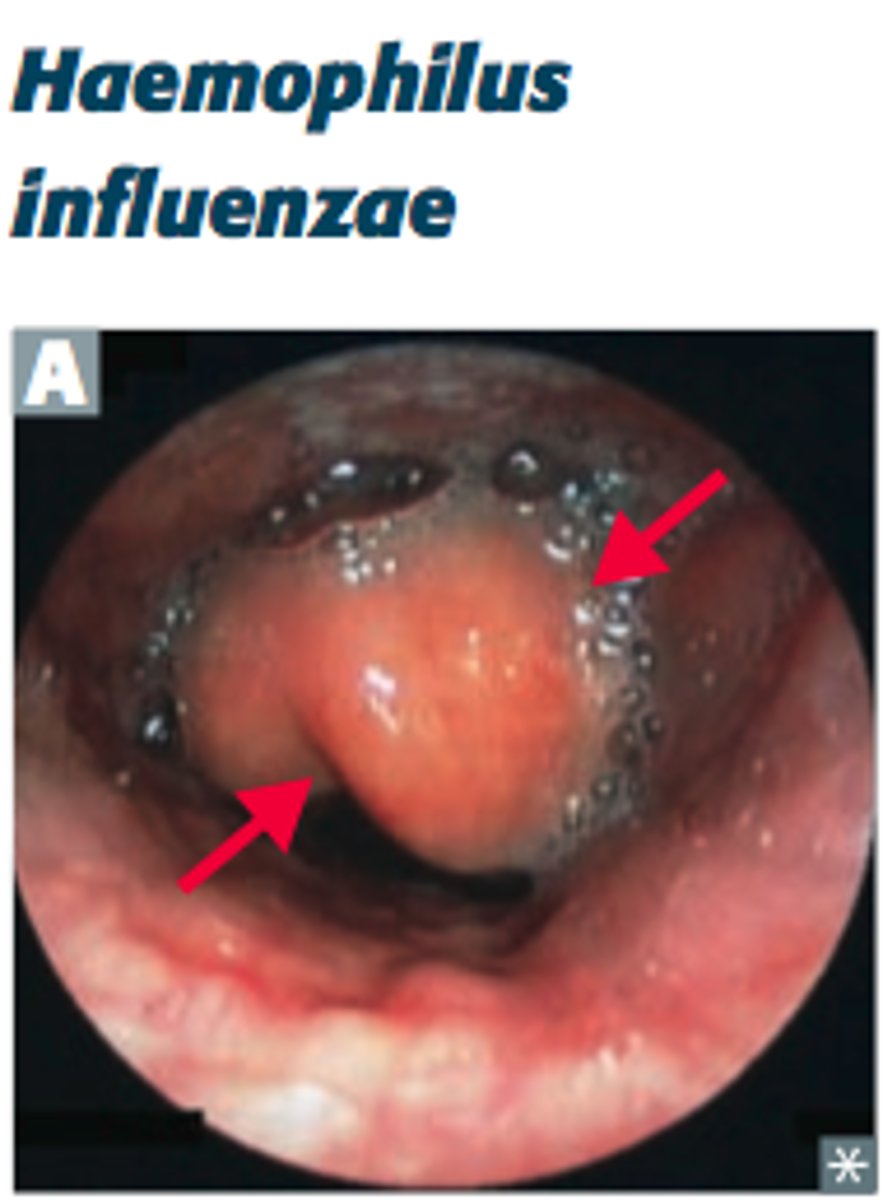
Haemophilus influenzae
-Small Gram-negative rod/coccobacillus; facultative anaerobe
-Transmission: aerosolized respiratory secretions
-Diagnosis: culture on chocolate agar and microscopic detection of bacteria in CSF
-Prevention: Vaccine
H. Influenzae Virulence Factors
-Required growth: chocolate agar
-Capsule
-Endotoxin
-IgA protease
-Pili and fimbriae
-LPS
-Colonization of nasopharynx
-Invasion of nasal mucosa
H. influenzae susceptibility factors
-Age – elderly and young children
-Immune status – patients with complement deficiency, asplenic patients
-Prior infection – esp. viral and otitis
Haemophilus influenzae Disease
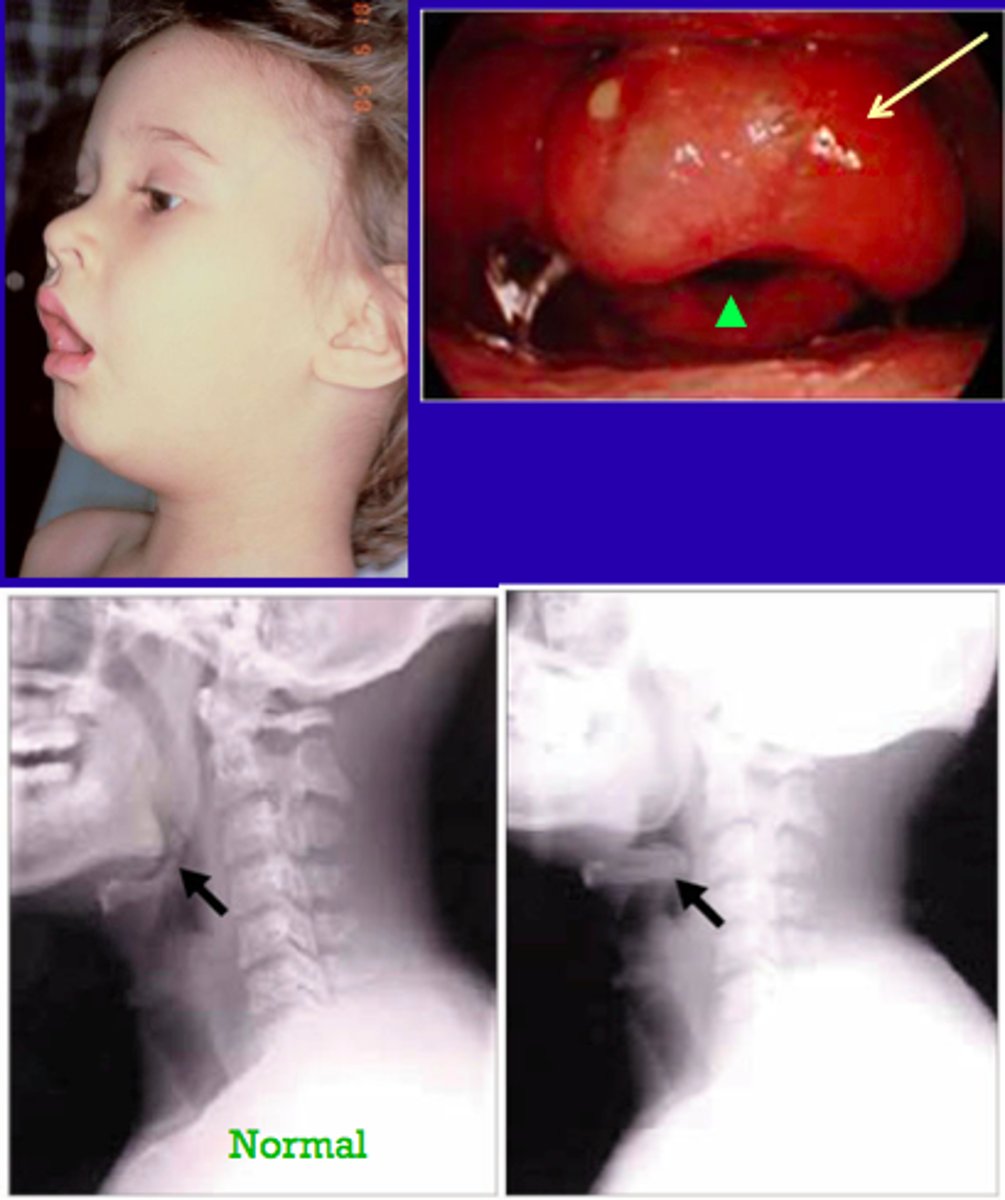
-Epiglottitis
-Cherry-red epiglottis
-Life-threatening emergency!
-Begins as pharyngitis, fever, and difficulty breathing which can rapidly progress to airway obstruction and death → “thumb print sign”
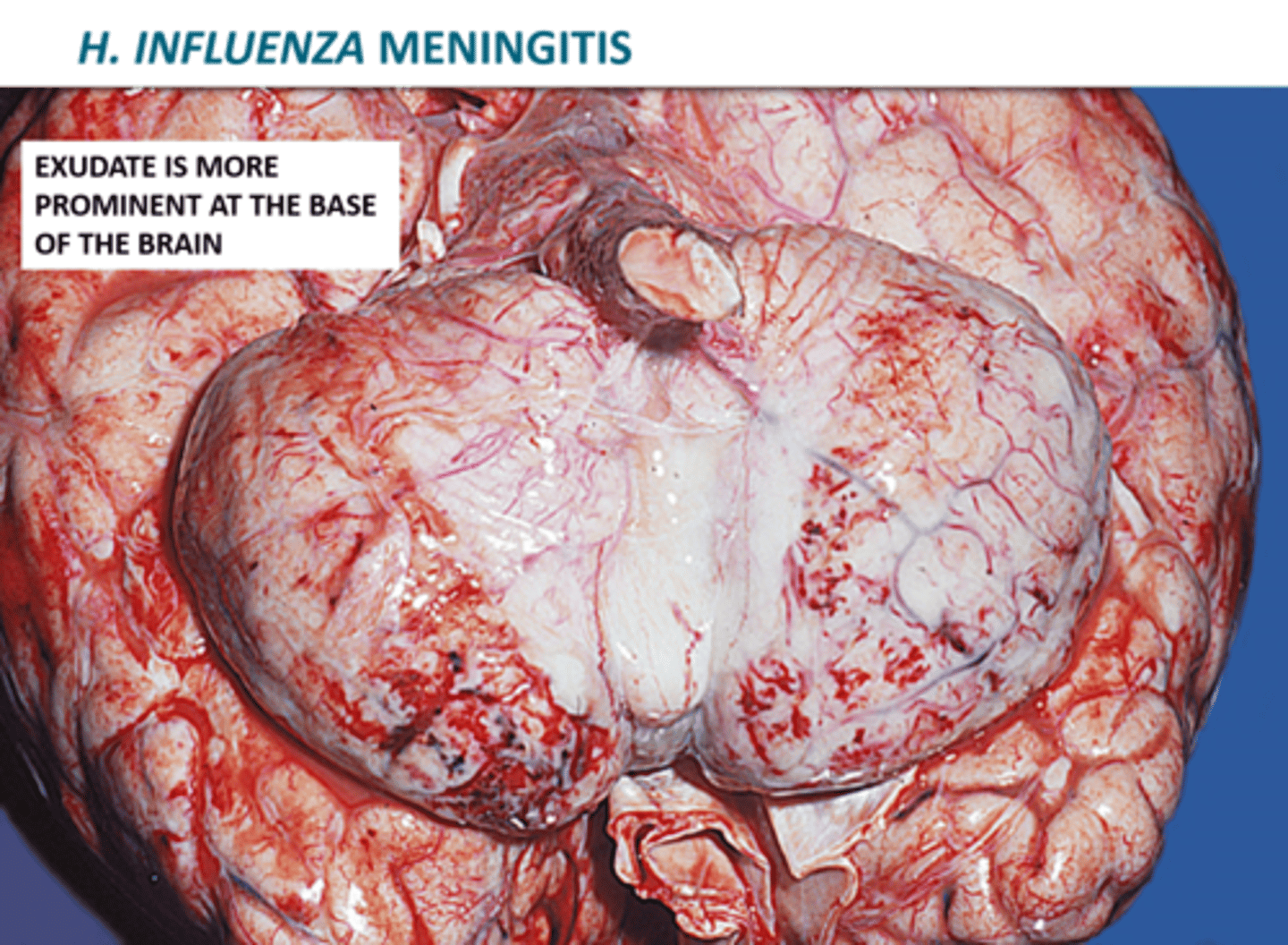
Haemophilus influenzae: Meningitis
-Due to hematogenous spread of bacteria from nasopharynx to CNS
-With appropriate treatment, mortality is <10%
Haemophilus influenzae: Cellulitis
Fever and cellulitis which presents as reddish-blue patches on cheeks and periorbital areas
Haemophilus influenzae affect what population
Mostly pediatric, but adults are also susceptible
Haemophilus influenzae prevention and treatment
-We have a conjugated Hib vaccine reduced infections in children (<5 yr old) by >95%
-Cefpodoxime or ceftriaxone (for life-threatening infections) or amoxicillin-clavulanate
unique features of serratia marcescens
-produce red pigment
-often spread on hands of hospital staff
morphology of pertussis
small rods, aerobe
-non motile
-
Catarrhal stage of pertussis
mild URT, first stage
Paroxysmal stage of pertussis
LRT infection
-middle stage
-5-20 coughs per 20 secondss
convalescent stage of pertussis
less severe but persistent cough; final staage
pertussis virulence factors
-AB tooxin
-active portion is AADP ribosyl transferase
-dysregulates cAMP
how can you grow H. influenza on an agar?
chocolate agar supplemented with factors X and V
Epiglottitis
-disease of H. influenza
-cherry red epiglottis presentation, life threatening emergency!
-begins as pharyngitis, rapidly progresses to airway obstruction