New analytical chemistry exam 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is so special about atomic absorption spectroscopy
very specific, measures trace metals that are not as easily excited
uses a hollow cathode lamp containing the analyte
uses a chopper
uses a nebulizer and flame
uses a graphite furnace
In atomic absorption spectroscopy absorbances is…
proportional to the analyte concentration
what does a chopper do in AAS?
allows differentiation between light transmitted vs light emitted
what does the nebulizer and flame do in AAS?
-disperses sample
-converts metal ions into atoms in their ‘ground state’
where does the monochromator sit in relation to the sample and the photodetector in AAS?
Between the sample and the photodetector
What is the chemical interference with AAS and how is it overcome?
Phosphate interfers w/ calcium measurement, this is overcome by adding lanthium or strontium to bind the phosphate
What is so special about chemiluminescence?
there doesnt need to be a light source or monochromator, it is also proportional to its concentration
How are turbidimetry and nephelometry similar
both depend on wavelength and size (suspension)
Both are sensitive and used in immuno assays
Interference with turbidimetry and nephelometry
lipidemia, non-scratched cuvet
What does turbidimetry measure?
Decrease in light transmitted
what does nephlometry measure?
light scattered at a defined angle
Why is turbidimetry special?
it can be used to measure large macromolecules
detected at a 0* angle
Inversely related to particle concentration
In nephlometry, the bigger the particle size the…
more forward and straight the scattering of light is
what is so special about phosphorescence?
Paired electrons in triplet excited state- light emissions continue
What is so special about luminescence ?
Best for Electron rich molecules
What is so special about reflectance spectrophotometry
inversely related to the analyte concentration
uses a flat surface
photodetector is set at a 90* angle relative to the light source
Disadvantage to fluorescence ?
quenching- sensitivity to enviromental changes like temp. and ph
Advantage to fluorescence ?
Specificity and sensitivity
What is fluorescence ?
when exposed to short wavelength, high-energy radtion, certain molecules absorb the energy and become excited, when these molecules come down from that high to their resting state, they emit longer wavelengths, lower energy radiation
-porportional to the concentration
excitation stage is first, then emission phase
what do exit and entrance slits do in regards to the size of the slit?
narrow slits make the bandpass smaller, leading to a better resolution.
Whats do filters do?
construcive interference that occurs as light passes through a thin film
What do prisms do?
as light enters the glass at an angle, it bends b/c of the difference between the speed of light in air and in the glass
glass cuvet is used for
visible light
tungsten is used for
visible light and greater than 360nm
quarts cuvet is used for
uv light
deterium is used for
uv light, and greater than 165nm
What is bandpass?
defines the range of wavelengths trasnmitted through
a decrease in bandpass correlates with a higher resolution, but a lower noise-noise ratio
-requires less than 1/5 natural bandpass
what does a monochromator do?
A wavelength selector that isolates desired wavelengths & excludes others
what is diffraction grating?
Light reflected off the surface will produce constructive interference for different wavelengths at different angles of reflection
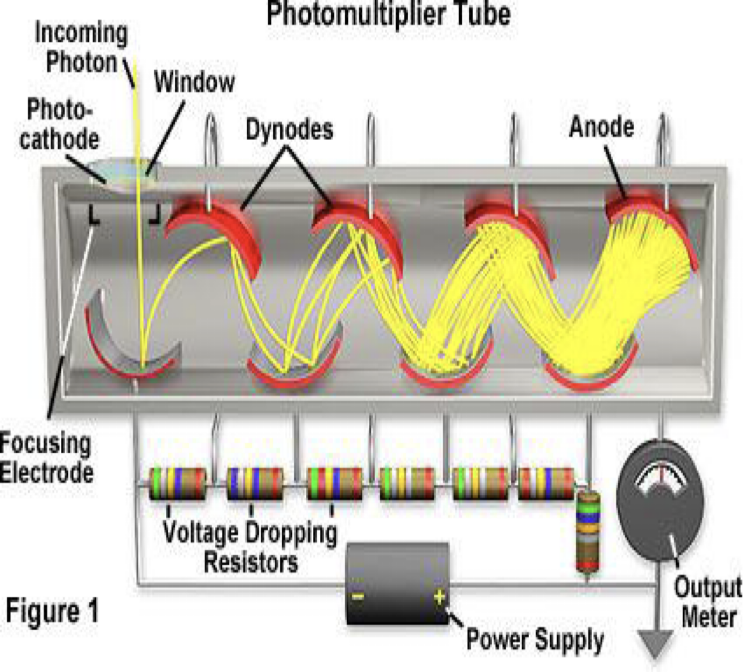
What is this?
photmultiplier tube
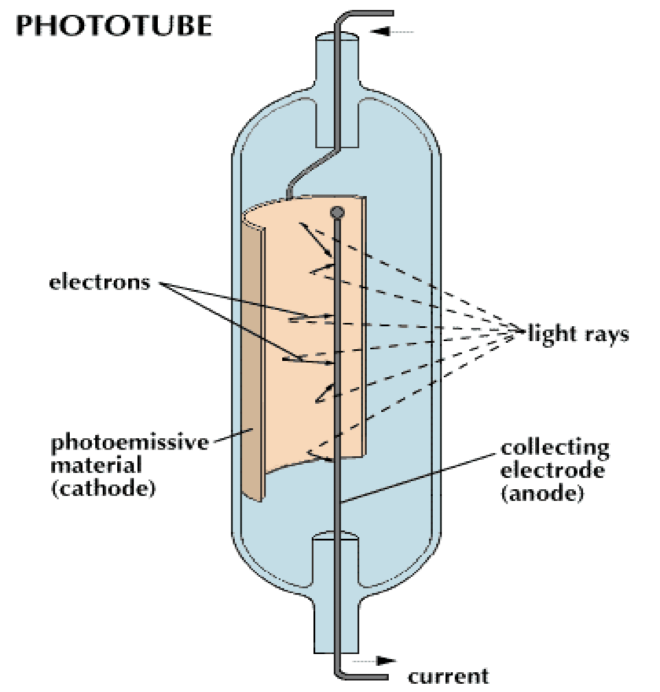
What is this?
Phototube
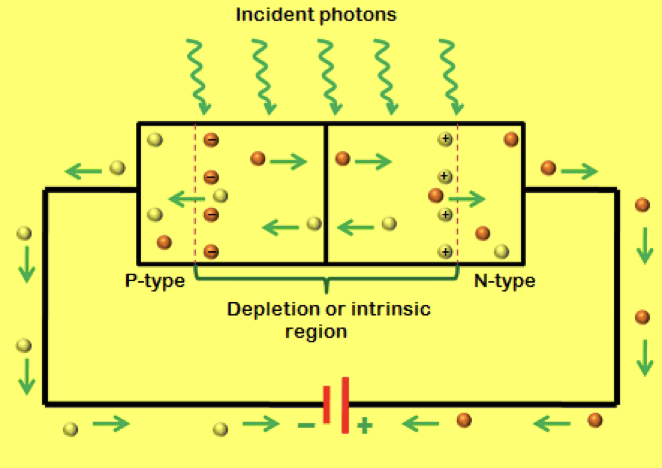
What is this?
photodiode
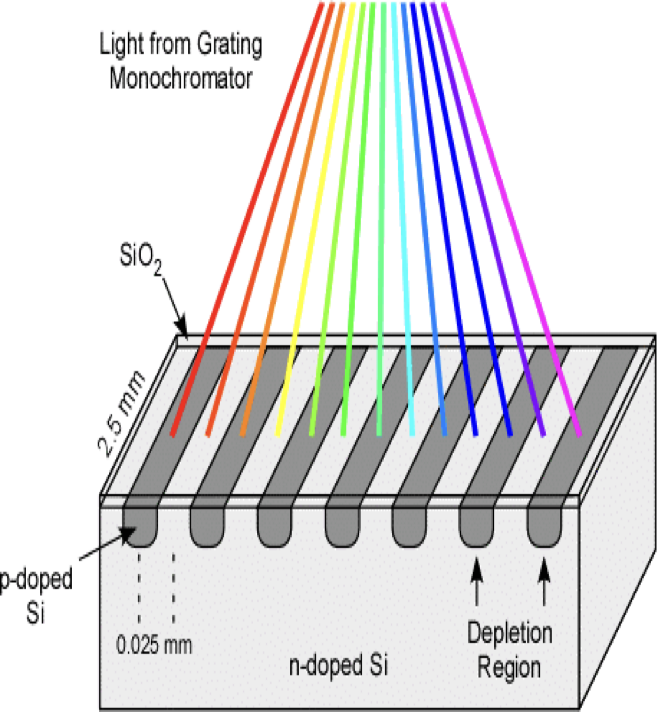
What is this?
Diode arrays
The 1st step in any spectrophotometric measurement is…
establishing the optimal absorbance wavelength (۸max) for the analyte
-By running a spectral absorption curve
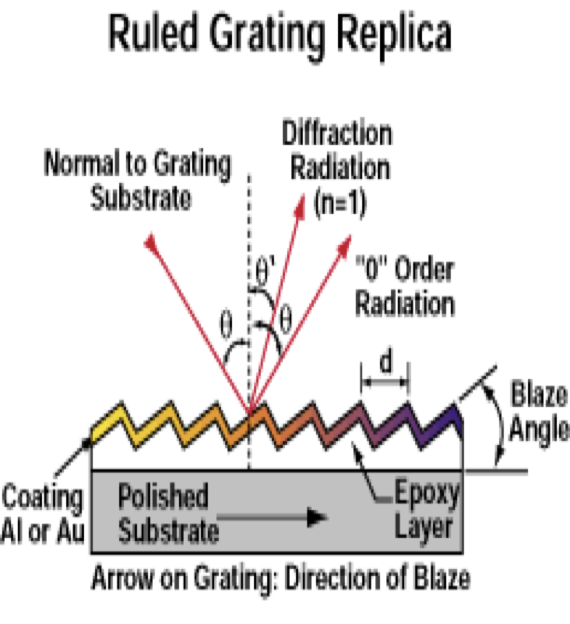
What is this?
Diffraction grating