9-Phase Equilibria of Mixtures
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
pressure vs mole chart
Gibbs Phase Rule F=2-pi+N
. =4-pi for 2 components
how many intensive properties F can be chosen
pi-# of phases
N-# of chemical species
F=4-pi in one phase =3
P,T,x defines the system in one phase
for VLE, pi=2 F=2
so T,x or P,x defines the system
for a given P,x
there is a temperature that gives two phases
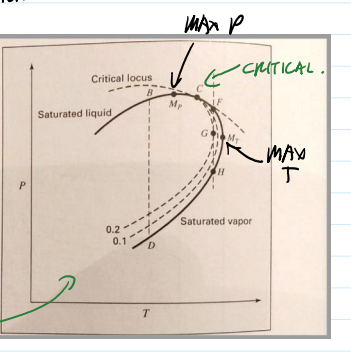
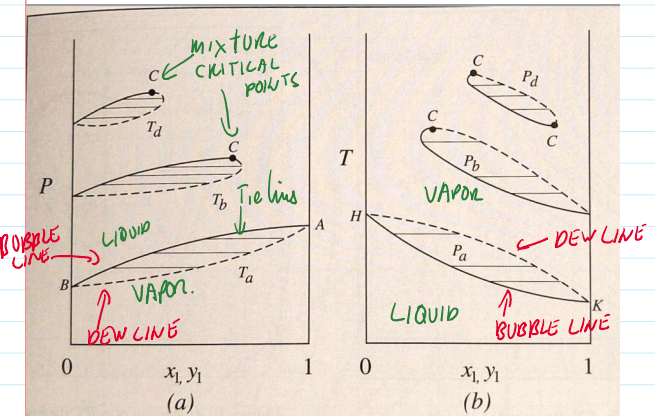
P,T graph varying composition
B—>D evaporation
F—>G—>H F: vapor condenses to a two phase mixtures through G, then vaporizes again (retrograde vaporization)
in a gas well, as we remove gas lower pressure
liquid can form. need to repressurize the well
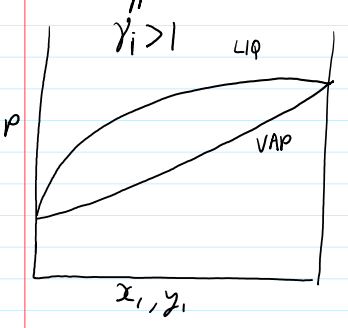
non ideal P-graph γi > 1
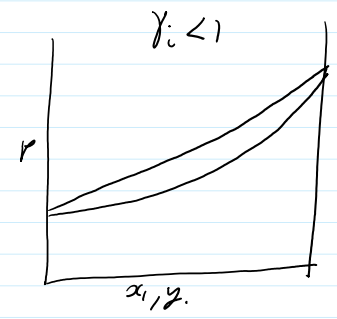
non ideal P-graph < γi 1
azeotrope-liquid and vapor composition are the same
T-graph 1. γi>1 2.γi<1
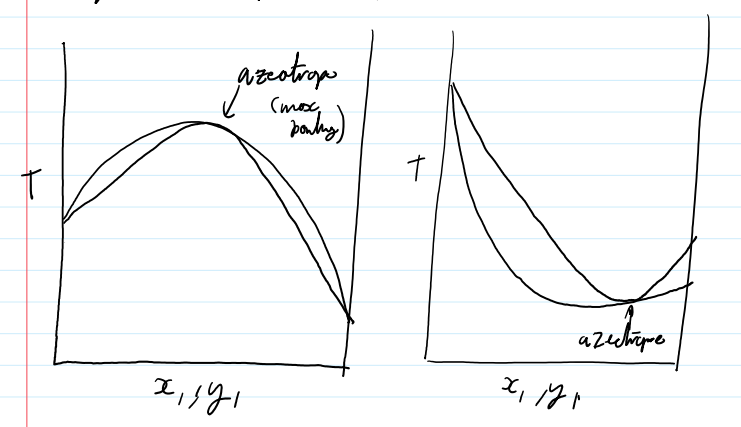
bubble point
the condition at which the first trace of gas(bubble) appears in the saturated liquid
dew point
condition at which the first drop of liquid appears in the saturated vapor
equilibrium condition
μi,L=μi,V fi,L=fi,V
activity coefficient equation
γi=ai/xi
ai=
fi(T,P,x)/fi(T,P,pure i)
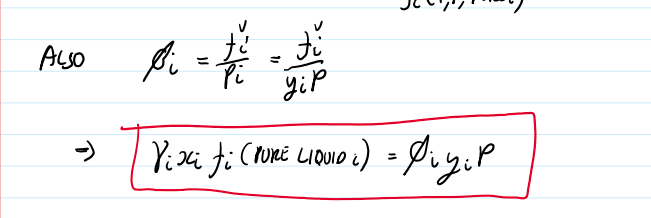
what does this equation reduce to if an ideal gas mixture and what is the pure component vapor pressure is low such that fi(PiL)=PiVP
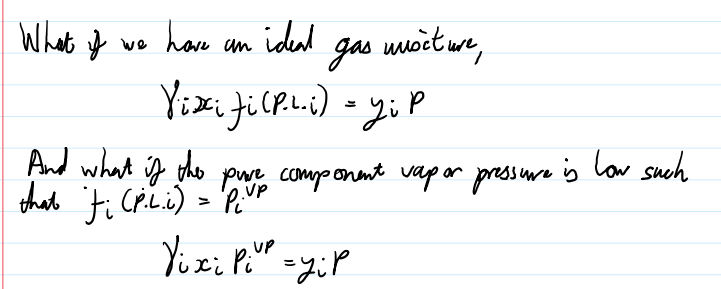
what is this equation reduced to if the liquid is ideal Raoults law
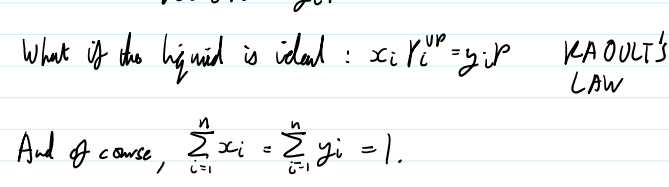
dew and bubble point ideal system(Raoults Law)

Henry’s Law
if above the critical point of a fluid, also assume that none of the species “dissolves“ in the liquid
used in dilution solutions
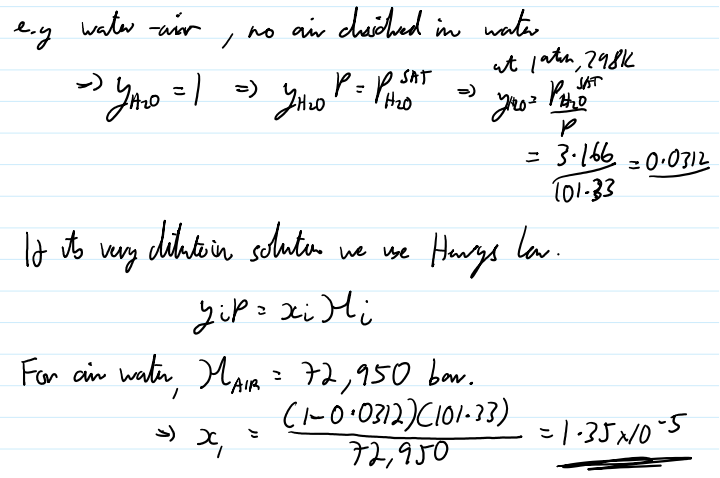
at low vapor pressure can assume an ideal gas but want to keep potential non-ideal in the liquid phase
can rearrange the formula
can use k-chart values

if y γi > 1,
there will be more of a component in the vapor phase from predicted by Raoult’s Law
the component doesn’t like its neighbor in the liquid phase
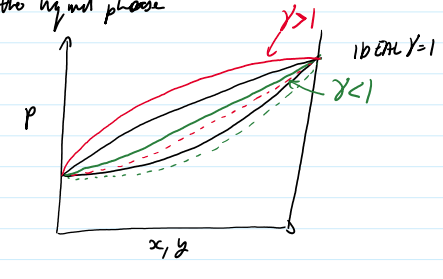
if y γi < 1
there will be less of the component in the gas phase then predicted by Raoults law
components like to be in the liquid phase with its new friends

How to get the excess gibbs equation from the difference in chemical potential
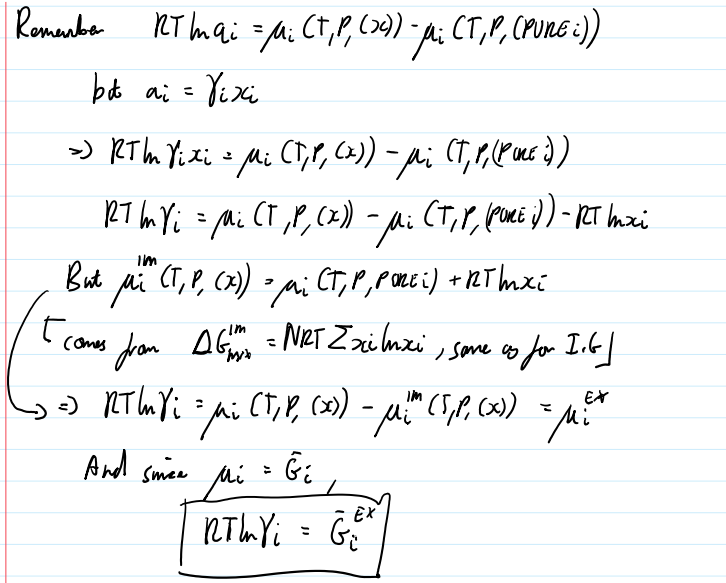
How to get excess gibbs equation from the gibbs duhem equation

in a binary system, if we have one actual coefficient, we can get the other
can use the general property of partial molar quantities
if we have VLE data, we can
fit the values of γi and get GE
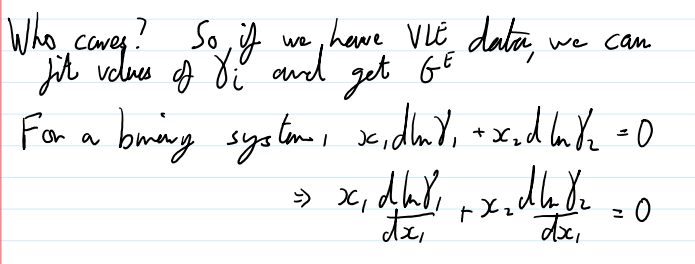
for any given fit equation for the excess G
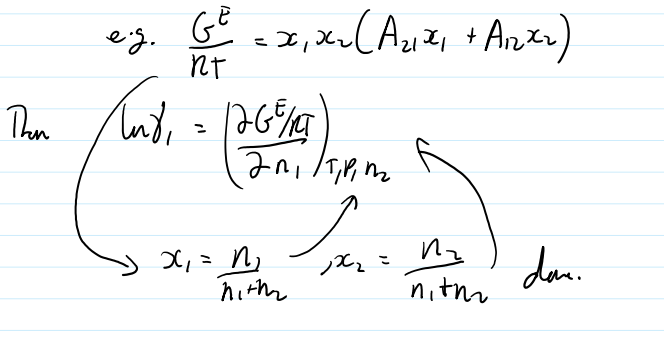
standard liquid-liquid equilibrium
common assumption in LLE is that although two phases are relatively pure eg. not much water in the oil and vice-versa from this we use γi,l = γ2,ll = 1

we expect the entropy of a phase separated system to be lower than a mixture how does this fit with minimizing Gibbs
conductive of stability for a binary system

case where :One constant Margules equation- GEX= cx1 x2

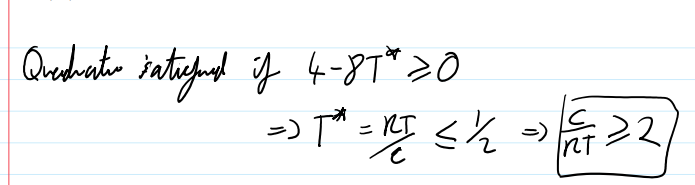
quadratic satisfaction if
so we get two phases for large c-parameter and/or low T—> entropy is overpowered by large non-ideality in the mixtures.
As T incr. C decr. entropy wins again
for VLLE, there is an additional phase but roles + m remain the same
degrees of freedom 2-3+2=1 Binary
eg. T for 3-phases determines the system
generally need to solve the system numerically
fi,v=fi,L=fi,L2
often simplify since the liquids are immiscible
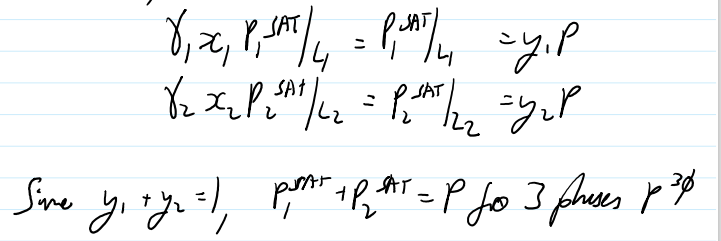
Boiling point elevation why does salt water boil at higher T
Let liquid solution 1 with salt 2 in it.
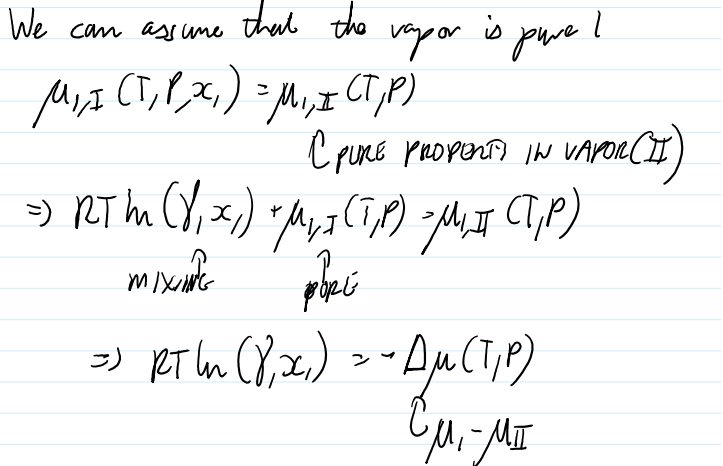
Δμ(T,P) is the chemical potential difference of the pure solvent in phase l vs. phase ll
T must be close to the boiling point of the pure species at which point
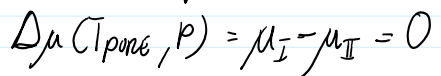
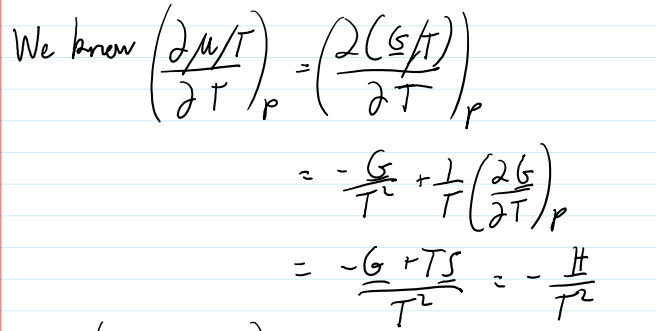
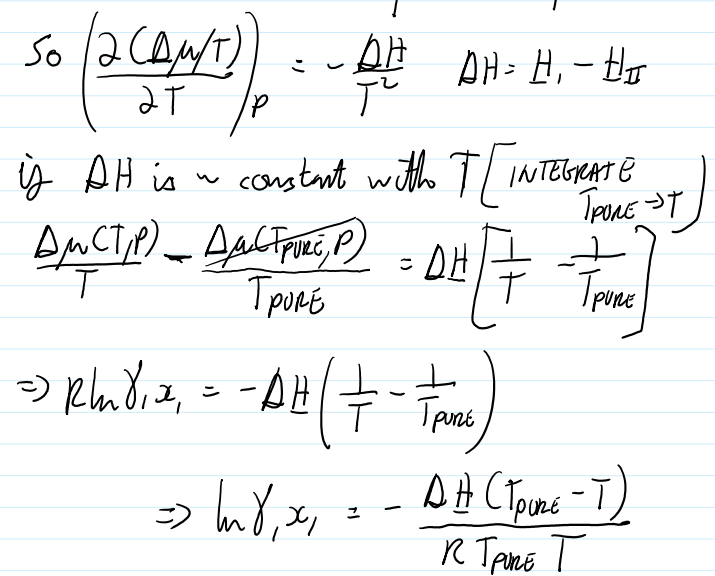
for dilute solutions

Phase l liquid, phase ll solid
