Neurology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
CN and their function?
Olfactory: Smell
Optic: Vision
Oculomotor: Eye movement
Trochelar: Coordination of binocular vision
Trigeminal: Sensory & motor to face
Abducens: Lateral eye movement (abduction)
Facial: Facial expression, Taste in anterior 2/3 of tongue
Vestibulocochlear: Hearing, balance, equilibrium
Glossopharyngeal: Taste in post 1/3 of tongue, swallowing, specific BP
Vagus: Speech, digestion, respiration, cardiac activity
Accessory: Head, neck, shoulder movement
Hypoglossal: Tongue movement & speech articulation
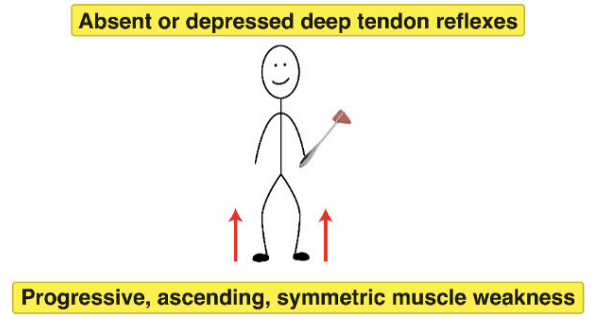
Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
RF: Campylobacter jejuni —> Follows resp/GI illness
S/S: Destruction of myelin in schwann cells —> Progressive symmetric ascending flaccid paralysis & weakness, ambulatory dysfunction, paresthesias, resp compromise, DTE decreased/absent
Dx: LP & CSF analysis —> Elevated CSF protein, EMG/nerve conduction studies
Tx: Vent support, plsamapharesis/IVIG
Cluster headache s/s, tx, prophylaxis?
S/S: Sudden onset of severe unilateral pain that occurs multiple times daily lasting 5min-3hrs, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, ptosis, miosis
Tx: 100% O2 + Sumatriptan
Prophylaxis: NDPH-CCB (Verapamil)
Trigeminal neuralgia vs Cluster headache?
Same s/s but trigeminal neuralgia has NO autonomic symptoms (lacrimation, rhinorrhea, ptosis) & precipitated by tapping nerve or movement
TN: Carbamazepine (anticonvulsant) vs CH: 100% O2
Migraine s/s, abortive tx, preventative tx?
S/s: Moderate-severe throbbing pain, photo/phono-phobia, N/V ± Aura (scotomna, decreased visual acuity, flashing lights, paresthesia), normal neruo exam
Abortive Tx: NSAID, acetaminophen, triptans
Preventative Tx: Anticonvulsants (valproate, topiramate), BBs (propanolol). TCAs (amitriptyline)
Tension headache s/s, abortive tx, preventative tx?
S/S: Gradual onset, pressure/tightness in band like distribution, muscle tension in head/neck, NO aura, N/V
Abortive tx: NSAIDS, acetaminophen
Preventative tx: TCAs (amitriptyline)
Encephalitis MCC, s/s, dx, tx?
Infection of brain parenchyma —> MCC HSV T1
S/S: Altered consciousness, AMS, confusion, personality changes, fever, headache, focal neuro deficits (hemiparesis, hyperreflexia)
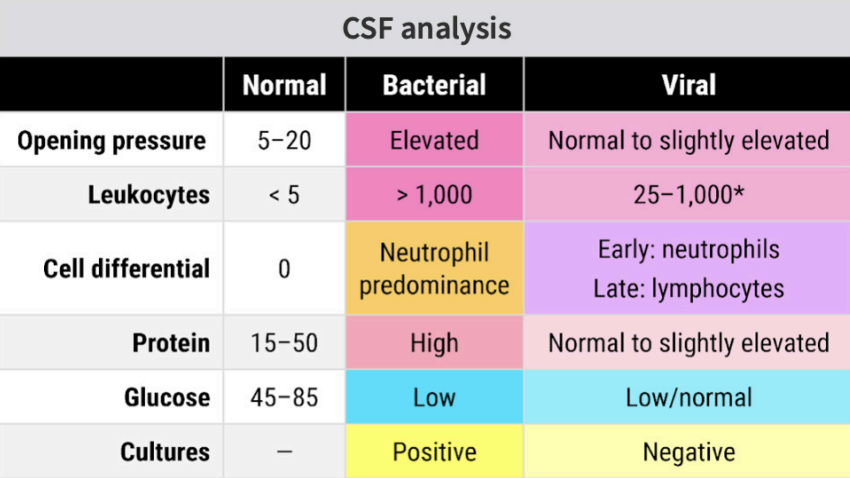
Dx: CSF shows Normal glucose, ↑ protein, lymphocytosis + Head CT to r/o space occupying lesion
Tx: IV acycylovir
Bacterial meningitis
S/s: Fever, neck stiffness, headache, AMS, seizures, meningeal signs (Kernig & Brudzinski)
Petechial/ecchymotic rash if Neisseria meningitidis
Dx: CSF shows ↑ opening pressure, predominant neutrophils, ↓ glucose, ↑ protein
Neonate Tx: Cefotaxime/Ceftriaxone + Ampicillin
Older children/Adults Tx: Cefotaxime/Ceftriaxone + Vancomycin
What do we give for listeria coverage in bacterial menigitis?
Ampicillin
Parkinson’s Disease patho, s/s, tx?
Patho: Deficiency of dopamine in basal ganglia
S/S: Resting tremor, bradykinesia, muscular rigidity, postural instability (impaired balance & coordination), resting “pill rolling” tremor, cogwheel rigidity (rigidity + tremor)
Tx: Carbidopa-Levodopa, dopamine agonists (pramipexole), MAO-B inhibitors (selegiline) amantadine
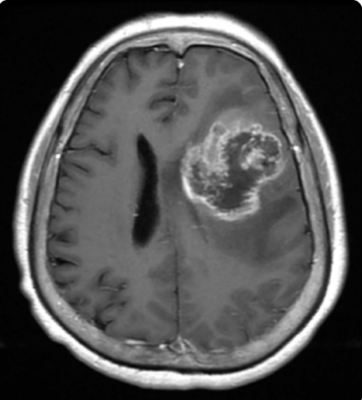
Glioblastoma s/s & dx?
S/S: Chronic headaches, N/V, cognitive/personality/ visual changes, seizure
Dx: Biopsy + Head MRI with gadolinium
Vascular dementia
Prior stroke or small vessel changes in the brain —> cognitive decline following stroke
CT/MRI: White matter lesions
Tx: No tx, focus on preventing progression by controllong RFs
Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Lewy body deposits on brain —> fluctuating cog impairment, hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, Parkinsonism features
CT/MRI: Atrophy of frontal & temporal lobes
Tx: Cholinesterase inhibitors: donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine
Frontotemporal dementia s/s & tx?
S/S: Genetic mutations cause early degeneration of frontal & temporal lobes —> Behavior/personality changes & word finding difficulty
No effective pharmacotherapy tx
Alzheimer’s s/s, dx, tx?
S/S: Amyloid plaques cause progressive decrease in cognition & memory, difficulty completing ADLs, short term memory loss
CT/MRI: Atrophy of medial temporal lobes & hippocampus
Tx: Cholinesterase inhibitors: donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine
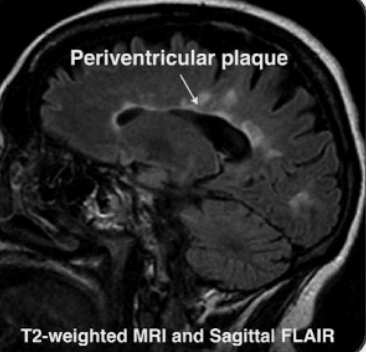
Multiple Sclerosis s/s, PE, dx, tx?
S/S: Demyelination of CNS —> fatigue, sensory changes, muscle spasticity, optic neuritis (painful monocular vision loss) & internuclear ophthalmoplegia (impaired horizontal eye movements)
PE: Relative afferent pupillary defect/Marcus Finn pupil (pupils dilate when light is shown), Lhermitte sign (electric shock-like sensation down the spine and into limbs when the neck is flexed), stoaccato speech pattern
Dx: MRI with gadolinium shows white plaques and Dawson’s fingers
Tx: IV CCS for acute, IV monoclonal antibodies for long term therapy
Myasthenia Gravis
Disorder of IgG antibodies at postsynaptic membrance
S/S: Improves in cooler temps, muscle weakness worsens with use & improves with rest, bulbar sxs (breathing, swallowing, facial mvmt problems), ocular sxs
Lambert Eaton
Glasgow Coma Scale
Protect the airway at 8 or below
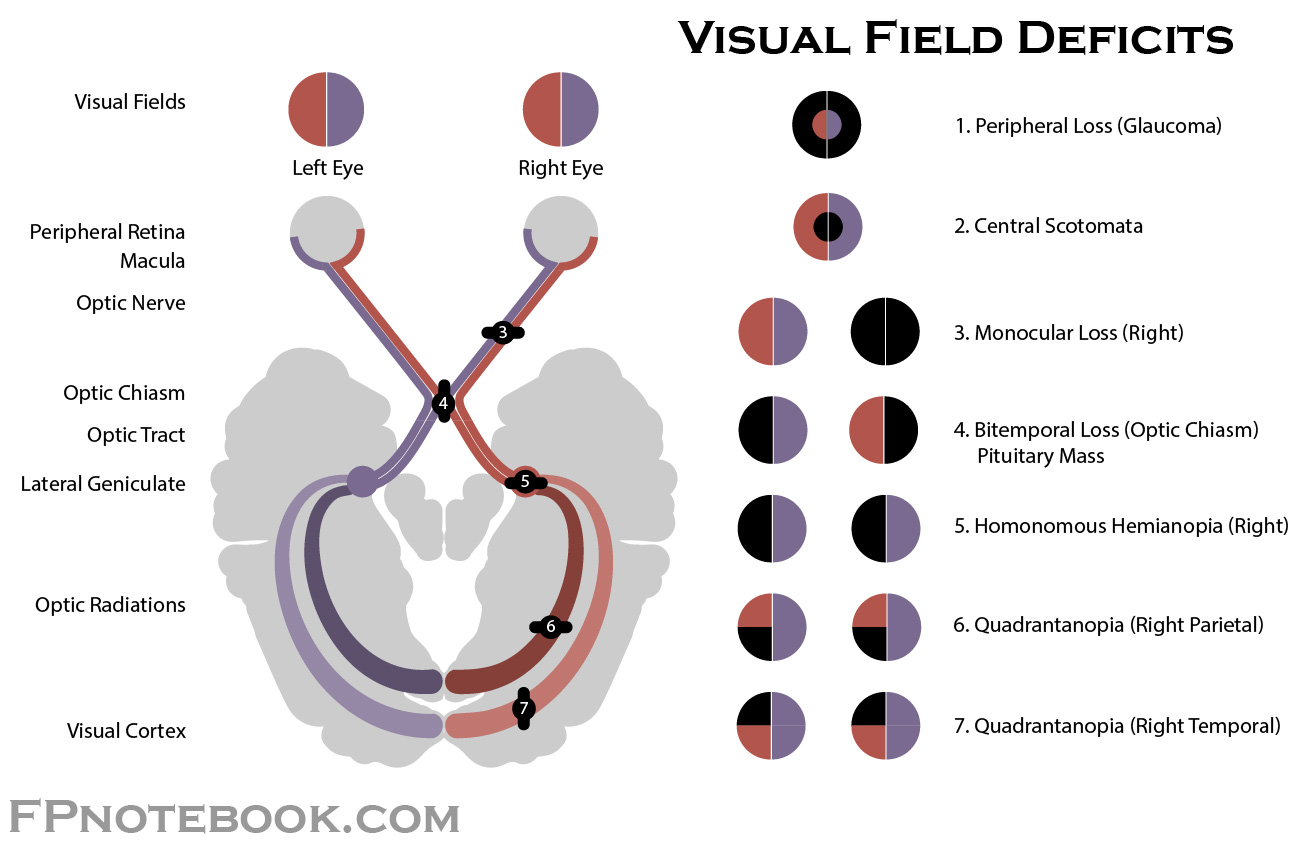
What occurs when there is a pituitary adenoma of the central optic chiasm?
#4: Bitemporal hemianopia (Tunnel vision)

Patient has a circular defect in their vision. What is the most likely dx?
Lesion on the retina —> Central scotomata #2
Child gazing to the right and unable to abduct the right eye while the adduction of the left eye is intact. What is the most likely dx?
CN 6 palsy (Abducens)
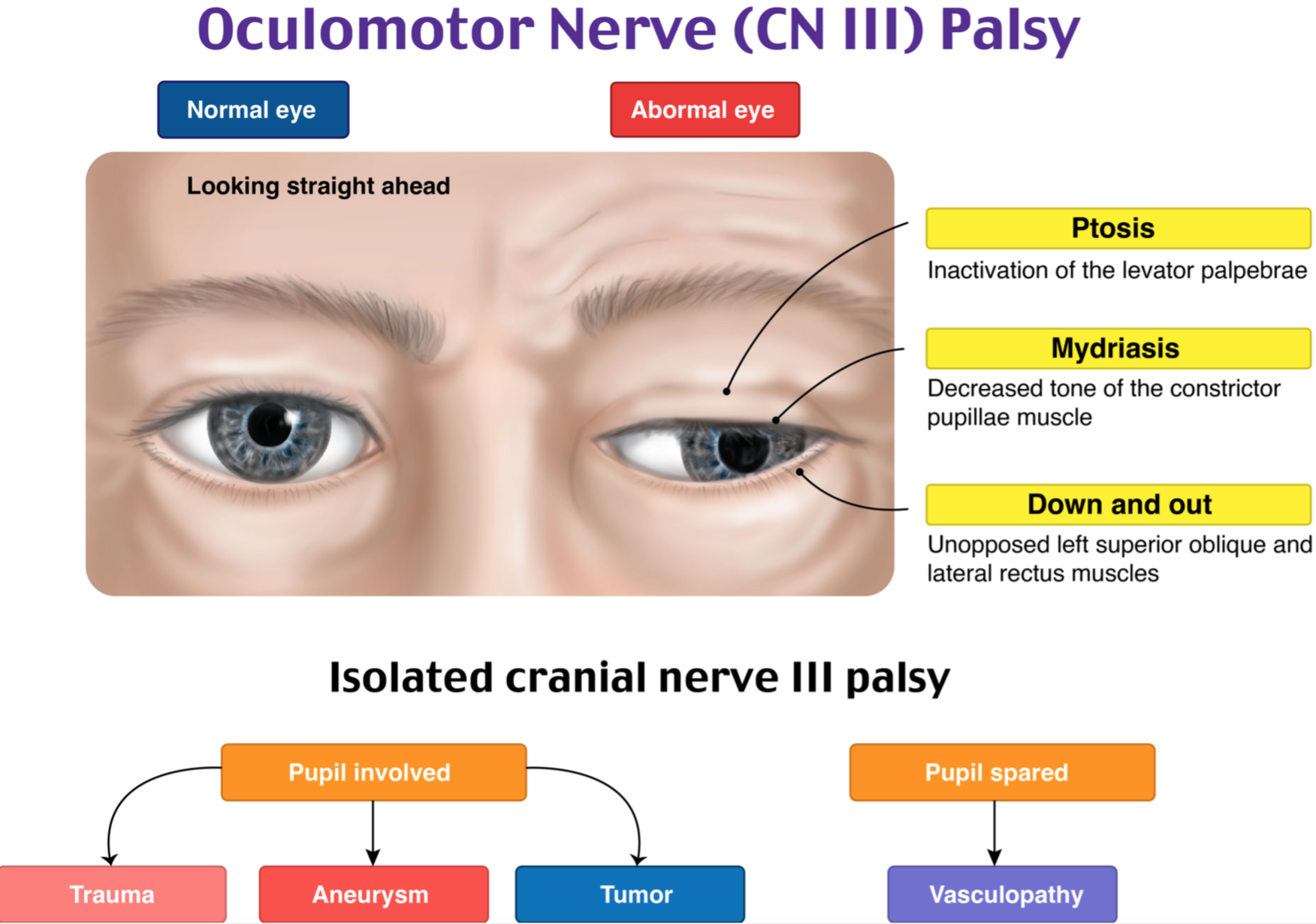
What is oculomotor (III) nerve palsy do?
Ptosis, mydriasis (dilation of pupil), down & out position of eye
Bells palsy vs Stroke
Bells cannot move forehead
Stroke can move forehead
BPPV
Meniere’s Disease