Physics - 15 Electromagnetism - 15.4 The Motor Effect & 15.5 The Generator Effect & 15.6 The Alternating-Current Generator
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Motor effect
force exerted on a current-carrying conductor due to a magnetic field
How can the force exerted on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field be increased? [2]
- increasing the current
- increasing the strength of the magnetic field
How does the angle of the conductor to the magnetic field affect the force on the conductor? [2]
- strongest when perpendicular
- zero when parallel
Conventional current
current that flows from the positive side of the battery to the negative side; used in diagrams
Fleming's left-hand rule
method of using the left hand to find one of the force, magnetic field or current acting on a wire
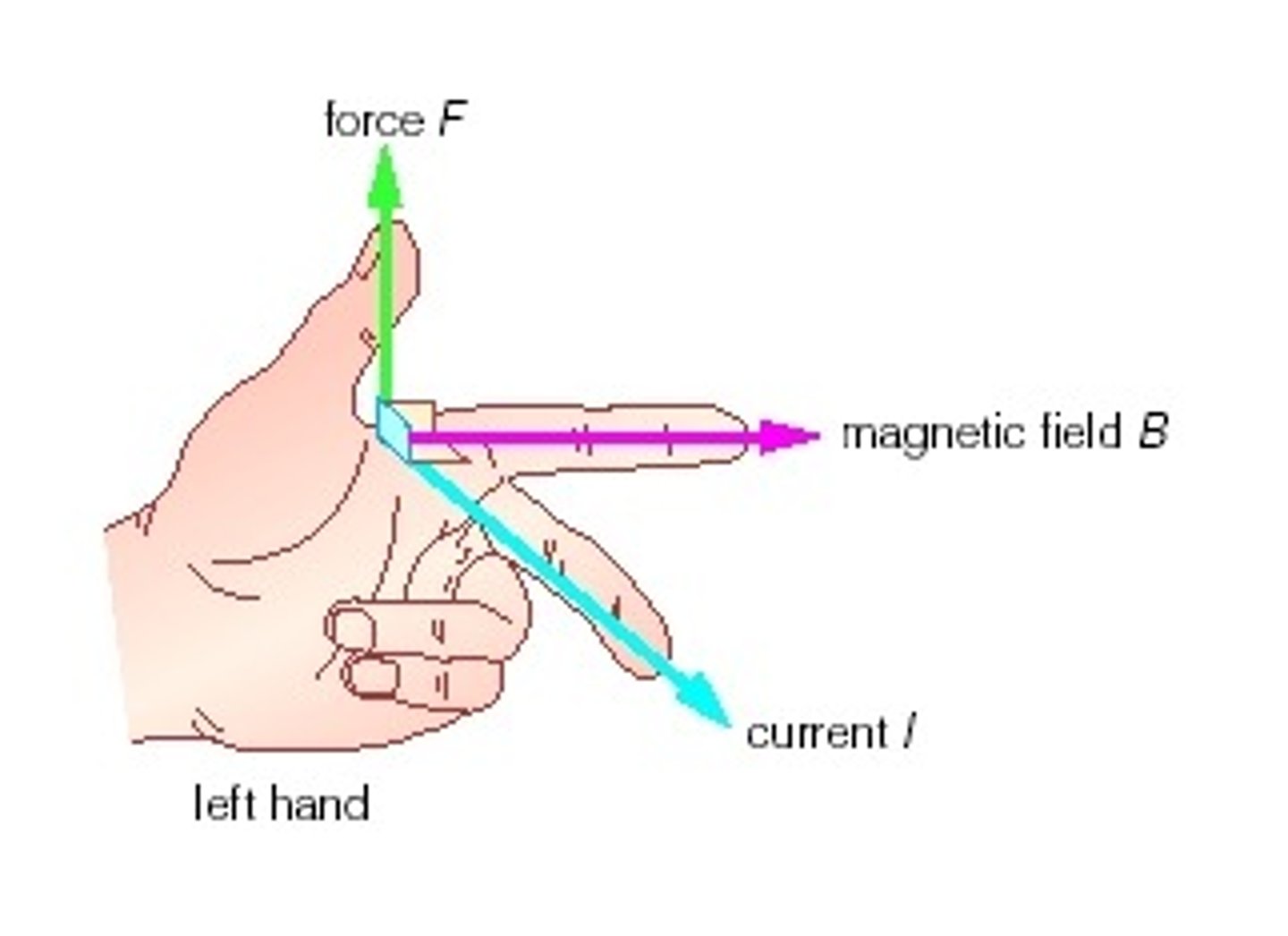
Fleming's left-hand rule: force
thumb
Fleming's left-hand rule: magnetic field
index finger
Fleming's left-hand rule: current
middle finger
What will an alternating current cause a wire in a magnetic field to do?
vibrate
Magnetic flux density
representation of the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field
What is the unit of magnetic flux density?
Tesla (T)
What is the symbol of magnetic flux density?
B
Word equation for force on a wire
force = magnetic flux density x current x length
Symbol equation for force on a wire
F = BIl
How does an electric motor work? [3]
- current-carrying coil of wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field
- opposite force is exerted on each side of the coil, causing it to rotate
- the direction of current is changed every half-turn by the split-ring commutator
Split-ring commutator
rotates with the coil in an electric motor and reverses the direction of the current every half turn
Why is the split-ring commutator necessary? [2]
- if a coil undergoes a half-turn, the forces on the wires will no longer point the correct direction to keep rotating in the same direction
- to maintain the same rotation, the split-ring commutator reverses the direction of the current
Brush (electric motor)
conductors which maintain a connection between the rotating coil and the circuit
Rotor/armature
rotating member of an electrical machine.
Generator effect
when a magnetic field moves relative to a conductor, a potential difference is induced across the conductor, driving a current in a complete circuit
Induce
to cause or produce
Electromagnetic induction
process of creating a current in a circuit by changing a magnetic field
Conservation of energy with a generator
generated induced current is a result of work done to change the magnetic field relative to the conductor
How can the current induced in a generator be increased? [4]
- increasing speed of movement
- increasing strength of magnetic field
- increasing number of turns in coil
- increasing surface area of coil
Solenoid rule
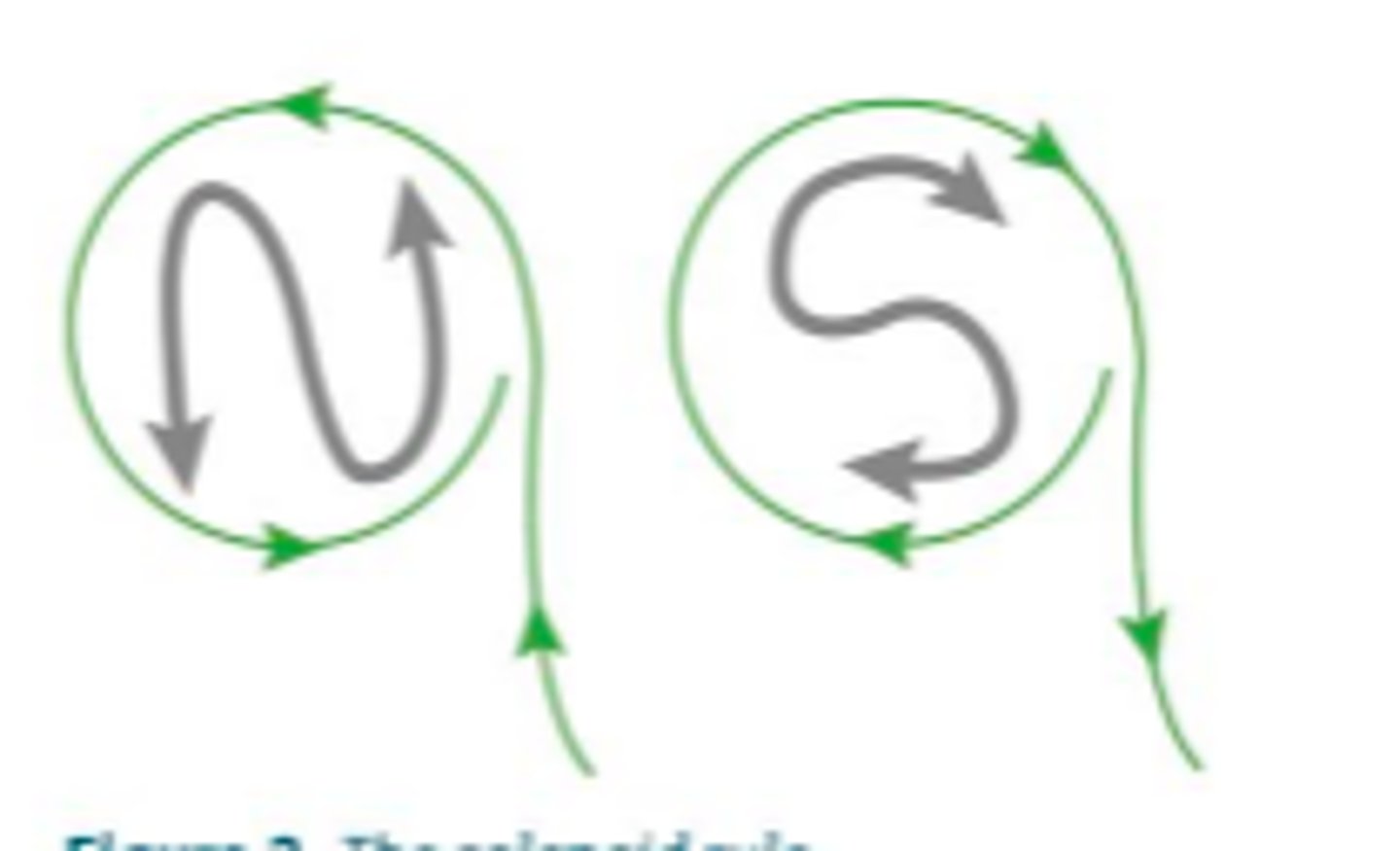
When the pole of a magnet is moved towards a solenoid, an (opposite/like) pole is induced in the solenoid which (repels/attracts) the magnet
like, repels
When the pole of a magnet is moved away from a solenoid, an (opposite/like) pole is induced in the solenoid which (repels/attracts) the magnet
opposite, attracts
What does reversing the direction of movement do to the induced current?
reverses the flow of current
Galvanometer
ammeter which can detect very small electrical currents
Why is the current induced by a generator an alternating current? [3]
- the coil rotates
- the circuit and slip rings are stationary
- so, the side of the coil connected to the circuit changes with each half-turn
What does increasing the speed of the rotation in a generator do? [2]
- increase the frequency of the alternating current
- increase the peak potential difference of the current
Alternating current graph
resembles a sine graph, with waves
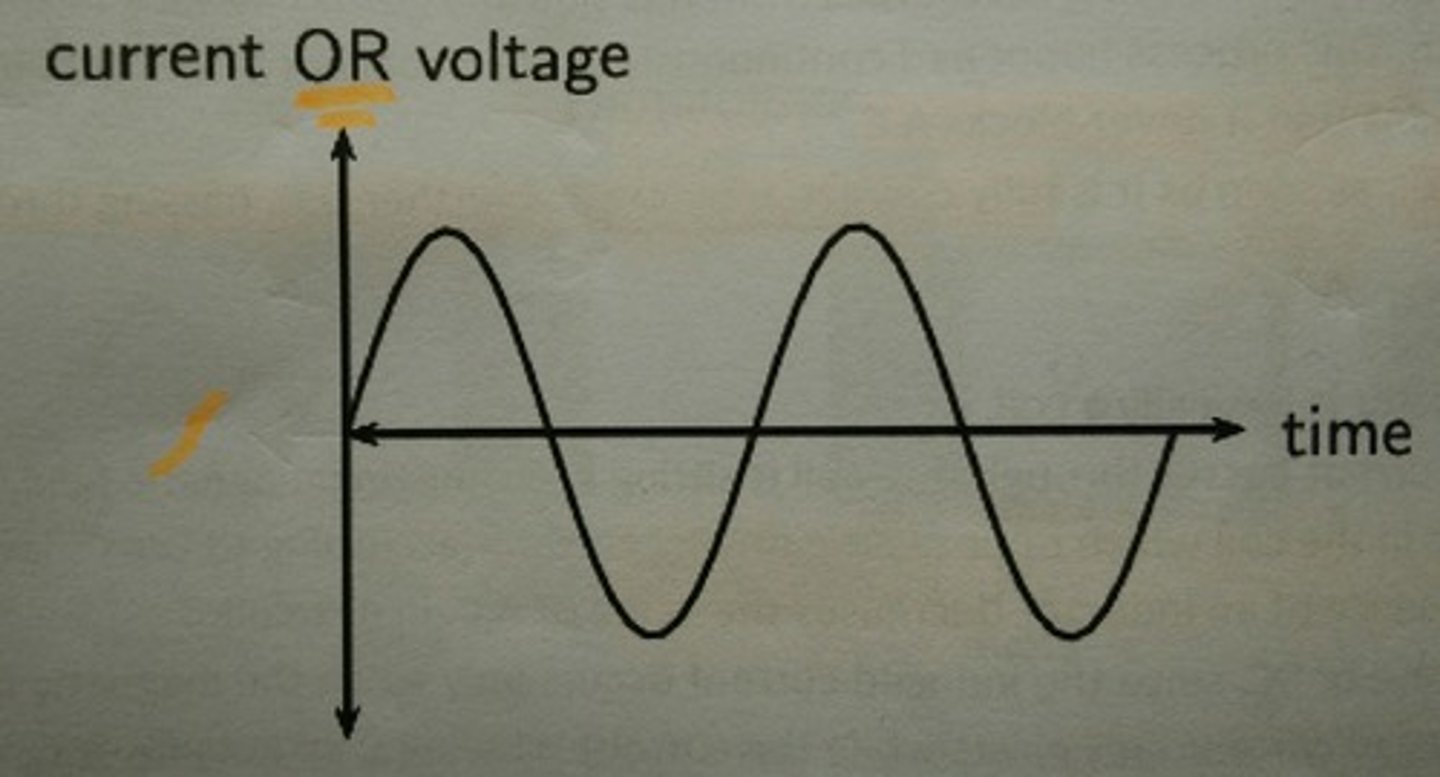
What position does the peak of an alternating-current graph correlate to in a generator?
sides of the coil crossing directly through the magnetic field
What position does the x-intersection of an alternating-current graph correlate to in a generator?
sides of the coil not crossing through the magnetic field
Slip ring
metal rings connected to the rotation coil in a generator; they make electrical contact with an external circuit
Dynamo
generator which generates a direct current
How does a dynamo generate a direct current? [3]
- dynamo works like an ordinary generator
- has a split-ring commutator, which switches the direction of current each half-turn
- since rotation causes a reverse, the commutator keeps it constant
What is the nature of the current from a dynamo? [2]
- goes from minimum to maximum value twice each cycle
- never changes polarity
Microphone
device for converting sound waves into electrical energy
Loudspeaker
device that converts pulses of electricity into sound waves
How does a microphone work? [4]
- sound waves cause a flexible membrane to vibrate
- this causes a permanent magnet to vibrate
- this induces an alternating current in a coil of wire
- current alternates with the same frequency as the sound wave
Why is the current from a microphone an alternating current?
the magnet moves in both directions relative to the coil
How does a loudspeaker work? [5]
- an alternating current is supplied to a coil of wire
- the coil becomes an electromagnet due to the current
- the magnetic field interacts with a permanent magnet, causing the coil to move back and forth
- coil is attached to diaphragm; generates sound waves
- sound waves have same frequency as supplied current
Why is the current supplied to a loudspeaker an alternating current?
the diaphragm needs to move both back and forth to generate sound waves