Principles of Taxation - Chapter 3 - Employment Income
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is employment income & what basis is it taxed on?
money or money’s worth arising from employment and is taxed on a receipts basis
What does income taxed as employment income include & how is taxed?
Salary - Tax the gross amount received on every pay day in the tax year
Tips - e.g. service charges added to restaurant bills are taxable on the staff who receive a share of those tips.
Bonus - Deemed to be received on the earlier of the date on which: - the bonus is paid - the individual becomes entitled to payment.
Which date do we use if the question does not mention the date someone becomes entitled to a bonus?
We use the actual date paid
Who is taxed when an employer provides a benefit where there is no specific rule for calculating the benefit & how?
the employee is taxed on the marginal cost to the employer
What happens if an employee has contributed to taxable benefits (& the employer has paid the rest)?
If the employee has contributed towards the benefit this can be deducted, except for the provision of private fuel
What do we do if the benefit was provided for only part of the tax year?
We time apportion to the nearest month
What is the tax treatment for non-cash voucher?
Explanation: A voucher or card exchangeable for goods or services (e.g. a book token)
Taxable amount: Cost to the employer, less any amount paid by the employee
What is the tax treatment for cash vouchers?
Explanation: A voucher or card exchangeable for cash
Taxable amount: Amount for which the voucher can be exchanged
What is the tax treatment for credit tokens?
Explanation: Usually a credit card, which can be used to obtain money, goods or services
Taxable amount: Cost to the employer, less any amount paid by the employee
Are trivial benefits exempt from tax? What’s the exception?
They are exempt
there is an annual cap of £300 in respect of such benefits when provided to certain directors
When is a benefit trivial?
A benefit that meets ALL of the conditions:
the cost of providing the benefit does not exceed £50
it is not cash or a cash voucher
it is not provided in recognition of services. - If any of the above conditions are not met, the benefit is taxed in the normal way.
What are the 23 benefits exempt from tax?
Use of free/subsidised on-site canteen (canteen must be available to all employees).
Sports facilities available to employees but not the public.
Workplace nurseries/childcare.
One each per year of health screening assessment and medical check-up
Glasses and eye tests for employees who use DSE (display screen equipment).
Up to £500 p.a. for recommended medical treatment to help the employee return to work.
Use of bicycles (and cycling safety equipment) if available to all employees.
Work buses and subsidies to use public bus services.
Vehicle battery charging facilities at or near the place of work where the vehicle is used by the employee.
Travel expenses when public transport disrupted, late night journeys and where car sharing arrangements break down.
Provision of a car parking space at/near place of work.
Employer’s contributions into a registered pension scheme.
Pension advice and associated tax planning available to all employees up to £500 p.a. (above which the full amount is taxable).
Mobile phone (one per employee for private use).
Work related training courses.
Up to £150 p.a. per head for social events. If an event costs more than £150 the full amount is taxable, not the excess. The party must be an annual event to qualify for the exemption. Where there is more than one event in the year, the total cost of events ≤ £150 will be exempt and the other events will be taxable.
Non-cash long service awards for ≥ 20 years’ service, maximum £50 per year of service.
Awards of up to £5,000 made under a staff suggestion scheme.
Non-cash gifts from third parties (up to £250 p.a. per donor) or entertainment provided by a third party (no limit).
Removal expenses up to £8,000.
Payments towards costs of working from home (need supporting documents if > £6 p.w.).
Personal incidental expenses when working away from home up to £5 per night in the UK and £10 when working abroad. If the limit is exceeded the whole payment is taxable.
Job-related accommodation (Section 1.6)
Is provision of living accommodation that is job-related taxable?
NO
Job-related living accommodation is either:
necessary for performance of duties e.g. level-crossing gate keeper, or
customary to be provided, e.g. prison governor, or
provided for security, e.g. soldier barracks.
When only will a director qualify for necessary or customary job-related accommodation?
If both conditions are met:
the director owns no more than 5% shares in company, and
the director is a full-time working director (unless the company is a charity/nonprofit making).
If living accommodation provided by an employer is not job-related, what does the taxable benefit depend on?
Whether the employer owns or rents the property.
If the employer rents a property, what is the benefit is the higher of?
the annual or rateable value (given in the question), and
the rent paid by employer.
What is the basic benefit if, the employer owns the living accommodation?
the basic benefit is the rateable value (given in the question)
When is there an additional benefit on living accommodation and how is it calculated?
if the original cost of the house exceeds £75,000
(‘Cost’ – £75,000) × official rate of interest at start of tax year
where ‘Cost’ is generally the original value when the employer purchased the property
Include capital improvements between the date on which ‘cost’ is determined (date of purchase/employee moving in) up to the start of the tax year.
If the employer owned the property for more than 6 years before employee moved in use the market value at the date the employee moved in as the ‘cost’ for calculating the benefit.
What is there further benefit for, in addition to the taxable benefit for the accommodation itself?
furniture – use rules for assets lent for private use (refer to section 2.7).
related living expenses paid for by the employer e.g. heating, lighting, cleaning, repairs, decoration – use cost to employer less any employee contribution.
What does a single car benefit charge cover? When is a separate benefit taxable?
A single car benefit charge covers the running costs of the car including insurance, maintenance and road tax
a separate benefit is taxable if the employer provides private fuel for the car.
What’s the formula for car benefit?
Car benefit = manufacturer’s list price × CO2 emissions %
What is there no car benefit for?
Incidental private use of genuine pool cars.
What is the CO2 emission percentage for zero-emissions cars?
2%
How do you calculate the CO2 emissions % for all other cars (not zero-emissions)
take the appropriate percentage from the tax tables (see below) then calculate the additional percentage if relevant:
Round the CO2 emissions down to nearest 5g/km
Add 1% for each complete 5g/km above 75g/km
Maximum CO2 emissions % = 37% (for both petrol and diesel cars)
What must we do for CO2 emissions calculations for diesel cars/
Add a 4% supplement to the relevant petrol percentage unless they meet the Real Driving Emissions Step 2 (RDE2)
Exam questions will state whether a car meets the RDE2 standard.
What do the CO2 emissions % for hybrid cars with emissions of 1 – 50g/km depend on?
the car’s battery range.
Exam questions will state the car’s battery range (also known as electric range) if it is required
How is private fuel benefit calculated?
The benefit for private fuel (petrol or diesel) provided by the employer is a flat rate regardless of how much fuel is paid for by the employer
It is calculated as £27,800 × CO2 emissions % (same percentage as for car benefit).
Unlike other benefits there is no deduction for employee contributions towards part of the cost of the fuel but if the employee makes good the whole cost of private fuel there is no benefit.
What is the van scale charge on private use of an employer’s van?
£3,960 but there is no benefit for vans with zero CO2 emissions.
Deduct any amount contributed by the employee from the value of the benefit.
Does a van that is used for travel between home and work and any other private use is insignificant have a benefit?
No
What is the taxable benefit on fuel provided for private use in company vans?
£757
There is no reduction for employee contributions towards fuel costs.
What is the benefit when the employer owns the asset & lends it to the employee?
Benefit = annual value: 20% × market value when first provided for private use
What is the benefit when the employer rents an asset & lends it to the employee?
Benefit = higher of:
annual value
rent paid by employer
Is there benefit for assets lent from employer to employee for private use?
There is no benefit if private use is not significant (e.g. using a work laptop for private email).
What is mean by insignificant use?
Insignificant use is not defined but is considered on a case-by-case basis.
In the exam this could be specified for example as ‘occasional’ or ‘less than 10% of overall use’.
Which system do employers deduct income tax and NIC on their employees’ employment income?
Through the PAYE system
How must employers report PAYE?
In real time
This means that each time the employer pays an employee, the employer must submit details of the pay and deductions to HMRC using payroll software.
How must an employer submit PAYE information?
The employer must submit the information on or before the day the employee is paid, using a Full Payment Submission (FPS)
When may an Employer Payment Summary (EPS) be required?
If the employer reclaims:
statutory maternity, paternity or adoption payments.
the employment allowance
What may an employer choose to do under voluntary payrolling?
Employers may opt to process benefits such as cars and medical insurance through the payroll instead of reporting the benefits via P11D forms
How does an employer do voluntary payrolling?
The employer reports the value of the benefits via the RTI system and treats the cash equivalent of the benefit like salary, so that the relevant tax is deducted under PAYE
Of the taxable benefits examinable in Principles of Tax, only employer provided living accommodation cannot be processed through the payroll.
An employer may choose which benefits to payroll (e.g. a company may choose to payroll company car benefits but not medical insurance).
What does an employer do at the end of the tax year regarding PAYE forms?
At the end of the tax year, the employer completes form P60 for each employee, giving the following details for the tax year:
gross pay
tax deducted
NICs paid by both employee and employer
When must an employer supply at P60 to each employee?
by 31 May following the end of the tax year.
What must employers provide to HMRC regarding benefits?
An employer must also provide HMRC with details of the benefits provided to each employee during the tax year using form P11D unless all benefits are payrolled
When must the employer submit at P11D to HMRC?
by 6 July following the end of the tax year and provide a copy to the employee by that date.
What is required for P11D?
A full P11D is not required for the benefits that are payrolled, but the employer must submit a P11D(b) showing the cash equivalents of these benefits.
Where all benefits are payrolled, the employer is not required to submit P11Ds, but if only some benefits are payrolled, a P11D will need to be submitted for any benefits not payrolled.
What is a P45?
Form P45 is a four-part form used when an employee leaves.
It contains a summary of taxable pay, tax and NIC deducted as well as employer’s NI contributions for the employee, up to the date of leaving
Does any information on the P45 need to be submitted to HMRC?
No
Instead, the employer will include the leaving date in the FPS for period in which the final payment is made
When are monthly payments of income tax & NIC due for payment to HMRC from employers?
It’s due for payment 14 days after the month ends.
The tax month runs from 6th to 5th of each month, so the payment due date is the 19th of each month.
What is the deadline extended to for monthly payments of income tax & NIC to HMRC from employers for electronic payment?
The deadline is extended to 22nd of the month for electronic payment
What must employers with at least 250 employees do regarding monthly PAYE payments?
They must make their monthly PAYE payments electronically.
Which employers cannot make income tax & NIC payments to HMRC quarterly & must do monthly?
Employers whose average monthly payments of PAYE and NICs are no more than £1,500 in total are allowed to make payments quarterly, rather than monthly
What is the penalty for the first late payment if it less than 6 months late?
£0
When can late payment penalties be suspended?
If the taxpayer agrees a time to pay arrangement, unless this arrangement is then abused
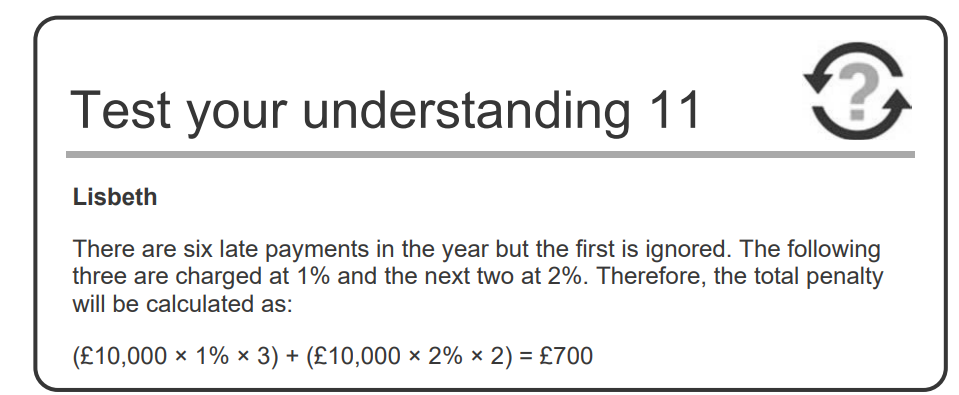
How do we calculated PAYE penalties?
Total = (Monthly amount x % from table x no. of months in that bracket)
Why does HMRC issue a tax code?
To enable the employer to deduct the correct amount of tax from each employee & it incorporates the deductions and allowances available to the individual.
Which 2 forms does HMRC issue in relation to each employee’s tax code?
Form P2 is sent to the employee and gives detail of how the PAYE code has been calculated.
Form P9(T) is sent to the employer and gives the PAYE code only.
How does an employer’s payroll software spread an employee's allowances?
evenly over the tax year
How do we calculate the PAYE code?
Calculate allowance and deductions (as in picture)
If allowances > deductions - take NET figure, remove last digit and add letter L
If deductions> allowances - take NET figure, deduct 1 and add the letter K at the start

What does L mean in a tax code?
L means the individual is entitled to basic personal allowance.
What will the letter in a tax code be if the taxpayer received part of a spouse or civil partner’s personal allowance via the marriage allowance?
M
What will the letter in the PAYE code by if the taxpayer transferred part of the personal allowance to a spouse or civil partner?
N
What can the coding notice be used for?
To show unpaid tax in earlier years, or income tax on the taxpayer's estimated savings income and dividend income in the current year.
Tax of up to £3,000 can be collected in this way.
When deducting the adjustment for underpaid tax gross up using the individual’s estimated marginal (i.e. highest) rate of tax.