Biology Finals: Identification
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
a frog (amphibian), part of Chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrates; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems; special outer covering (skin, scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs, arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
ectothermic: cold blooded, body temp varies w environment, cannot regulate metabolic rate very well

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
iguana (reptile), part of chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrates; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes, head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems, special outer covering (skin/scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs/arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
ectothermic: cold blooded, body temp varies with environment, cannot regulate metabolic rate very well.

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
bird (aves), part of the Chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrates; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes, head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems; special outer covering (skin/scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs/arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
endothermic: warm blooded, constant body temp despite environment, regulate metabolic rate

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
humans (mammals), part of Chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrates; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes, head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems; special outer covering (skin/scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs/arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
endothermic: warm blooded, constant body temp despite environment, regulate metabolic rate

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
what type of fish (why)
shark, part of the Chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrate; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes, head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems; special outer covering (skin/scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs/arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
can be both, most ectothermic: cold blooded; body temp varies with environment, cannot regulate metabolic rate very well

Identify:
what it is
characteristics
endothermic/ectothermic (why)
what type of fish (why)
fish, part of Chordates
bilaterally symmetrical; vertebrates; endoskeleton; central nervous system (brain/skull); very good eyes, head, sensory organs, heart + circulatory systems; special outer covering (skin/scales); 1-2 pairs of appendages (legs/arms); sexual reproduction; land/water
ectothermic: cold blooded, body temp varies with environment, cannot regulate metabolic rate very well

Identify:
what it is
Group + Phylum
Characteristics of all class members
Description of this worm
Earthworm
Annelids, Upper Invertebrates
Coelomate; digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory systems; NO respiratory systems (o2 thru skin); segmented into “septa” compartments; rings=annuli; hermaphroditic (cross fertilization); sexually + asexually (regeneration); terrestrial, freshwater, marine; 1mm-3m long
1 way digestive system, hermaphroditic but must still mate to mix gametes, regrow amputated segments
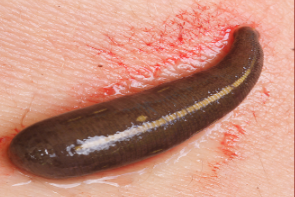
Identify:
what it is
Group + Phylum
Characteristics of all class members
leech
annelids, upper invertebrates
coelomate, digestive, circulatory, nervous, excretory systems; NO respiratory (o2 thru skin); segmented into “septa” compartments; rings=annuli; hermaphroditic (cross fertilization); sexually+asexually (regeneration); terrestrial, freshwater, marine; 1mm-3m long.

Identify:
what it is
Group + Class
Characteristics of all class members

Identify:
what it is
group + Phylum
characteristics of this class
limpet
mollusk, upper invertebrates
visceral mass+foot+mantle; coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; one way digestive system; cephalization with sensory organs; respiratory system; radula (tongue for feeding); sexual reproduction (dioecious/separate sexes)

Identify:
what it is
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
scallop
mollusk, upper invertebrates
visceral mass+foot+mantle; coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; one way digestive system; cephalization with sensory organs; respiratory system; radula (tongue for feeding); sexual reproduction (dioecious/separate sexes)

Identify:
what it is
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
squid and cuttlefish
mollusk, upper invertebrates
visceral mass+foot+mantle; coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; one way digestive system; cephalization with sensory organs; respiratory system; radula (tongue for feeding); sexual reproduction (dioecious/separate sexes)
Identify:
What are mollusks (name all phylum)
Distinct body parts of Mollusks
snails, slugs, clams, oysters, mussels, octopus, squid, cuttlefish
visceral mass (body porion with organs), foot (strong muscle for movement-tentacles), mantle (encloses visceral mass + shell)
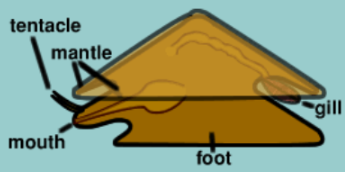

Identify:
what is it
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
centipede
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trachea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere

Identify:
what is it
Group + Class
Characteristics of all class members
Millipede
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trachea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere

Identify:
what is it
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
insect description
a beetle lol
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trach andea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere
exoskeleton=chitin, segmented head, antennae + eyes + legs + wings, digestive/respiratory/excretory/reproductive systems, most hatch from eggs, sexual reproduction, meta morphosis

Identify:
what is it
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
Scorpian (spider)
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trachea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere

Identify:
what is it
Group + phylum
Characteristics of all class members
Barnacles
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trachea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere

Identify:
what is it
group + phylum
characteristics
crab
arthropod, upper invertebrates
coelomate; bilaterally symmetrical; jointed appendages; exoskeleton of chitin (made by epidermis); 3 regions (head, thorax, abdomen); respiration by body surface, gills, trachea; open circulatory system; developed sensory organs (eye, antenna); complete digestive system with mouth, organs, anus; dioecious (fertilization usually internal); nervous system with dorsal brain; live everywhere
What are Chordates? Name all phylums
Frogs, toads, salamanders, reptiles, birds, mammals
What are upper invertebrates? Name all phylums
Annelids (worms): earthworm, leech
Mollusks (slimy): snail, slug, clam, oyster, octopus, squid, cuttlefish
Arthropods (joined): centipedes, insects, spiders, scorpian, barnacles, crabs, lobsters, shrimp, crayfish
Echinoderms (spikey skin): starfish, sea urchin, sand dollar, sea cucumber, brittle star
What are lower invertebrates? name all phylums
Porferia (pore bearers): sea sponges
Cnidarians (stinging needles): jellyfish, anemones
Plathetheminthes (flatworms): Flukes, tapeworms, parasitic Flatworms, free living flatworms
Nematodes (roundworms): tiny non earthworm worms 🙂

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
sea star tube feet
starfish
echinoderms, lower invertebrates
coelomate; radially symmetrical (penta radial); calcareous skeleton; water vascular system; digestive system; open/reduced circulatory system (no heart) with central ring + vessels; simple radial nervous system (no brain); gonads=reproductive system; sexual reproduction (fertilization outside body, cillated, freeswimming larvae)
5 arms with eyespot at end, 2 stomachs, water vascular systyem (central ring→ canals→tube feet)
TUBE FEET FOR: movement, feeding, bringing in water for gas exchange

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
sea urchin
echinoderms, lower invertebrates
coelomate; radially symmetrical (penta radial); calcareous skeleton; water vascular system; digestive system; open/reduced circulatory system (no heart) with central ring + vessels; simple radial nervous system (no brain); gonads=reproductive system; sexual reproduction (fertilization outside body, cillated, freeswimming larvae)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
sand dollar
echinoderms, lower invertebrates
coelomate; radially symmetrical (penta radial); calcareous skeleton; water vascular system; digestive system; open/reduced circulatory system (no heart) with central ring + vessels; simple radial nervous system (no brain); gonads=reproductive system; sexual reproduction (fertilization outside body, cillated, freeswimming larvae)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
brittle star
echinoderms, lower invertebrates
coelomate; radially symmetrical (penta radial); calcareous skeleton; water vascular system; digestive system; open/reduced circulatory system (no heart) with central ring + vessels; simple radial nervous system (no brain); gonads=reproductive system; sexual reproduction (fertilization outside body, cillated, freeswimming larvae)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
sea cucumber
echinoderms, lower invertebrates
coelomate; radially symmetrical (penta radial); calcareous skeleton; water vascular system; digestive system; open/reduced circulatory system (no heart) with central ring + vessels; simple radial nervous system (no brain); gonads=reproductive system; sexual reproduction (fertilization outside body, cillated, freeswimming larvae)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
stucture
Sea sponge
Porferia, lower invertebrates
filter feeders; non coelomate; asymmetrical; GVC; spicules skeleton; hermaphroditic (sexually no self, or asexually by budding or regeneration); sessile;
In through ostia, out through osculum, lined with collar cells for current

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
tentacle function
box jelly
Cnidarians, lower invertebrates
non-coelomate (Endoderm, ectoderm, mesoglea); radial symmetry; GVC; nervous system; hermaphroditic (sexually no self, or asexually budding/Regen), 2 stages-motile (medusa), sessile (polyp)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylums
characteristics
sea anemone
cnidarians, lower invertebrates
non-coelomate (Endoderm, ectoderm, mesoglea); radial symmetry; GVC; nervous system; hermaphroditic (sexually no self, or asexually budding/Regen), 2 stages-motile (medusa), sessile (polyp)

Identify:
what is it
group + phylum
characteristics
jellyfish
cnidarians, lower invertebrates
non-coelomate (Endoderm, ectoderm, mesoglea); radial symmetry; GVC; nervous system; hermaphroditic (sexually no self, or asexually budding/Regen), 2 stages-motile (medusa), sessile (polyp)

Identify:
group + class
characteristics
nematodes, lower invertebrates
pseudocoelomate; cephalization; no respiration or circulation; dioecious (sexual); unsegmented bodies; epidermis=cuticle made of collagen so it doesn’t dry out; longitudinal muscles (wiggly); parasitic and freeliving forms
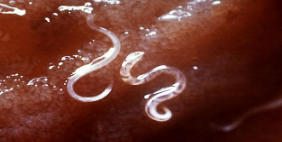
Identify:
group + class
characteristics
nematodes, lower invertebrates
pseudocoelomate; cephalization; no respiration or circulation; dioecious (sexual); unsegmented bodies; epidermis=cuticle made of collagen so it doesn’t dry out; longitudinal muscles (wiggly); parasitic and freeliving forms

Identify:
group + class
characteristics
nematodes, lower invertebrates
pseudocoelomate; cephalization; no respiration or circulation; dioecious (sexual); unsegmented bodies; epidermis=cuticle made of collagen so it doesn’t dry out; longitudinal muscles (wiggly); parasitic and freeliving forms

Identify:
group + class
characteristics
platytheminthes, lower invertebrates
noncoelomate; nervous system+cephalization (feat. eyespots); gastrovascular cavity (+organ systems for digestion + excretion); no circulatory or respiratory systems (take in 02 from surface); hermaphroditic (sexually) or asexually by budding or regeneration
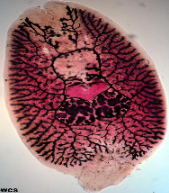
Identify:
group + class
characteristics
platytheminthes, lower invertebrates
noncoelomate; nervous system+cephalization (feat. eyespots); gastrovascular cavity (+organ systems for digestion + excretion); no circulatory or respiratory systems (take in 02 from surface); hermaphroditic (sexually) or asexually by budding or regeneration
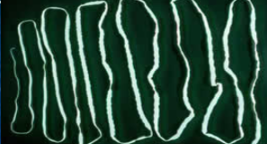
Identify:
group + class
characteristics
platytheminthes, lower invertebrates
noncoelomate; nervous system+cephalization (feat. eyespots); gastrovascular cavity (+organ systems for digestion + excretion); no circulatory or respiratory systems (take in 02 from surface); hermaphroditic (sexually) or asexually by budding or regeneration
Protist characteristics
eukaryotic, heterotrophic/autotrophic, single/multicellular,
ALGAE= plant like protists
PROTOZOA=animal like protists (ameoba)
SLIME/WATER MOLDS= fungi like protists
Ameoba
Animal like protist.
have pseudopods or “false feet” that help with movement and engulfing food
reproduce asexually by fission
can be harmful (amoebic dysentery)
Paramecium
Animal like protist. Move by cilia (for feeding and attachment), reproduces by division, most are freeliving and harmless
Plant like protists
algae
autotrophic (photosynthetic), primary producers of marine life, can be small or big, very few cause disease (red tide)
Bacteria shapes
bacillus (rod shaped)
cocci (circle shaped)
Spirillum (spiral shaped)
Archaea
live in extreme environments
methanogens (gas)
thermoacidophiles (heat/acid)
halophiles (salt)
adaptations
Change over a period of time
increase chance of survival (to reproduce)
natural selection=charles darwin=survival of the fittest
genetic diversity of genes among a population (increase chance of survival)
genetic drift=speciation (create new species)
adaptive radiation
darwin’s finches
founders effect (small group showed up)
geographic isolation (didn’t allow groups to breed)
natural selection (selected birds with best fitness to reproduce)
Ultimately created adaptive radiation that developed several new species (of finches)
characteristics of all viruses
non cellular, do not respire, do not respond to stimuli, do not grow, only reproduce inside a host (parasitic), contain genetic material (dna, rna, both), contain a protein coat around the dna/rna, contain small amounts of enzymes, can be stored for long periods of time
general structure of viruses
helical (rod)
spherical (sphere)
complex
types of viruses
animal, plant, bacteria
how are viruses spread
water, insects, blood
lytic cycle
attachment
penetration (insert genetic material)
replication (replicated within cell. can stay dormant=lysogenic pathway while dna replicates normally)
assembly
release
repeat
vaccines
best treatment of prevent spread disease
a weakened virus is injected to build immunity. body produces antibodies that can destroy the virus if it enters
cells
smallest living unit of life
most are microscopic
cell theory
all living things are made up of cells
cells come from cells
structure of all organisms
prokaryotic cells
first cell type
bacteria/archaea
no membrane bound organelles or nucleus
eukaryotic cells
membrane bound nucleus
fungi, plant, animals,
lots of organelles
divided into plant and animal cells. plants have cell walls and are photosynthesizers
3 Ecological Importances of Arthropods
get any:
pollination
production of honey, wax, silk
recycle biological materials
symbiotic relationships with other organisms
large portion of the food chain