Ch18 Renal Function
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APK2105C @ UD | Dr. Nguyen | Module 4 | Ch 18
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
ions; blood; osmolarity; waste
Main functions of the kidneys:
Ensure there’s enough _____ in the blood (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.)
Ensure an appropriate ______ volume
Ensure an appropriate _______ (solutes to plasma)
Mechanism to remove metabolic _______ and foreign substances
Ultimately regulate ALL body fluid volume and composition
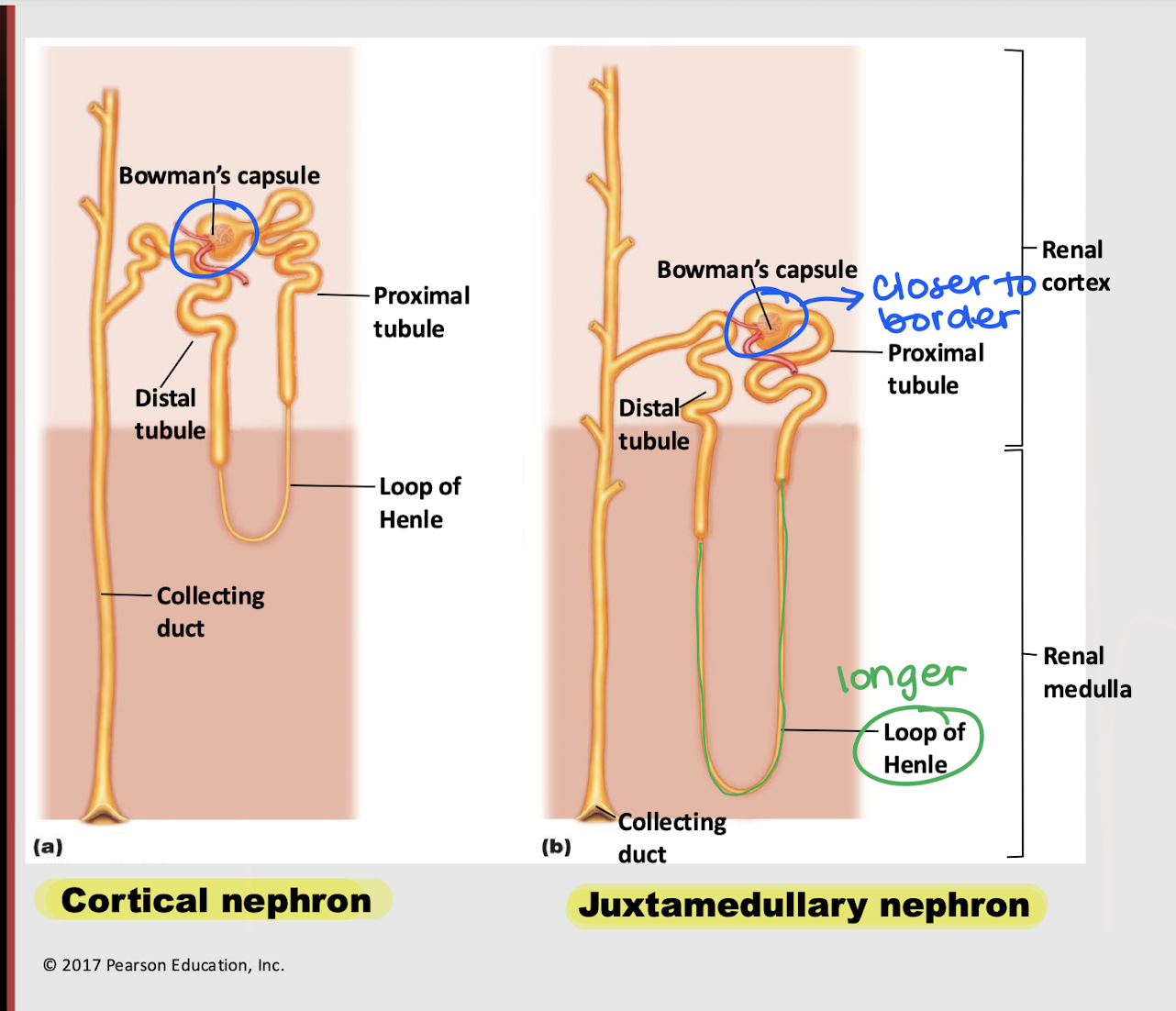
cortical nephron
Which nephron is found primarily in the kidney’s cortex?
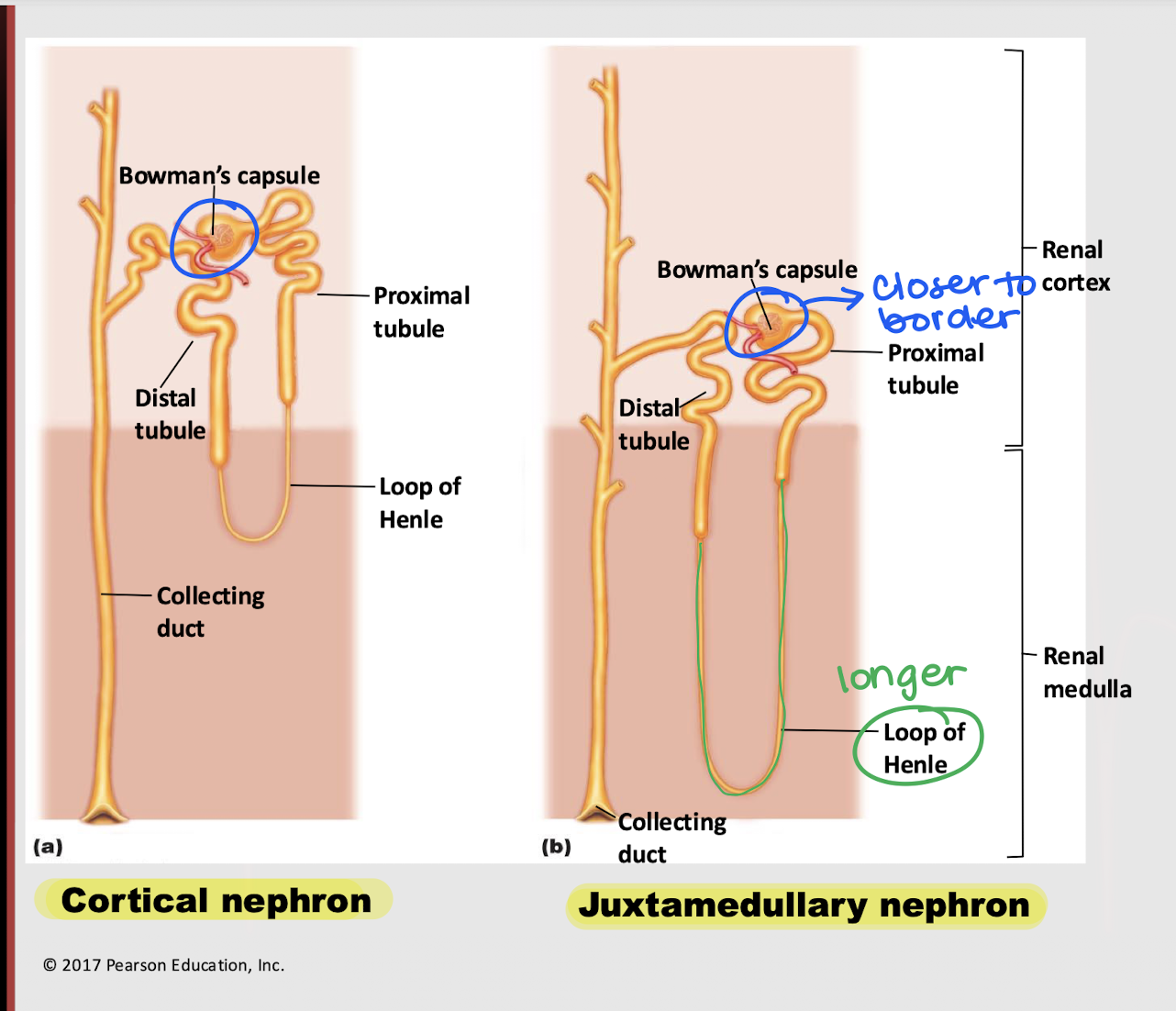
juxtamedullary nephron
Which nephron is found b/t the border of the cortex and medulla?
longer; vasa recta
Besides being (1) closer to the cortical/medullary border and (2) having a ______ loop of Henle, what is another characteristic of the juxtamedullary nephron?
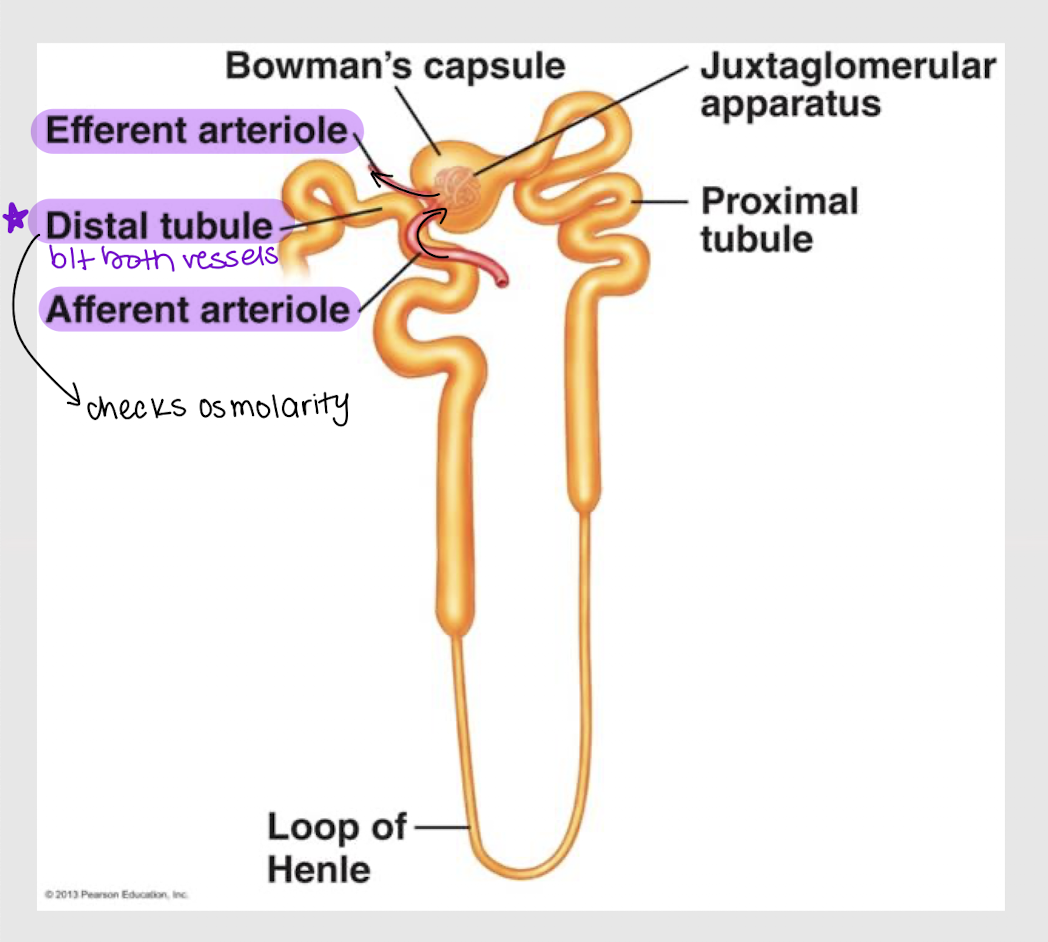
distal; arterioles
In the juxtamedullary nephron, the _______ tubule is wedged b/t the efferent and afferent _________.
collecting duct; urine
The term renal filtrate is always used until it leaves the _________ ______, where it’s then called ______.
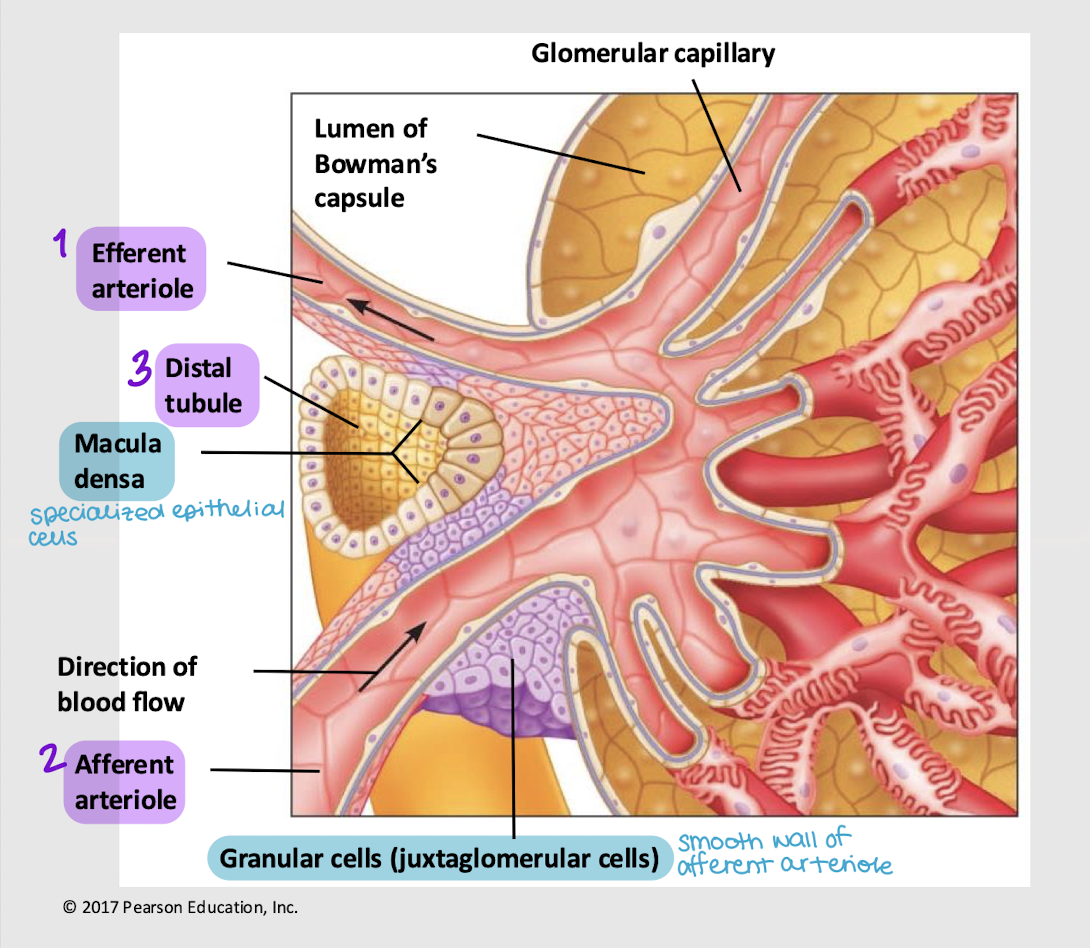
granular cells; renin
What specialized cells (AKA juxtaglomerular cells) are found in the wall of the afferent arteriole? What hormone do they secrete, that ensures there’s enough driving force (i.e. blood pressure and volume) for the blood to enter the glomerulus?
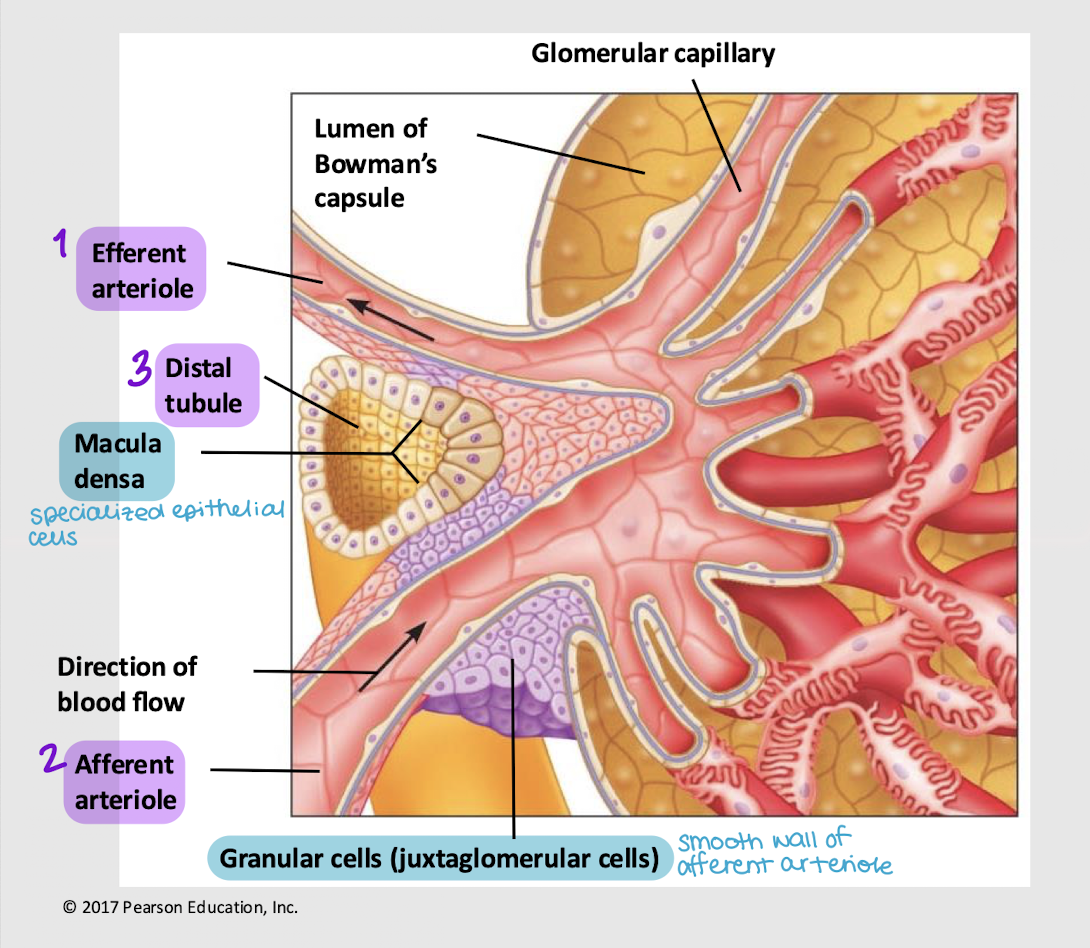
macula densa cells; paracrine
What specialized cells are found in the wall of the distal tubule? What hormone do they secrete if osmolarity and water content aren’t normal (thus affecting blood volume and pressure)?
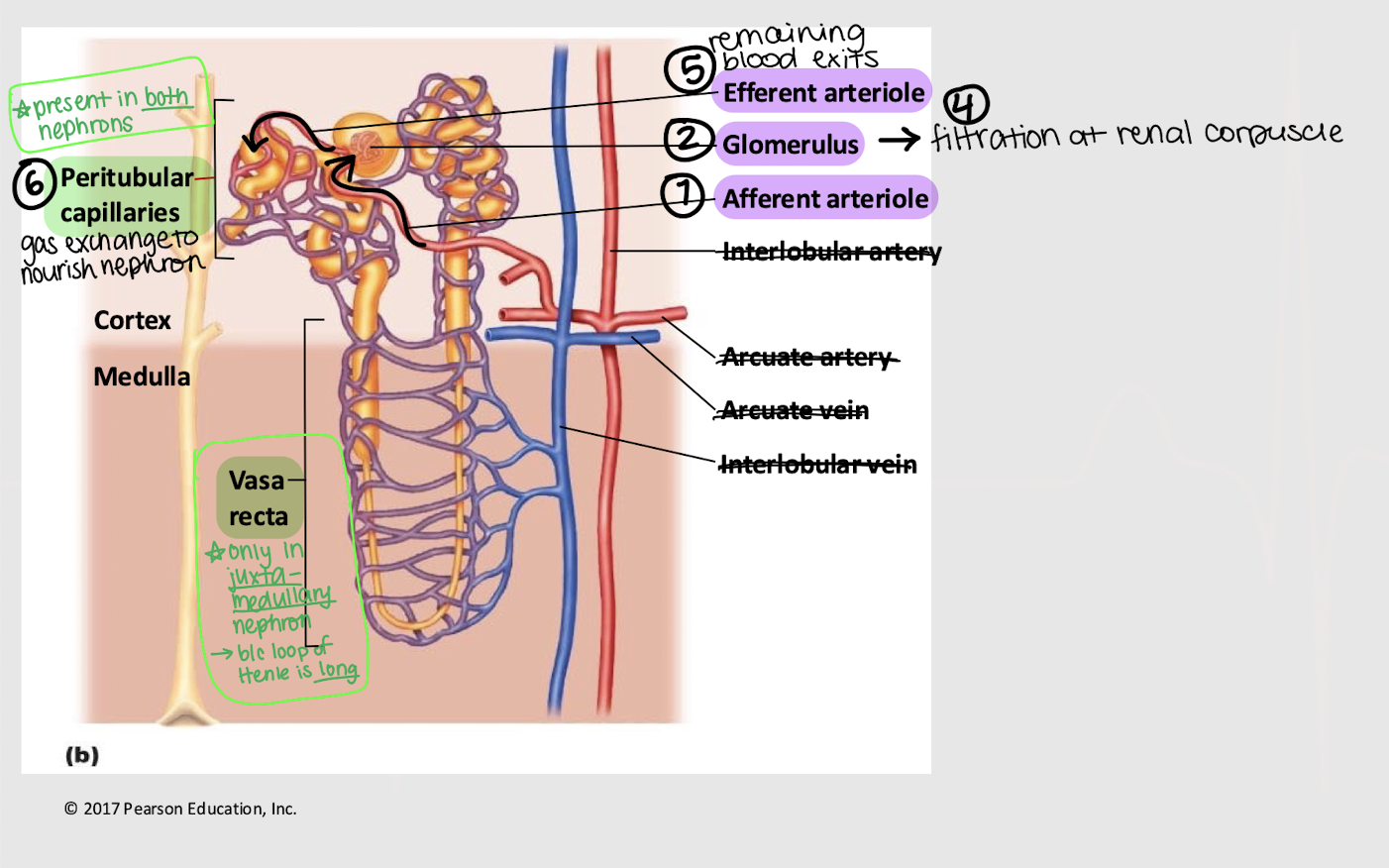
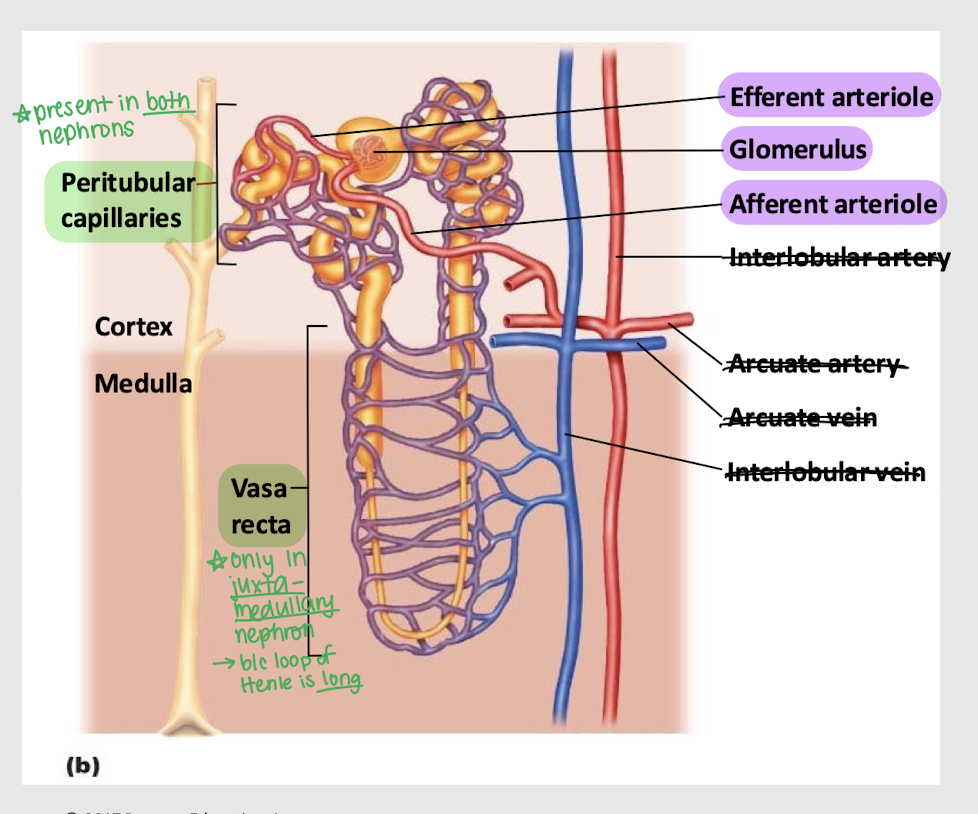
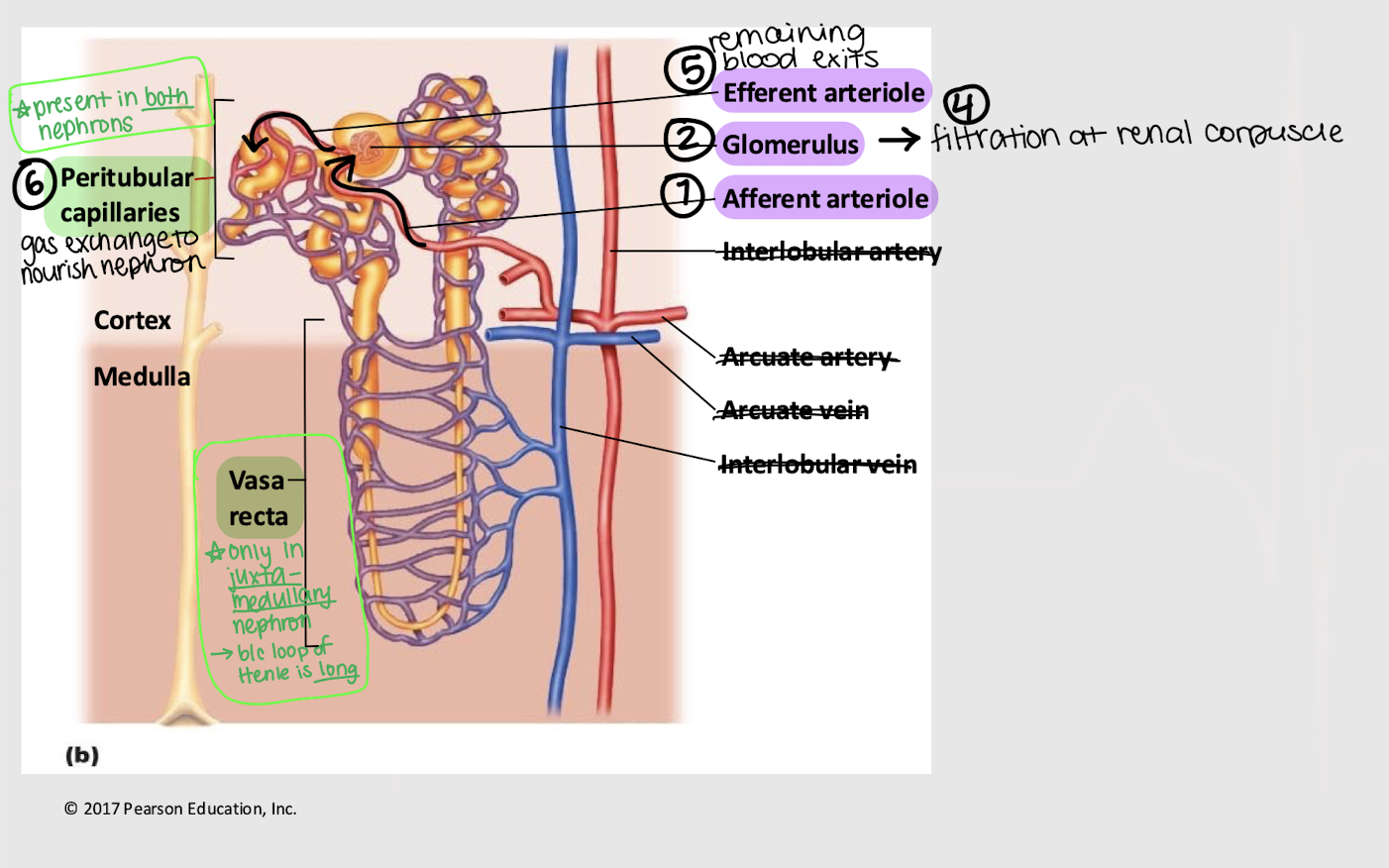
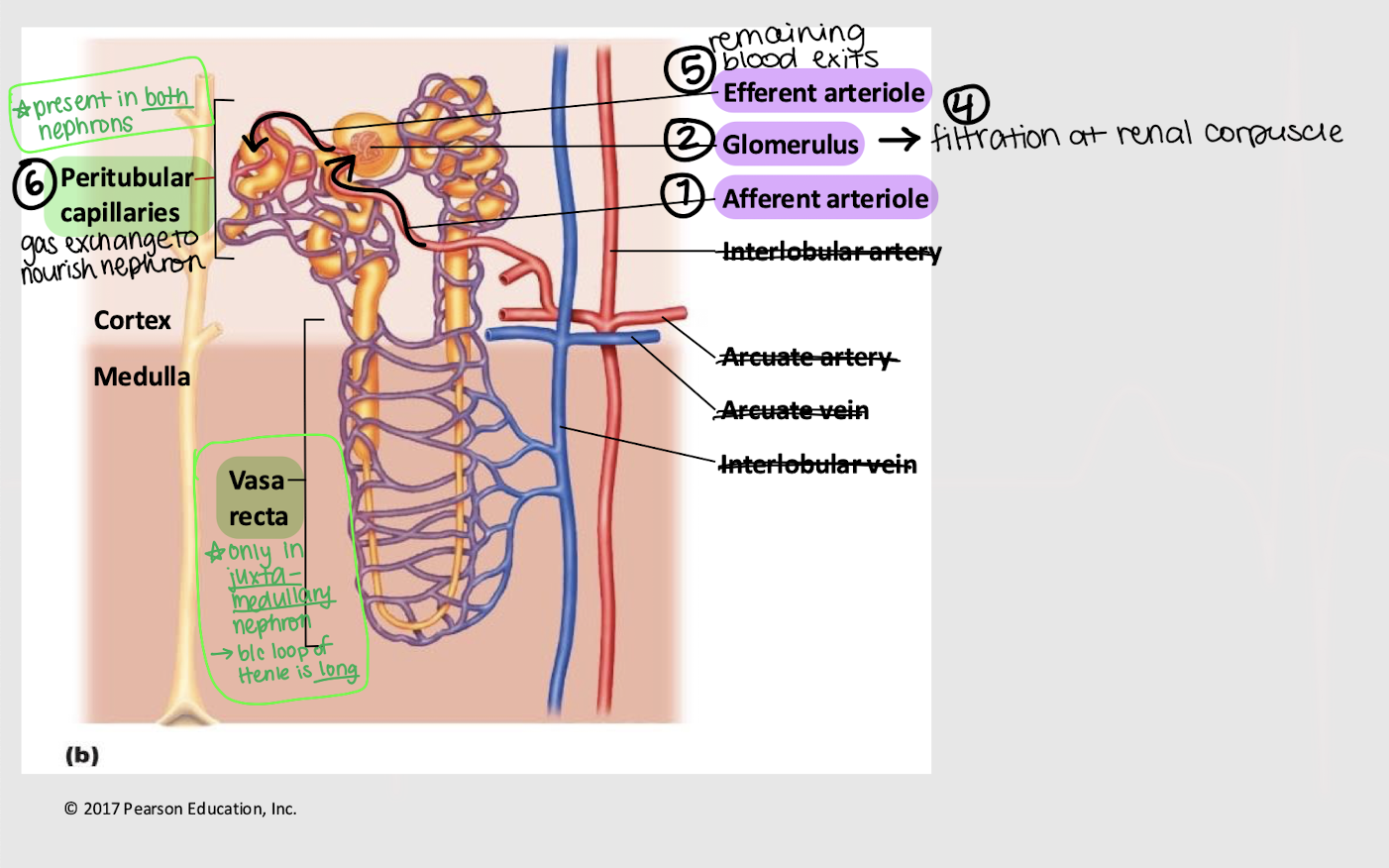
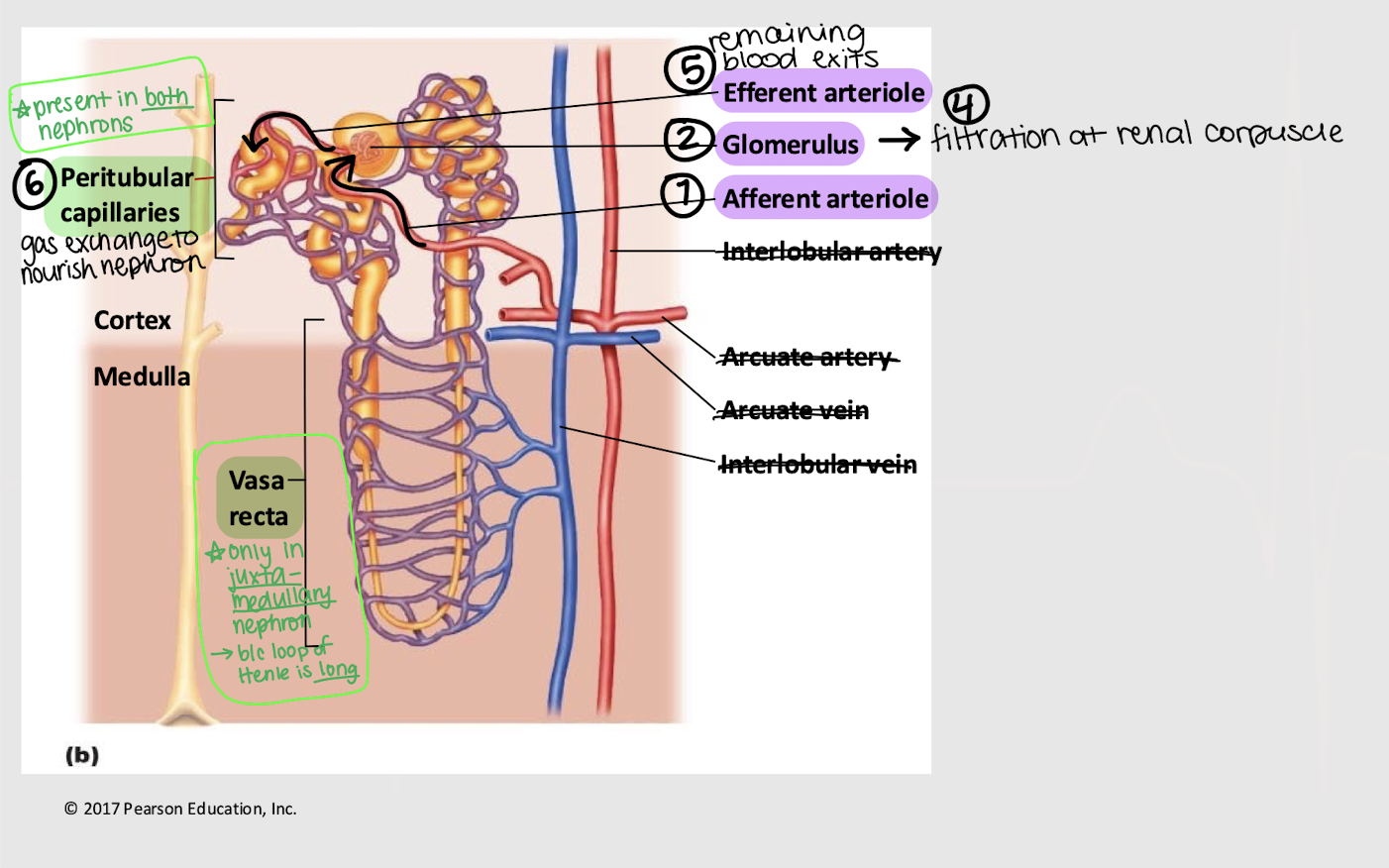
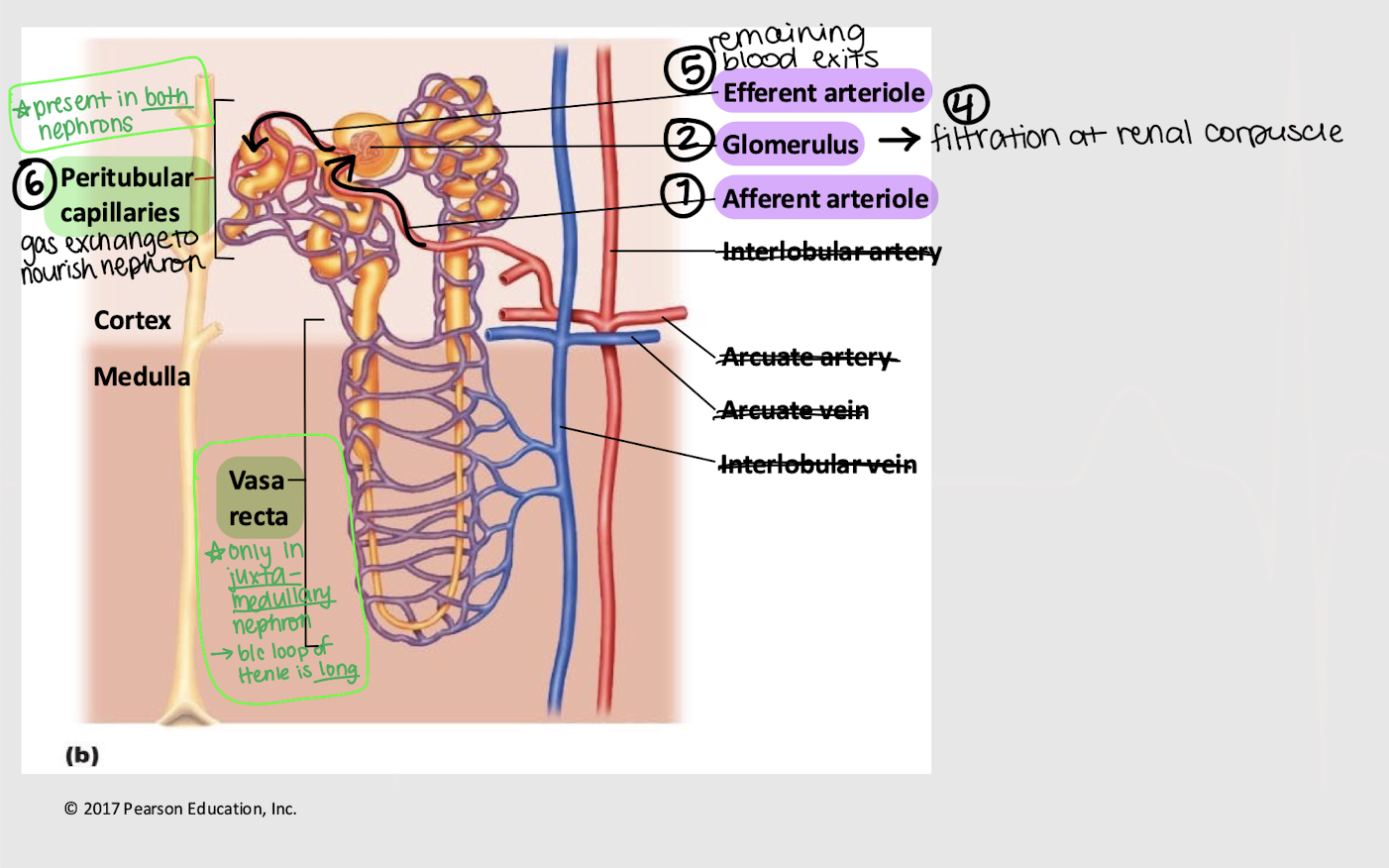
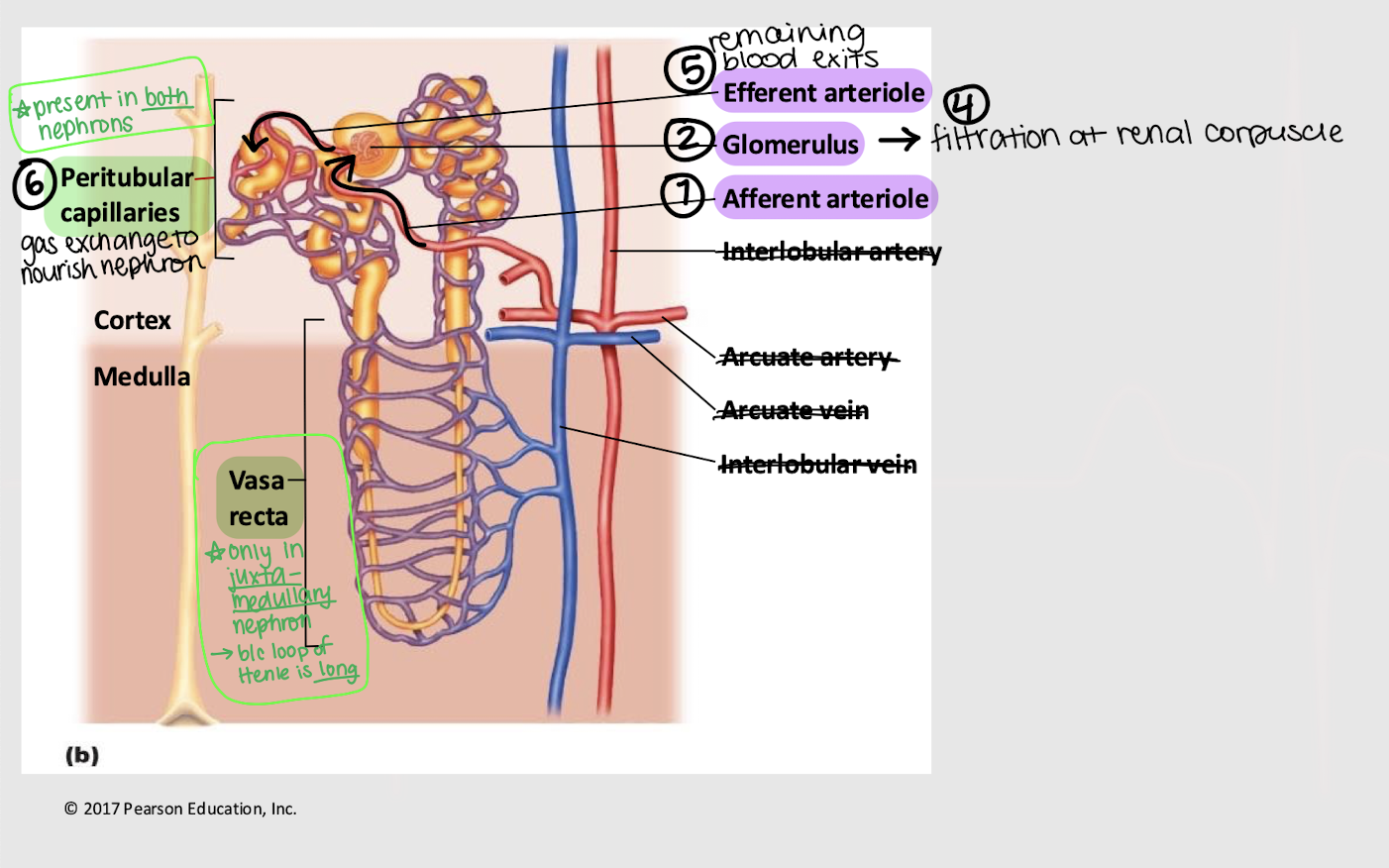
afferent; glomerulus; efferent; peritubular; vasa recta
Series blood flow in the kidneys:
Blood enters _______ arteriole
Goes into _______
Blood is filtered into Bowman’s capsule
Remaining blood exits via the _______ arteriole
Blood enters the _______ capillaries, where gas exchange for the nephron occurs
[In juxtamedullary nephron only] Blood enters _______ _______
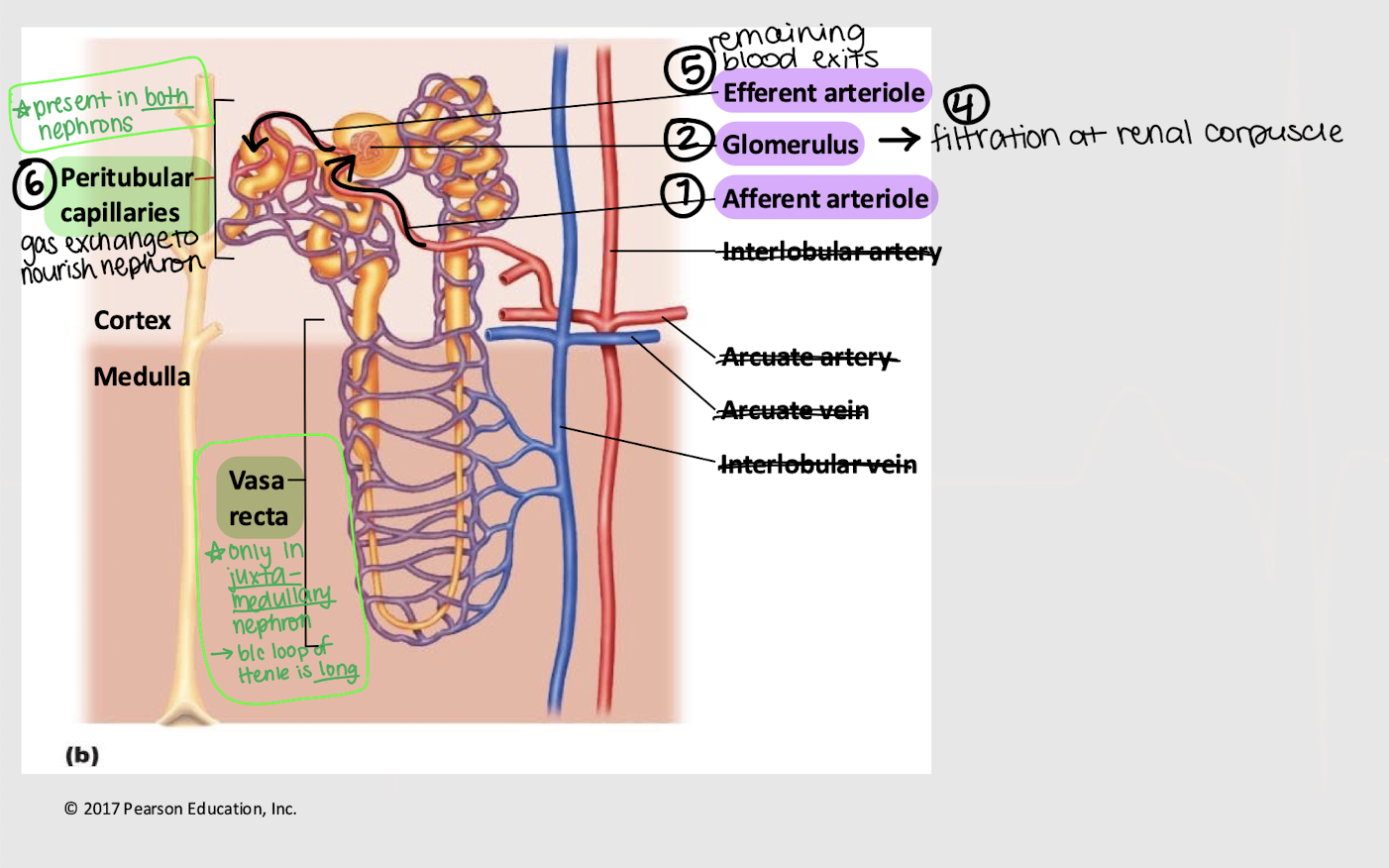
filtration
Basic nephron functions:
Bulk flow of protein-free plasma → Bowman’s capsule
Non-specific
Internal env. → external env.
reabsorption
Basic nephron functions:
Transport of molecules from renal tubule lumen → peritubular capillaries
External env. → internal env.
secretion
Basic nephron functions:
Transport of molecule from the peritubular capillaries lumen (i.e. plasma) → renal tubule (i.e. renal filtrate)
Internal env. → external env.
filtration and secretion
Which process(es) involve(s) movement from the internal → external environment?
reabsorption
Which process(es) involve(s) movement from the external → internal environment?
renal filtrate
Plasma-derived liquid that gets filtered at the renal corpuscle and travels through the tubular portion of the nephron
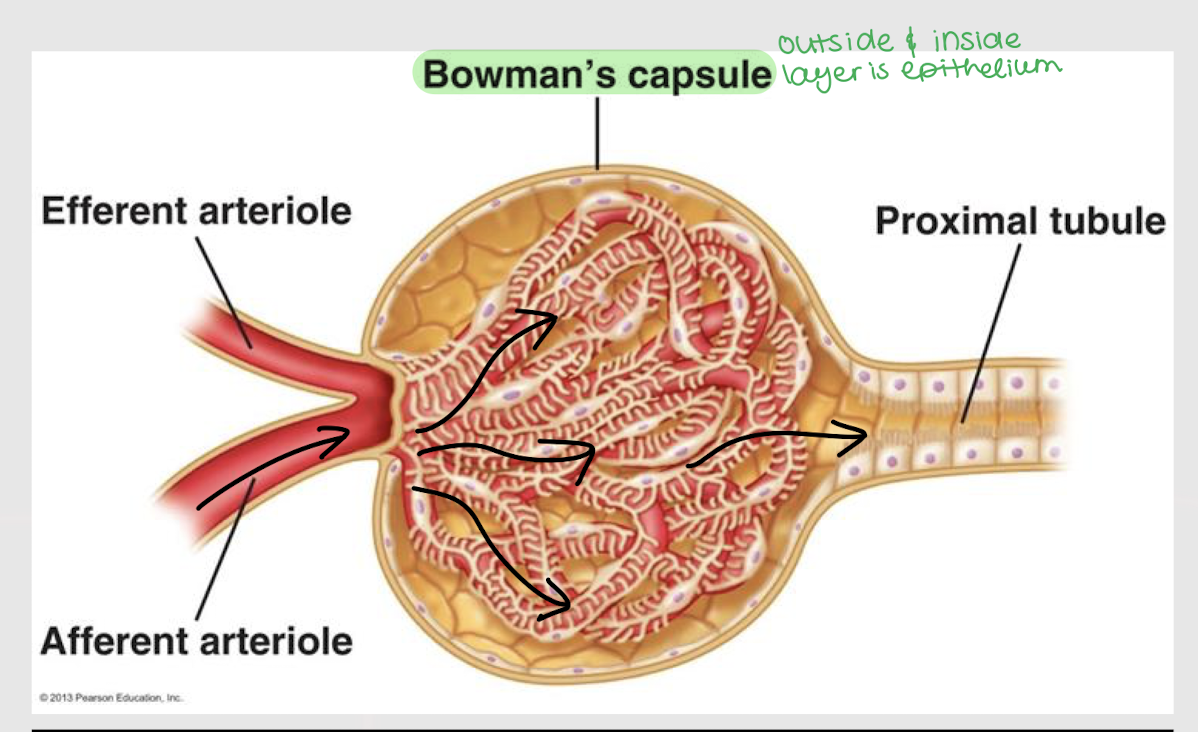
epithelium
Bowman’s capsule has a layer of ________ in both its inside and outside layer.
internal
A capillary is part of the ________ environment.
external
Bowman’s capsule/space and tubules are part of the ________ environment.
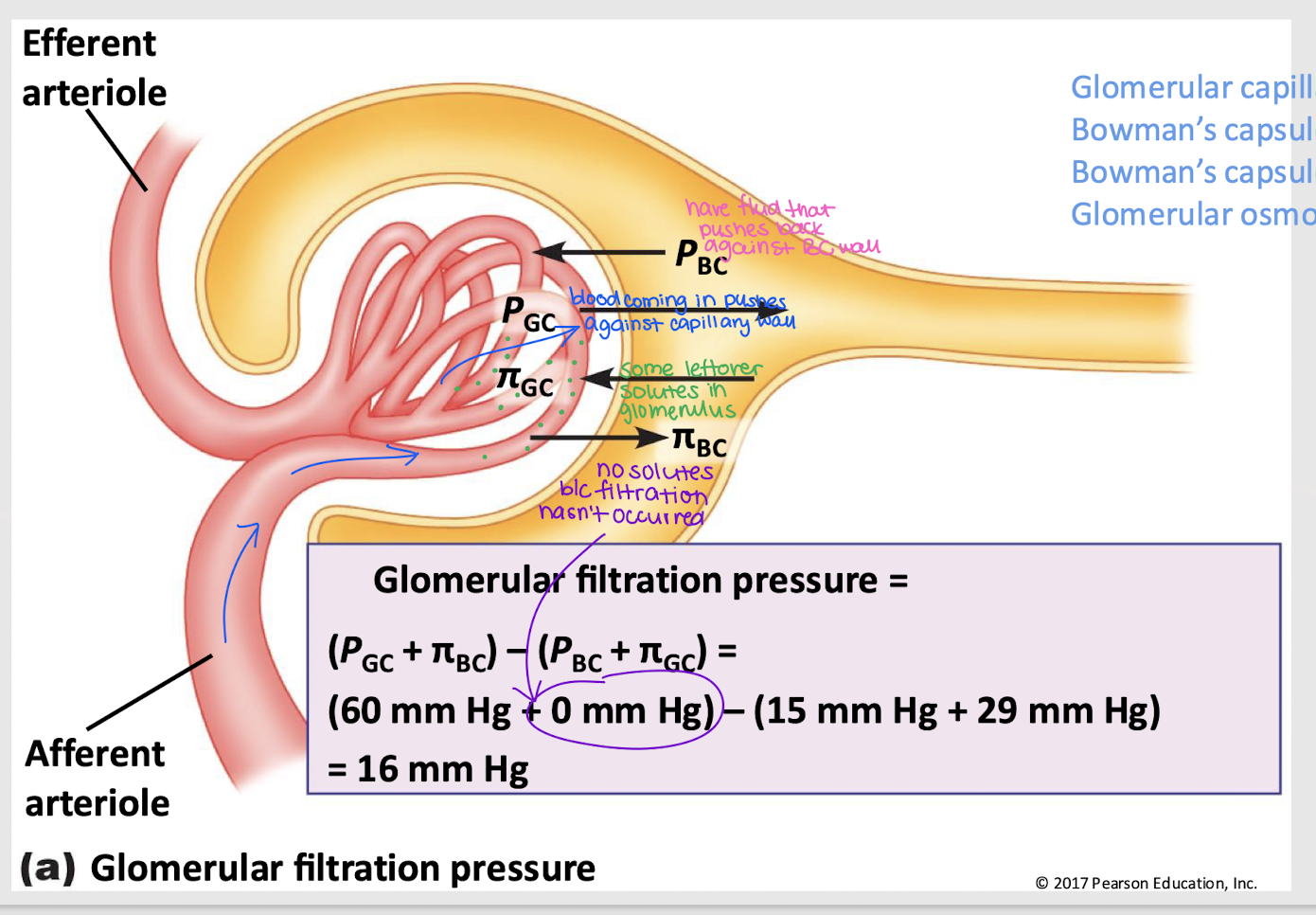
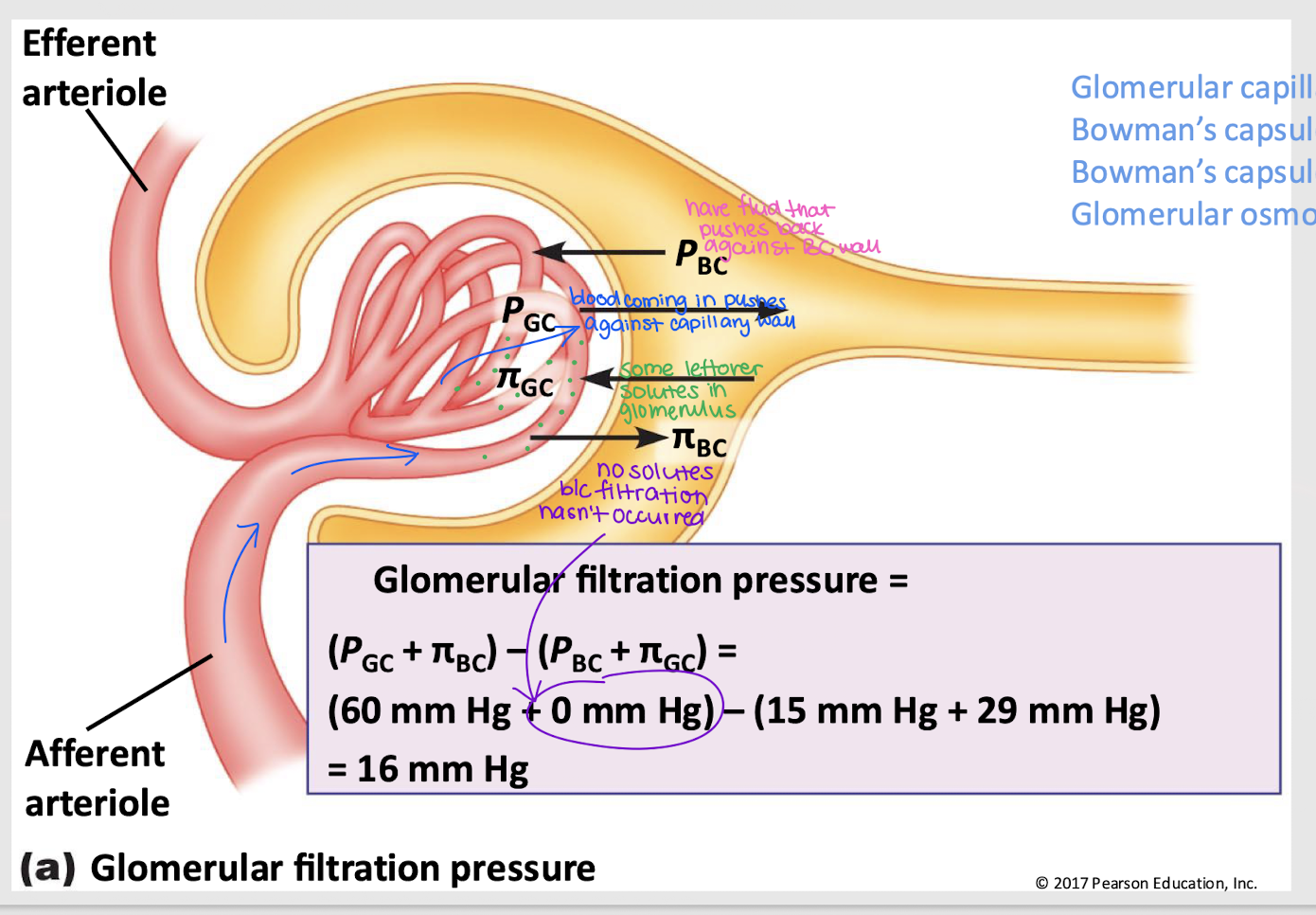
glomerular filtration pressure (GFP)
Net filtration pressure of four forces: PGC, πGC, PBC, and πBC
GFP = (PGC + πBC) - (PBC + πGC)
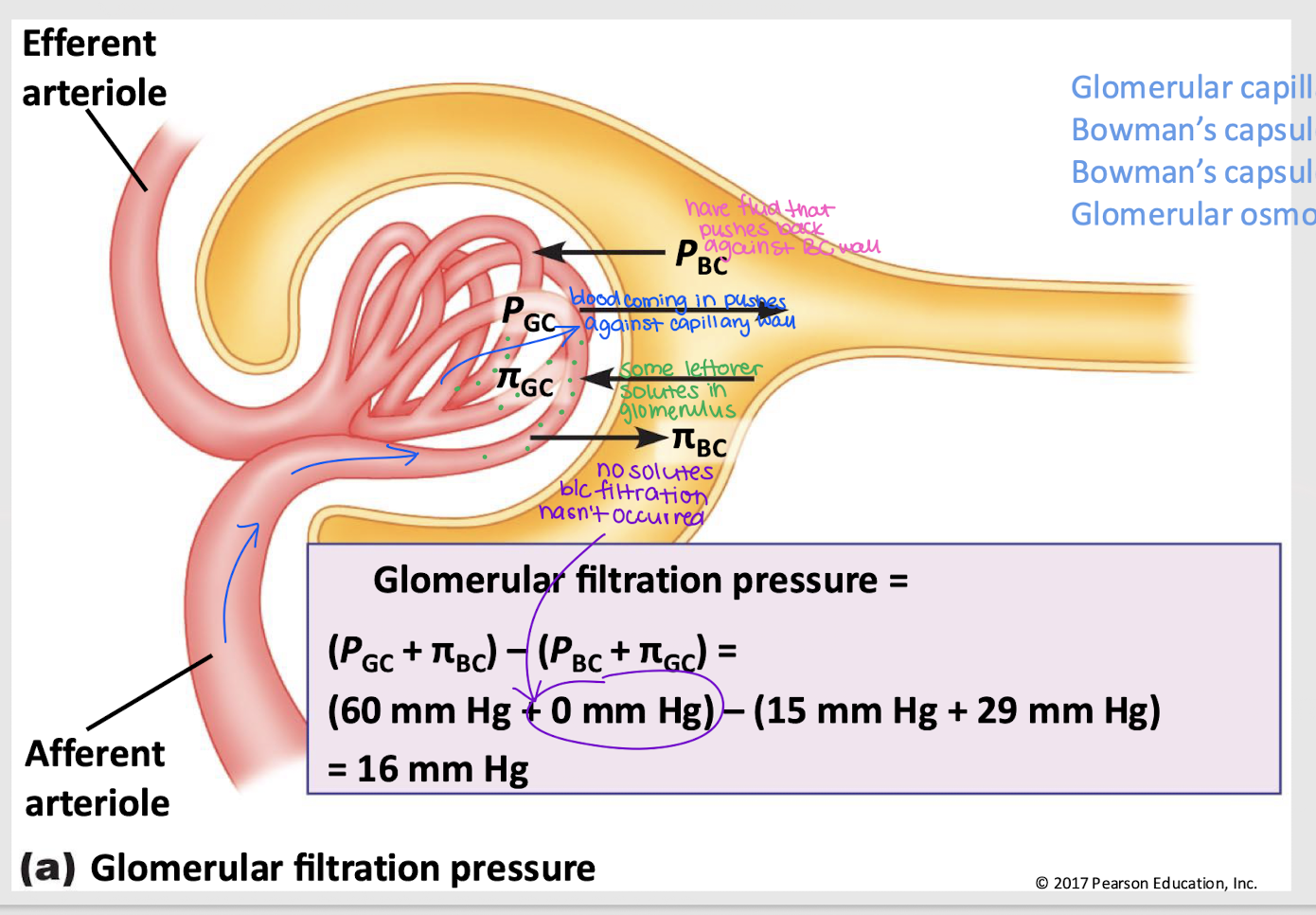
GC hydrostatic pressure (PGC)
Pressure that pushes fluid out of the glomerular capillaries into the Bowman’s capsule; favors filtration
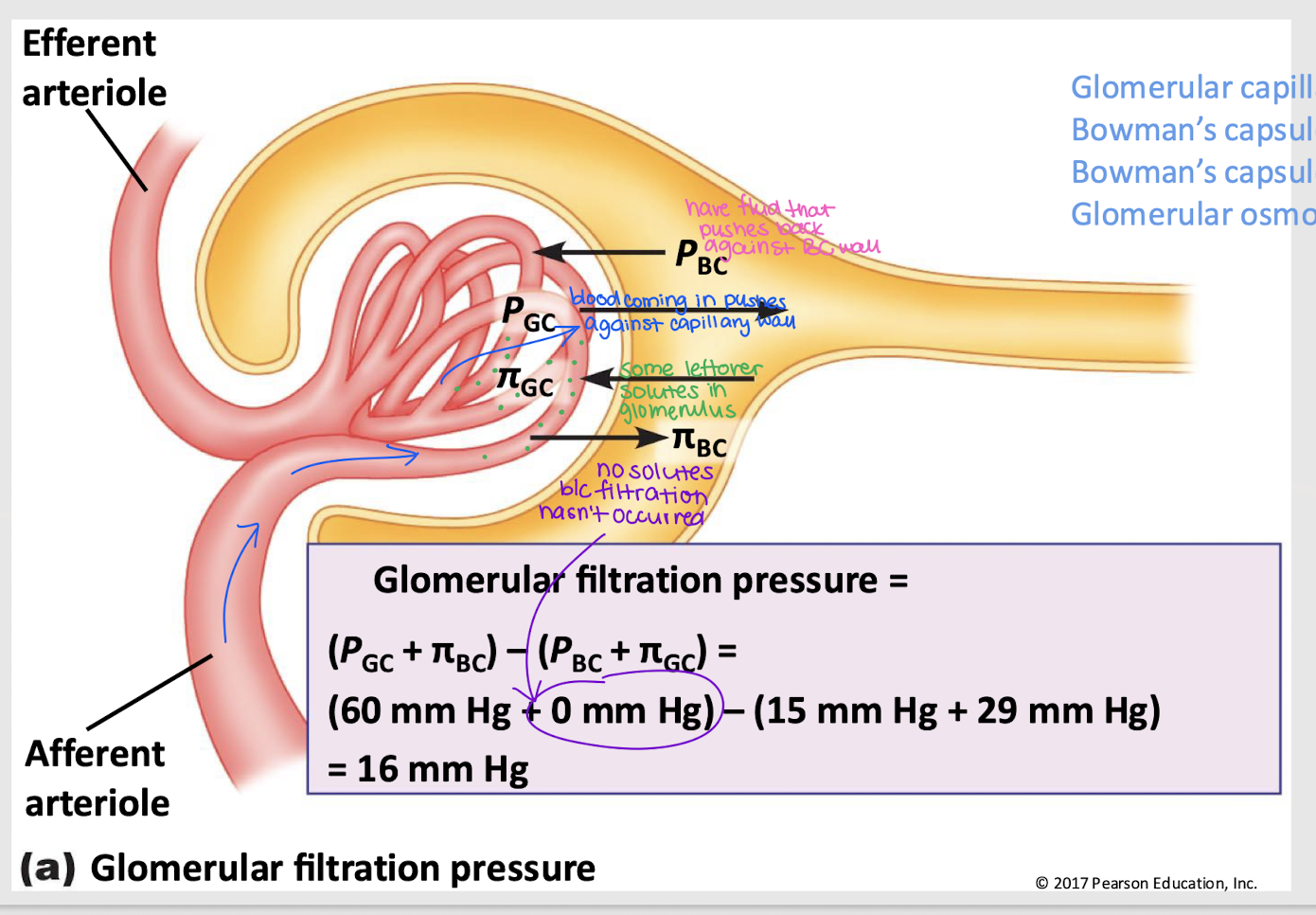
GC osmotic pressure (πGC)
Pressure that pulls fluid into the glomerular capillary, primarily due to proteins; against filtration
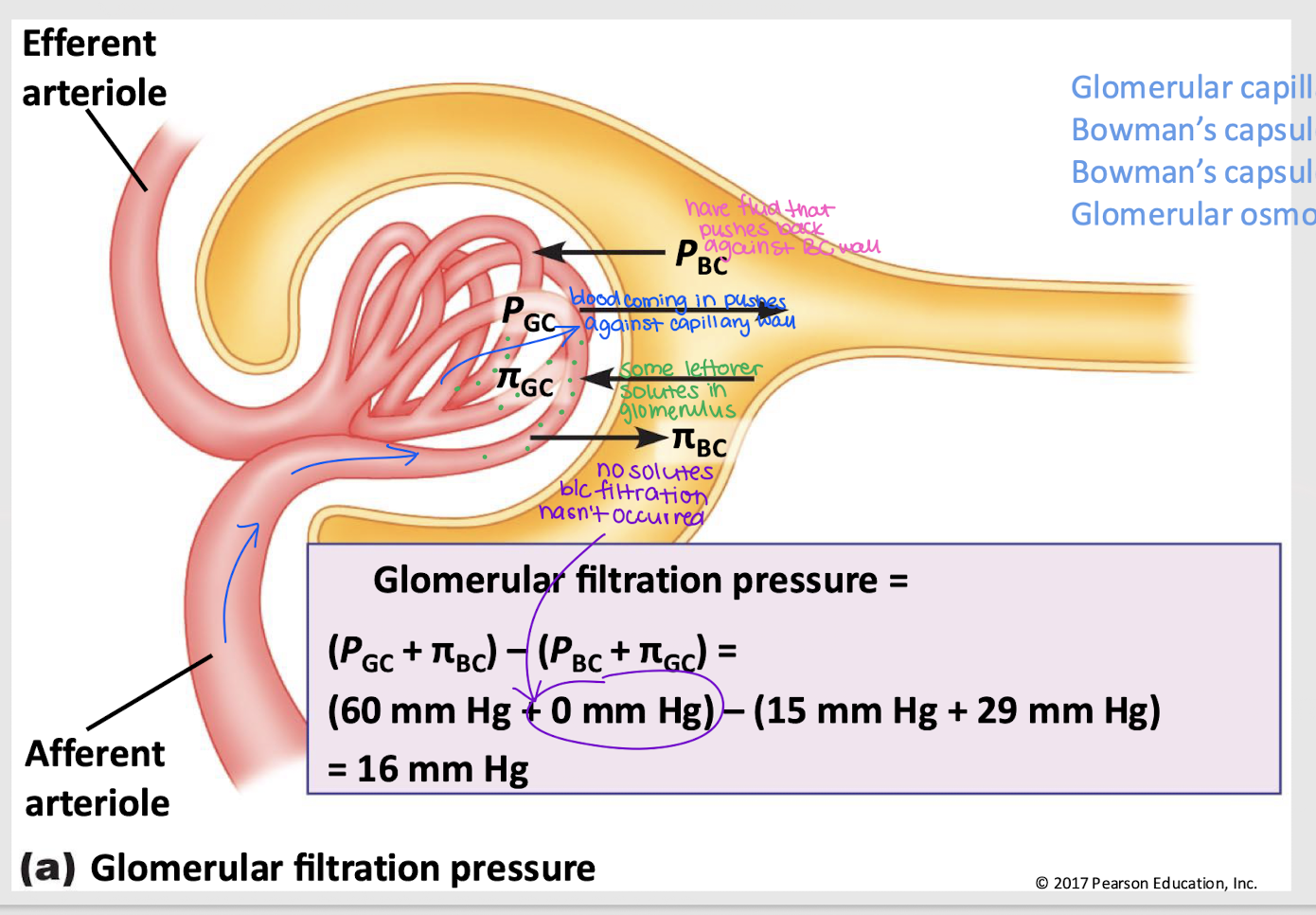
BC hydrostatic pressure (PBC)
Pressure from fluid that pushes it back into the glomerular capillary; against filtration
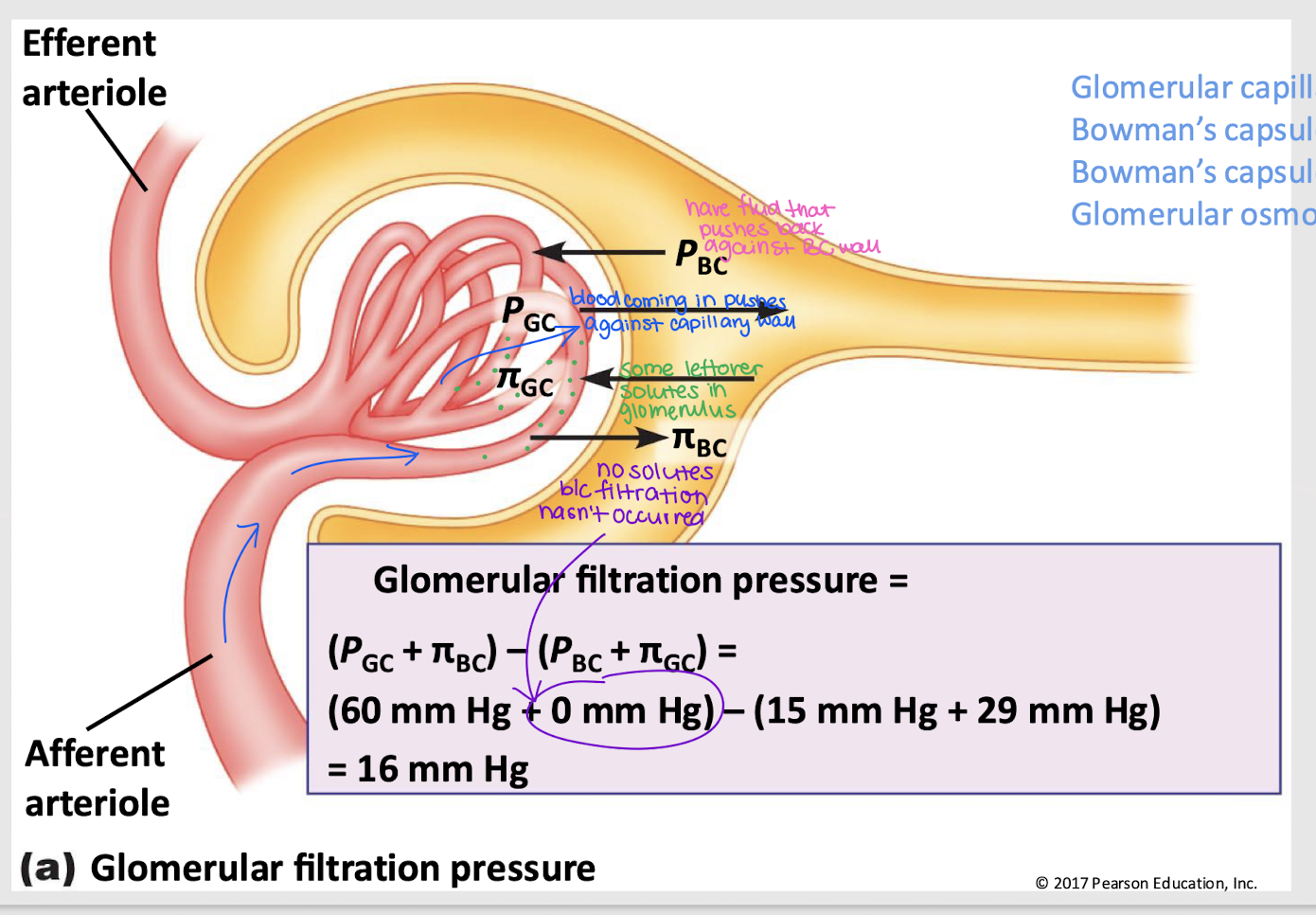
BC osmotic pressure (πBC)
Pressure that pushes water into Bowman’s capsule; favors filtration
favor filtration
Do PGC and πBC favor or oppose filtration?
oppose filtration
Does PBC and πGC favor or oppose filtration?
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
volume of plasma filtered per min; typically 125 mL/min
filtration fraction
ratio of the GFR to renal plasma flow (typically 625 mL/min)
125 / 625 mL/min = 20%
filtered load
The quantity of a solute that is filtered per min
GFR x Plasma [X] (how much of the solute is in the plasma)
Will increase if either of these terms increases
reabsorbed; work
Because GFR is so large, even small changes would result in a HUGE effect on the volume of fluid filtered. So, if GFR increases, more solute must be ________, requiring more _______.
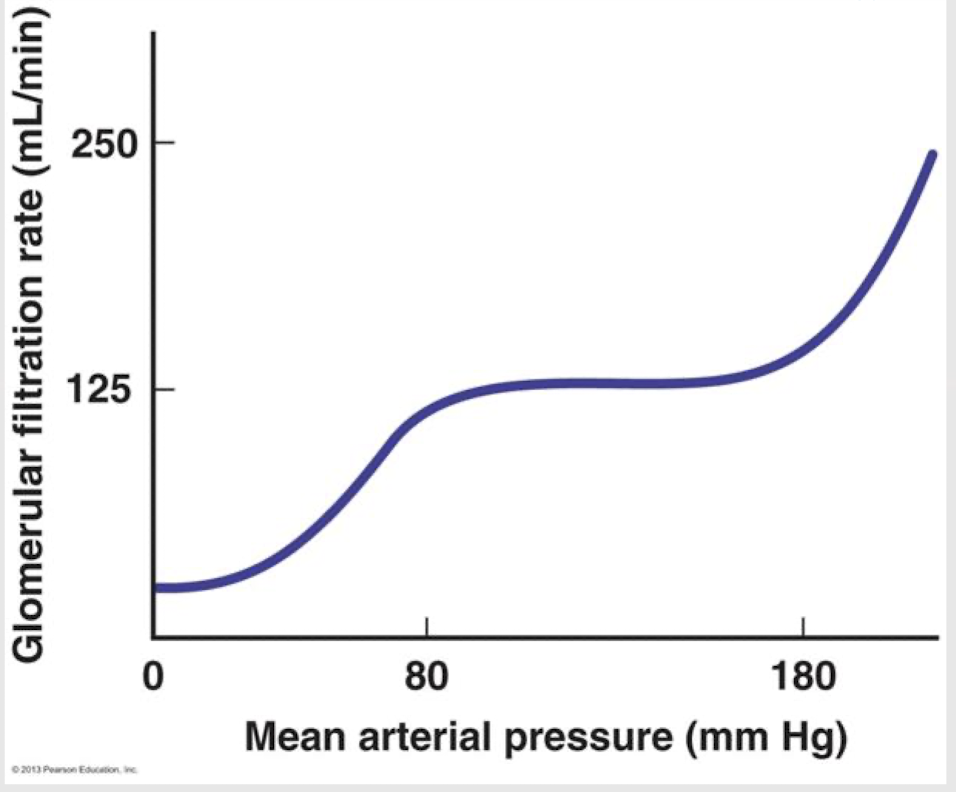
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
What is the primary factor in GFR?
GC hydrostatic pressure
Which of the Starling forces is impacted by a change in MAP?
plateau; work; normal fluctuations
The ______ in this graph shows that the body doesn’t need to ______ more for GFR for ________ __________ in BP.
actively
Are solutes mainly passively or actively reabsorbed?
renal tubule wall (cuboidal epithelium)
Which structure has a greater barrier to reabsorption?
capillary wall (simple epithelium)
Which structure has a smaller barrier to reabsorption?
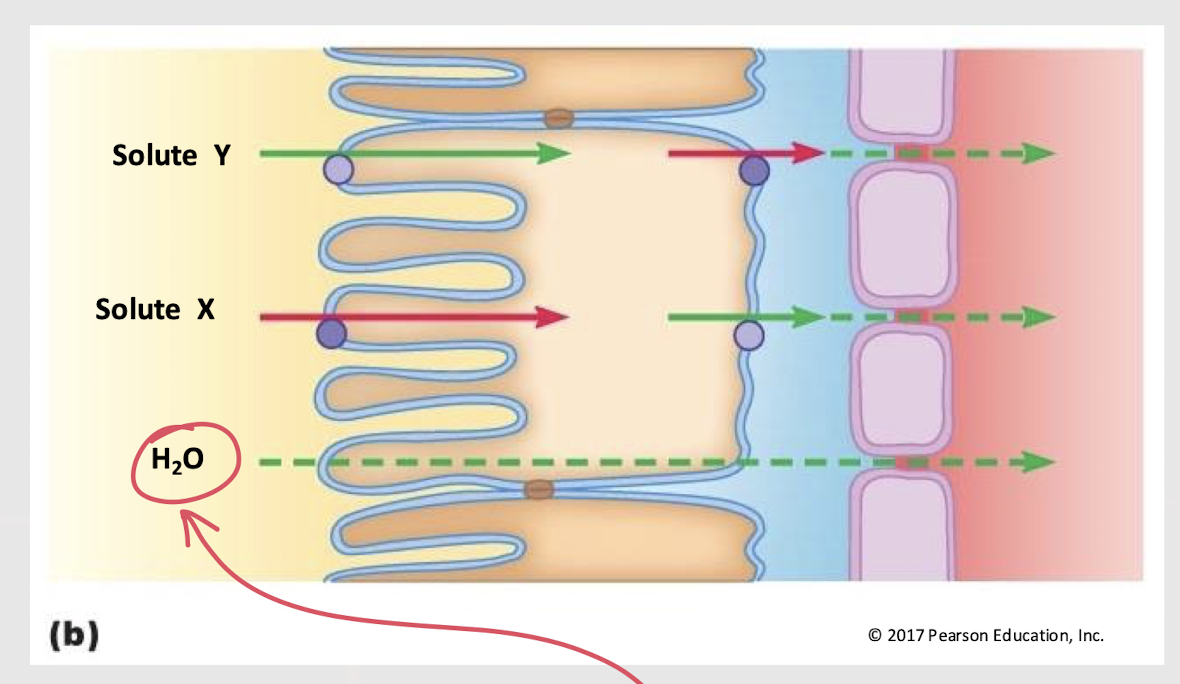
water; up
________ reabsorption follows solute movement. It moves ____ the osmotic pressure gradient.
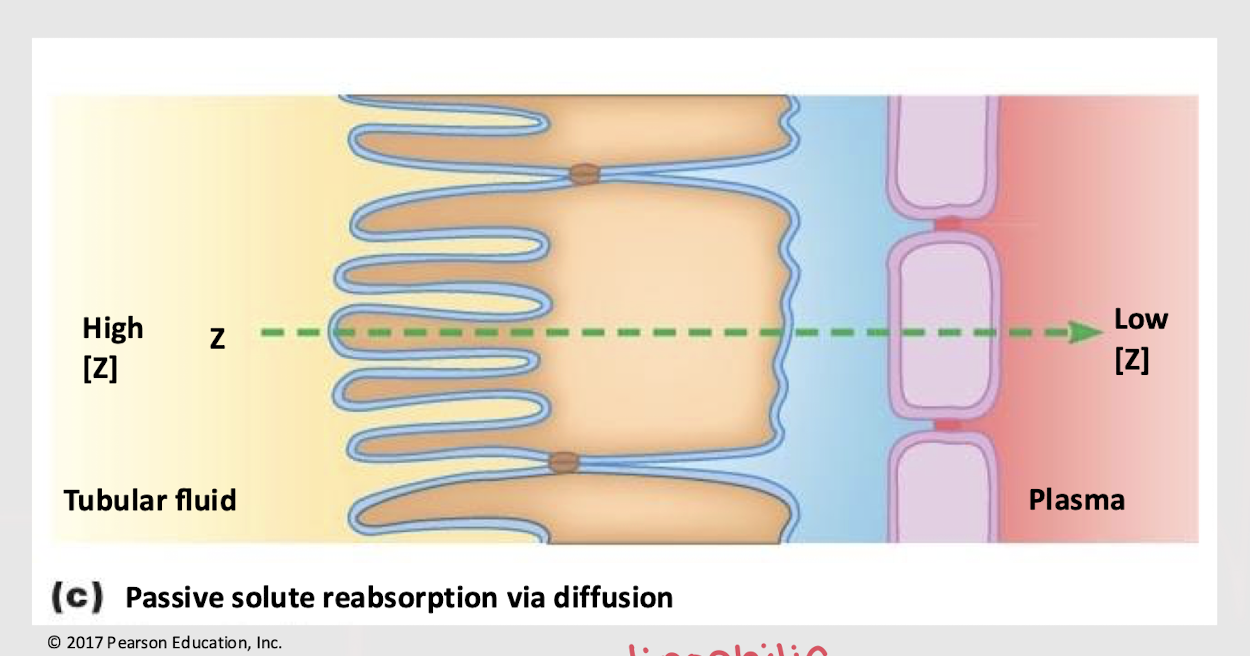
simple diffusion; lipophilic; concentration gradient
In order for a solute to be passively reabsorbed through ______ ______, it must be membrane-permeant (i.e. _______) and follow a _______ ______.
transport maximum (Tm)
Highest rate (mg/min) at which reabsorption can occur for a substance.
Remember: Carrier proteins can become saturated.
Different molecules have different number of receptors.
renal threshold
Plasma concentration of a solute at which “spillover” into the urine occurs.
Means that it has already reached the transport max.
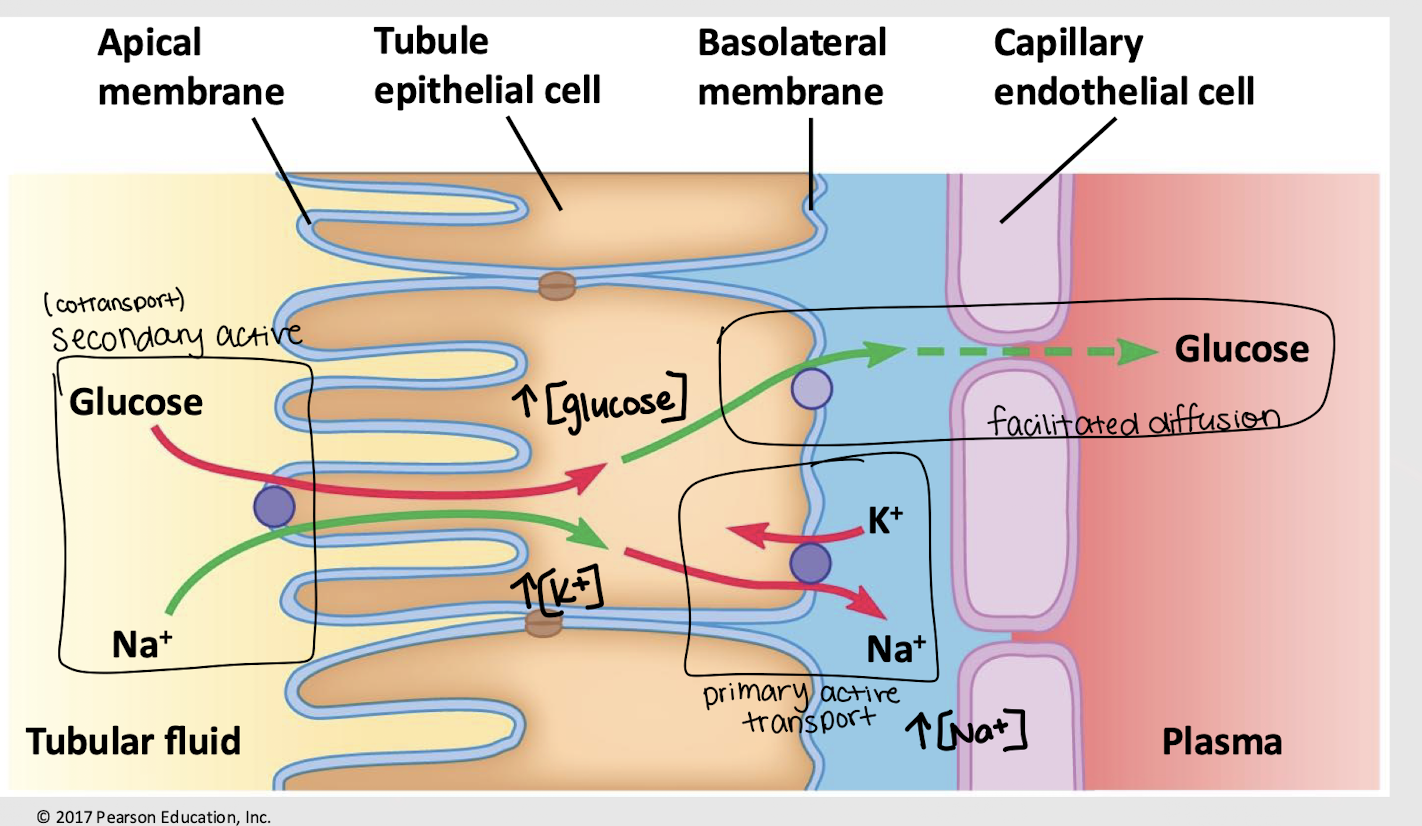
increases; decreases; glucose; facilitated diffusion
Glucose reabsorption:
The Na+/K+ pump ________ [K+] and ________ [Na+] inside the cell via primary active transport
Na+ is brought into the cell w/ ________ via secondary transport
Increased [glucose] drives it to be passively reabsorbed into the plasma/capillary via ________ ________
increased; increased; decreased; decreased
Clinical correlation - Diabetes and renal disease:
Elevated plasma [glucose]
________ solute in renal filtrate (b/c carriers are saturated)
________ osmolarity of renal filtrate
________ water reabsorption (b/c water remains in renal tubule)
________ water in plasma (b/c of less reabsorption)
Diuresis, dehydration, thirst
active transport
Through which type of transport are ions, waste products, and foreign substances secreted?
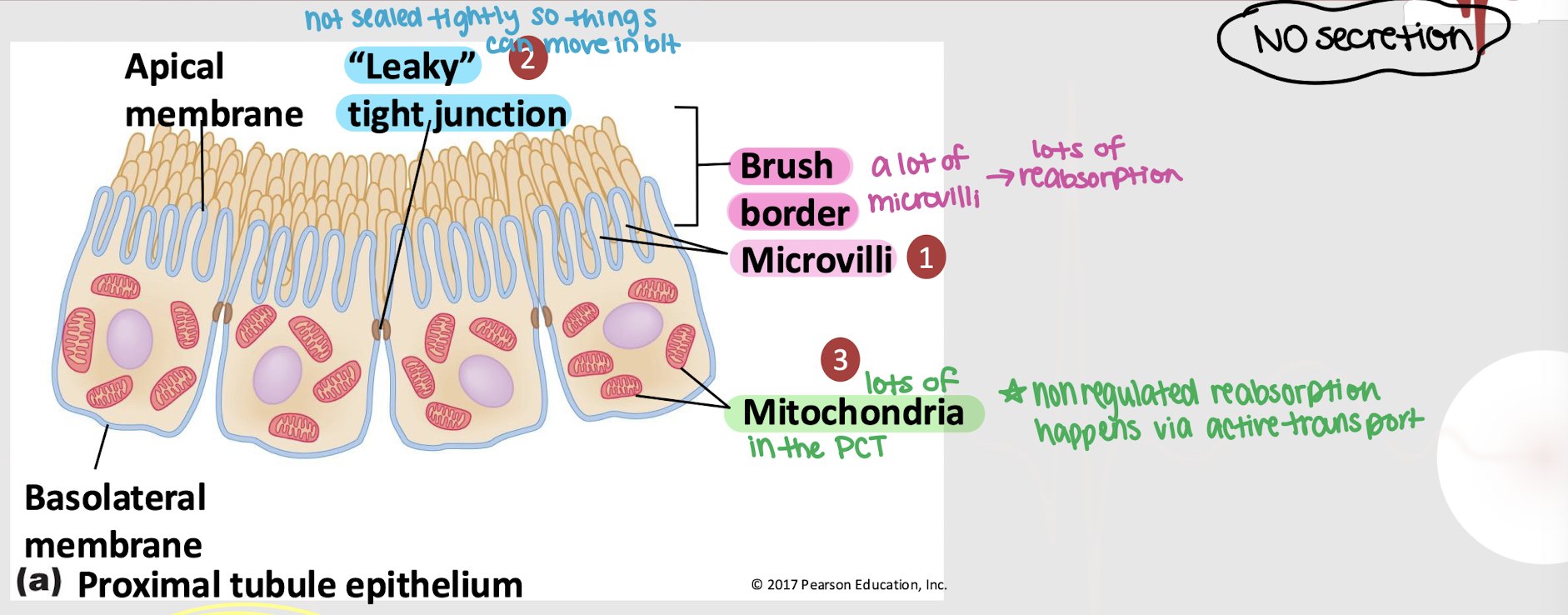
PCT; leaky; microvilli; mitochondria; active
Non-regulated reabsorption occurs in the ______ and is characterized by…
______ tight junction
A lot of ________
A lot of ________, meaning it occurs via _______ transport
NO secretion
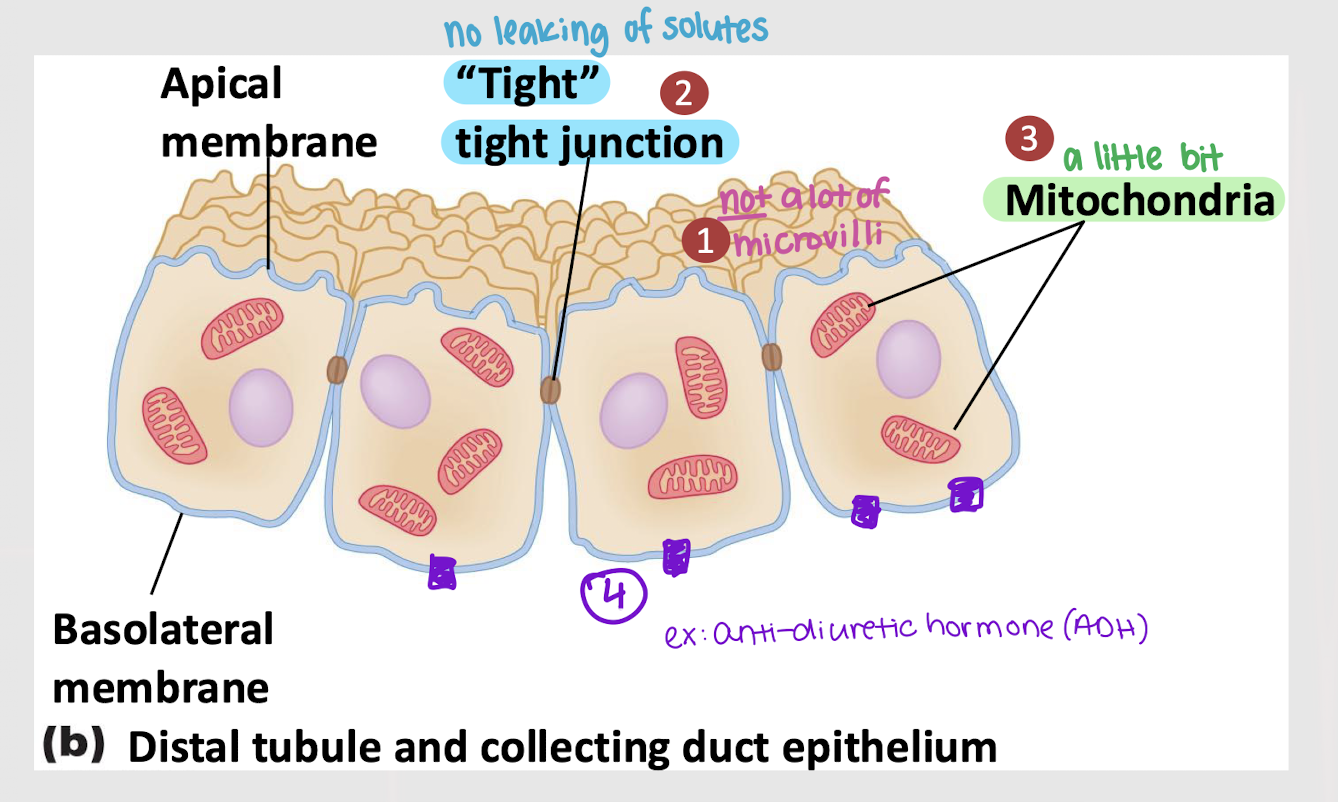
DCT; microvilli; mitochondria; ADH
Regulated reabsorption occurs in the ______ and is characterized by…
______ tight junction
Little amount of _______
Little amount of _______
______ receptors on the basolateral membrane
Secretion
PCT
Is all glucose reabsorbed in the PCT or DCT?
PCT
Where is most of Na+ and H2O (follower) reabsorbed?
PCT
Does most reabsorption occur in thee PCT or the DCT?
excretion
Elimination of solute and water in the form of urine
filtration; secretion; reabsorbed
Substances can enter the tubule via ________ or _______. It is all excreted unless it is ________.
E = F - R + S