ECON 201 - Final Exam (JMU)
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
economics
the study of how society allocates its scarce resources
absolute advantage
the ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
opportunity cost
whatever must be given up to obtain some item
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
market
a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
law of demand
the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises
normal good
an increase in income leads to an increase in demand
inferior good
an increase in income leads to a decrease in demand
substitutes
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
complements
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in demand for the other
law of supply
the quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises
determinants of demand
income, price of sub/complements, taste, expectation, # of buyers
determinants of supply
input prices, technology, expectations, number of sellers
where on a graph does the quantity demanded equal the quantity supplied ?
market equilibrium
surplus occurs when ..
market price is above the equilibrium price
shortage occurs when ..
market price is below the equilibrium price
elasticity
measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in one of its determinants
price elasticity of demand equation
computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price
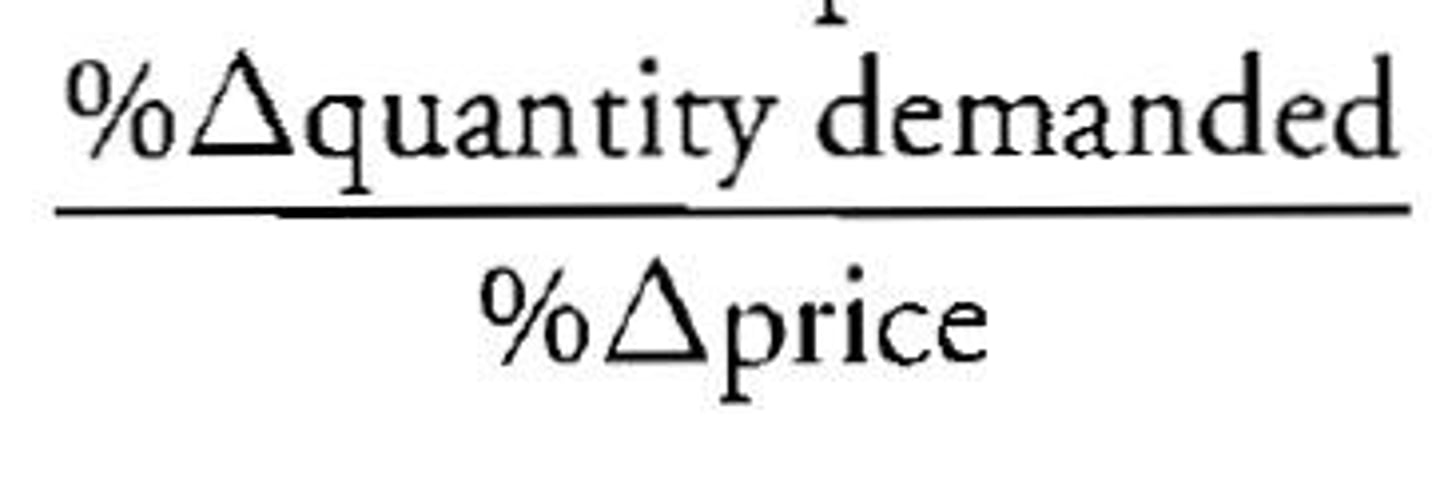
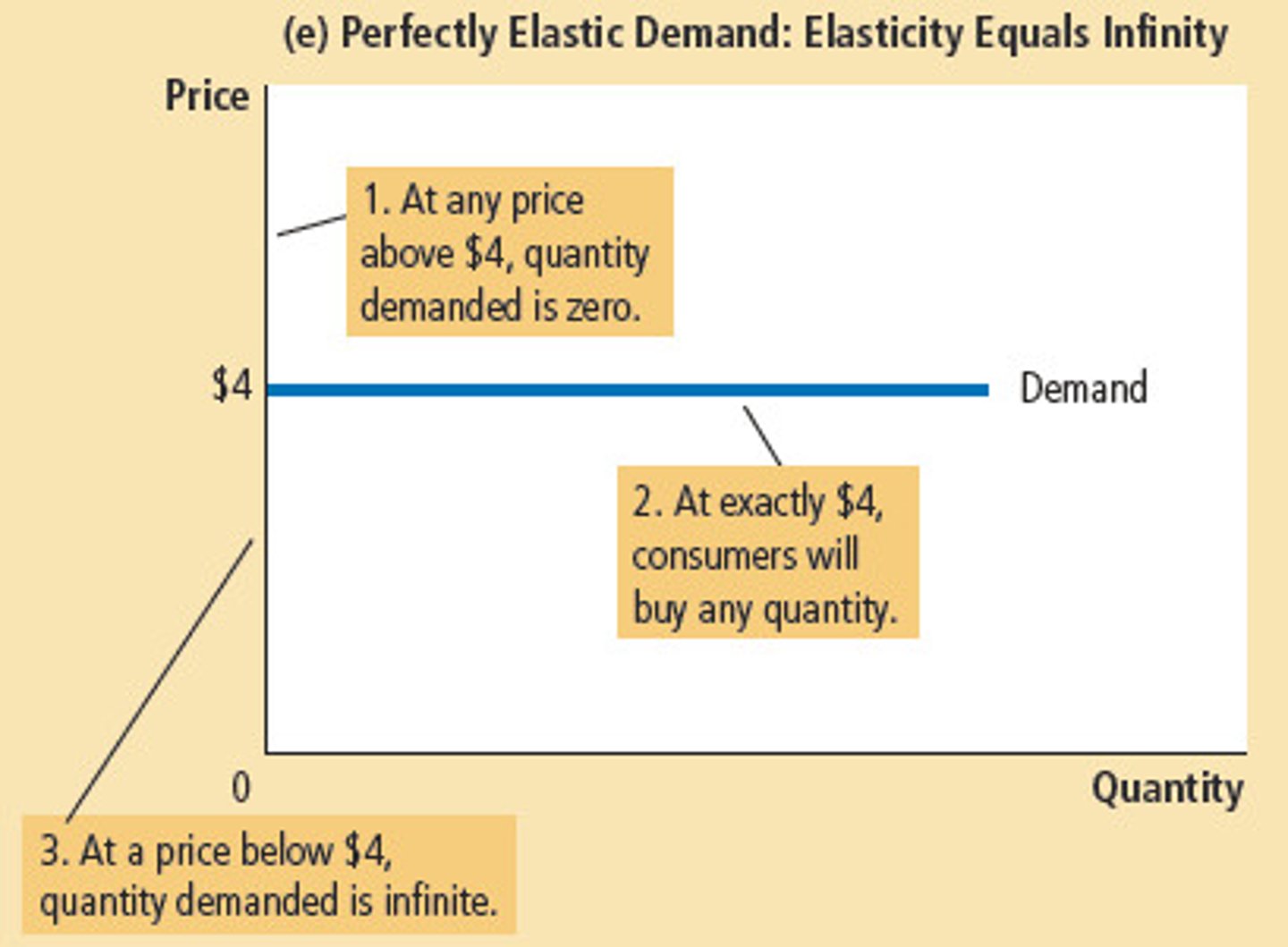
elastic demand
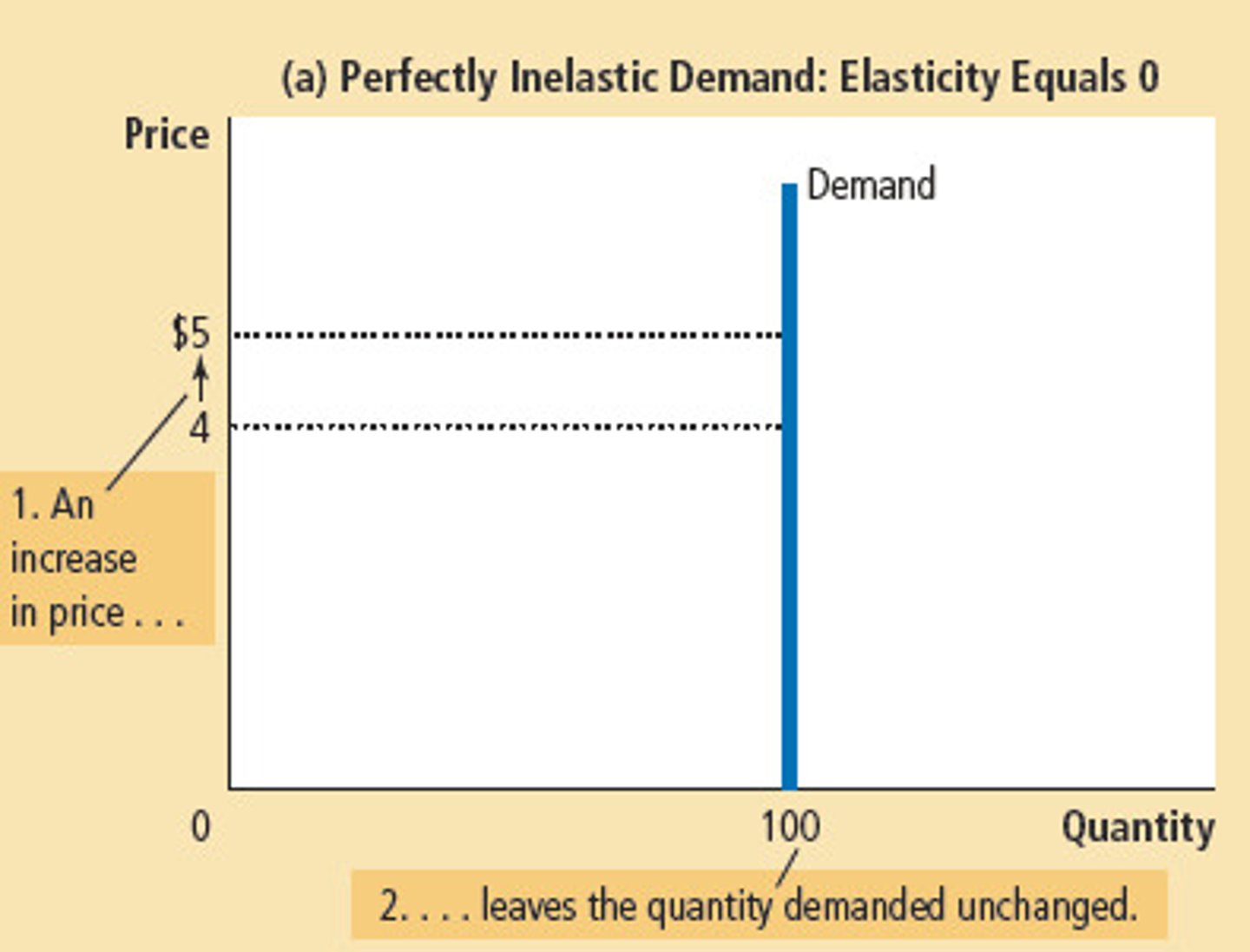
inelastic demand
total revenue
The amount of money received by firms when they sell a good or service. TR = P x Q.
income elasticity of demand
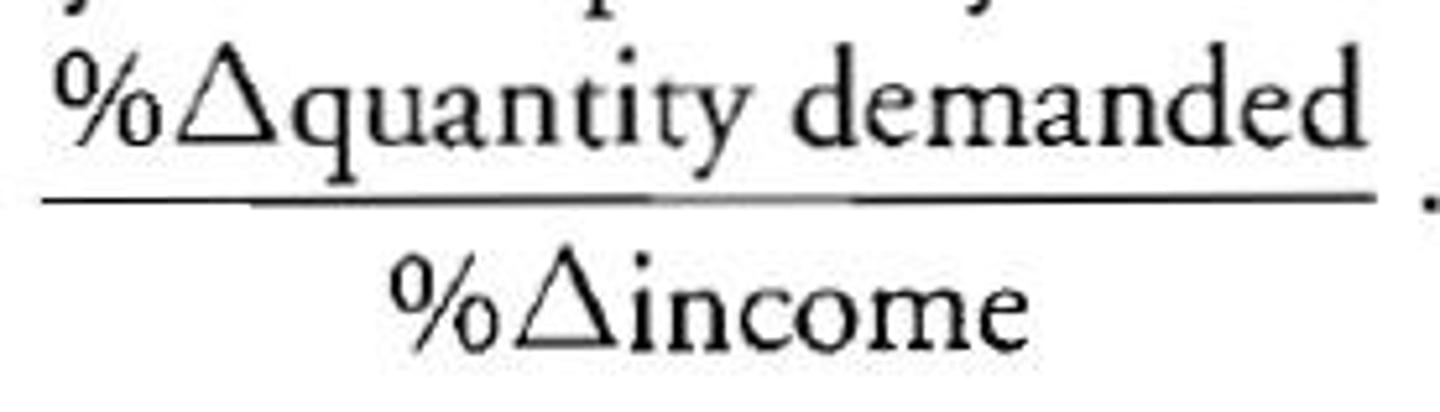
cross-elasticity of demand
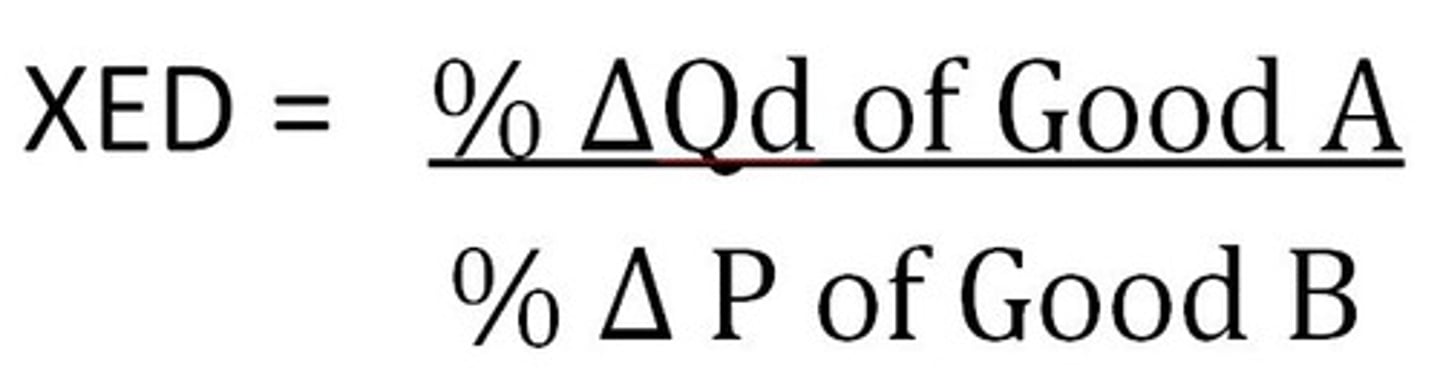
price elasticity of supply
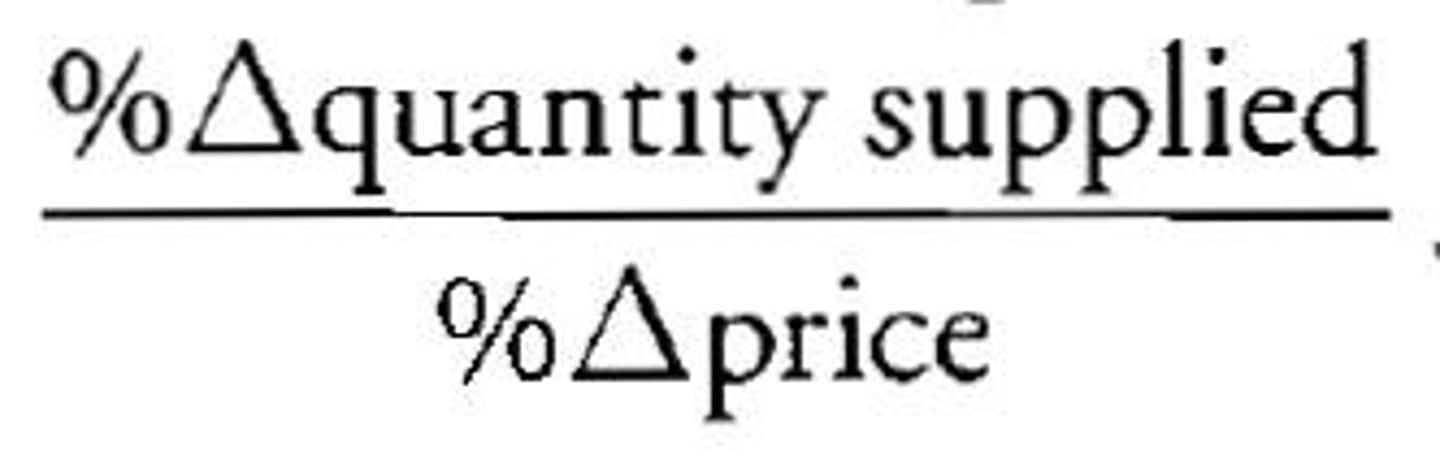
elastic supply
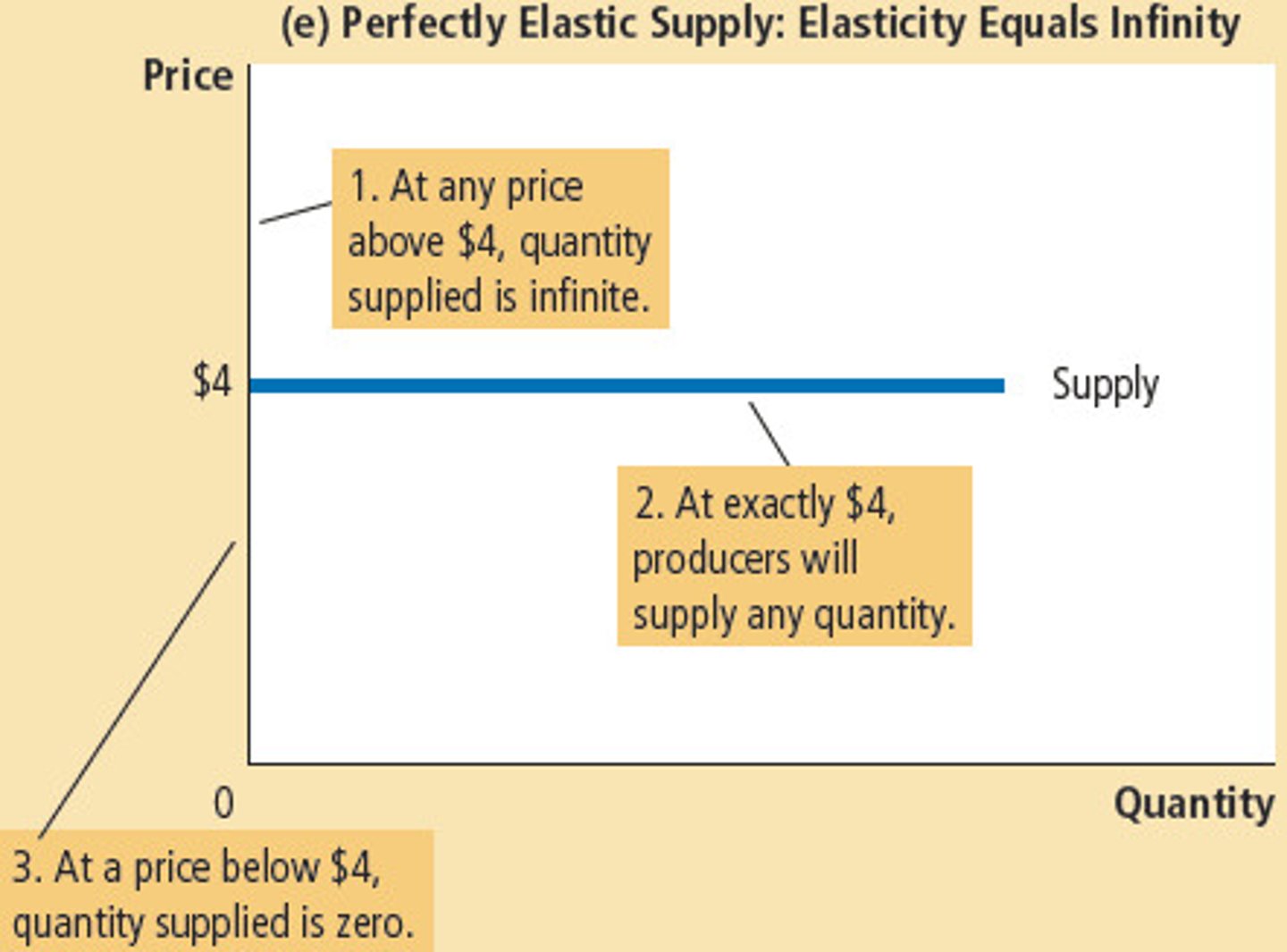
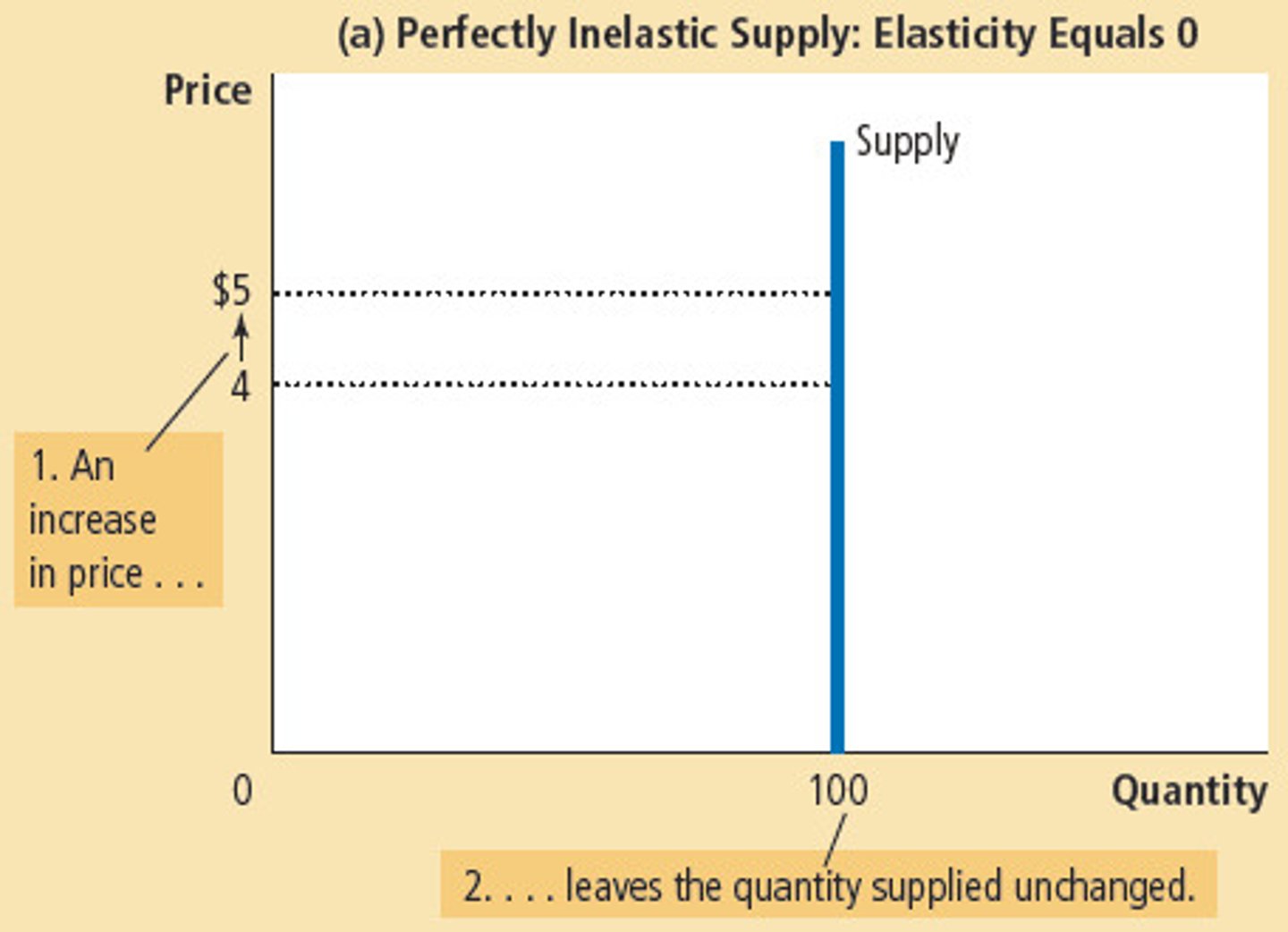
inelastic supply
If close substitutes are available, if the good is a luxury, if the market is narrowly defined.. demand tends to be more ....
elastic
If quantity demanded moves proportional less than the price, adding the elasticity is less than 1.. demand tends to be more ....
inelastic
price ceiling
a legal max on the price at which a good can be sold
price floor
a legal min on the price at which a good can be sold
When a price ceiling is above the equilibrium price..
non-binding price ceiling
When a price ceiling is below the equilibrium price..
binding price ceiling
When a price floor is below the equilibrium price..
non-binding price floor
When a price floor is above the equilibrium price..
binding price floor
tax incidence
the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a market
when the government levies a tax on a good...
the equilibrium quantity of the good falls
the incidence falls more on the consumer with a ________ supply and _________ demand
elastic supply ; inelastic demand
the incidence falls more on the producer with a _______ supply and ________ demand
inelastic supply ; elastic demand
consumer surplus
the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it (area below the demand curve and above the price)
cost
the value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good
producer surplus
the amount a seller is paid for a good minus the sellers cost of providing it (below the price and above the supply curve)
total surplus
value to buyers - cost to sellers
when a tax is levied on buyers, the demand curve shifts ..
downward
when a tax is levied on sellers, the demand curve shifts..
upward
tax on a good causes the size of the market for the good to ..
shrink
deadweight loss
the fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion, such as a tax
Laffer curve
a graphical representation of the relationship between tax rates and total tax revenues raised by taxation.
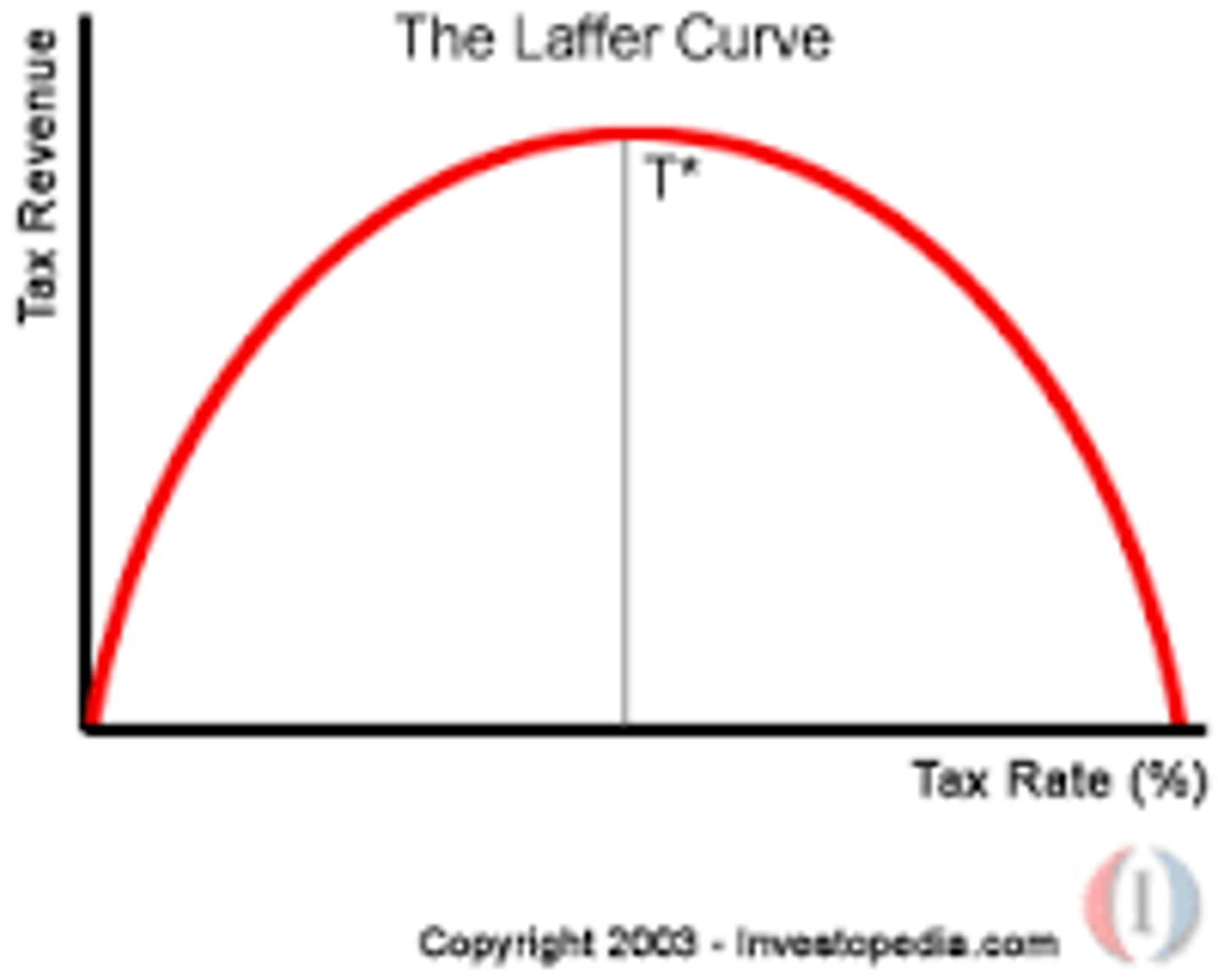
T/F: the deadweight loss decreases as the size of the tax increases
False
world price
the price of a good that prevails in the world market for that good
once trade is allowed, the domestic price equals the
world price
tariff
a tax on goods produced abroad and sold domestically
externality
the uncompensated impact of one persons actions on the well-being of a bystander
Coase theorem
the proposition that if private parties can bargain without cost over the allocation of resources, they can solve the problem of externalities on their own
with negative externalities, the socially optimal quantity is ______ than the equilibrium quantity
less
with positive externalities, the socially optimal quantity is _____ than the equilibrium quantity
greater
how will the government react to a negative externality ?
corrective taxes
how will the government react to a positive externality ?
subsidies
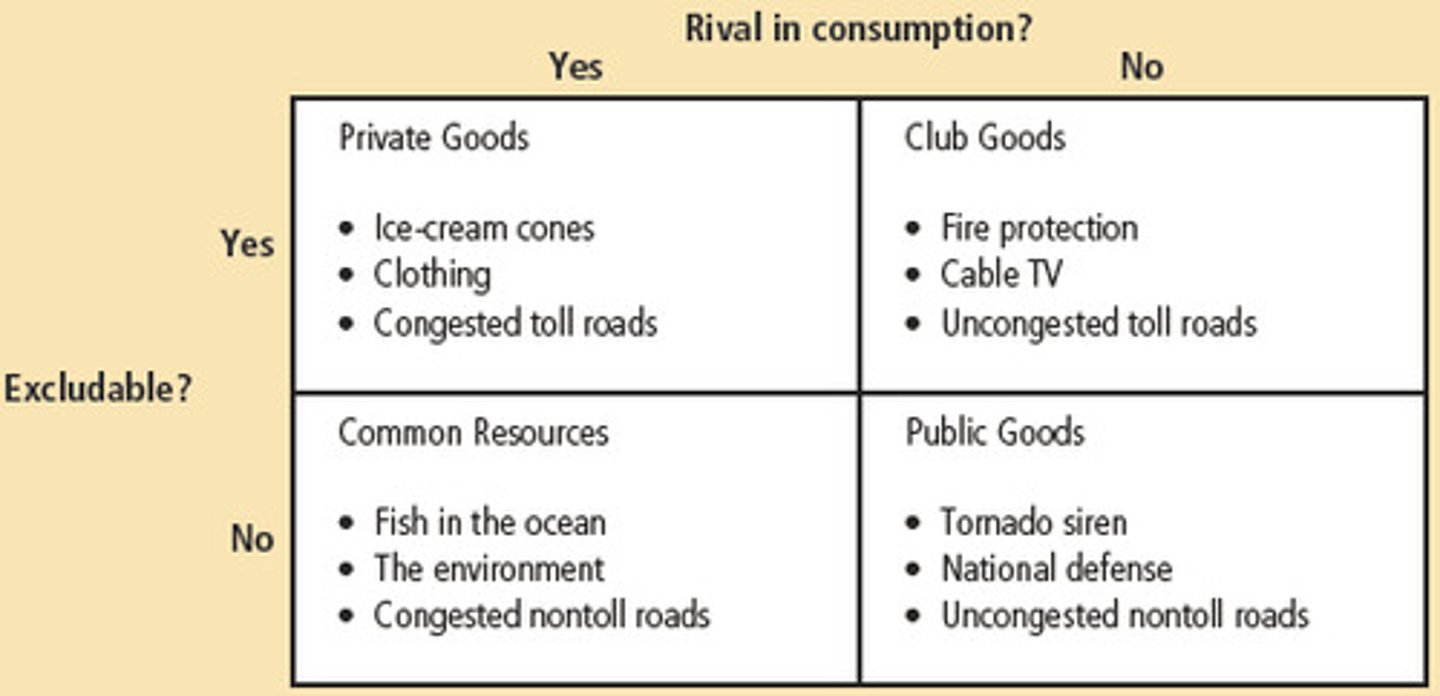
excludability
the property of a good whereby a person can't be prevented from using it
rivalry in consumption
the property of a good whereby one person's use diminishes other people's use
private goods
excludable
rival
public goods
not excludable
not rival
common resources
not excludable
rival
club goods
excludable
not rival
four types of goods
free rider
a person who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it
explicit costs
input costs that require an outlay of money by the firm
implicit costs
input costs that do not require an outlay of money by the firm
economic profit
total revenue - total cost ; includes both implicit and explicit costs
accounting profit
total revenue - total explicit costs
marginal product
the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input
fixed cost
costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced
variable costs
costs that vary with the quantity of output produced
average fixed cost
fixed cost divided by the quantity of output
average variable cost
variable cost divided by the quantity of output
marginal cost
the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unit of production
marginal cost equation
Change in total cost / Change in quantity
average total cost equation
Total Cost / Quantity
economies of scale
when the long-run ATC falls as the quantity of output increases
diseconomies of scale
when the long-run ATC rises as the quantity of output increases
the goal of firms
to maximize profit
where does the marginal-cost curve cross the average total cost curve ?
at the minimum of average total cost
many costs are ______ in the short run, but ______ in the long run
fixed; variable
competitive market
a market with many buyers and sellers trading identical products so that each buyer and seller is a price taker
perfectly competitive market characteristics (2)
1. there are many buyers and sellers
2. goods offered by the various sellers are largely the same
average revenue
total revenue divided by the quantity sold
marginal revenue
the change in total revenue from an additional unit sold
shut down
short run decision to not produce anything during a specific period of time b/c of current market conditions
Exit
long run decision to leave the market
T/F: most firms cannot avoid their fixed costs in the short run but can do so in the long run
True
T/F: a firm that shuts down temporarily doesn't have to pay its fixed costs
False
a firm should do what when their TR > VC
shut down
a firm should do what when their P < AVC
shut down
sunk cost
a cost that has already been committed and cannot be recovered
a firm should do what when their TR < TC
exit
a firm should do what when their P > ATC
enter
a firm should do what when their P < ATC
exit
Profit equation
Profit = (P - ATC) x Q
price of the good in a competitive market equals
the firm's average revenue and its marginal revenue
T/F: a competitive firms supply curve is also its marginal-revenue curve
False, marginal -cost *
increase in demand raises prices and leads to ..
profits