Carbon Chemistry and Functional Groups in Organic Molecules
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Why is carbon considered the backbone of life?
Carbon is the basis of nearly all biological molecules, including proteins, DNA, and carbohydrates.
What is organic chemistry?
The study of carbon compounds, regardless of their origin, ranging from simple to complex molecules.
What are organic molecules?
Molecules that contain carbon, which can form diverse structures due to its ability to bond with four other atoms.
How does carbon's electron configuration influence its bonding?
The electron configuration determines the kinds and number of bonds carbon can form, leading to a variety of organic molecules.
What shape do carbon atoms form when bonded to four other atoms?
A tetrahedral shape.
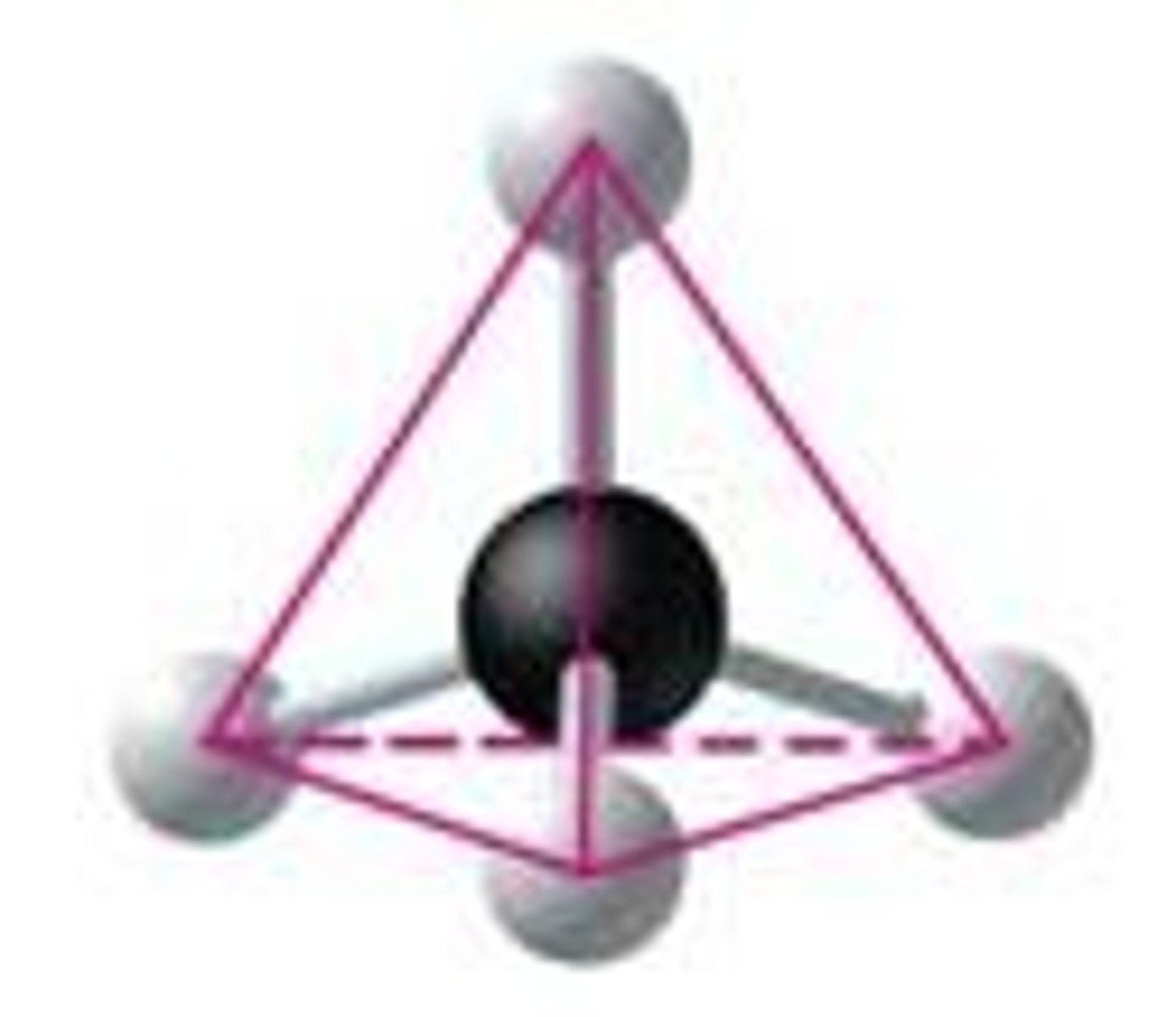
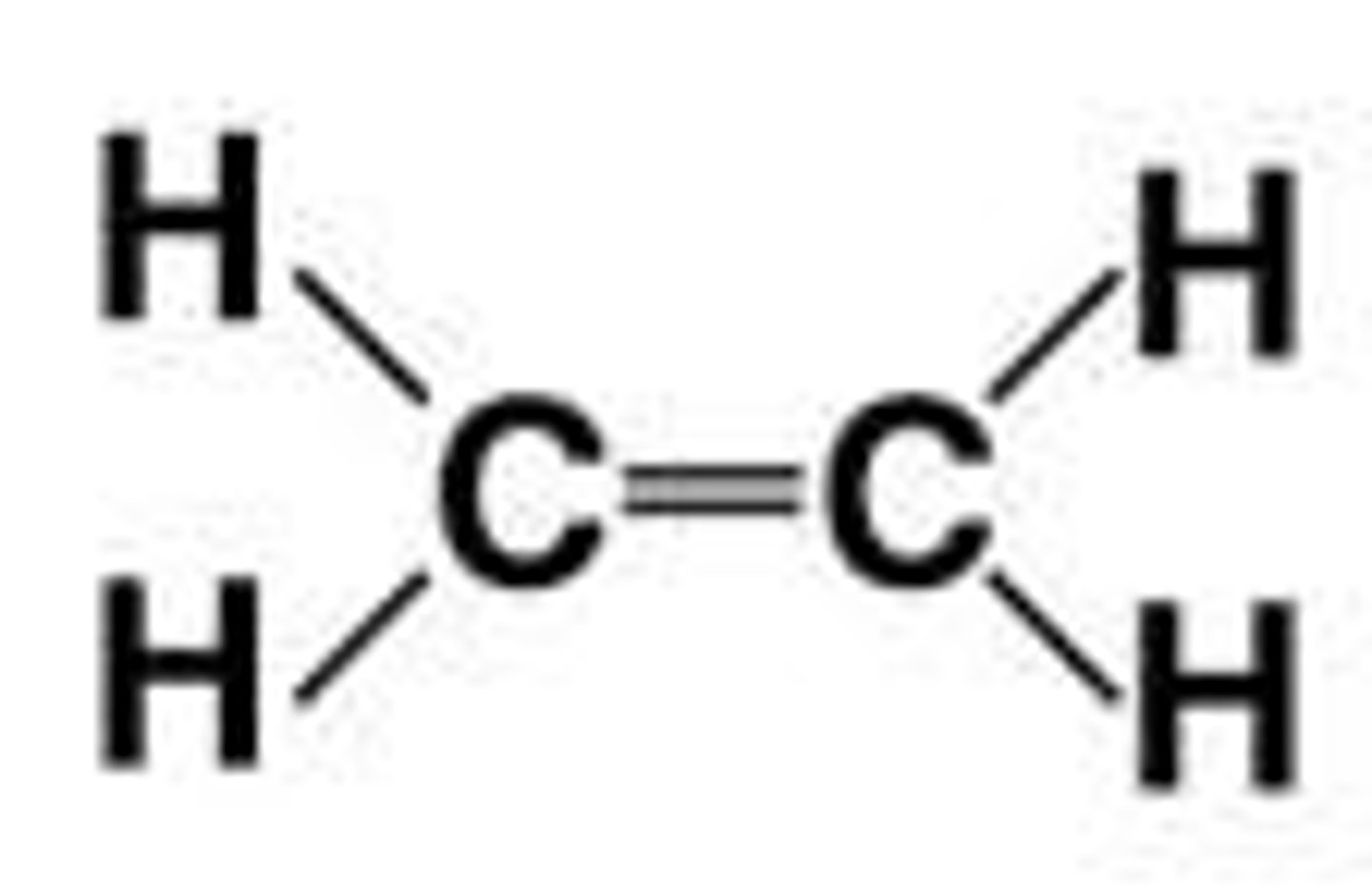
What happens to the shape of carbon molecules when double bonds are present?
Atoms joined to carbon atoms with a double bond are in the same plane as the carbons.
What are hydrocarbons?
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen, which are hydrophobic and can release large amounts of energy.
What are isomers?
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties.
What are structural isomers?
Isomers that have different covalent arrangements of their atoms.
What are cis-trans isomers?
Isomers that have the same covalent bonds but differ in their spatial arrangements.
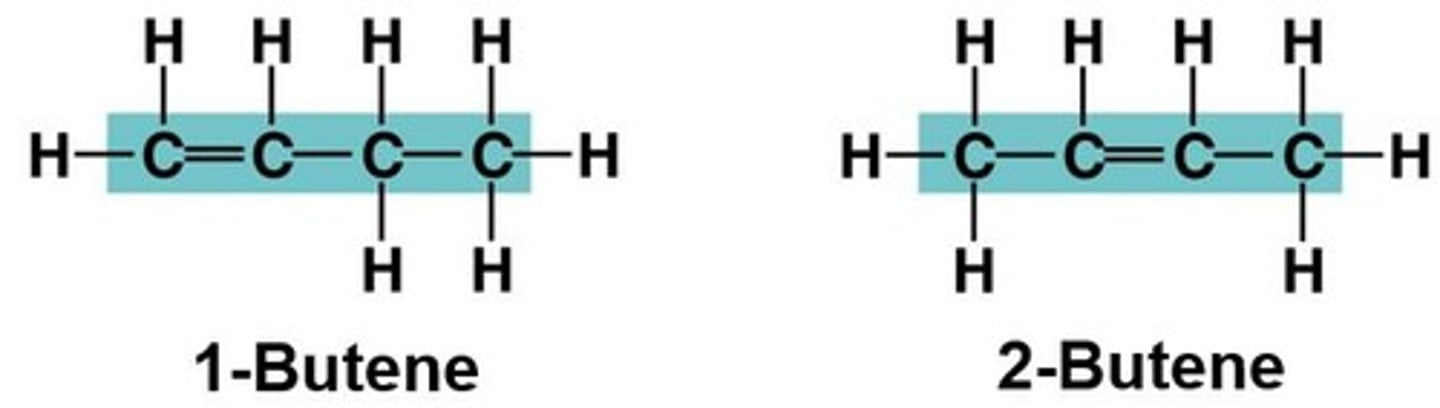
What are enantiomers?
Isomers that are mirror images of each other, often having different biological effects.
Why are enantiomers important in pharmaceuticals?
Different enantiomers can have different effects, with usually only one being biologically active.
What is the role of functional groups in organic molecules?
Functional groups change the characteristics of the carbon backbone, giving each molecule unique properties.
What is the hydroxyl group and its significance?
A polar group found in alcohols, such as ethanol, that forms hydrogen bonds with water.
What distinguishes ketones from aldehydes?
Ketones have a carbonyl group within the carbon skeleton, while aldehydes have it at the end.
What is the carboxyl group and its function?
A functional group that acts as an acid, known as carboxylic acid or organic acid.
What is the amino group and its role in amino acids?
A charged, basic group that allows amino acids to act as zwitterions, possessing both positive and negative charges.
What is the phosphate group and its importance?
A charged group that contributes a negative charge and is involved in many important chemical reactions in cells.
What is ATP and why is it significant?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an important organic phosphate that stores energy for cellular reactions.
What is the chemical reaction involving ATP?
ATP reacts with water, releasing energy that can be used by the cell.
How do variations in molecular structure contribute to biological diversity?
Different parts of molecules lead to new chemistries and emergent properties, forming the foundation of biological diversity.
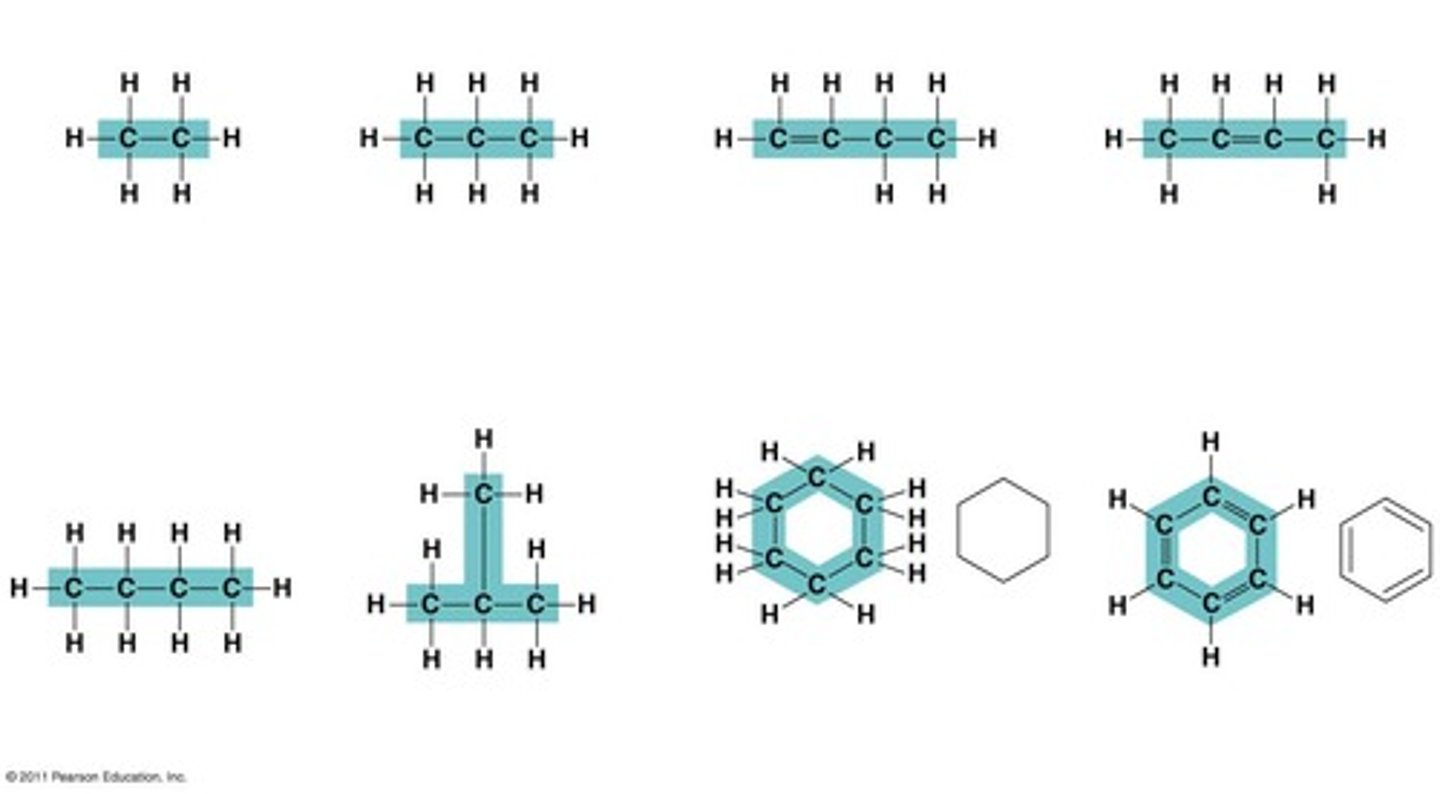
What is the significance of carbon skeletons in organic molecules?
Carbon skeletons can vary in length, branching, and presence of double bonds, affecting the properties of the molecules.
Who visualized the ring structure of benzene?
German chemist August Kekulé in 1865.
What are the two shapes that carbon rings can have?
Carbon rings can have various shapes, including those found in compounds like benzene.
What are the seven functional groups most important in life?
Hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, sulfhydryl, and methyl groups.