Chapter 17 Cardiovascular Emergencies (EMT B)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Atherosclerosis
Disorder in which calcium and fatty material called cholesterol build up
Defibrillation
Applying a shock to the heart to reset the rhythm
Acute Coronary Syndrome
angina pectoris (chest pain), and myocardial infarction
Blood flow to the heart suddenly gets blocked or reduced
Aortic Aneurysm/Dissection
Walls weaken and cause a bleb (bubble expansion out of a vessel)
Dissection: When the bleb opens and bursts the blood vessel
Pulmonary Edema
Fluid buildup in the lungs
Treated with the CPAP machine to push liquid out of the lungs into vessels
Thromboembolism
An embolism, but specifically a BLOOD clot embolism
An Embolism is something like a blood clot, air bubble, or particle that blocks a blood vessel
You can get this from stagnant blood, like when you sit all day and legs are stagnant
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
Records electrical activity of the heart.
Shows how fast your heart is beating
Shows If the rhythm is normal or irregular
Sinoartrial Node
Housed in the right atrium, Is the hearts natural pacemaker
Controls the hearts rhythm and rate
Sends electrical signals to make the heart beat
60-100 beats per minute
There is a p wave
Add ons
Right atrium gets blood from the body → then sends to the right ventricle to the lungs
left atrium gets blood from the lungs →then sends to left ventricle to the body
Atrioventricular Node
Part of the hearts electrical system that helps control the heartbeat
Housed lower, right between the atrium and ventricle
Its pace is 40-60, there is no P wave with AV node
On the ECG it will look like a dip or pothole, or it’s just flat
What is the rate of the ventricles? (how fast they are beat)
20-40 bpm
ECG electrode placement
Goal is to obtain the ECG within 10 minutes of first contact with a patient to detect heart problems, investigate symptoms like chest pain, monitor heart health, check pacemaker function

Unstable Angina
Occurs in the absence of a significant increase in oxygen demand
Stable Angina
Occurs in response to exercise or activity that increases demand on the heart muscle
→ Treat angina patients like AMI patients
Acute
Condition that comes on suddenly and is usually severe but short-term
QRS
Ventricles contracts, makes it bigger making a big v shape on a monitor
CHF
Congestive heart failure
Signs
Shortness of breath
swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, fatigue irregular heartbeat
Rapid or shallow breathing
Treatment
Oxygen
Nitroglycerin
Dependent/Peripheral Edema
When the heart has problems on the right side
Blood backs up into the rest of the body, especially the limbs
Signs
Swollen, big hands and feet, think cankles
What must the blood pressure be to give Nitroglycerin?
Systolic pressure of 90
Remember this is sublingual
AMI
Acute Myocardial Infarction, when blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked usually by a blood clot (heart attack)
Most likely to occur in the left ventricle
Signs
Weakness
Nausea
sweating
chest pain
discomfort
Syncope
lower jaw/arm/back/abdomen/neck pain
Sputum
Treatment
Aspirin
Nitroglycerin
Oxygen
Dysrhythmia
Heart rhythm abnormalities
Premature Ventricular Abnormalities
A QRS wave without a preceding P-wave or post T-wave

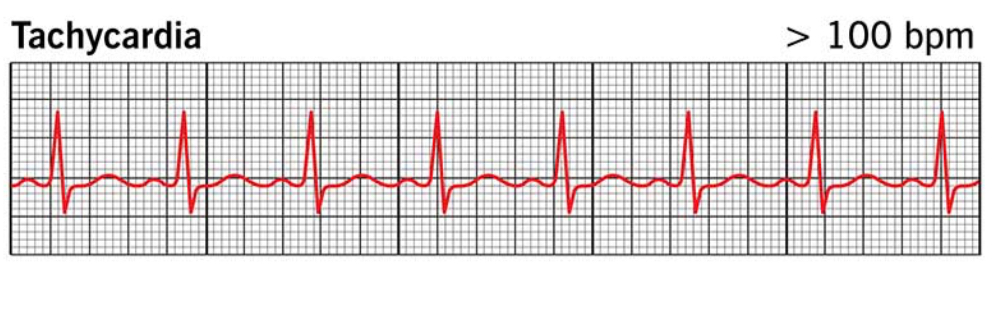
Tachycardia
Heart rate that is over 100 beats per minute
Causes
Anxiety
Fever
Drugs
Exertion
→ You HAVE to be able to explain why a patient is tachycardic
→ Tachycardic picture provided
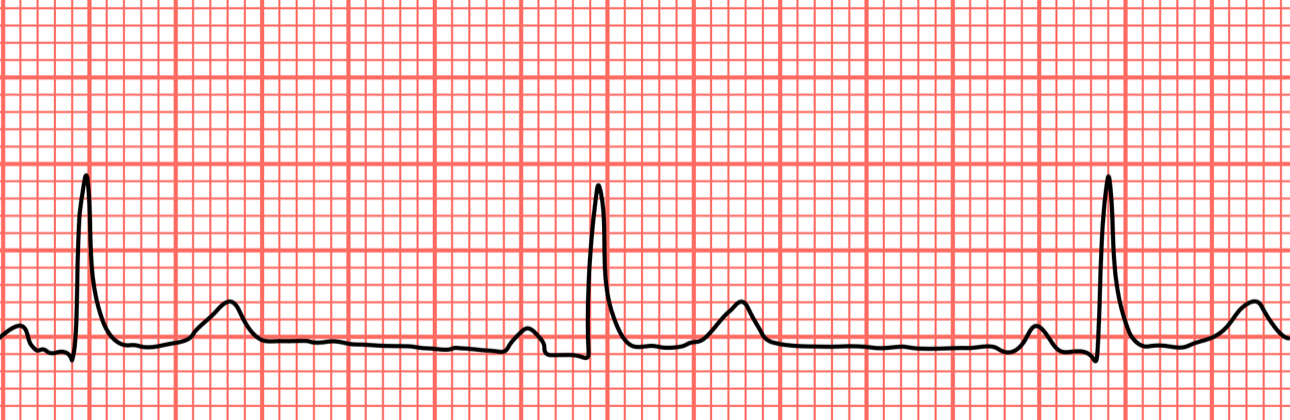
Bradycardia
Heart rate less than 60 beats per minute
Causes
Aging
Sleep Apnea
Athletic heart
SA Node is slow
→example picture
Ventricular Tachycardia
When the ventriculars beat too fast that is life threatening (150-200bpm) → can lead to cardiac arrest
Ventricles are only supposed to beat 20-40 bpm
electrical activity starts in the ventricle
Shockable
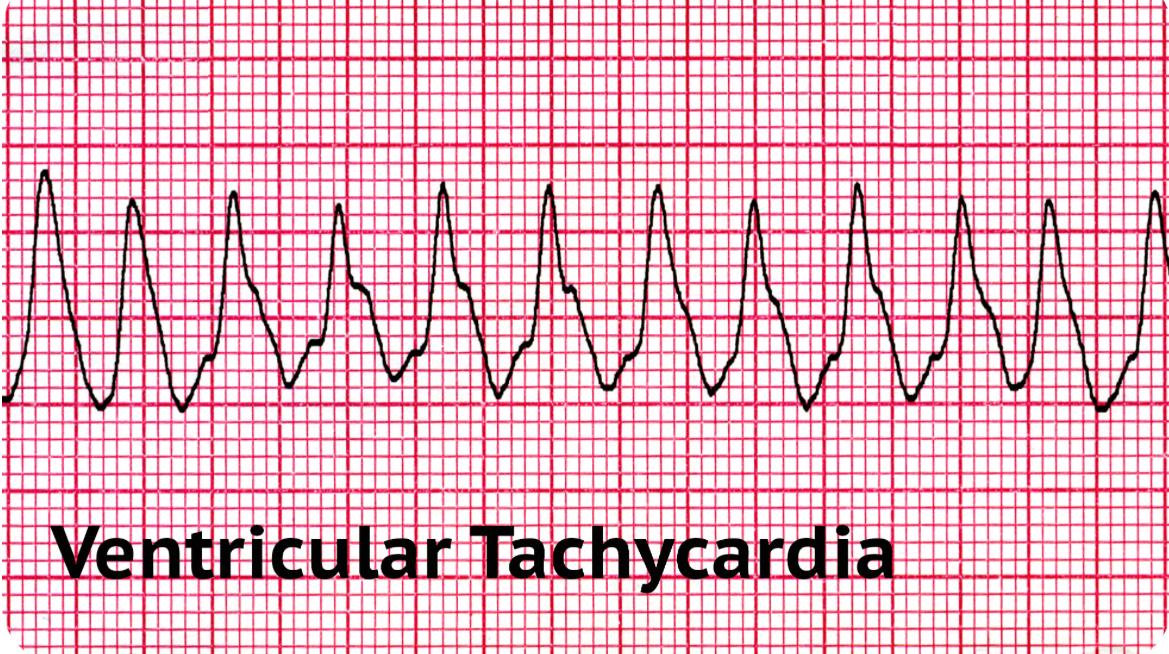
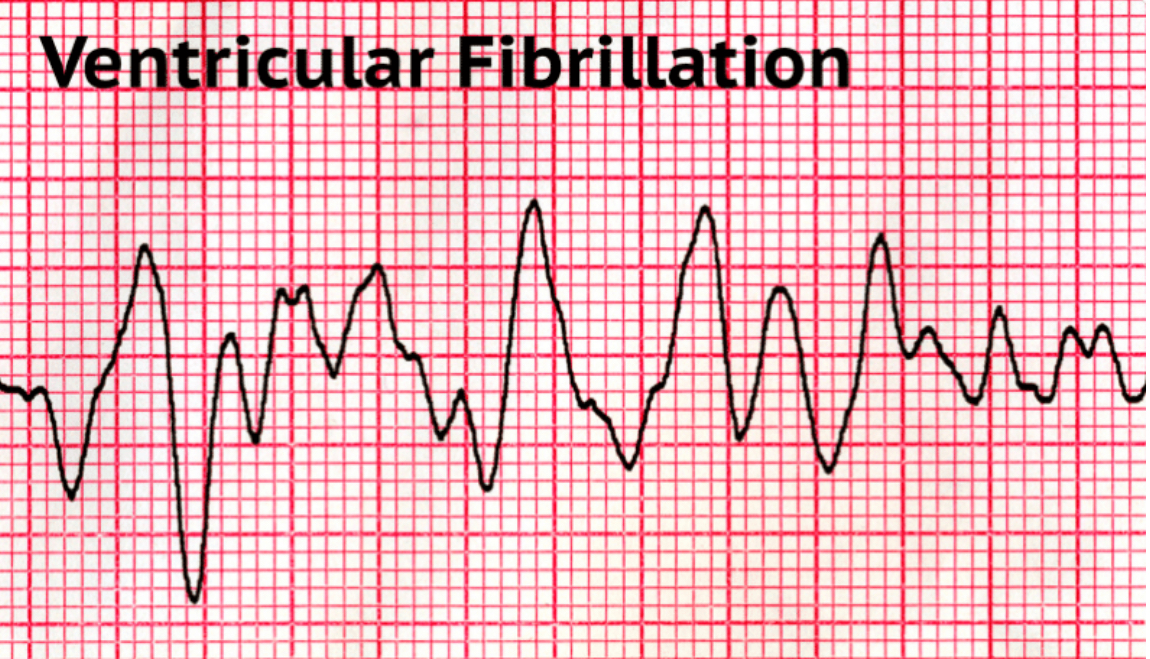
Ventricular Fibrillation
Causes ventricles to go buck wild, fibrillate, shake, dance, etc
No pulse
Shockable rhythm
Use AED on these patients
Hypertensive Emergency
When the systolic number is over 180
For example, a blood pressure of 180/110 could be hypertensive a hypertensive emergency
you need to be able to explain hypertension situations on a patient
→ do not give a patient nitroglycerin, they may have a bleed
Hypertension may be supporting blood flow to their brain, if you give nitroglycerin, you may let their internal bleed flow, leading to their death
LVAD
Left Ventricular Assist Device
Pumps blood for the patient, they will have no pulse
The device creates a continuous blood flow instead of the heart’s normal pumping action (beat-by-beat)

Aortic Aneurysm
Weakness in the wall of the aorta that makes it susceptible to rupture
Cardiac Arrest
When the heart stops beating
Hearts electrical system malfunctions which causes the blood to stop pumping properly
This is not the same as heart attack, which is caused by a blocked artery. However, a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest.
Signs
Person suddenly collapses
No pulse
Not breathing
Unconscious and unresponsive
Ischemia
lack of oxygen that deprives tissue of nutrients, resulting from partial or complete blockage of blood flow.
Stroke Volume
Volume of blood ejected with each ventricular contraction
ROSC
Return of Spontaneous Circulation
The return of pulse and effective blood to the body in a patient who previously was in cardiac arrest
Cardiac Output
Measure of the volume of blood circulated by the heart in 1 minute
Calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate
Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm occurs when?
The inner layers of the aorta become separated
Cardiogenic shock following AMI is caused by what?
Decreased pumping force of the heart muscle
The right coronary artery supplies blood to the?
Right ventricle and inferior wall of the left ventricle
What sign is commonly observed in patients with right-sided heart failure?
Dependent Edema
Angina Pectoris
Chest pain or discomfort that happens when the heart isn’t getting enough oxygen-rich blood
Feels like pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest and can spread to the arms, neck, jaw, or back
Lasts 3-8 minutes
usually disappears with rest, supplemental oxygen, or nitroglycerin
The three ways AMI differs from Angina
May or may not be caused by exertion and can occur at any time, sometimes when a person is sitting quietly or even sleeping
Does not resolve in a few minutes; it can last between 30 minutes and several hours
May or may not be relived by rest or nitroglycerin
AMI can have three serious consequences what are they?
Sudden death
Cardiogenic shock
Congestive heart failure
Dysrhythmia
Abnormality of the heart rhythm
Asystole
Absence of all heart electrical activity
Myocardium
Heart muscle
Myocardial Ischemia
Heart muscle isn’t getting enough oxygen-rich blood
Happens because of narrowed or blocked arteries