CNC huehuehue (copy)
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Lathe Machine
•The lathe is a machine tool used principally for shaping articles of metal (and sometimes wood or other materials) by causing the workpiece to be held and rotated by the lathe while a tool bit is advanced into the work causing the cutting action.
Engine Lathes
•are large lathe and is usually floor mounted. It can handle more machining jobs
Turret Lathes and Special Purpose Lathe –
are usually used in production or job shops for mass production and specialized parts.
bed
•is the foundation of the working parts of the lathe to another
headstock
is located on the operator’s left end of the lathe bed. It contains the main spindle and oil reservoir and the gearing mechanism for obtaining various spindle speeds and for transmitting power to the feeding and threading mechanism
main spindle
•is mounted on bearings in the headstock and is hardened and specially ground to fit different lathe holding devices. The spindle has a hole through its entire length to accommodate long workplaces
Centers, collets, drill chucks, tapered shank drills and reamers
may be inserted into the spindle
Chucks, drive plates, and faceplates
may be screwed onto the spindle or clamped onto the spindle nose.
tailstock
•is located on the opposite end of the lathe from the headstock. It supports one end of the work when machining between centers, supports long pieces held in the chuck, and holds various forms of cutting tools, such as drills, reamers, and taps.
carriage
•includes the apron, saddle, compound rest, cross slide, tool post, and the cutting tool. The function of the carriage is to carry and move the cutting tool.
saddle
carries the cross slide and the compound rest. The cross slide is mounted on the dovetail ways on the top of the saddle and is moved back and forth at 90° to the axis of the lathe by the cross slide lead screw
compound rest
is mounted on the cross slide and can be swiveled and clamped at any angle in a horizontal plane. The compound rest is used extensively in cutting steep tapers and angles for lathe centers
cutting tool and tool holder
are secured in the tool post which is mounted directly to the compound rest
apron
•contains the gears and feed clutches which transmit motion from the feed rod or lead screw to the carriage and cross slide
roughing tool
has a radius ground onto the nose of the tool bit that is smaller than the radius for a finishing or general purpose tool bit
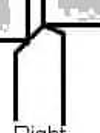
right-hand turning tool
bit is shaped to be fed from right to left. The cutting edge is on the left side of the tool bit and the face slopes down away from the cutting edge
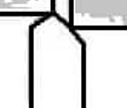
left-hand turning tool
bit is the opposite of the right-hand designed to cut when fed from left to right
round-nose turning tool
bit is very versatile and can be used to turn in either direction for roughing and finishing cuts.
Parting Tool
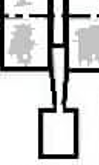
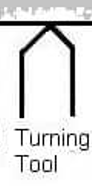
Turning Tool
Right Hand turning Tool
Left Hand turning tool
radius forming turn tool

thread cutting tool
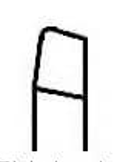
chamfering tool
Right Hand roughing
right hand finishing

left hand roughing
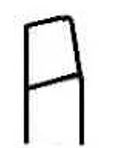
left hand finishing.
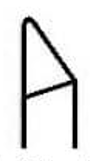
left hand facing
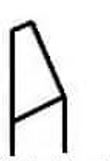
round nose grooving
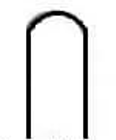
round nose turning

round corner forming
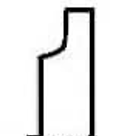
grooving undercutting parting
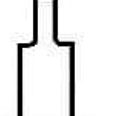
radius forming
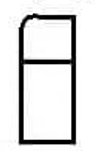
threading
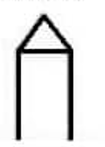
threading acme

Facing
machining the ends and shoulders of a piece of stock smooth, flat, and perpendicular to the lathe axis
Straight Turning
sometimes called cylindrical turning, is the process of reducing the work diameter to a specific dimension as the carriage moves the tool along the work
Shoulders
•are machined to add strength for parts that are to be fitted together, make a corner, or improve the appearance of a part. The three common shoulders are the square, the filleted, and the angular shoulder
Corners
•are turned on the edges of work to b
• and to add to the general appearance of the work. Common types of corners are chamfered, rounded, and square
Undercuts
are the reductions in diameter machined onto the center portion of workplaces to lighten the piece or to reduce an area of the part for special reasons, such as holding an oil seal ring
Grooves
(or necking) is the process of turning a groove or furrow on a cylinder, shaft, or workpiece. The shape of the tool and the depth to which it is fed into the work govern the shape and size of the groove. The types of grooves most commonly used are square, round, and V-shaped
RADII AND FORM TURNING
•Form turning is the process of machining radii and these irregular shapes.
TAPER TURNING
•When the diameter of a piece changes uniformly from one end to the other, the piece is said to be tapered. Taper turning as a machining operation is the gradual reduction in diameter from one part of a cylindrical workpiece to another part, Tapers can be either external or internal
SCREW THREAD CUTTING
•A thread is a uniform helical groove cut inside of a cylindrical workpiece, or on the outside of a tube or shaft.
Knurling
•Knurling is a process of impressing a diamond shaped or straight line pattern into the surface of a workpiece. The diamond is the most common pattern and the medium specially shaped hardened metal wheels to improve its pitch is used most often. The coarse pitch is used for large appearance and to provide a better gripping surface.
DRILLING
•holes will need to be drilled using the lathe before other internal operations can be completed, such as boring, reaming, and tapping. Before drilling the end of a workpiece on the lathe, the end to be drilled must be spotted (center- punched) and then center- drilled so that the drill will start properly and be correctly aligned.
BORING
•Boring is the enlarging and truing of a hole by removing material from internal surfaces with a single-point cutter bit
RECESSING
•Recessing, sometimes called channeling or cambering, is the process of cutting a groove inside of a drilled, bored, or reamed hole. Recesses are usually machined to provide room for the tool run out needed for subsequent operations such as internal threading