autism spectrum disorders
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is autism spectrum disorder?
a neurodevelopmental disorder which is characterised by persistent impairments in:
- social communication
- social interaction
- repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests or activities
what is DSM-5?
diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders
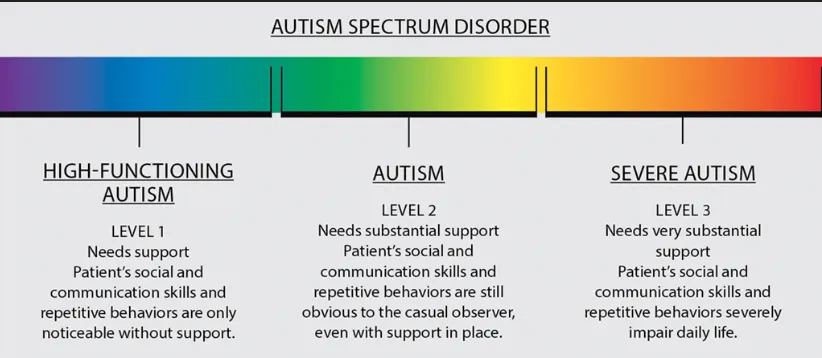
what are the 3 levels of autism according to DSM-5?
level 1 - high functioning autism
level 2 - autism
level 3 - severe autism
what is high functioning autism (HFA) also called?
aspergers - they have normal or above average intelligence
what support is needed for HFA?
- moderate support is needed
- behaviours only noticeable without support
what support is needed for level 2 - autism?
- substantial support
- behaviours may still be noticeable even with support
what support is needed for level 3 - severe autism?
- high support
- behaviours will severely impair everyday life
what does WHO ICD-10 classify autism and aspergers as?
pervasive developmental disorders (PDDs)
why has the prevalence of ASD increased?
changes of definitions and increased awareness
what is the estimated prevalence of ASD worldwide?
1 - 2%
how much more common is ASD in males than females?
4 times more common
which other neurodevelopmental disorders is ASD associated with?
- ADHD - seen in up to 50% pts with ASD
- LD - seen in up to 45% pts with ASD
when are the clinical features of autism usually observable by?
3 years old
what are some social features of ASD? (6)
- lack of eye contact
- delay in smiling
- avoiding physical contact
- unable to read non-verbal cues
- difficulty in establishing friendships
- not wanting to share attention - play with others
what are some communication features of ASD?
- delay absence or regression in language development
- lack of appropriate non-verbal communication
- difficulty with imaginative or imitative behaviour
- repetitive use of words or phrases
- lack of pragmatic communication - ability to select the right words for the situation
what are some behavioural features of ASD?
- greater interest in objects, numbers or patterns, over people
- stereotypical repetitive movements
- intensive and deep interests that are persistant + rigid
- repetitive behaviour + fixed routines
- anxiety and distress with routine changes
- extremely restricted food preferences
what is meant by stereotypical repetitive movements?
self-stimulating movements used to comfort themselves e.g. hand-flapping or rocking
what are the general categories for the complex aetiology of ASD? (4)
- genetic
- family history
- advanced parental age
- environmental factors
what are the examples of genetic causes?
- tuberous sclerosis complex
- fragile X syndrome
- chromosome 15q11-13 duplication syndrome
- angelman syndrome
- rett's syndrome
- down syndrome
what maternal and paternal ages are associated with increased risk of ASD?
maternal > 40
paternal > 50
what environmental factors can cause ASD?
- toxin exposure
- prenatal infections
what is the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for ASD?
1) persistent deficits in social communication + interaction
- deficits in social-emotional reciprocity
- deficits in non-verbal comms
- deficits in relationship understanding + development
2) restricted repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests or activities manifested by at least 2 currently or by history:
- stereotyped or repeititive motor movements
- insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines
- hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input
3) symptoms must be present in early developmental period (but may not fully manifest until later on in life)
4) symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning
what is the ICD-10 criteria for typical pervasive developmental disorder?
presence of abnormal and/or impaired development that manifests before 3 y/o - in all 3 areas; reciprocal social interaction, communication + restricted, repetitive behaviour
what is the ICD-10 criteria for atypical pervasive developmental disorder?
a pervasive developmental disorder that differs from autism in terms of age onset or failure to fulfil all 3 sets of diagnostic criteria
what are the differentials of autism?
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- social (pragmatic) communication disorder
- global developmental delay/intellectual disability
- developmental language disorder
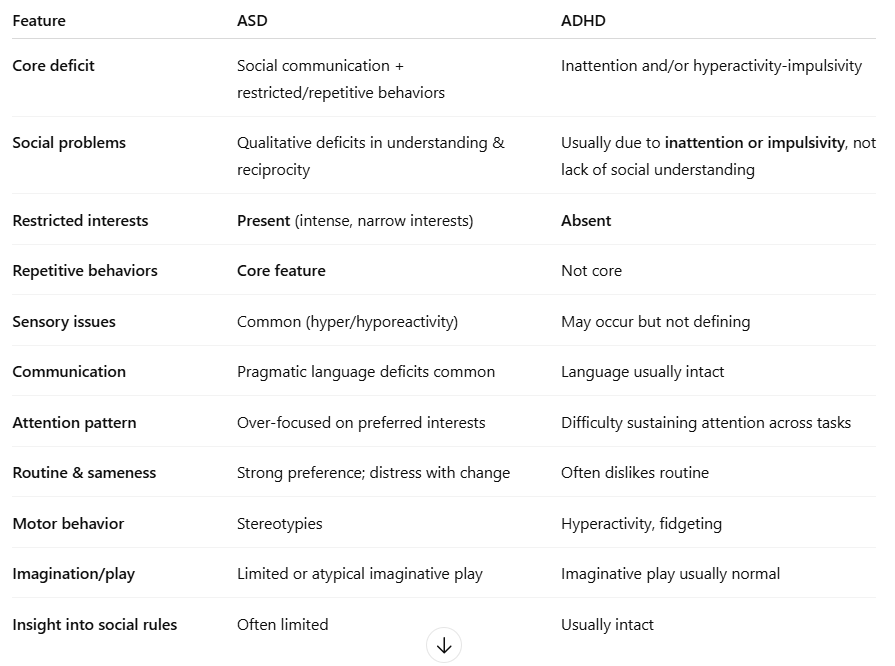
what are the similarities and differences between ASD and ADHD?
sim - social communication difficulties
diff -
- normal pragmatic language skills, nonverbal social behaviour + imaginative play
- lack of restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests + activities
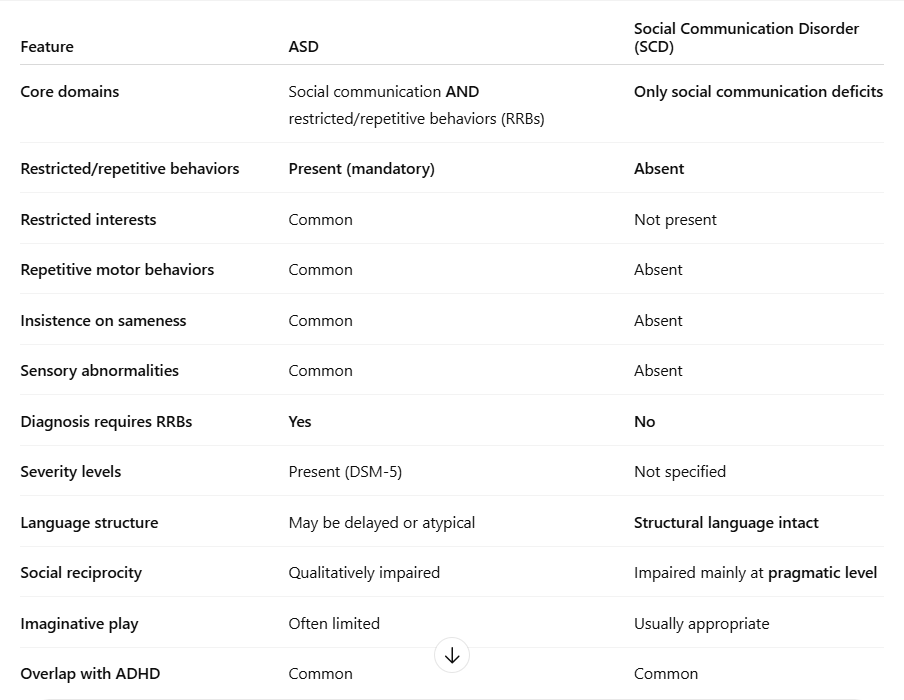
what are the similarities and differences between ASD and social communication disorder?
sim - social communication and interaction difficulties
diff - lack of restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests or activities
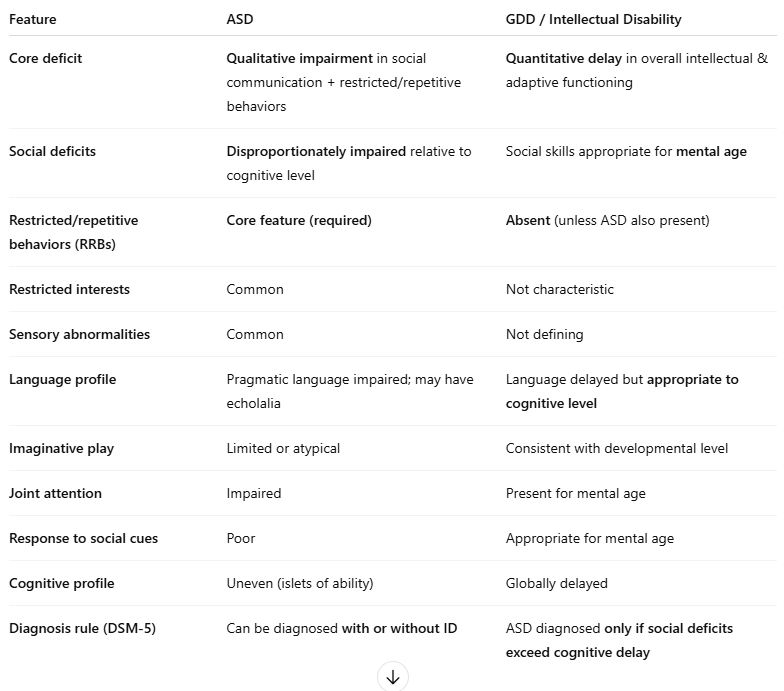
what are the similarities + differences between ASD and global developmental delay/intellectual disability?
sim - language delay, repetitive behaviours
diff - social responsiveness + communication appropriate
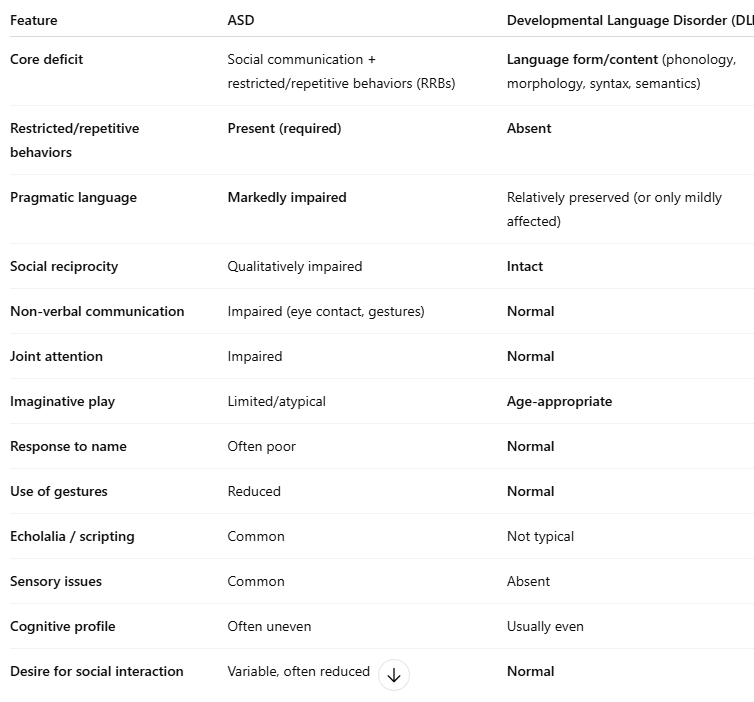
what are the sim + diff between ASD and developmental language disorder?
sim - social communication difficulties
diff - normal reciprocal social interactions
what are the goals in management of ASD?
- increase functional independence and quality of life
- improve learning + development, social skills and communication
- decrease disability + comorbidity
- aid to families
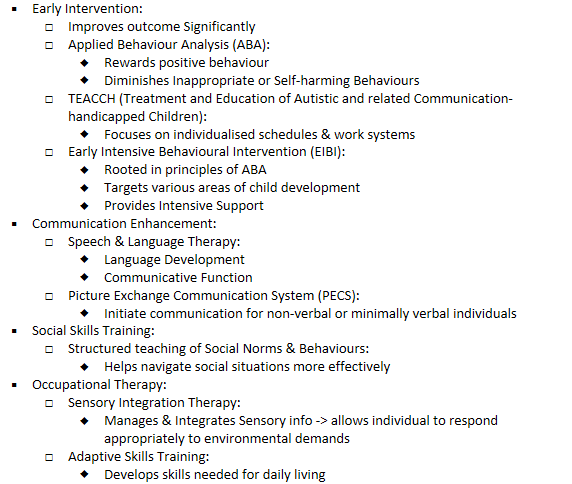
what are examples of non-pharmacological therapy?
- behavioural + educational interventions
- psychosocial interventions
- interventions for life skills
- interventions for speech and language problems (SALT)
- intervention for sleep disorders
when might pharmacological interventions be needed?
- hyperactivity
- inattention
- impulsivity
- aggressive behaviour
- anxiety
- depression
what drug may be used for anxiety and depression?
SSRIs
what drug type may be used for aggression and self-injury?
antipsychotic drugs
what drug may be used for ADHD?
methylphenidate