ICE May 2025
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
ADL vs IADL
ADL = Activities of Daily Living (basic self-care tasks essential for daily functioning, like bathing, dressing, and eating)
IADL = Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (more complex tasks necessary for independent living, like cooking, managing finances, and using transportation)
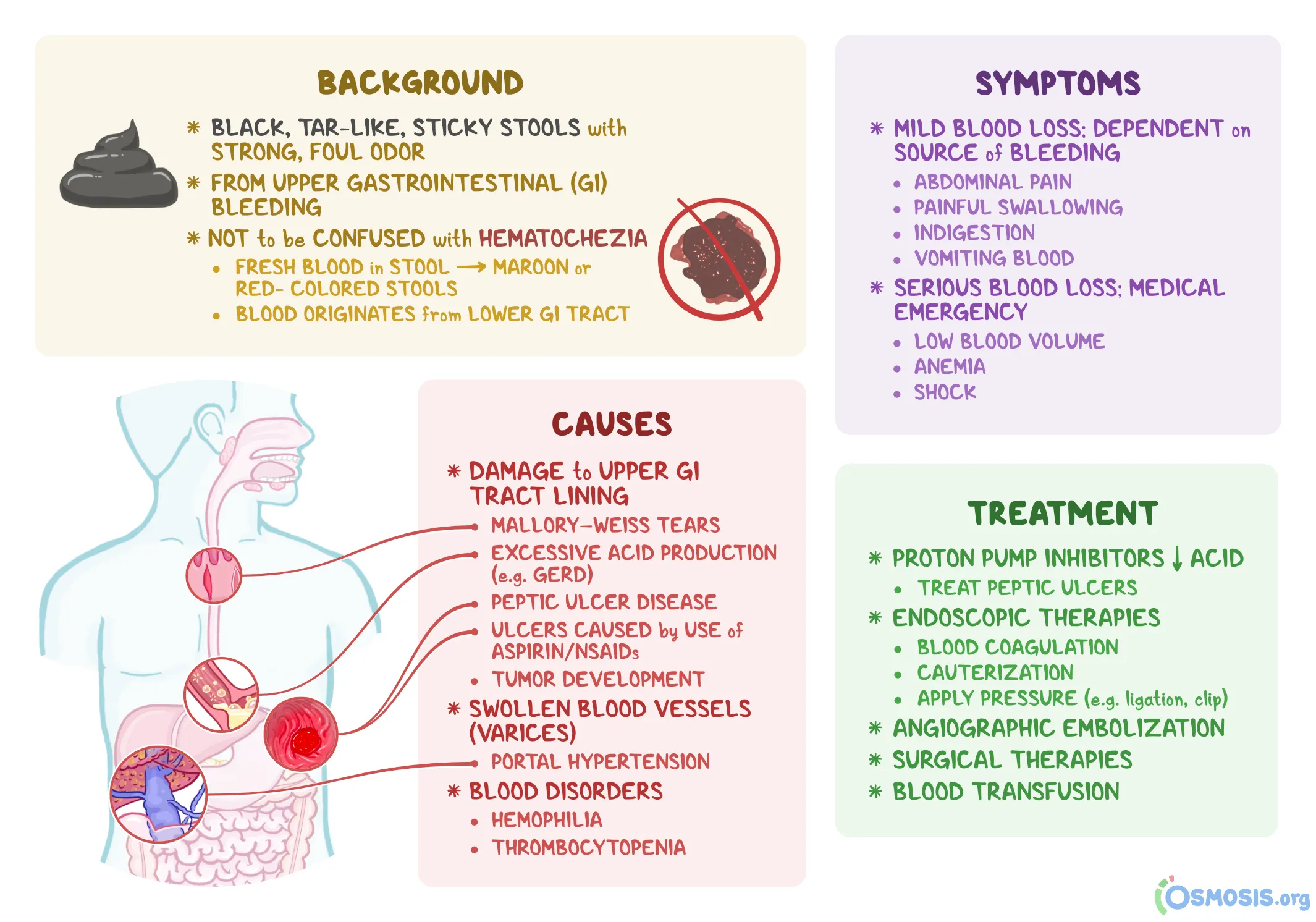
melena
black, tarry stool that comes from bleeding in your upper GI tract
EGD
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
What: A common diagnostic medical procedure to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum (upper part of small intestine). Uses thin flexible tube called endoscope.
prodrome
early signs or symptoms of an illness or health problem that appear before the major signs or symptoms start
eg a runny nose is often “prodromal” to a cold, meaning that a runny nose is a risk factor for developing a cold but not everyone with a runny nose will go on to develop a cold
syncope
fainting or passing out— a sudden loss of consciousness
“syncope with a prodrome of dizziness”
this means the patient faints (loses consciousness) after a period of feeling dizzy/lightheaded
MDM
Medical Decision Making
clinicians’ process of making decisions about diagnosis and treatment based on patient data
C. diff
Clostridium difficile
What: A bacterium that can cause inflammation of the colon. Highly contagious, so you must gown up in the hospital! And wash hands really well. Don’t need a mask.
hypokalemia
What: Condition where potassium levels in the blood are lower than normal.
Cause: Vomiting, diarrhea, or meds like diuretics. Poor dietary intake. Increased excretion by the kidneys.
Symptoms: Muscle weakness/cramping, fatigue, arrhythmias, nausea/vomiting, numbness/tingling, constipation.
prophylaxis
an attempt to prevent disease
“prophylaxis” in a routine dental checkup bill would likely refer to what
thoroughly examining and cleaning the teeth to prevent dental diseases and health issues
BSC
bedside commode
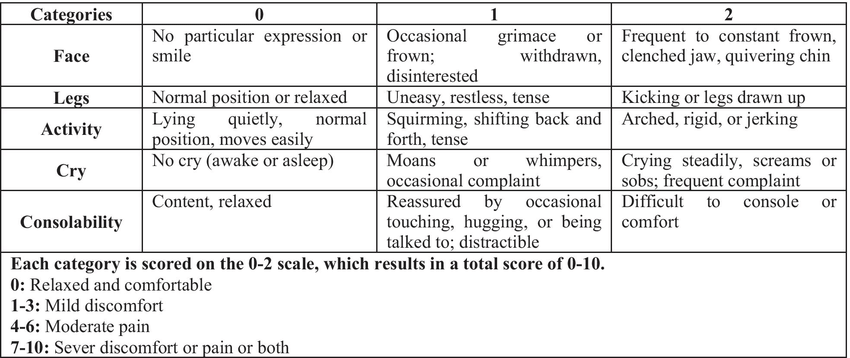
FLACC
Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, and Consolability
Behavioral observation pain scale used to quantify pain usually in infants and young children.
LRAD
Least Restrictive Assistive Device
Could also be…
Lower Respiratory Airway Disease
to describe conditions affecting the lower airways— pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, COPD
CRP unit of a hospital
Cardiac, Renal, Pulmonary
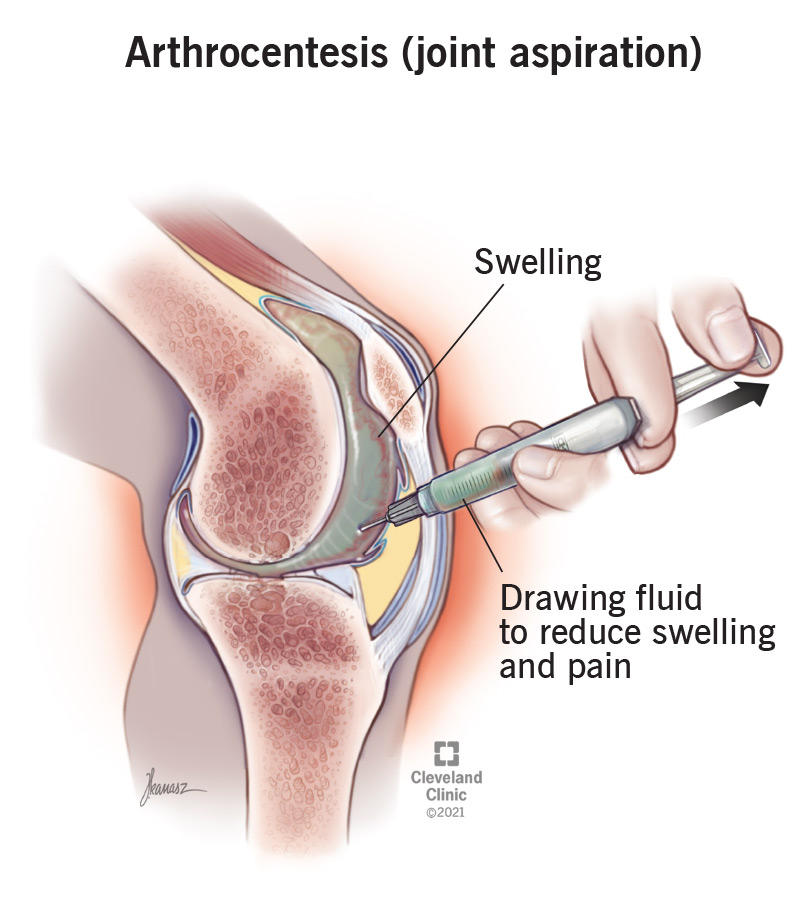
arthrocentesis
procedure where a sterile needle and syringe are used to remove fluid from a joint space
can be used to collect fluid for diagnostic testing or as treatment to reduce pressure around a joint and improve movement
I&D
Incision and Drainage
minor surgical procedure that involves making an incision to release pressure and allow the pus to drain out, with the goal of relieving pain, preventing infection spread, and promoting healing
dysphonia
abnormal voice; might sound hoarse, rough, raspy, strained, or breathy
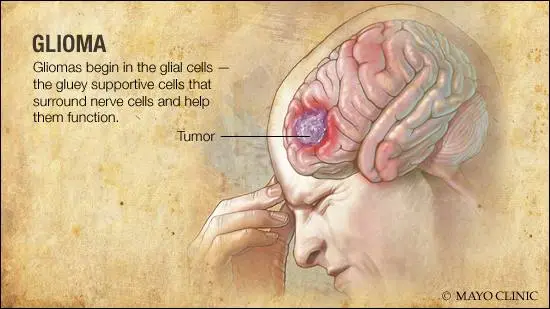
glioma
A type of brain tumor that develops from glial cells, which are the supportive cells of the brain and spinal cord. These tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
craniotomy
surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain (usually to treat a tumor or blood clot before replacing the bone)
LOC
Level Of Consciousness
(how awake, alert, and aware of surroundings a patient is)
nail avulsion
complete or partial removal of a fingernail or toenail from its bed
Transient Global Amnesia (TGA)
temporary memory disorder where someone suddenly loses their ability to form new memories and has difficulty recalling recent events
they still retain their identity and language skills, but they might repeatedly ask the same Q’s and appear disoriented + struggle to remember events from the past few minutes, hours, or days
TGAs are temporary— they usually last b/w 2-8 hours, but can last up to 24 hrs. Once the episode’s over, memory + cognition typically return to normal except for events within the TGA’s duration
nystagmus
condition where eyes make rapid, repetitive, uncontrolled movements
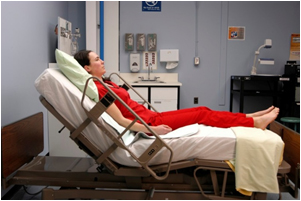
Semi-Fowler’s position
supine with HOB elevated 30-45 deg
pt’s legs can be straight or bent
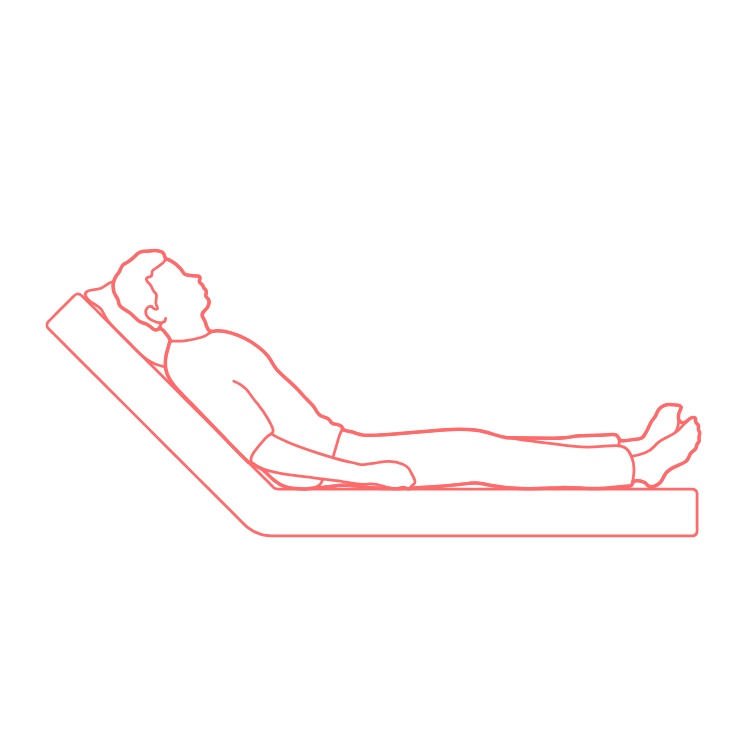
Fowler’s position
pt is in semi-sitting position with HOB elevated 45-60 deg
pt’s legs can be straight or bent
cannula
cannulated
cannula = a small, hollow tube used for insertion into the body
cannulation = the process of inserting a cannula (into a body cavity, vessel, etc)
URI
Upper Respiratory Infection
common infection of the upper respiratory tract (including nose, throat, and sinuses)
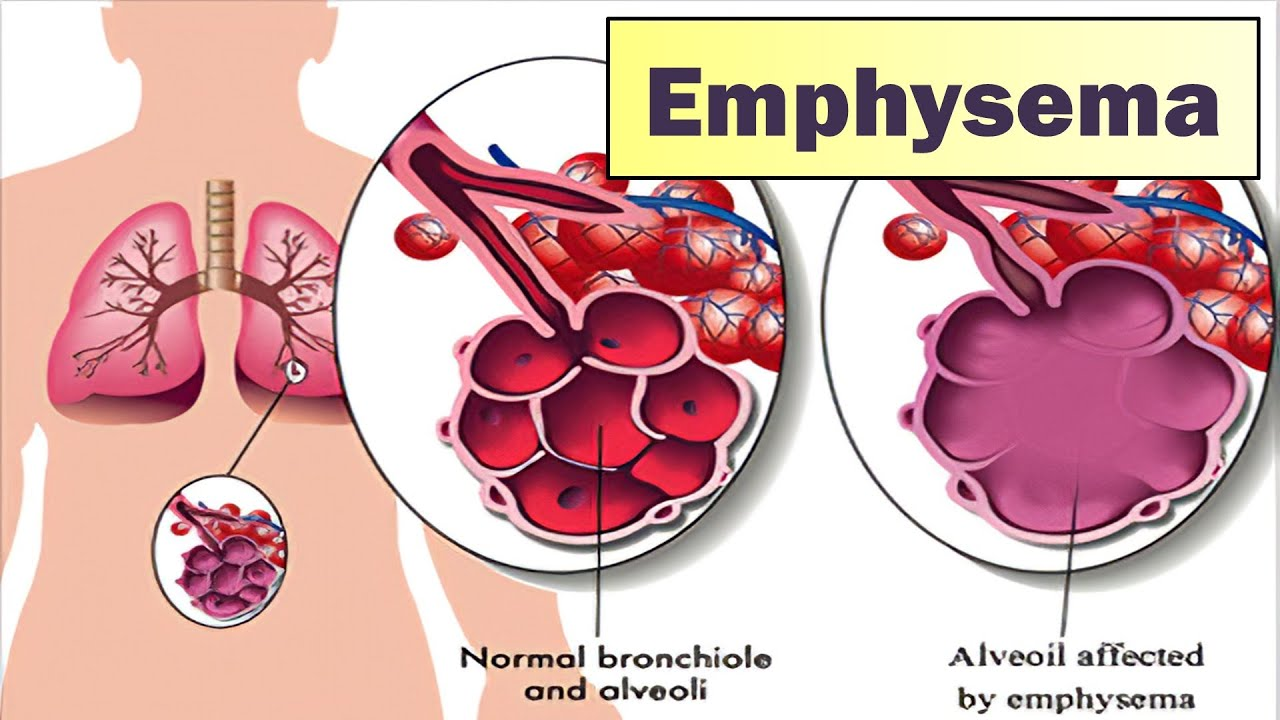
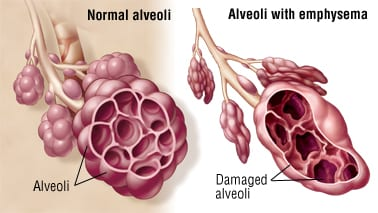
emphysema
the inner walls of the air sacs (alveoli) are damaged, causing them to eventually rupture
the result is one larger air space instead of many small ones, therefore less surface area available for gas exchange, therefore SOB
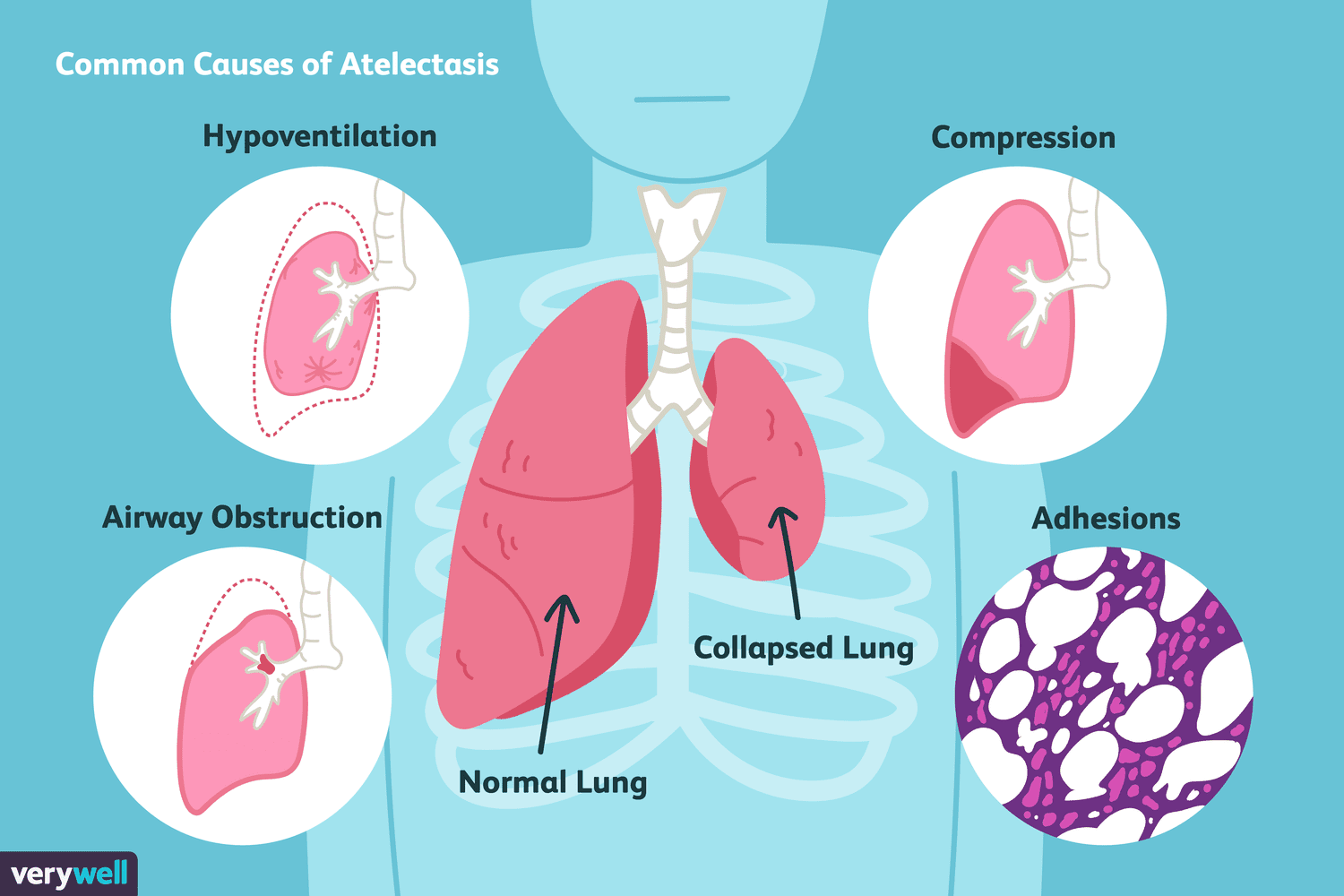
atelectasis
condition where part or all of a lung collapses, as a result of alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs) becoming filled with fluid air, preventing them from expanding properly
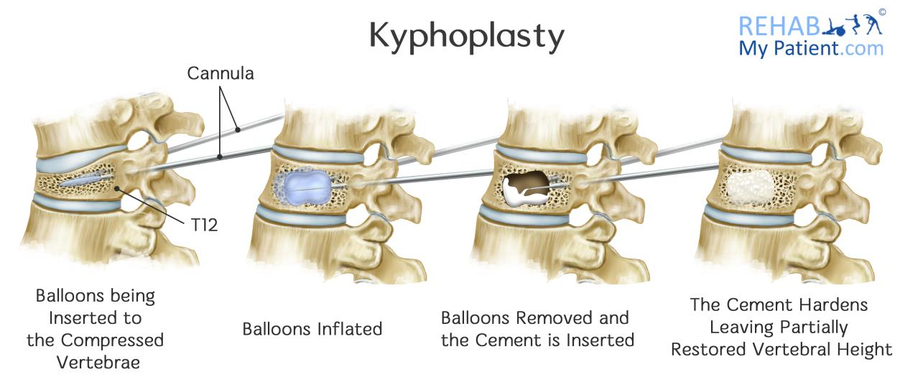
kyphoplasty
minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat compression fractures of the spine, particularly those caused by osteoporosis or other conditions leading to bone weakness
LAB VALUES
troponin is a protein primarily found where
in muscle tissue, particularly the heart
why would troponin be elevated?
when heart muscle is damaged, troponin is released into the bloodstream, and a blood test can detect its levels.
elevated troponin levels are often indicative of heart damage, including heart attack