Cognitive and Motor Development: Piaget and Vygotsky
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Jean Piaget
Pioneer of cognitive development theory.
Genetic Epistemology
Study of knowledge development through genetics.
Constructivist
Belief that knowledge is constructed through experiences.
Nature and Nurture
Interaction of genetics and environment in development.
Schemas
Mental frameworks for organizing information.
Assimilation
Integrating new information into existing schemas.
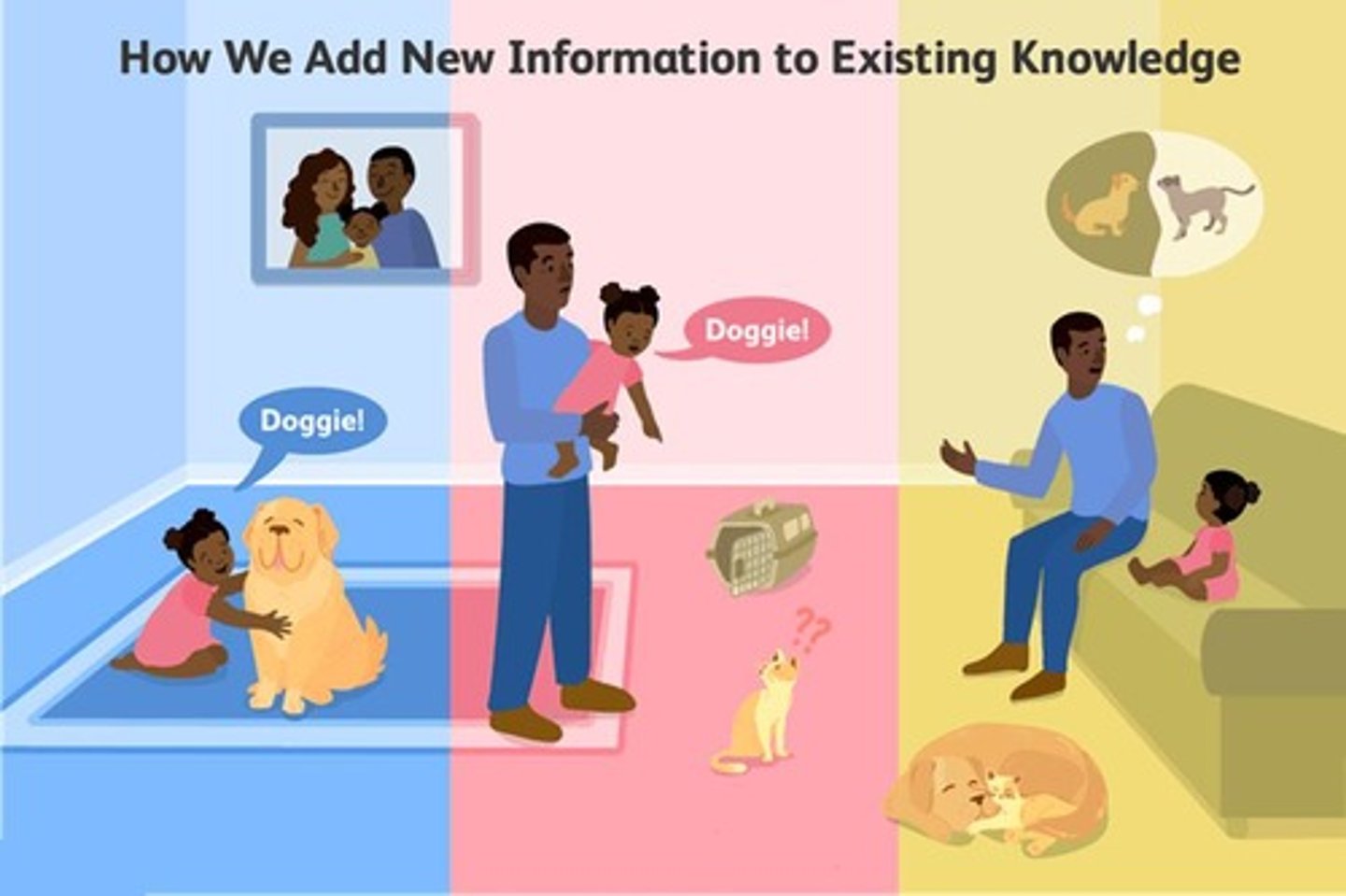
Accommodation
Modifying schemas to incorporate new information.
Equilibrium
State of balance between schemas and reality.
Discontinuity
Development occurs in distinct, hierarchical stages.
Qualitative Change
Fundamental shifts in cognitive abilities.
Invariant Sequence
Fixed order of developmental stages.
Sensorimotor Stage
Birth to 2 years; knowledge through sensory experiences.
Preoperational Stage
2 to 7 years; symbolic representation and egocentrism.
Concrete Operations Stage
7 to 12 years; logical reasoning about concrete objects.
Formal Operations Stage
12 years and up; abstract and systematic thinking.
Piaget's A-Not-B Task
Test for object permanence in infants.
Three-Mountain Task
Test for egocentrism in children.
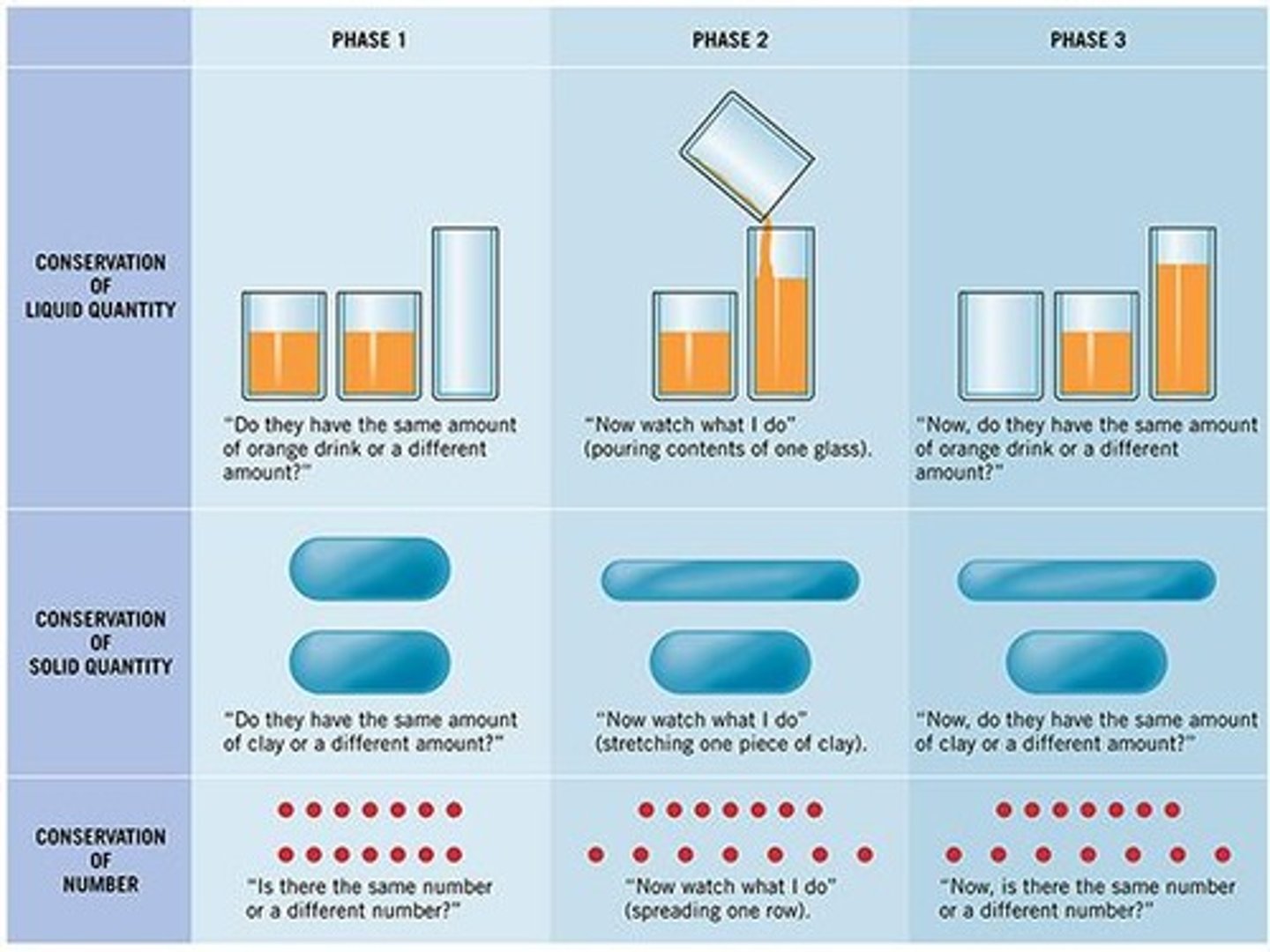
Conservation Concept
Understanding that quantity remains unchanged despite changes.
Lev Vygotsky
Proponent of sociocultural theory of cognitive development.
Scaffolding
Support provided to help learners achieve tasks.
Zone of Proximal Development
Difference between what learners can do alone and with help.
Guided Participation
Learning through social interaction and collaboration.
Educational Implications
Practical applications of theories in teaching methods.