DP1 Biology DNATranscription & Translation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Transcription
Process that creates RNA from a segment of DNA / 1st step in protein synthesis / gene expression
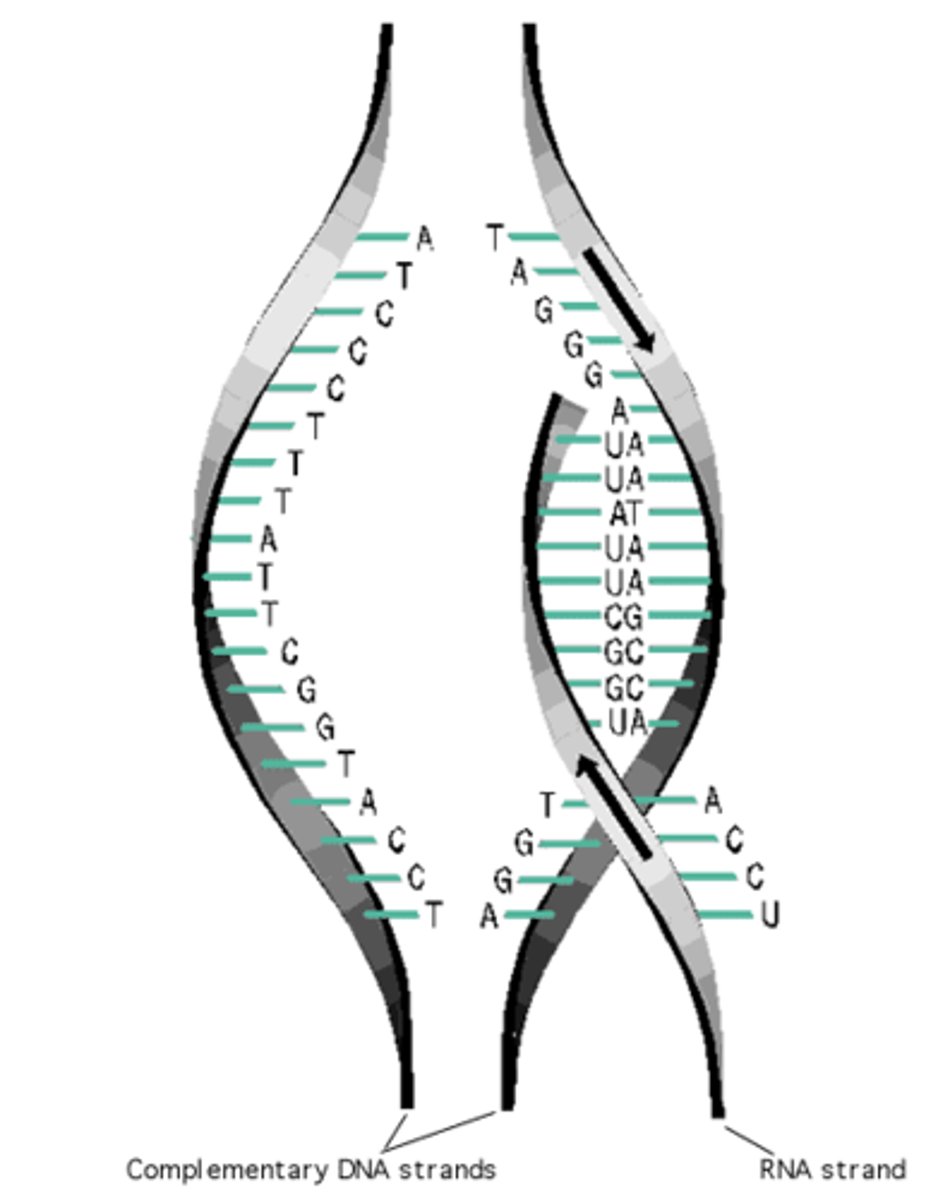
Translation
Creation of a polypeptide chain (sequence of amino acids) / 2nd step of protein synthesis
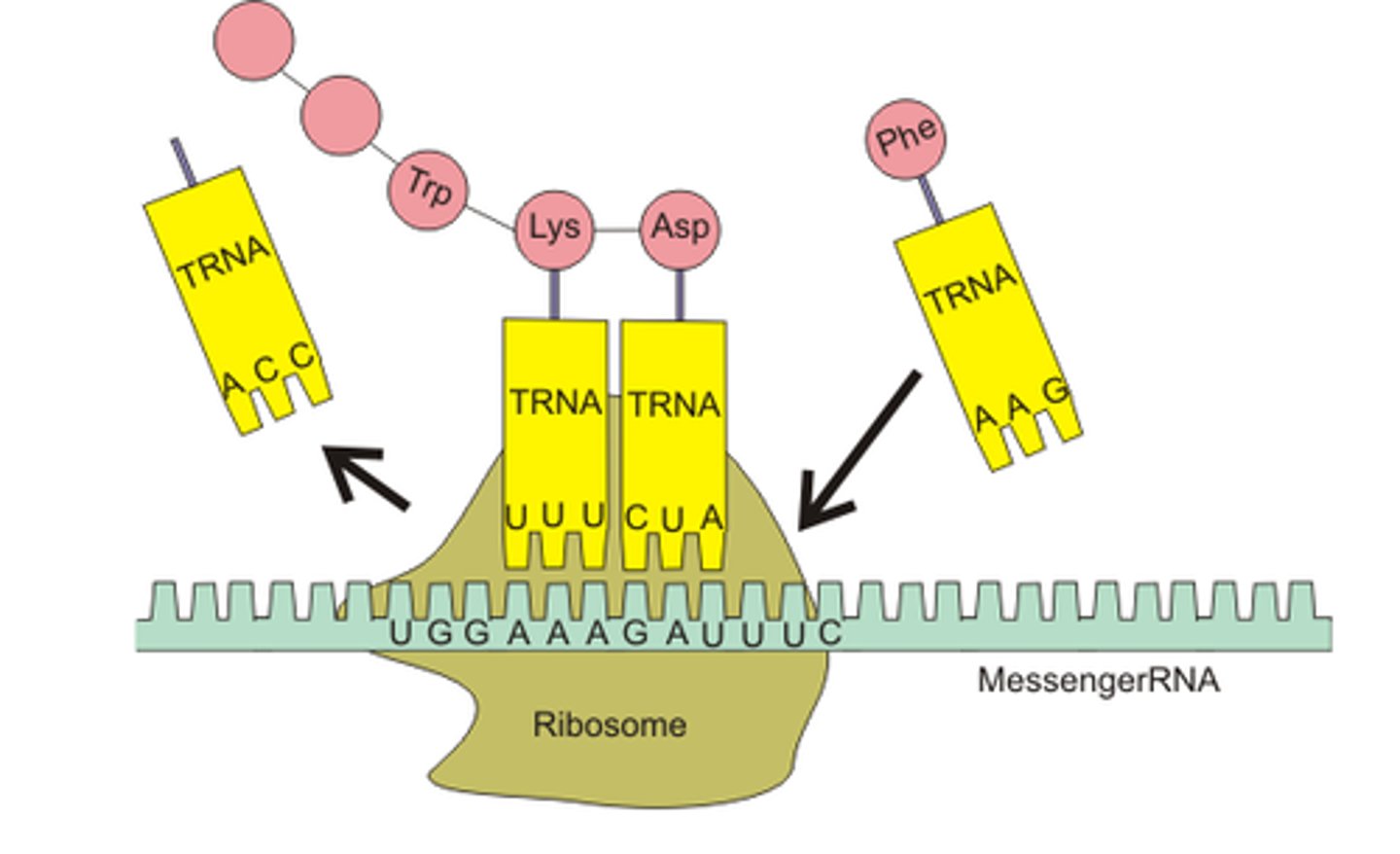
tRNA
Transfer RNA - carries amino acids (and anticodon) over to the ribosome during translation
mRNA
Messenger RNA - carries codons from nucleus to ribosome and is "read" to indicate what amino acids will be used to create the polypeptide chain
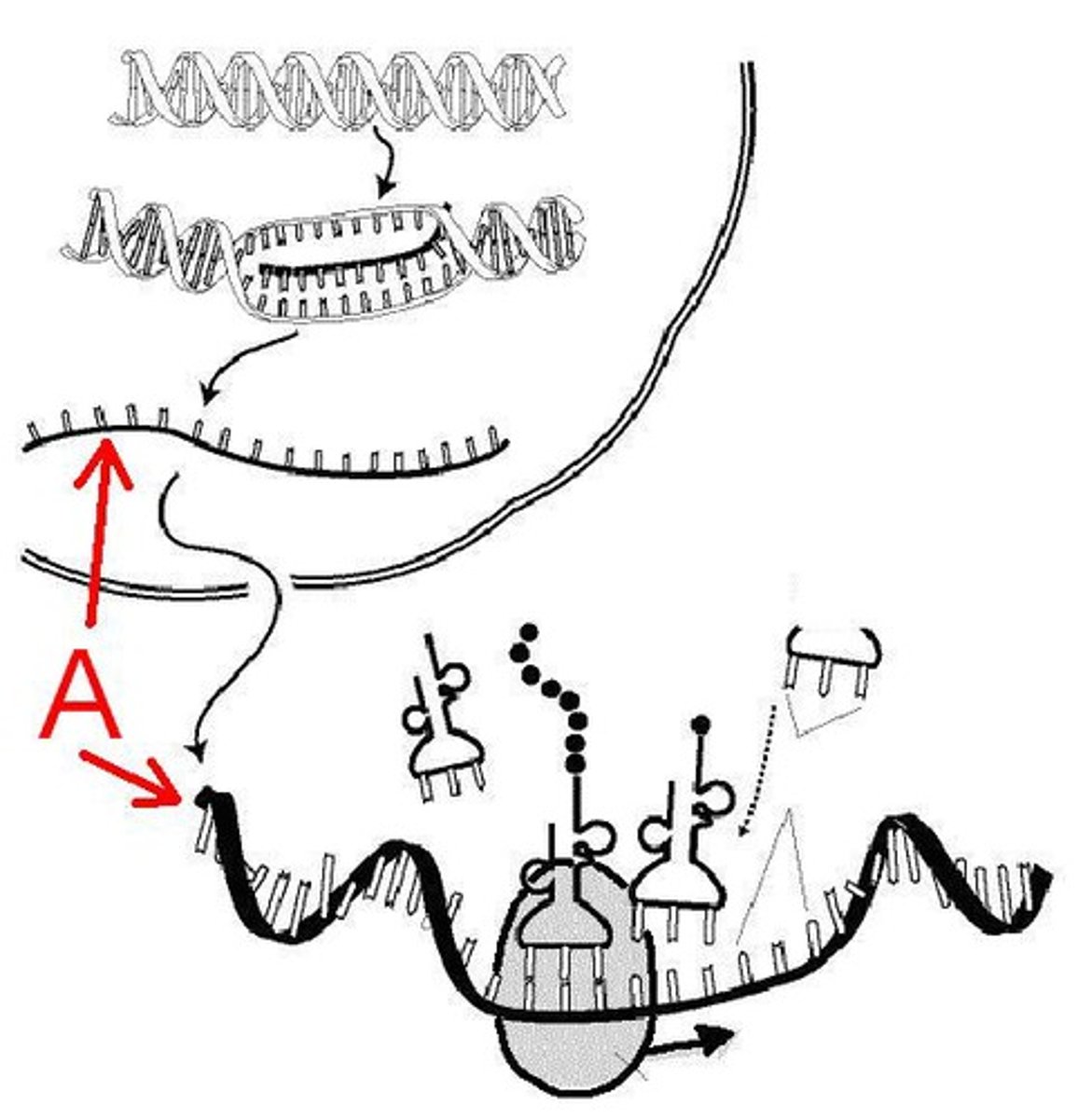
Ribosome
Location of translation in the cell
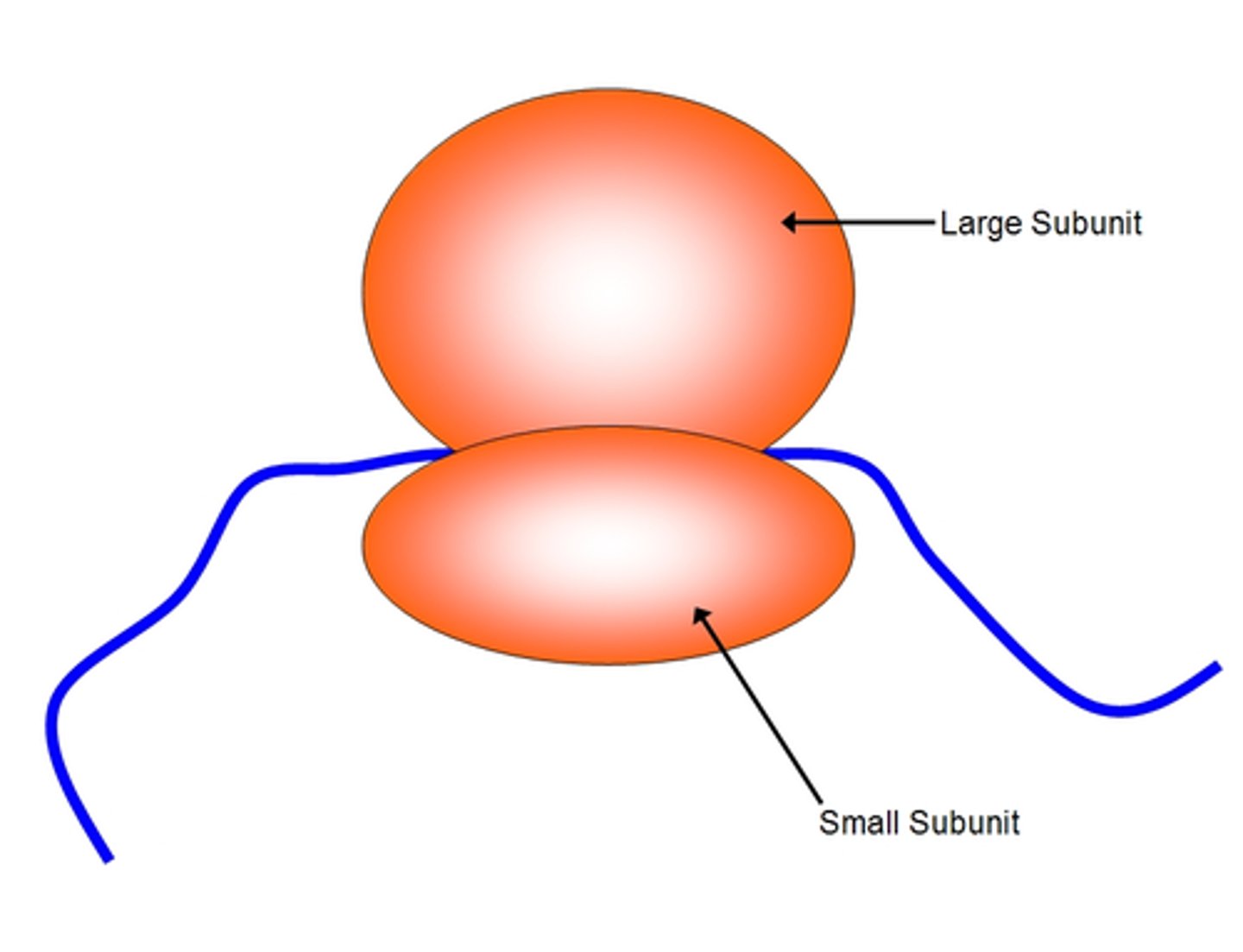
Gene
segment of DNA that holds information for making polypeptide chains
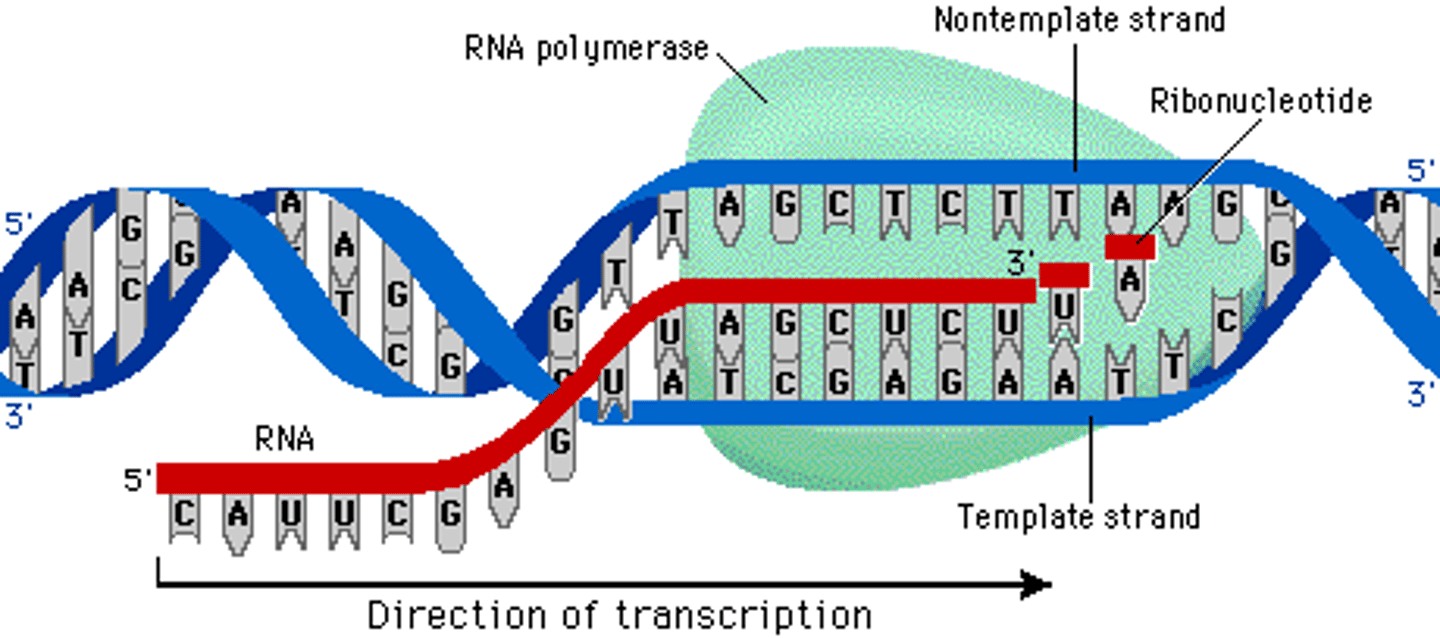
RNA polymerase
Unwinds the DNA helix, breaks open hydrogen bonds, and adds free floating RNA nucleotides during the process of transcription
Antisense strand
The side / strand of DNA that is used by RNA polymerase as a guide for making RNA during transcription. (Only 1 side is used because RNA is only single-stranded)
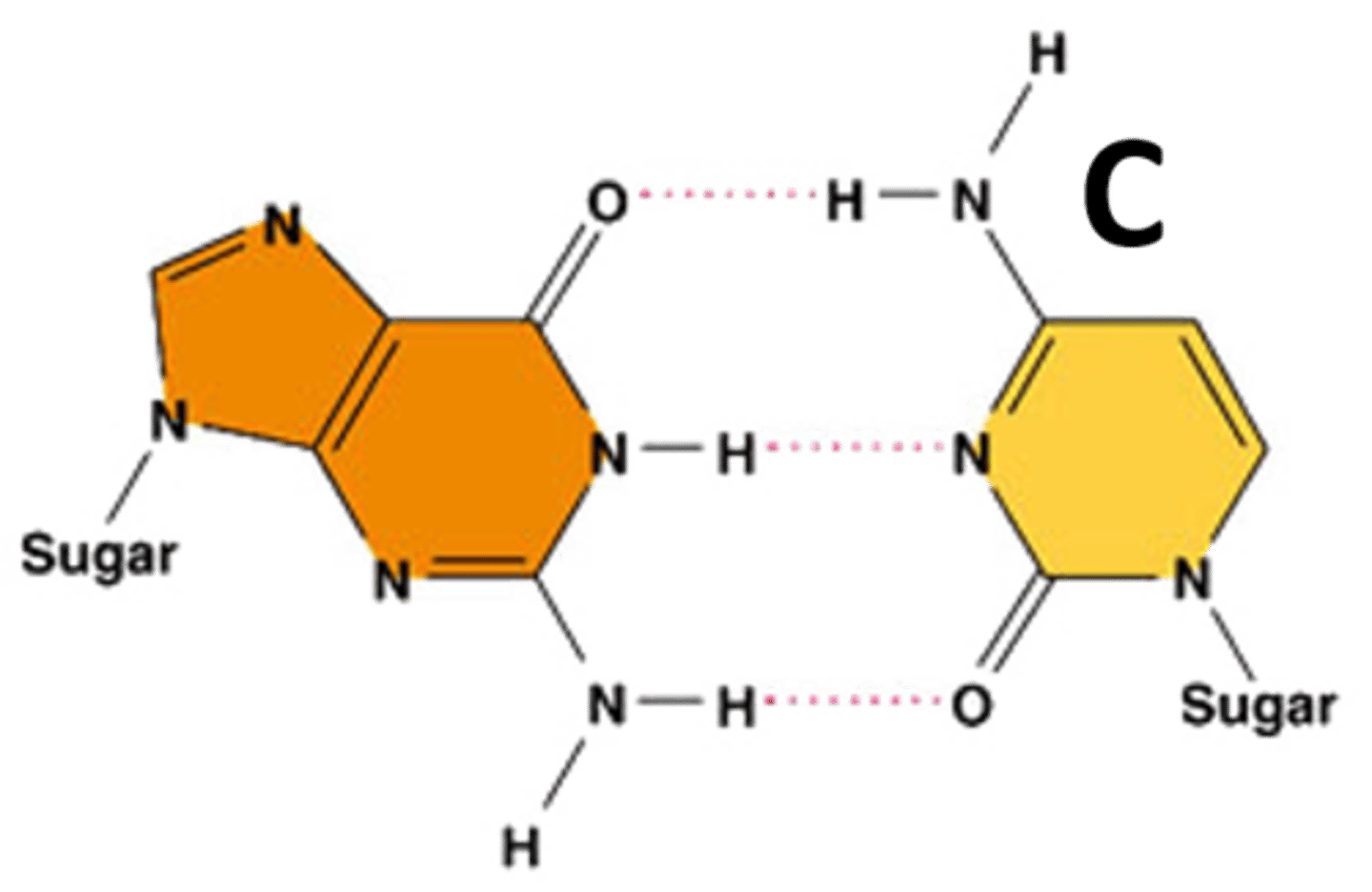
Hydrogen bond
Attraction that holds the 2 strands of DNA together - located between the bases (A-T and C-G)
Uracil
This nitrogen-containing base is only found in RNA
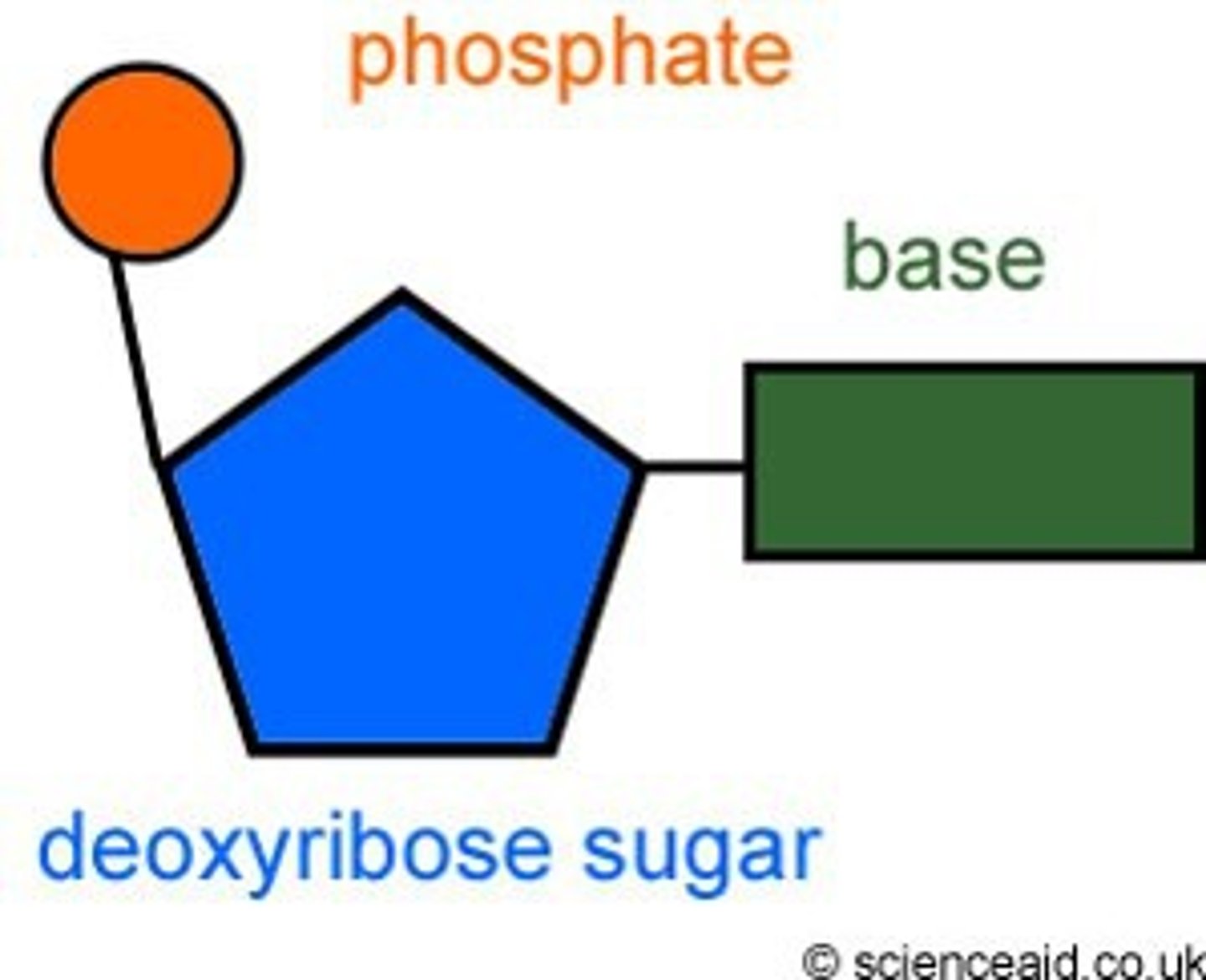
Phosphate
Represented by a circle in our DNA diagrams - part of the backbone of DNA
Amino Acid
The building blocks of protein
Thymine
This nitrogen-containing base if only found in DNA
Nitrogen-containing base
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Uracil, and Cytosine are the various types of this part of DNA and RNA
Codon
3-letters (nucleotides) at a time on the mRNA (messenger RNA)
Anti-codon
3-letters (nucleotides) on the tRNA - ensures the correct amino acid is brought over to the ribosome
Stop codon
The 3 letters (nucleotides) that stop the process of translation / signal for the ribosome to detach from the mRNA, tRNA, and the amino acid chain
DNA
a double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited traits of organisms and viruses.
Nucleotide
a building block of DNA or RNA, consisting of a sugar, a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
Guanine
the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide cytosine in DNA or RNA.
Cytosine
the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide guanine in DNA or in RNA.
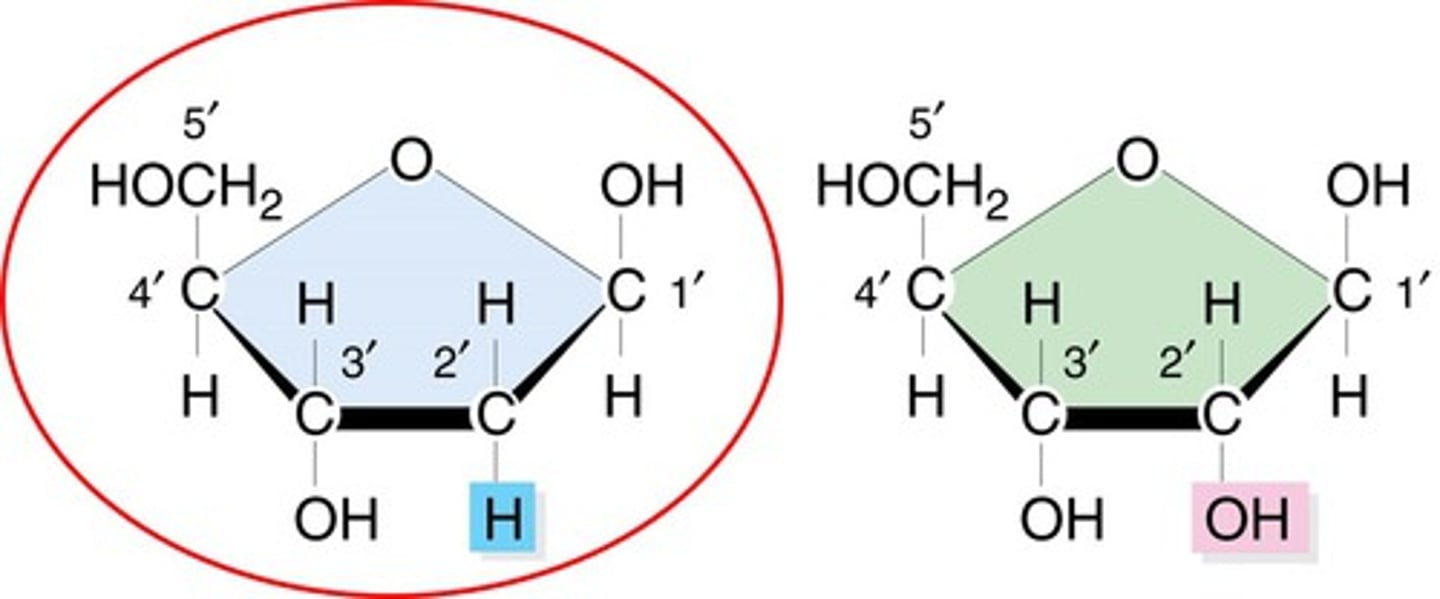
Ribose
the sugar included in a nucleotide building block of RNA.
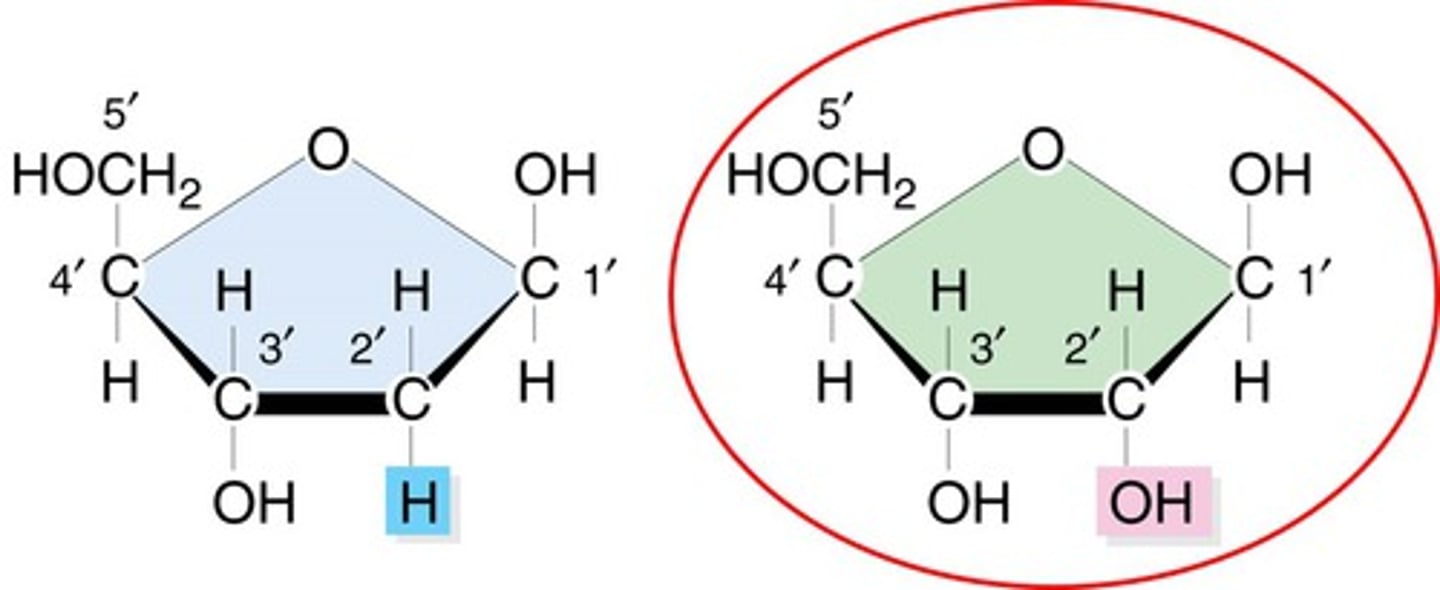
Deoxyribose
the surgar included in a nucleotide building block of DNA.
Promoter
The non-coding DNA sequence that lies BEFORE a gene that indicates to RNA polymerase where to START transcription - usually containing the bases TATA.
Terminator
The DNA sequence that indicates the end of a gene - tells RNA polymerase and RNA to detach from DNA
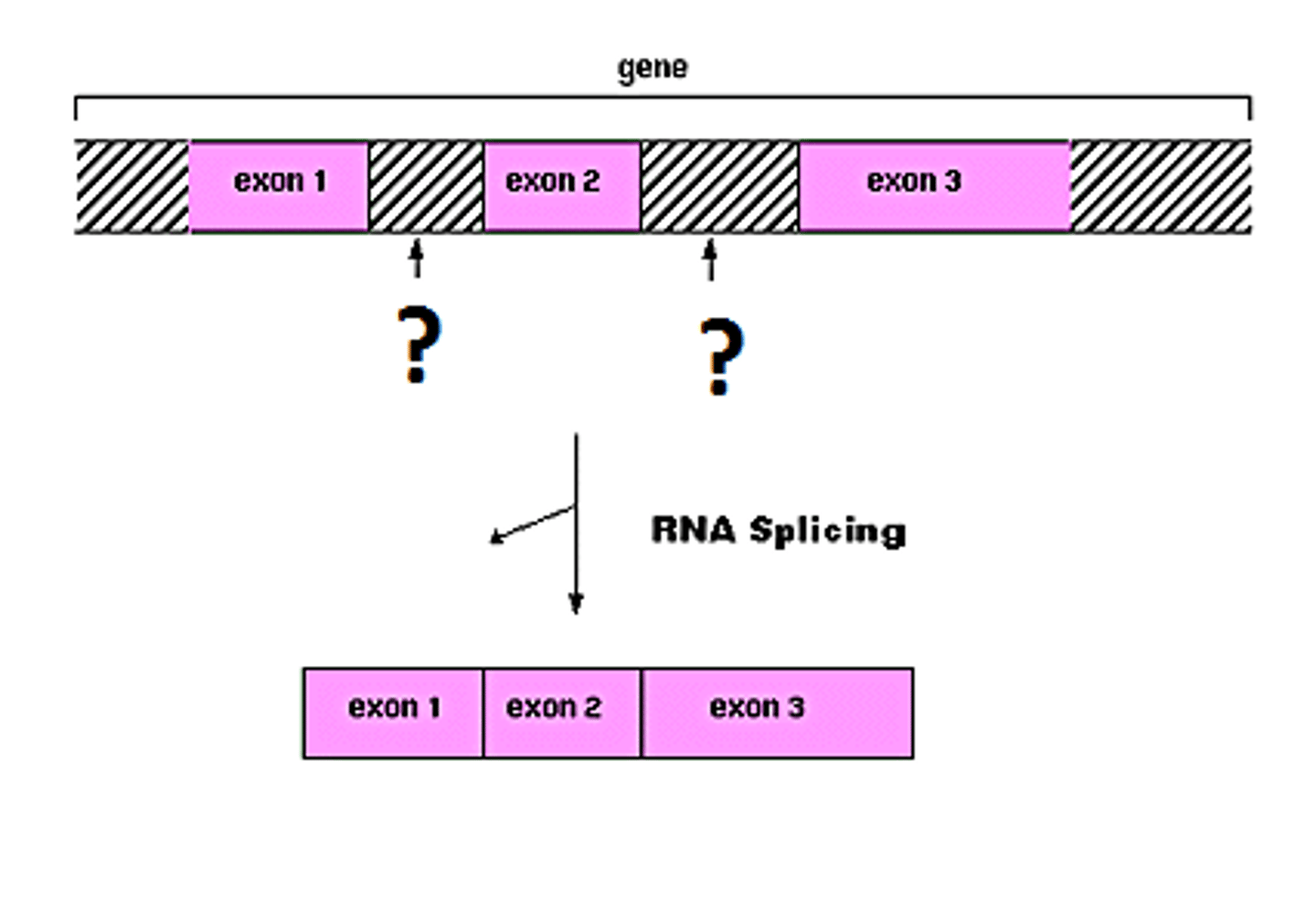
Introns
Non-coding segments of the mRNA that are transcribed but are cut OUT of the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus
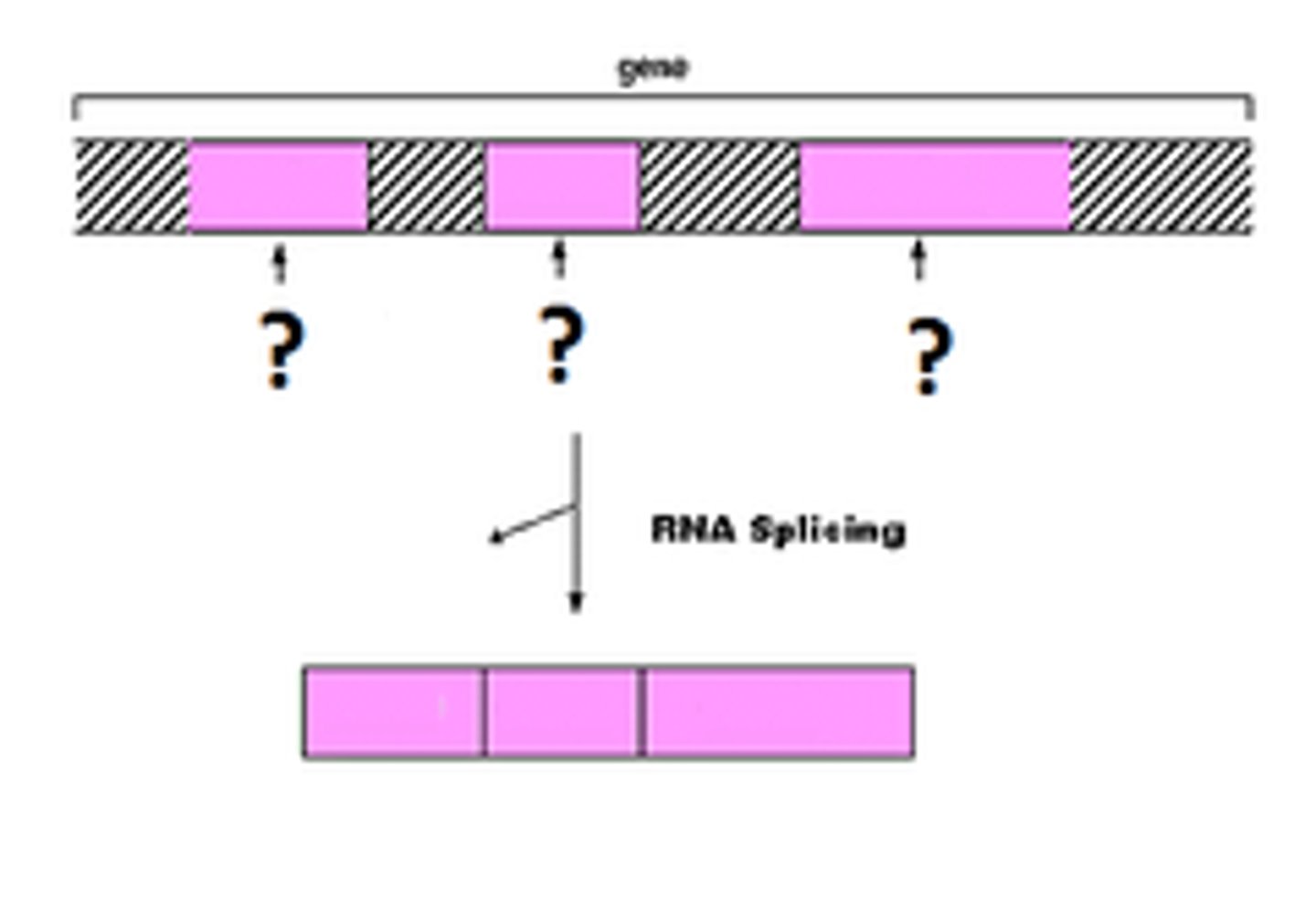
Exons
Coding segments of the mRNA that are spliced together, creating the mature mRNA
5' cap and 3' tail
Added to the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus to aide its movement through the nuclear pore, prevent its degradation, and help it attach to the ribosome
Initiation, Elongation, Translocation, Termination
The steps of translation - as a ribosome "reads" mRNA and creates a polypeptide chain
Polysome
Many ribosomes attached to the same mRNA to create several copies of the same polypeptide chain simultaneously
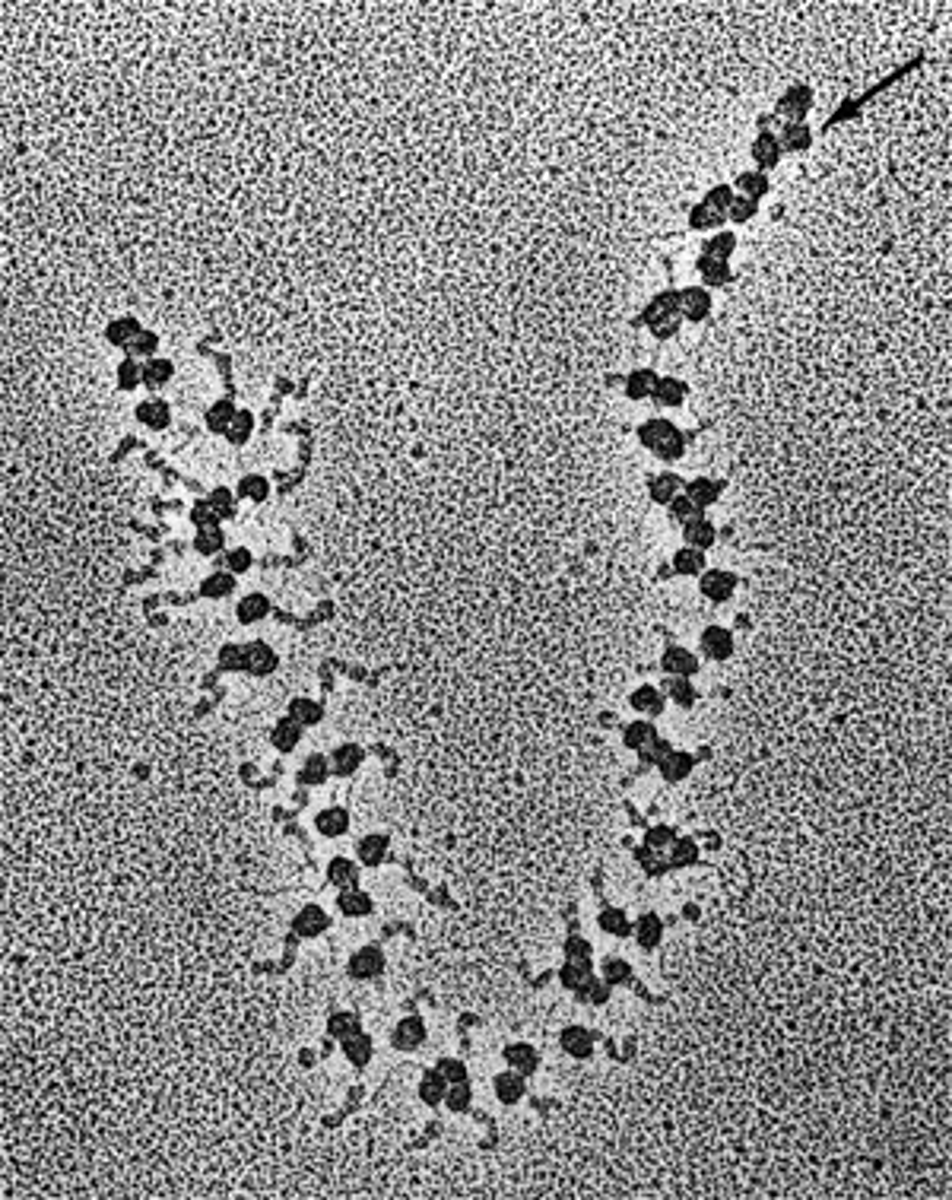
Free ribosomes
Organelles that create protein that will be used INSIDE the cell (not exported)
Bound ribosomes
Organelles attached to the endoplasmic reticulum that will be creating proteins intended for export out of the cell (with the help of golgi apparatus)
tRNA activating enzyme
Enzymes that attach the appropriate amino acid to its matching tRNA.
5' to 3'
The direction that transcription both translation all occur in
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Used x-ray crystallography to create diffraction patterns to study DNA structure
The discovery of the double helix was based off their work
James Watson and Francis Crick
The scientists credited with building the first correct model of the structure of DNA
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Determined that genetic DNA, not protein, was the genetic material using experiments about bacteriophages