Lecture 3: Clinical Photon Beams
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Depth Dose Distribution (PDD)
Describes dose fall off as a function of depth at constant SSD, normalized to maximum dose (dependent on energy and field size).
What is surface dose measured with?
Parallel-plate ionization chambers
What contributes to surface dose?
scattered photons, electrons produced from photon interactions in air and shielding, backscattered photons from patient
Does surface dose increase or decrease with energy?
Decrease
Does surface dose increase or decrease with field size?
Increase
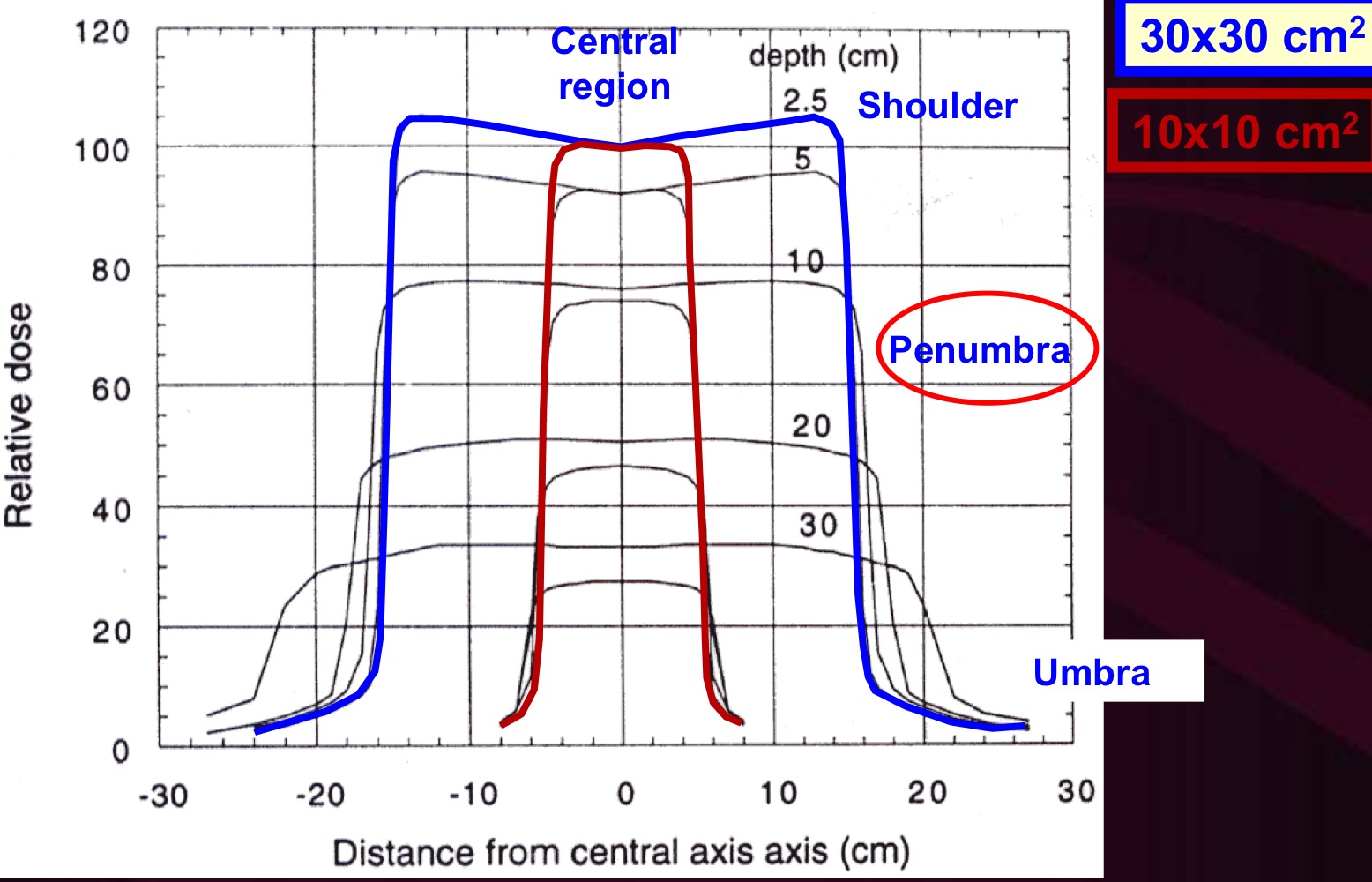
Beam Profile: Central Region
Dose profile does not change significantly. Depends on inverse-square dose fall-off, flattening filter, energy of electrons, and target
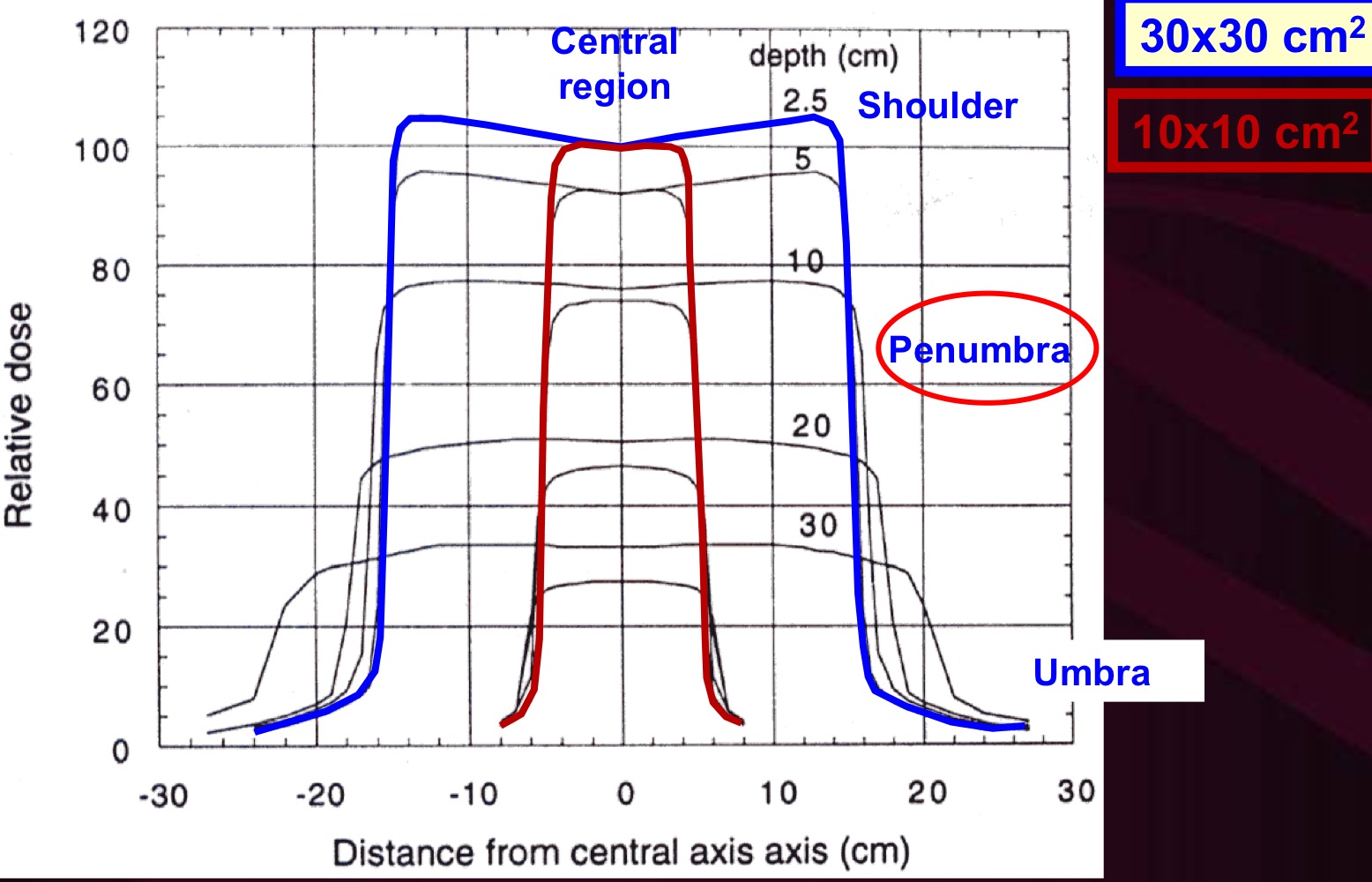
Beam Profile: Shoulder
Photons begin scattering out of the field more than in (disequilibrium)
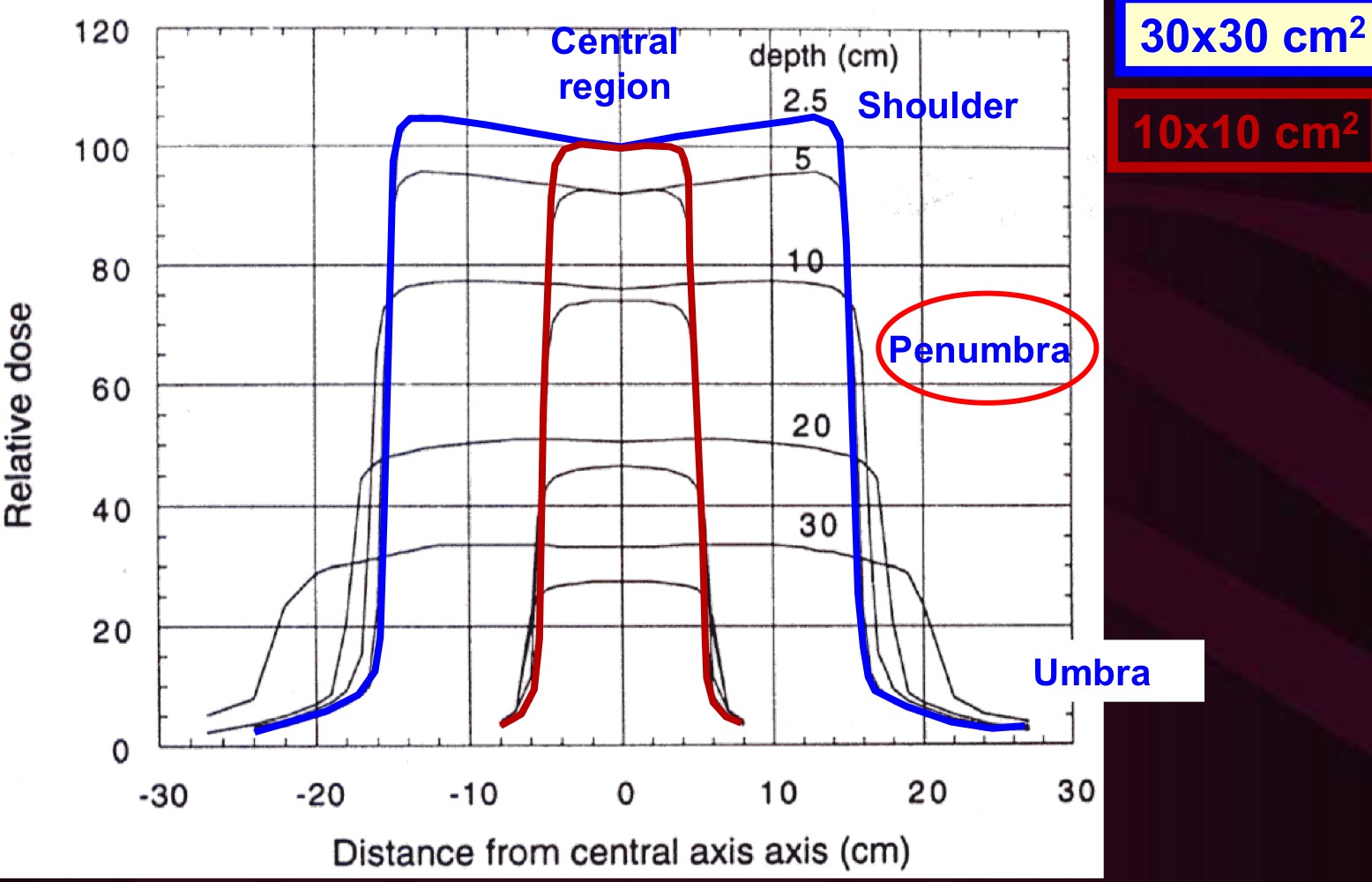
Beam Profile (Penumbra):
Characterized by 20/80% width. Depends on beam energy, source size, SCD, and depth
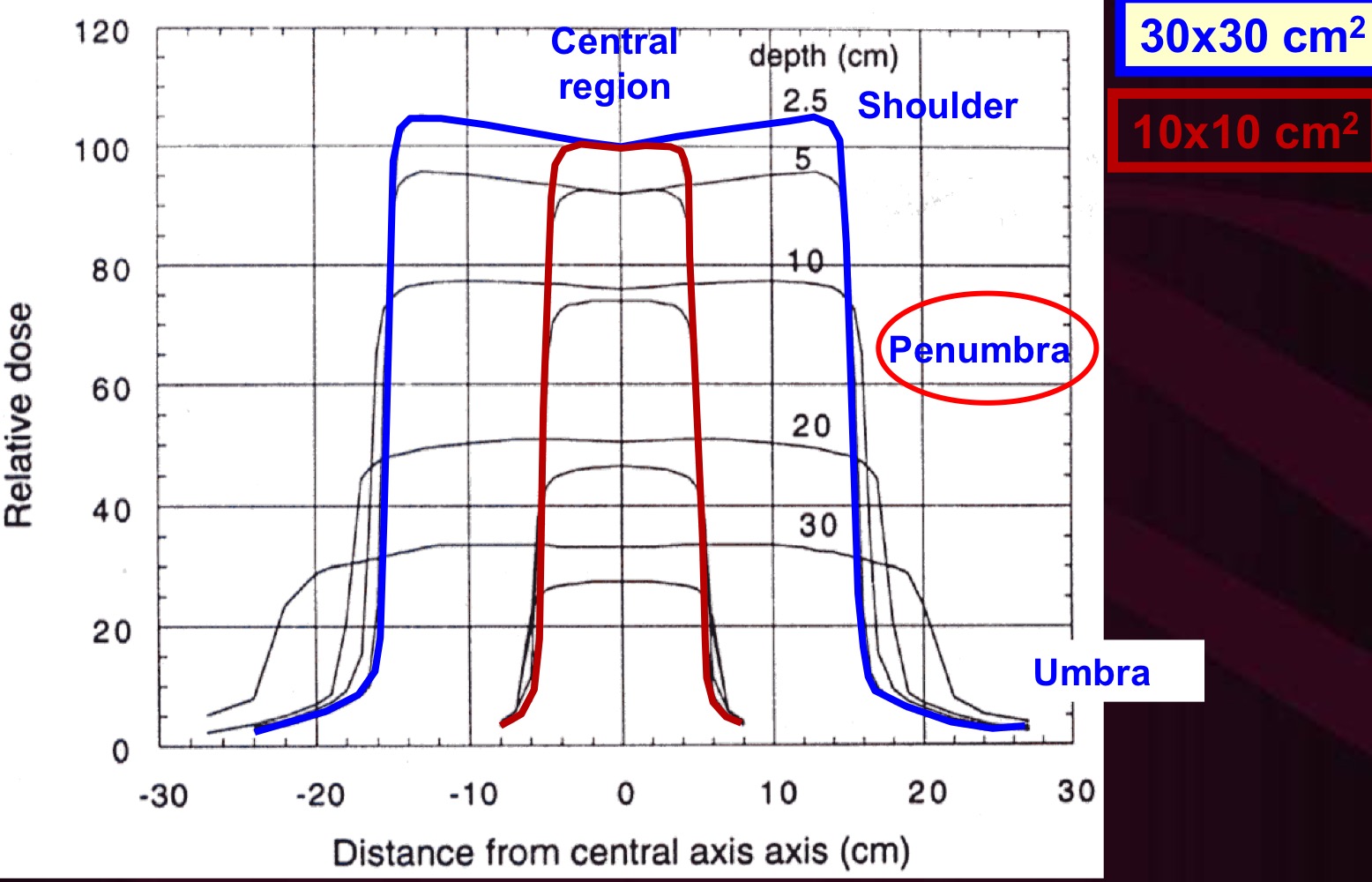
Transmission Penumbra
Due to transmission through jaws
Geometric Penumbra
Due to finite source size
Scatter Penumbra
due to inpatient x-ray scatter
Beam Profile: Umbra
Due to outscattered photons and transmission through jaws
Beam flatness (F) is required to be less than what percentage using the variance method?
3%
What causes horns in beam profiles
Over-flattening at zmax and under-flattening as z increases
What percent symmetry change from baseline is allowed for 2009 TG142?
1%
Off-axis ratio (OAR)
the ratio of dose at an off-axis point to the dose on the central beam axis at the same depth in phantom
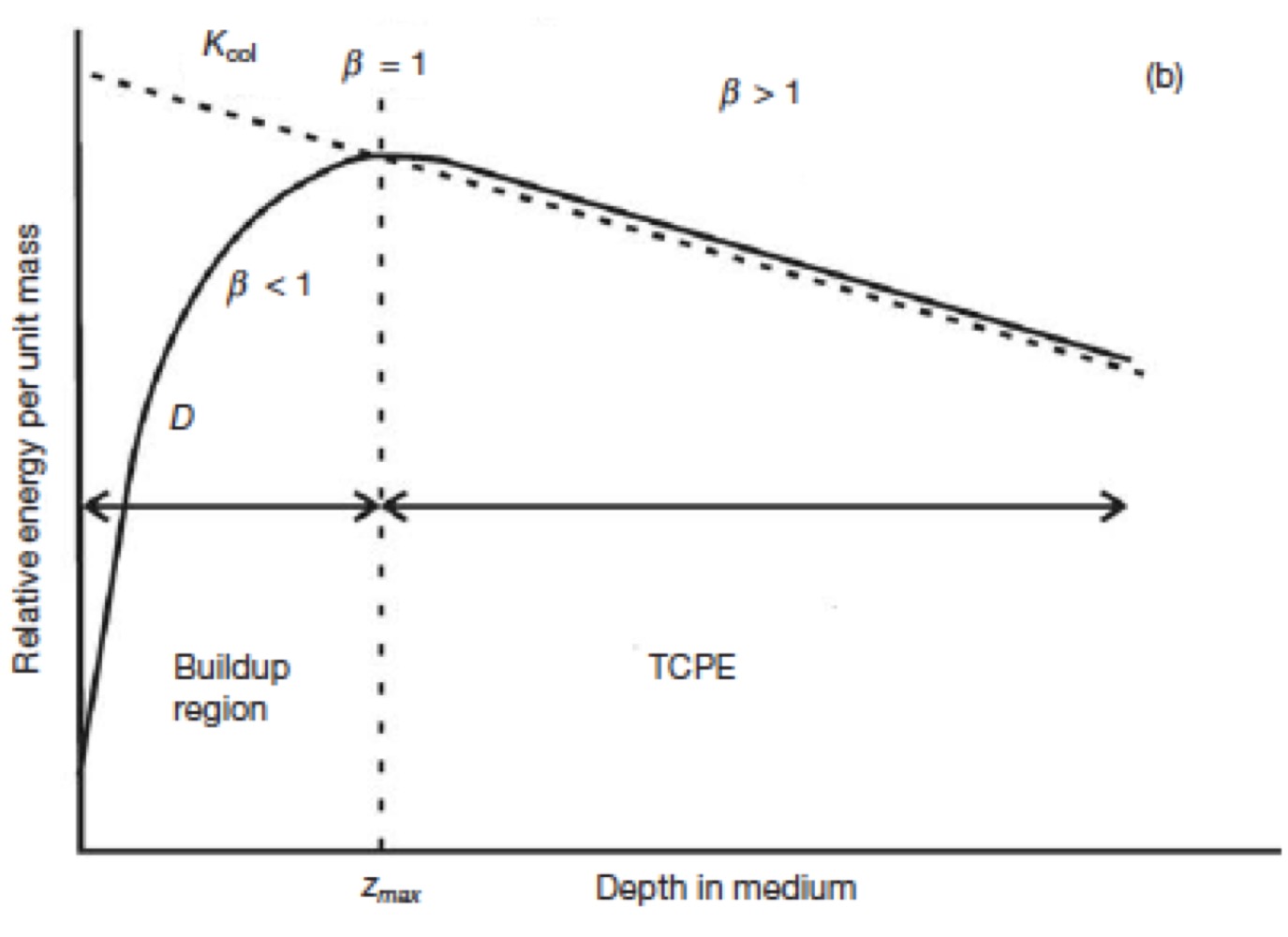
PDD: Buildup Region (z < zmax)
CPE does not exist (D < Kc); secondary electrons are released and deposits kinetic energy at larger depths
When is CPE reached on a PDD (D = Kc)
z = zmax (~range of secondary charged particles)
PDD: TCPE (z > zmax)
D and Kc decrease due to photon attenuation resulting in transient CPE
PDD: Does zmax decrease or increase with beam energy?
increase