A&P unit 3 - neurons and neurotransmitters (copy)
1/68
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
components of CNS vs PNS
CNS = brain, spinal cord
PNS = nerves, ganglia (bundles of nerves)
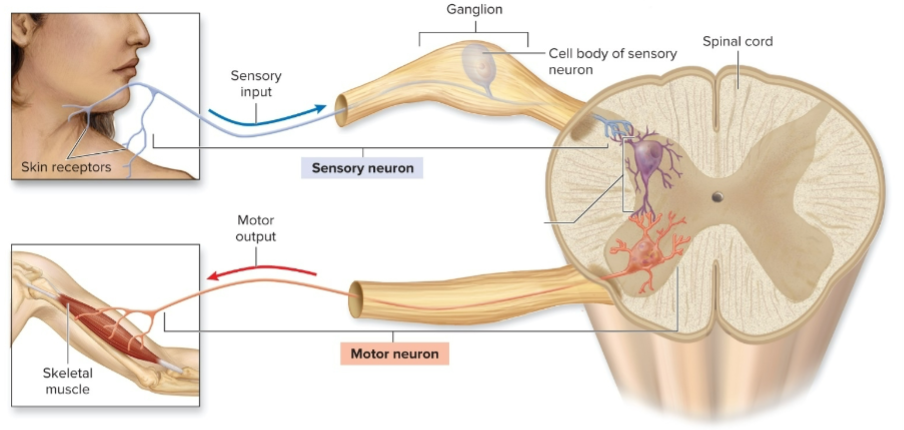
Afferent nervous system
sensory neurons, go TO CNS
(afferent = arrive)
-somatic and visceral
somatic sensory system
-afferent
-detect stimuli we consciously perceive
→ 5 senses, propioreceptors
visceral sensory system
-afferent
-detect unconscious stimuli
→ signals from internal organs
Efferent nervous system
initiate motor output FROM CNS
(efferent = effect)
→ somatic and autonomic motor systems
→ sympathetic and parasympathetic
somatic motor system
-efferent
-send voluntary signal to skeletal muscles
autonomic/visceral motor system
-efferent
-send involuntary signal to cardiac and smooth muscle
-includes sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic vs parasympathetic
sympathetic = fight or flight
parasympathetic = rest and digest
afferent, efferent motor system diagram (photo)
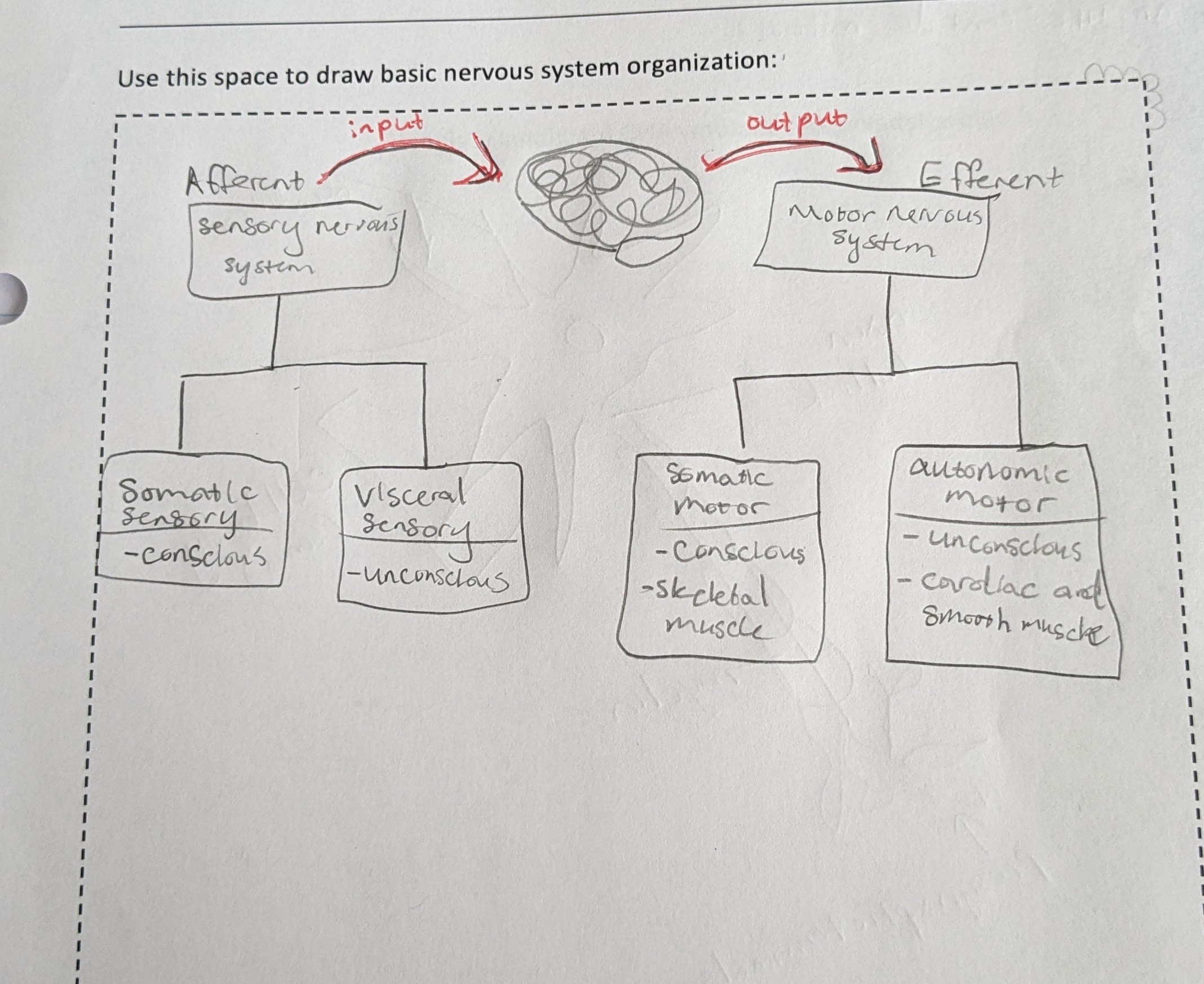
nerve diagram
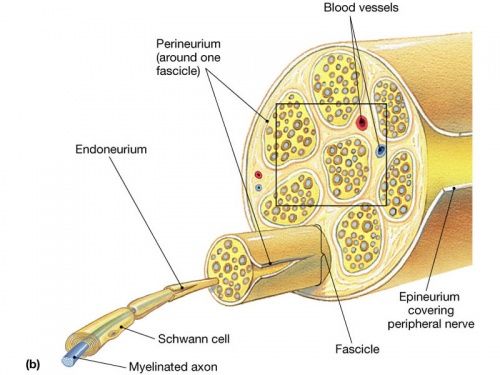
need to know
-epineurium
-perineurium
-endoneurium
-fasicle
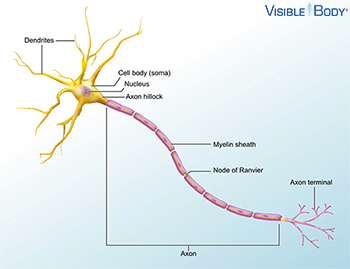
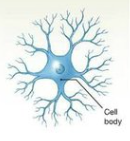
neuron diagram
dendrites = receive input
-cell body/soma = integrate incoming signals
-axon hillock = trigger zone for new signal
-pre-synaptic terminals/axon terminals = send output to other cells
What are the 5 characteristics of neurons?
1) excitability - respond to a stimulus
2) conduct signal across axon
3) secrete neurotransmitter
4) longevity - lasts across your lifetime
5) amototic - can’t do mitosis
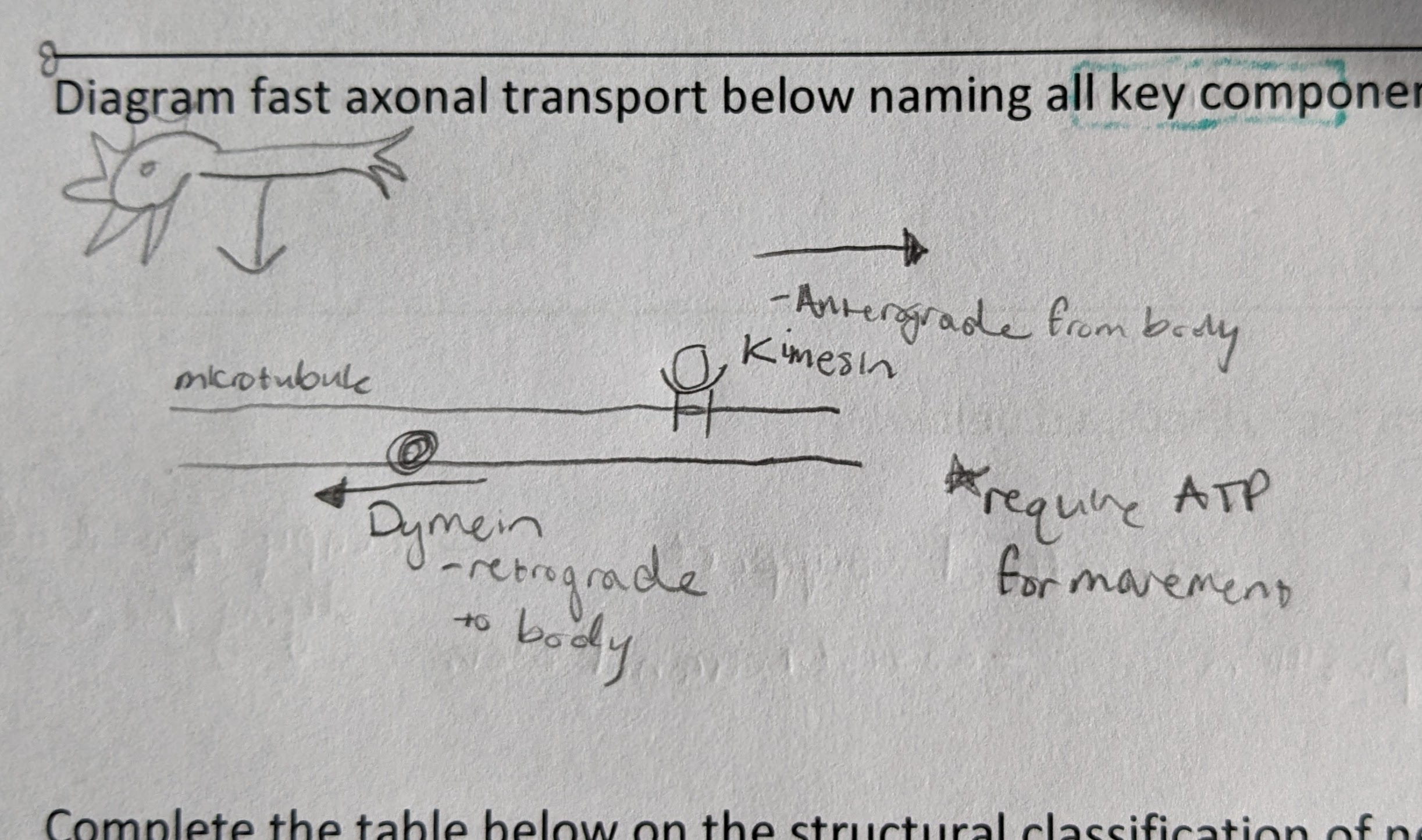
anterograde transport
move FROM cell body
-move newly synthesized material toward synaptic knob
retrograde transport
move TO cell body
-moves used materials from axon for breakdown/recycling
Fast axonal transport (image)
Kinesin = anterograde
Dynein = retrograde
*both require ATP
-move 400mm per day
slow axonal transport
-move 0.1-3mm per day
-flow of axoplasm (axon cytoplasm)
-only in anterograde direction (from body)
-moves enzymes, cytoskeletal components, new axoplasm
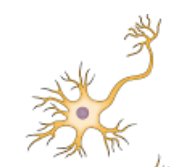
multipolar neuron
-many dendrites
-1 axon
→ all motor neurons
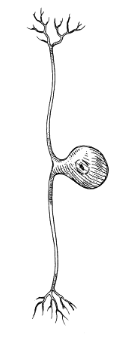
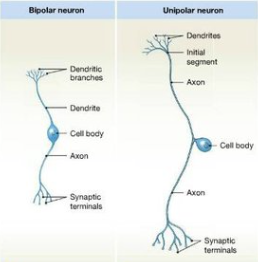
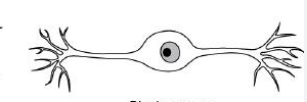
bipolar neuron
-1 dendrite
-1 axon
-soma in middle
→ sensory neurons of 5 senses
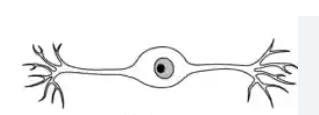
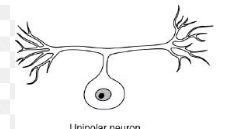
unipolar neuron
-single short process from cell body → 1 axon
-one side of axon in peripheral direction (to PNS), one side in central direction (to CNS)
→ sensory neurons
anaxonic neuron
-no axons
-dendrites come directly off cell body
→ interneurons
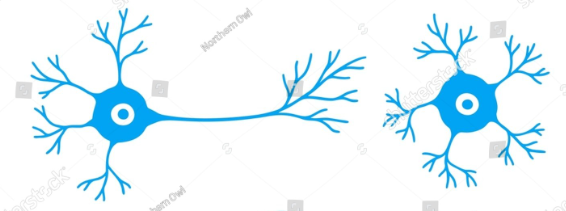
neuron input, output diagram
sensory neurons
-afferent (conduct input to CNS)
-unipolar and bipolar
motor neurons
-efferent (conduct input from CNS to effectors)
-multipolar
interneurons
-in between afferent and efferent neurons
-receive and process info from other neurons
-multipolar or anaxonic
-make up 99% of neurons
components of glial cells
-non-excitable
-capable of mitosis
-protect & nourish neurons
-physical scaffold for neurons
-90% of cells in CNS
what kind of cells do brain tumors form from?
glial cells → they are capable of mitosis and neurons are not
Astrocytes
-most common glial cell
-form blood brain barrier
-structural support
-assist neuronal development
-occupy space of dying neurons
-regulate tissue fluid composition (ex. can regulate [K+])
![<p>-most common glial cell</p><p>-form blood brain barrier</p><p>-structural support</p><p>-assist neuronal development</p><p>-occupy space of dying neurons</p><p>-regulate tissue fluid composition (ex. can regulate [K+])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8bacc2c4-1c36-41c7-8cb7-2a7b64400124.jpeg)
Ependymal cells
-glial cell
-line cavities in brain and spinal cord
-cushion neurons and provide nutrients
-produce CSF of CNS
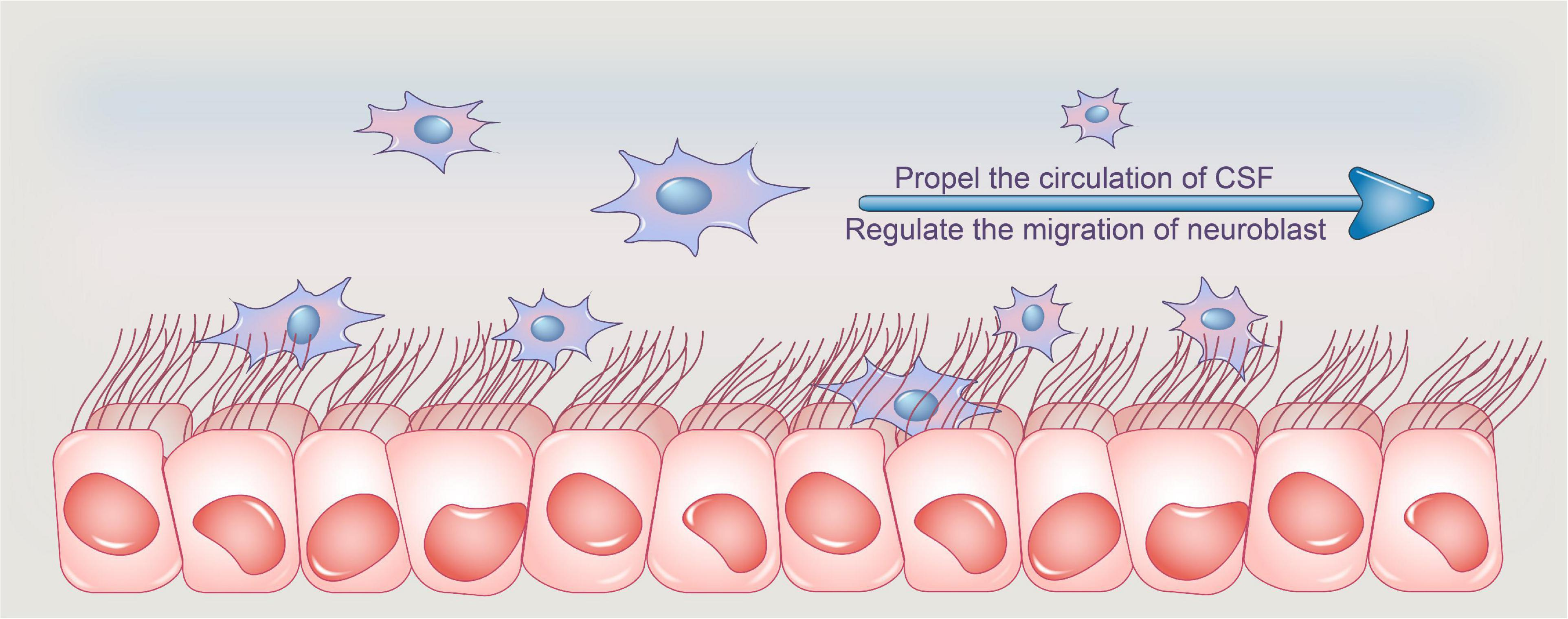
Microglia
-smallest glial cells
-phagocytic, immune system
-wander CNS and replicate during infection
-also remove debris
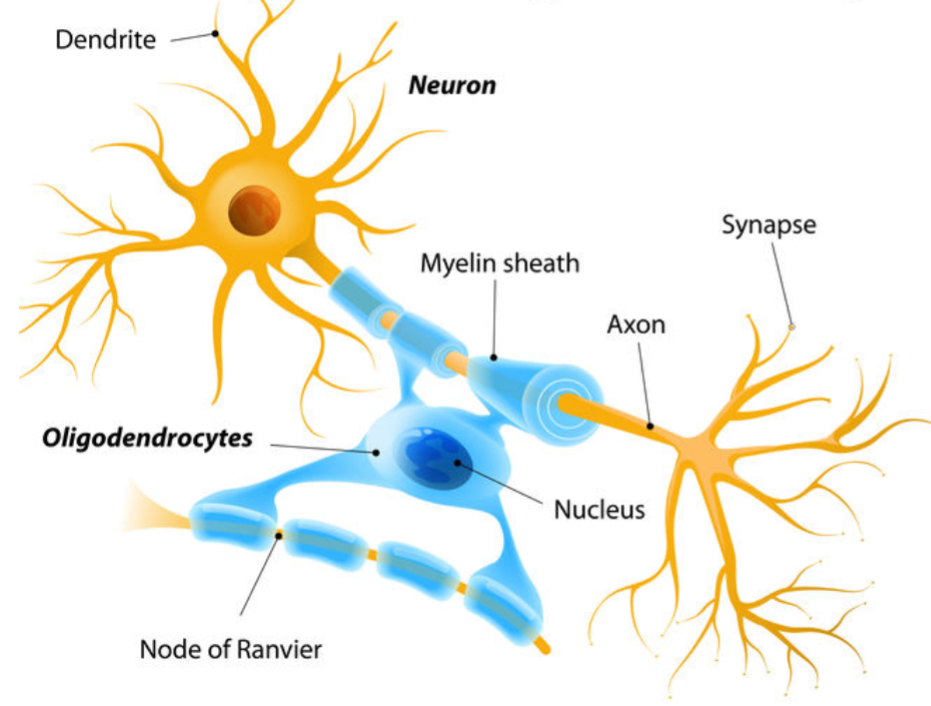
Oligodendrocyte
-very large glial cells
-form myelin sheath of CNS
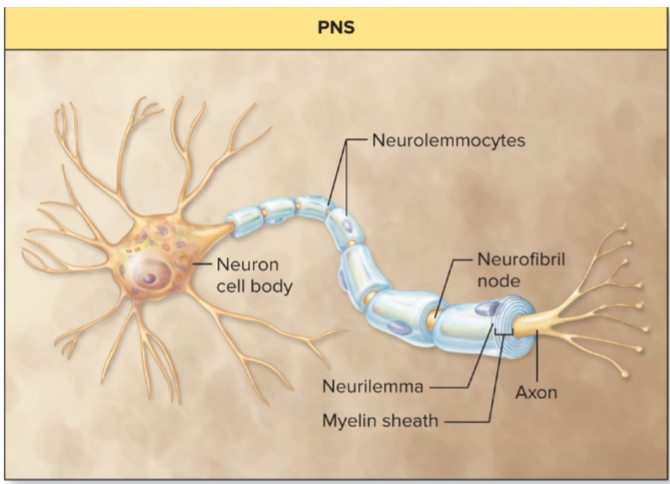
Neurolemmocytes
-glial cells
-Schwann cells
-form myelin sheath of PNS
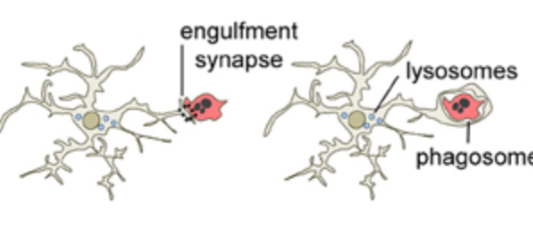
synaptic plasticity / plasticity
neuron signal pathway can be strengthened or weakened over time depending on how much we use it → how learning happens
post synaptic facilitation/inhibition vs
presynaptic facilitation/inhibition
post = EPSP/IPSP thru synapse
→it is axosomic = axon to soma of next cell, 2 cell action
pre = axoaxonal - axon release directly onto axon, 3 cell action
postsynaptic facilitation/inhibition image

how does presynaptic inhibition work?
(ADD IMAGE)
cell B release NT → opens chem gated Cl- channel on Cell A
Cell A gets more negative → prevent Ca VGC opening → no new NT release onto cell C
result = AP is not transferred
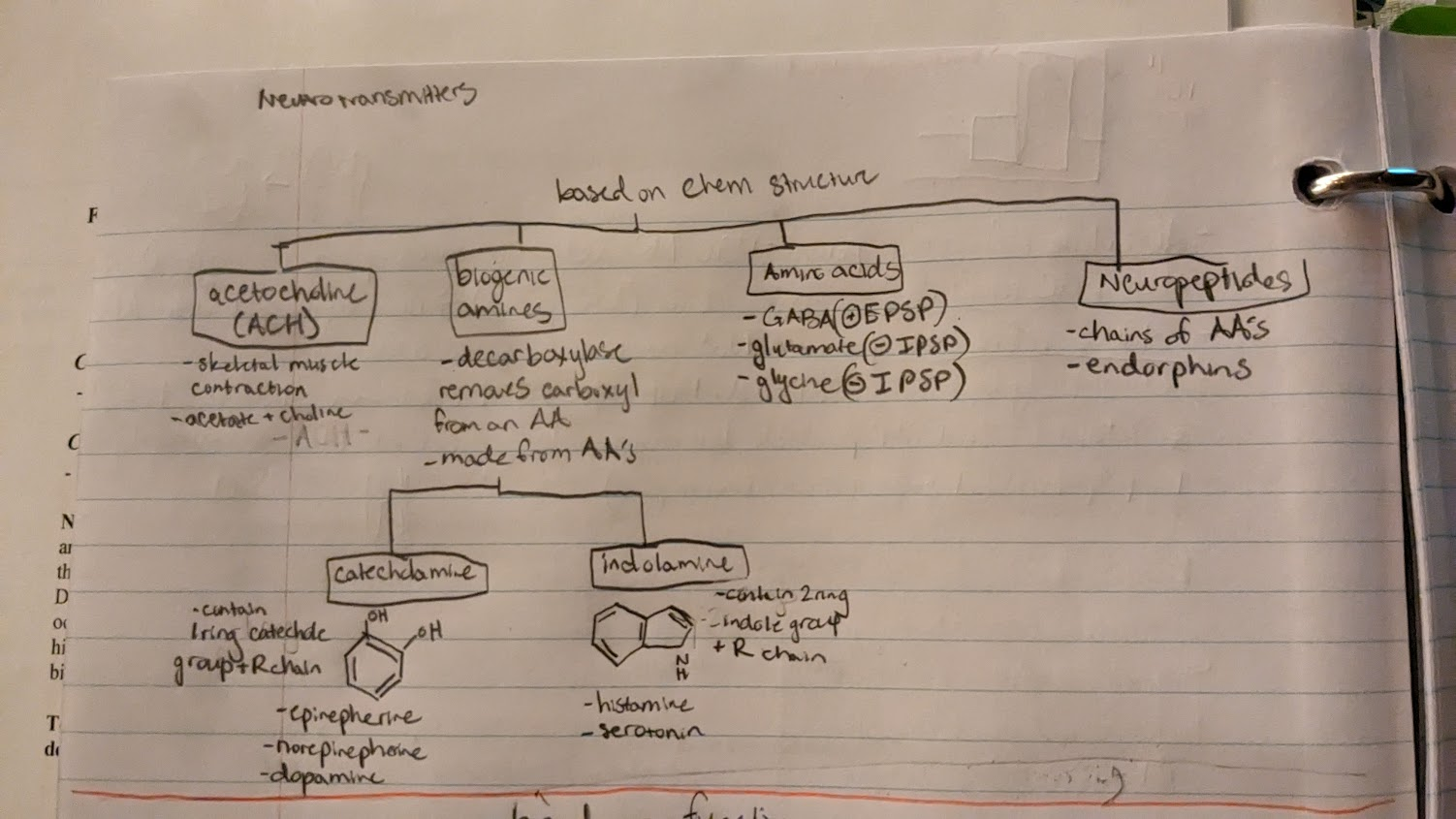
NT chemical structure category
1) Acetylcholine (ACH)
-needed for skeletal muscle contraction
-different structure than amino acid based categories
NT chemical structure category
2) biogenic amines
-modified Amino acid
-decarboxylase takes carboxyl off an AA
-includes catecholamine and indolamine
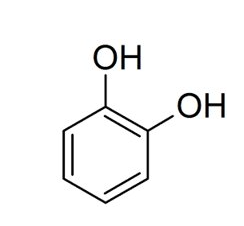
catecholamines
-subclass of biogenic amine
-has single ring catechol + R group
epinephrine
norepinephrine
dopamine
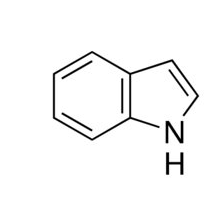
indolamines
-subclass of biogenic amine
-has double ring indole + R group
histamine
serotonin
NT chemical structure category
3) Amino acids
-unchanged form of AA acting as a NT
GABA - EPSP
glutamate - IPSP
glycine - IPSP
NT chemical structure category
4) neuropeptides
-long chains of AAs
endorphins
NT chemical structure image/graph
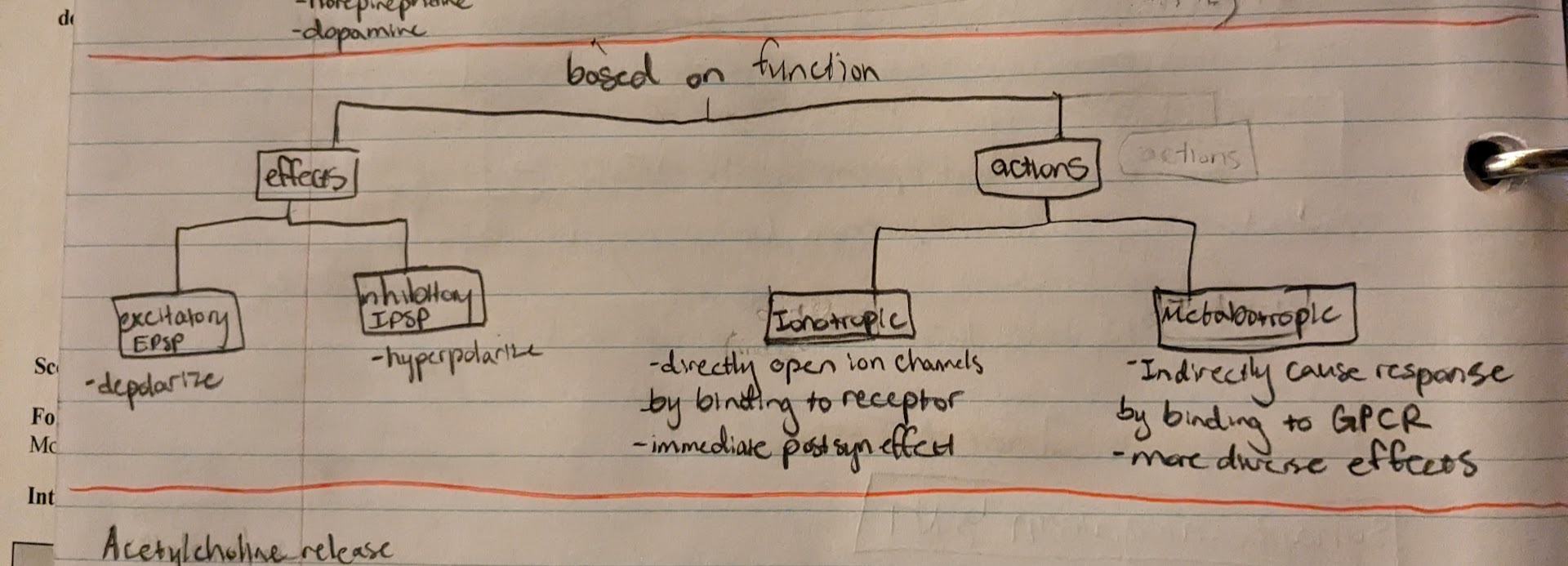
NT function category
effects
divided into excitatory (EPSP) or inhibitory (IPSP)
NT function category
actions - Ionotropic
-NT directly opens ion channels by binding to receptor
-immediate postsynaptic effect
NT function category
actions - Metabotropic
-NT indirectly causes response by binding to GPCR
-slower, but more diverse effects
NT function image/graph
Acetylcholine synthesis
A) synthesis = acetate + choline, then gets stored in vesicles. released when AP signal
-more signal → more ACH release
Acetylcholine removal
B) removal from cleft = acetylcholinesterase breaks ACH into acetate and choline. binds to muscarinic receptors
-type of muscarinic determines if it’s EPSP or IPSP
how do MAOI’s work?
“monoamine oxidase inhibitors”
monoamine oxidase = enzyme that breaks down NT
→ MAOI inhibits this enzyme so NT doesn’t get broken down
→ more NT available = more released = more binding to post-synaptic cell
How do tricyclics and SSRI’s work?
both block reuptake so NT stays in synapse longer = greater chance NT will bind to post-synaptic cell
→ tricyclics = serotonin & norepinephrine
→ SSRIs = serotonin ONLY
What are the 3 types of Antidepressants?
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI’s)
Monamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Tricyclic
How does an SSRI work?
They block the reuptake of Serotonin allowing it to continue to pass messages.
How does an MAOI work?
They block the destruction of Neurotransmitters that are outside vesicles.
How do Tricyclic antidepressants work?
They block reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine.
They also act as antagonists for other receptors such as Histamine.
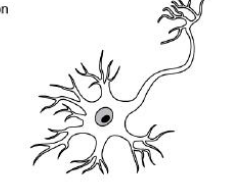
Multipolar
All motor Neurons
Bipolar
Sensory Neurons
Unipolar
Sensory Afferent Neurons
Anaxonic
Interneurons
Name the Motor Proteins
Kinesin and Dynein
3 Chemically Gated Channels
Cation
Cl
K
Glutamate is what kind of NT?
Ammino Acid
GABA is what type of NT?
Ammino Acid
Glutamate is what kind of NT?
Ammino Acid
Serotonin, Histamine, Dopamine are all kinds of what NT?
Biogenic Ammines
Endorphin is what kind of NT?
Peptide
Function of acetylcholine
Muscle Contraction
Define Axosomatic
Inhibition/Facilitation occurs from the axon towards the Soma of the Postsynaptic cleft.
Define Axoaxonal
Inhibition/Facilitation occurs at the axon of one of the competing nerves.