Chloroplasts
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
3 Differences between mitochondria and chloroplasts
-Chloroplasts do not have stuff in the inner membrane like mitochondria
-Thylakoid membranes have chlorophyll
-Stroma instead of matrix
Chlorophyll a = main pigment
Peaks at purple/violet and red
Wider spectrum than chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll b
Peaks at blue and yellow
Slightly narrower than chlorophyll a spectrum
chlorophyll c
found in algae and bacteria
what are the 2 main stages of photosynthesis?
1: light reactions (create energy as ATP & NADPH)
2: carbon fixation / calvin cycle (energy can't leave chloroplast...must be used)
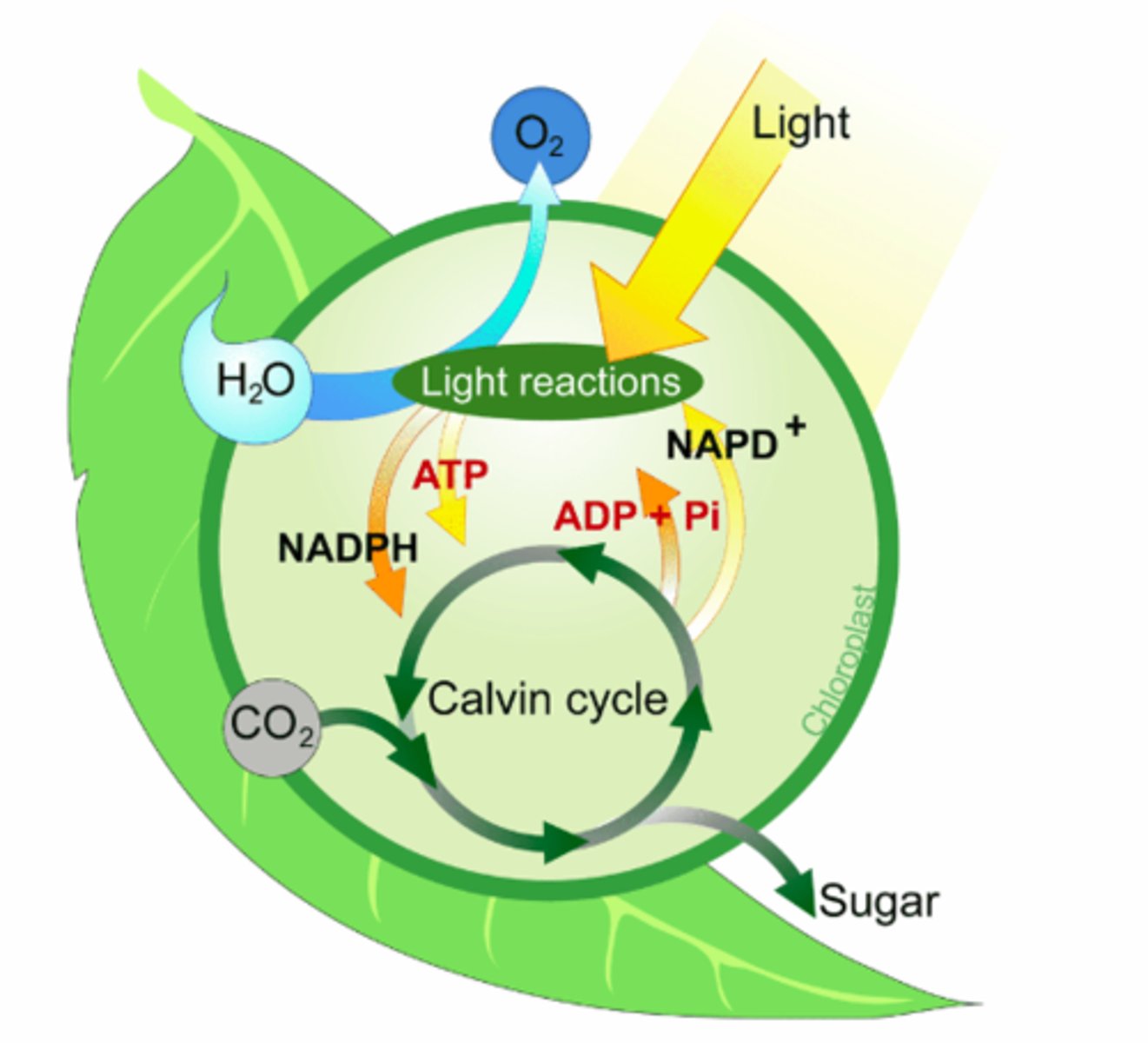
photosynthesis stage 2: carbon fixation / calvin cycle
-light independent
-calvin cycle
-ATP and NADPH can't leave chloroplast so the energy must be converted into organic molecules
-creates organic molecules for the plant to use
Antenna complex & Reaction center
-Antenna complex embedded in thylakoid membrane
-Reaction center is a chlorophyll dimer (it holds electrons at a lower energy by utilizing proteins that lower their energy)
-Light excites electron → Excited electron jumps from antenna to antenna until it hits the reaction center.
-After reaction center the electron is transferred to an electron carrier and then to the ETC / photosystems
Photosystem I: NOT independent
-Electron transferred from antenna complex
-Receives electrons from PS2
Photosystem II: semi-independent
-Necessary for photosystem I to run.
-ATP created on stroma side.
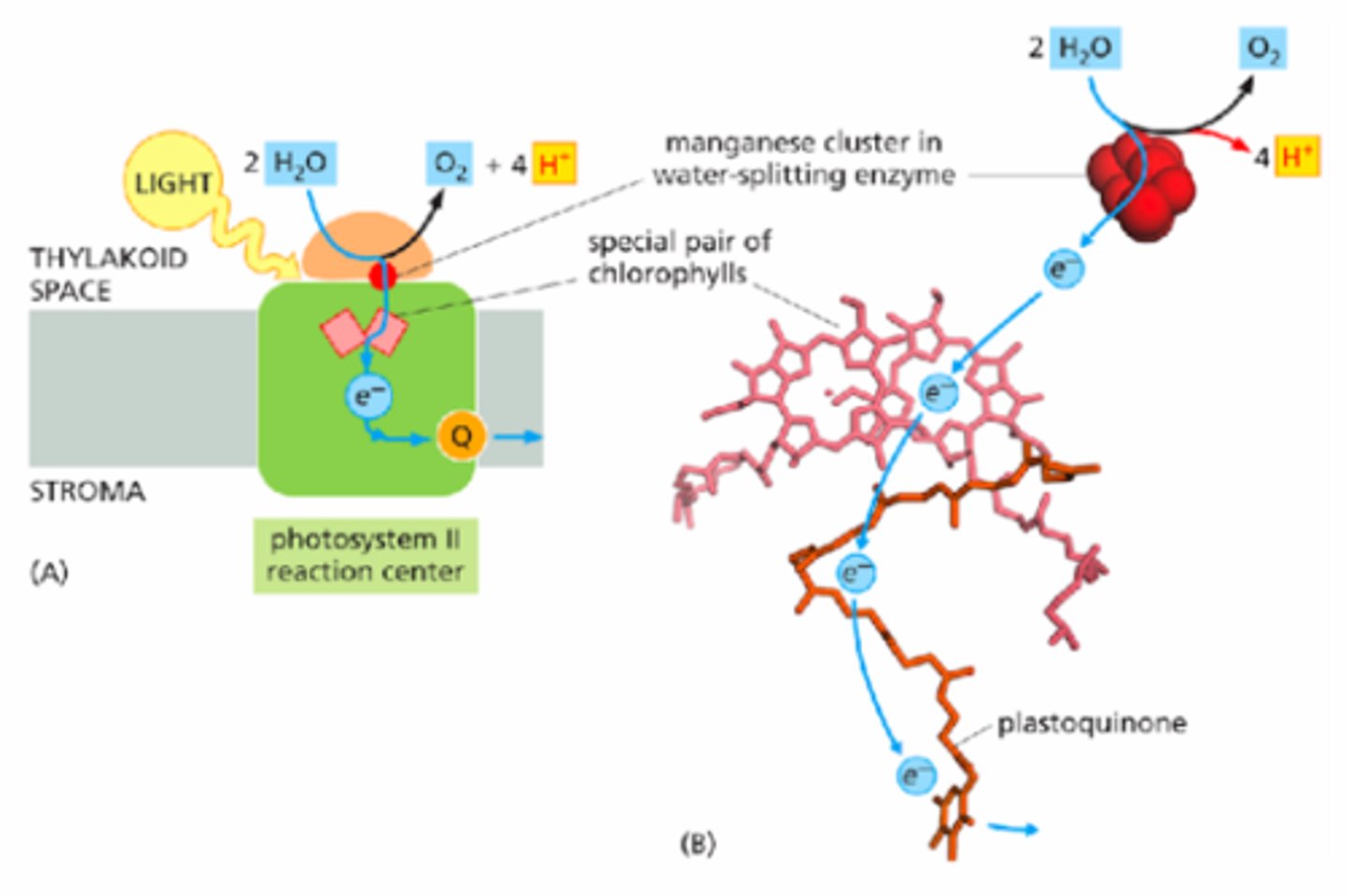
-H2O splitting
-provides electrons to PS1
Water splitting complex
-Occurs in photosystem II
-4 rounds of energy transfer must occur before water splitting enzyme can release 4H+ and 1 O2 from 2 water molecules
ATP and NADPH production in Chloroplasts
-Photosystems II and I boost electrons to a higher energy level which is necessary to produce atp and nadph
-ATP and NADPH cannot leave the chloroplast → must be used in stage 2 of photosynthesis (carbon fixation)
-RuBisCo: transforms inorganic carbon into an organic molecule
Calvin Cycle (carbon fixation)
1: Rubisco uses CO2
2: sugar formation
3: 1 molecule of Glyceraldehyde leaves the cycle
relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Products of photosynthesis are used in cellular respiration to make usable energy --> Without cellular respiration, the energy from photosynthesis cannot be used
Cyanobacteria vs. Chloroplasts
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic prokaryotes; chloroplasts share many features including thylakoid membranes and pigment systems.
Chlorophyll Types
Includes chlorophyll a (main pigment) and b (accessory pigment) in plants
Carotenoids
-Accessory pigments that extend the range of light absorption.
-protects from light damage by quenching singlet oxygen.
-alpha & beta forms
Phycobilins
-Water-soluble pigments found in cyanobacteria and red algae that absorb light in wavelengths chlorophyll doesn't.
-phycocyanin & phycoerythrin
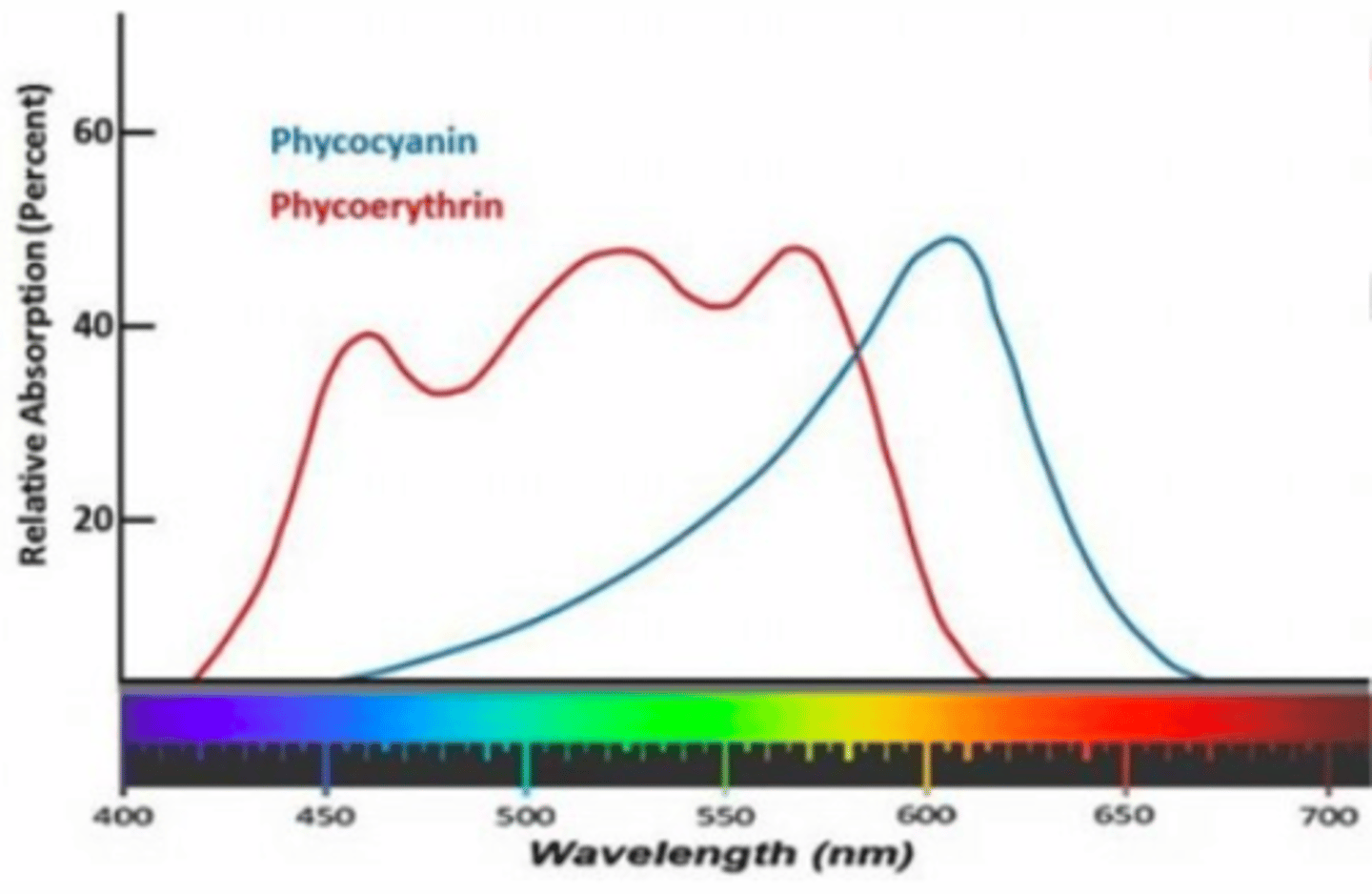
Phycoerythrin
A red or pink pigment that absorbs blue and green light efficiently.
Phycocyanin
A blue pigment that absorbs orange and red light, complementing chlorophyll's absorption.
Light Reactions
-Light absorption --> electron transferred to reaction center --> electron transport through PSII cytochrome b6f --> electron carried to PSI reaction center --> ferrodoxin NADP+ reductase produces NADPH while ATP synthase produces ATP
-Occur in thylakoid membranes.
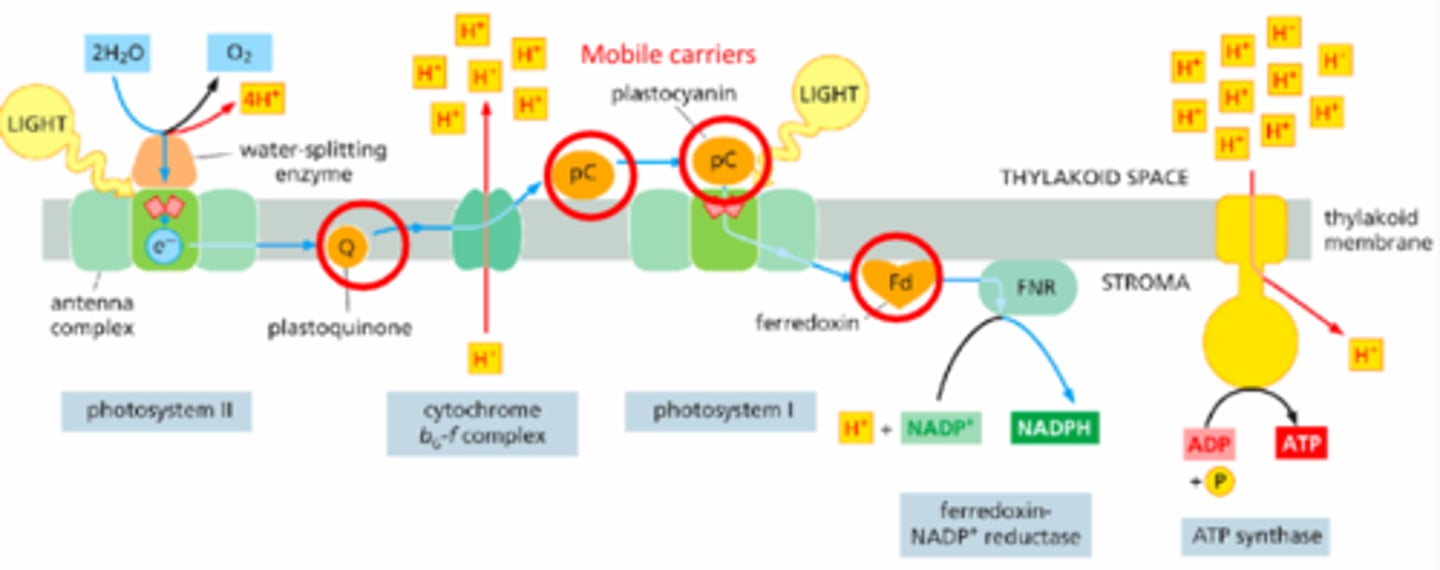
How do PSII and PSI help produce ATP and NADPH?
PSII & PSI boost electrons to the energy level needed for ATP and NADPH production
Carbon Fixation / calvin cycle
-Occurs in stroma
-The ATP and NADPH generated are used to convert inorganic CO₂ into sugars.
Antenna Complex
A group of pigments that collect light energy and funnel it to the reaction center.
Reaction Center
A specialized chlorophyll pair that donates a high-energy electron to the electron transport chain.
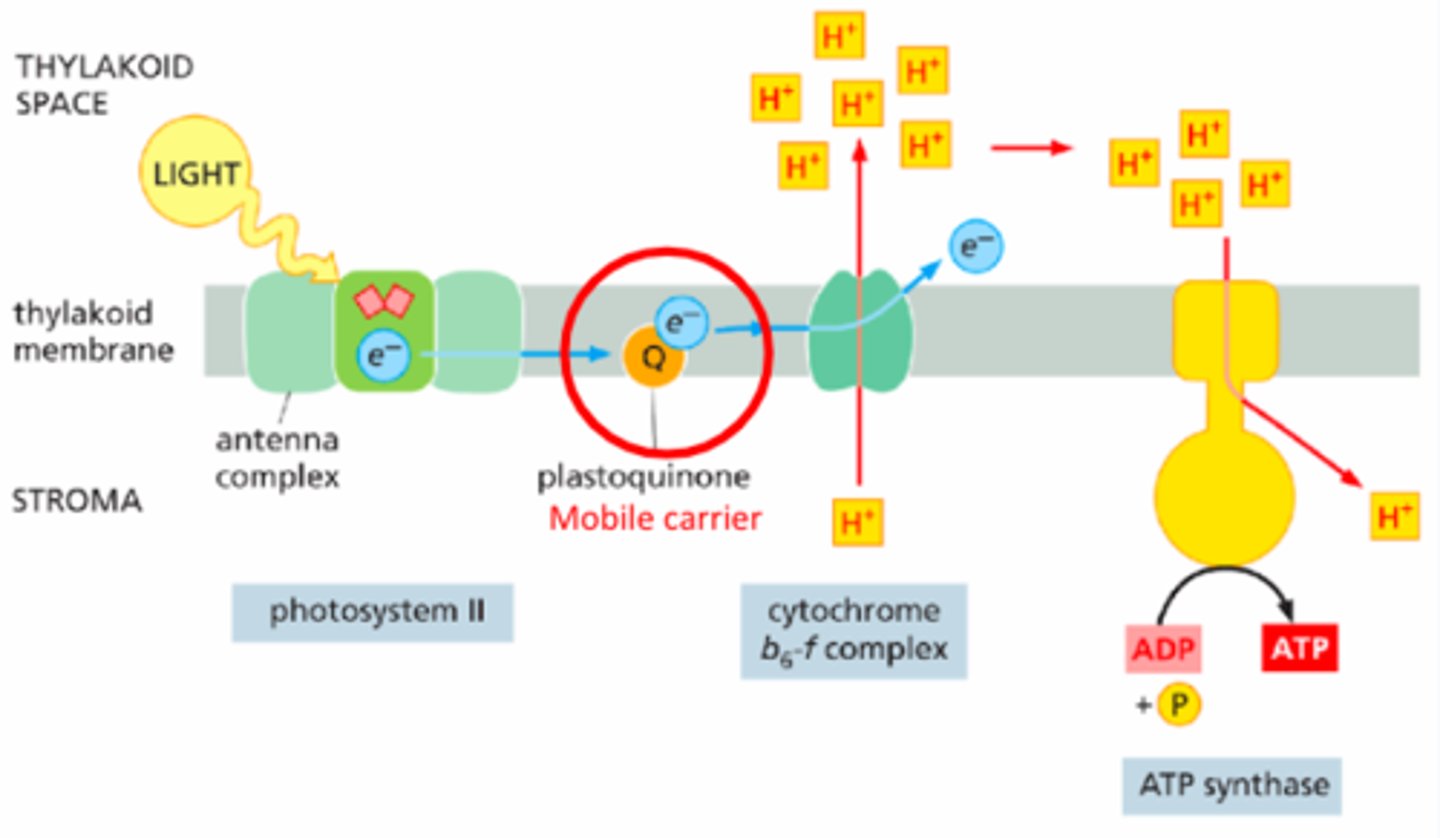
Photosystem II (PSII)
The first complex in the light reactions; uses light energy to split water and generate ATP.
-electrons from reaction center --> mobile carrier brings them --> enter cytochrome b6f --> pumps H+ across membrane --> H+ gradient powers ATP synthase.
Photosystem I (PSI)
The second complex; boosts electrons to a higher energy level to reduce NADP⁺ into NADPH.
-electrons PSII go to reaction center --> ferro mobile carrier--> ferro NADP+ reductase --> creates NADPH from NADP+
-gets electrons for reaction center from PSII
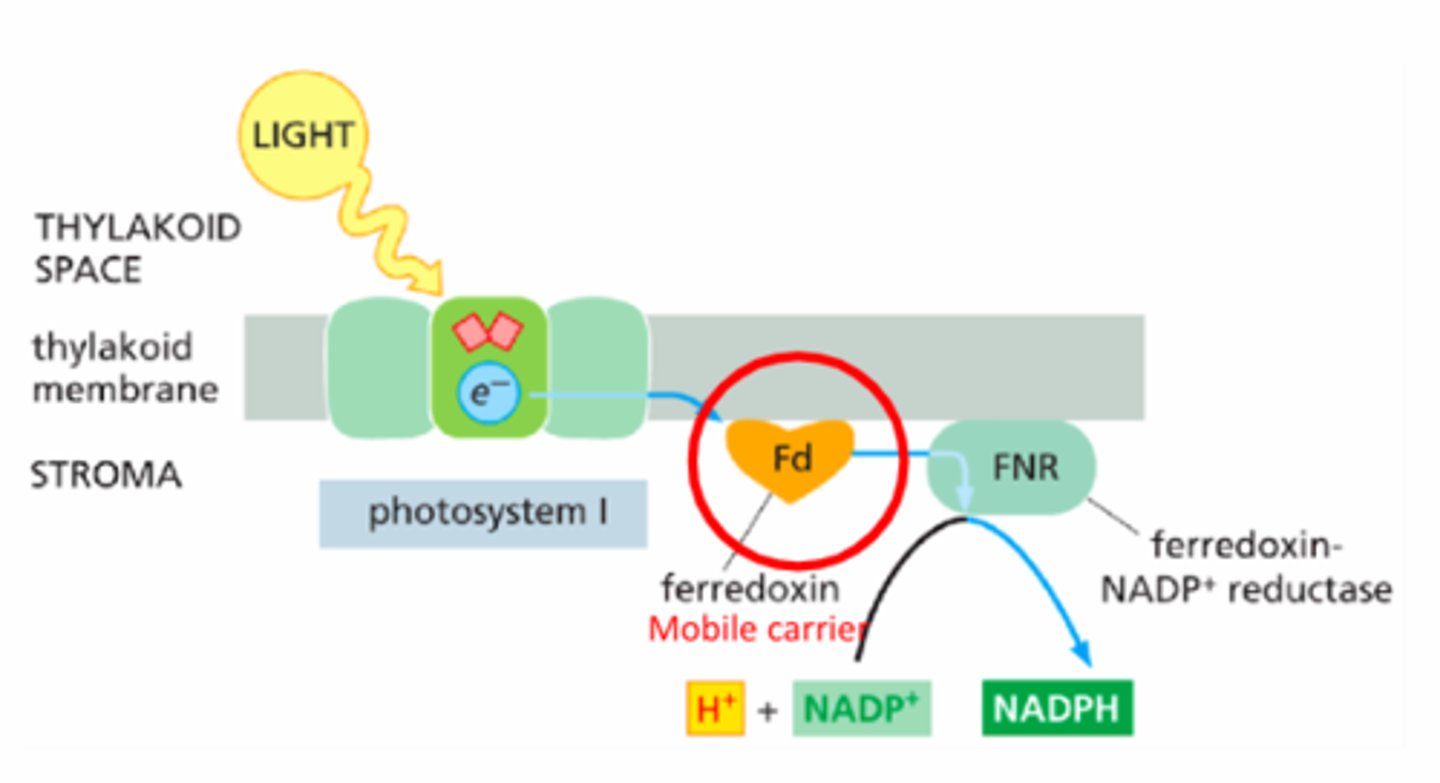
How are electrons replenished in the reaction centers?
-water splitting (PSII)
-ETC (PSI)
Water-Splitting Complex
Found in PSII; provides replacement electrons by oxidizing water, releasing O₂ as a byproduct.
Electron Flow Between Photosystems
Electrons move from PSII to PSI via mobile carriers, forming a linear electron transport chain.
Mobile Carriers
Include plastoquinone, cytochrome b6f, and plastocyanin — shuttle electrons between components of the transport chain.
ATP Production
Driven by proton gradient created by electron transport; ATP synthase in the thylakoid membrane synthesizes ATP.
NADPH Production
Generated by Photosystem I when high-energy electrons reduce NADP⁺ to NADPH.
ATP & NADPH Use
Remain inside the chloroplast and fuel the Calvin cycle in the stroma.
Calvin Cycle
A series of enzymatic reactions that fix atmospheric CO₂ into 3-carbon sugars using ATP and NADPH.
Rubisco
-used during calvin cycle / carbon fixation
-the enzyme that catalyzes the fixation of CO₂ into organic molecules.
-pyrenoids are in chloroplasts of algae & use rubisco
Pyrenoid
A chloroplast subcompartment that concentrates Rubisco and enhances the efficiency of carbon fixation.
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (G3P)
A 3-carbon sugar produced by the Calvin cycle; can be used to synthesize glucose or other organic molecules.
metabolite production in photosynthetic cells
sugars from photosynthesis exit the chloroplast --> sugars in cytosol --> sugars release metabolites --> sugars enter the mitochondria for citric acid cycle (like pyruvate)
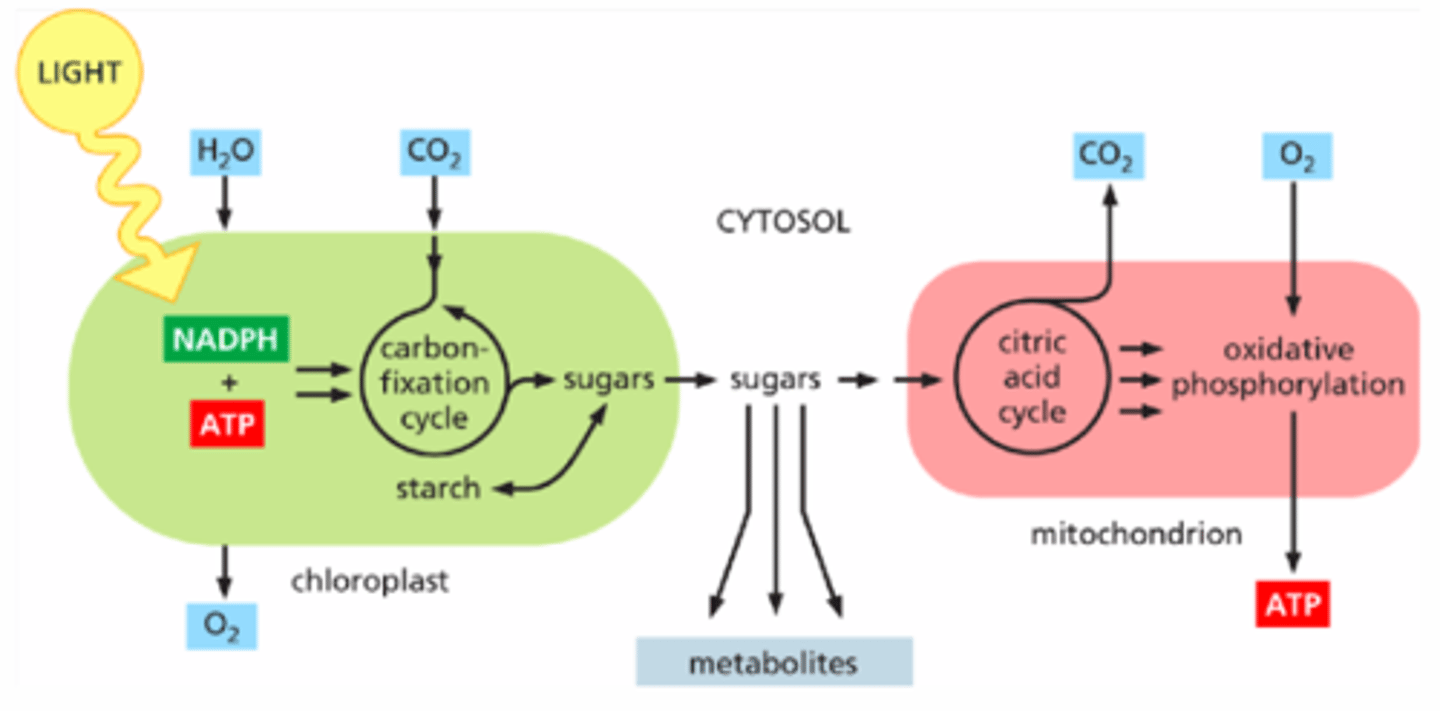
Organic Molecule Storage
-Photosynthetic cells convert G3P into starch for storage for later use.
-lipids can be stored as fat droplets in the cytosol