Psych Brain&Behavior
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Trepanning (trephination)
a surgical intervention in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull (6500 b.c.)
Hippocrates's view of brain
Believed that the brain is the seat of intelligence (460bc-370bc). Key for sensation and perception, disrupted in epilepsy. First person to propose these theories
Rene Descartes
A firm believer that the mind and body exist as separate entities. Dualism
Dualism
The mind and body are two distinct substances and the brain is seen as the tool or medium
Descartes’ Reflex Arc
Proposed one of the earliest models of how the body responds automatically to stimuli without input from the brain
Franz Joseph Gall
(1758–1828) was a German doctor who started phrenology
Phrenology
The study of the conformation (build) of the skull as indicative of mental faculties and traits of character. A pseudoscience.
John Marthyn Harlow
(1819 -1907) American physican attended the surgery for phineas gage
Phineas Gage
a railroad worker whose frontal lobe was penetrated by an iron rod, survived, but he experienced severe personality changes, became very impatient, impulsive, easily disrupted
Pierre Paul Broca
(1824-1880) Physician, did postmortem brain studies of patients his area becomes known to be critical for producing speech, critical in the development of lateralization.
Carl Wernicke
(1849-1905) Physician, did postmortem brain studies of patients his area becomes known to be critical for language comprehension, critical in the development of lateralization.
Lateralization
The specialization of the two brain hemispheres for different functions.
Neuroscience
is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord,
and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders
Neuroscientists
study the function of the nervous system in focus of Molecular level, Cellular level, Functional level, Behavioral level, Evolutionary perspective, Computational, Clinical perspective, Highly interdisciplinary field!
Brain
Controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing,
temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body
Spinal cord
A collection of brain cells running from the base of the brain down the
center of the back
Spinal reflex
Automatic movement without brain input
Anatomical orientation
give clarity and precision when describing locations, pathways, and
relationships. Rostral, Caudal, Dorsal, Ventral, Lateral, Medial.
Neuraxis (neuraxis)
Denotes the direction in which the central nervous system lies, in humans it bends at the brainstem
Spatial Orientation
Refers to the 3D positioning of the brain in space, especially when describing planes and axes.
The frontal or coronal plane
a vertical plane in a medial to lateral direction. Dividing the brain into front and back pieces
The sagittal plane
a plane through the midline of the brain. Dividing the brain into right and left regions
The horizontal plane
plane falls along the horizon. Dividing the brain into top and bottom regions
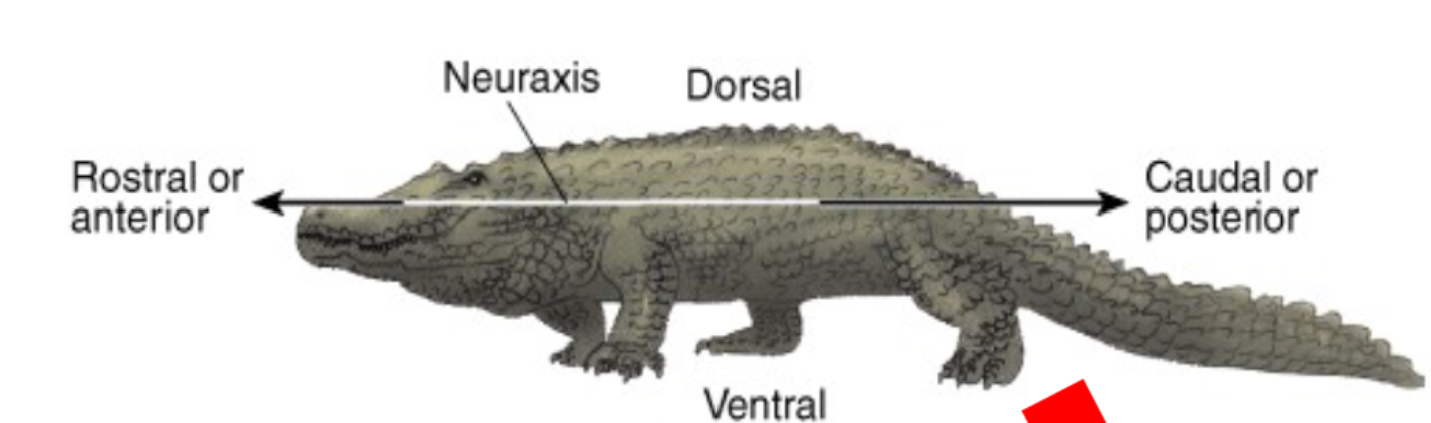
Dorsal
( from Latin dorsum 'back’): refers to the back Anatomical orientation
Ventral
(from Latin venter 'belly’): refers
to the front, or lower side, of an organism Anatomical orientation
Rostral
(from the Latin rostrum, meaning
"beak"): refer to the beak/nose Anatomical orientation
Caudal
(from the Latin cauda, meaning "tail"): refer to the back Anatomical orientation
Lateral
away from the midline Anatomical orientation
Medial
toward the midline Anatomical orientation
Meninges
series of three protective membranes that cover the CNS
Dura mater
Outermost meningeal layer, Thick, tough and fibrous, and Contains venous sinuses that drain blood from the brain
Arachnoid layer
Middle layer, thin, web-like membrane, Acts as a cushioning membrane, Subarachnoid Space, Between arachnoid mater and pia mater, Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Pia mater
Innermost meningeal layer, very thin and delicate, Adheres tightly to the brain’s gyri and sulci
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
a clear, colorless body fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and acts a shock absorber for the brain along with provides buoyancy, delivers nutrients and removes waste products of metabolism and
excess neurotransmitter