Unit 10 - Renal Transplant
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the role of ultrasound when scanning a renal transplant?
Monitor for rejection & other complications after the transplant
What are other complications after a renal transplant?
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
Obstructive nephropathy
Extraperitoneal fluid collections
Hemorrhage
Infarction
Recurrent glomerulonephritis
Graft rupture
Renal emphysema
Most renal transplant patients have had ______ term renal failure without ___________ nephropathy.
Long, obstructive
What are the pre-transplant risk factors that are considered?
Age
Primary diagnosis
Medical complications
Transplant source
What patients have the lowest risk when considering a renal transplant?
16-45 year olds
Primary renal disease
What is the major problem with renal transplants?
Graft rejection
With a living kidney donor, what is the average survival rate?
75%, 5-years
With a cadaver kidney donor, what is the average survival rate?
60%, 5-years
What is the surgical procedure of a renal transplant?
Removal of donor’s kidney (Lt.), vessels, ureter
Rotated & placed in recipient’s Rt iliac fossa
Anastomosed to iliac vessels
Ureter inserted in bladder
With a renal transplant, when is the baseline US exam performed?
Within 48 hours after the transplant
What does a sonographer look for in the baseline US exam?
Renal size
Calyceal pattern / Hydronephrosis
Extrarenal or Perirenal fluid collections
Blood Perfusion exam / Doppler PW & Color
Rejection (high RI’s)
Bladder exam
What should be done with Longitudinal & Transverse scans of the kidneys?
Made parallel & perpendicular to long axis of the kidney
What RI’s are needed to be evaluated in the Doppler portion of the exam?
Main Renal Artery (>correct)
Anastomosis, mid, distal
Iliac Artery (>correct)
Main Renal Vein (>correct)
Indirect Doppler
Color flow to demonstrate perfusion
A _______ is needed to diagnose rejection, US guidance is used.
Biopsy
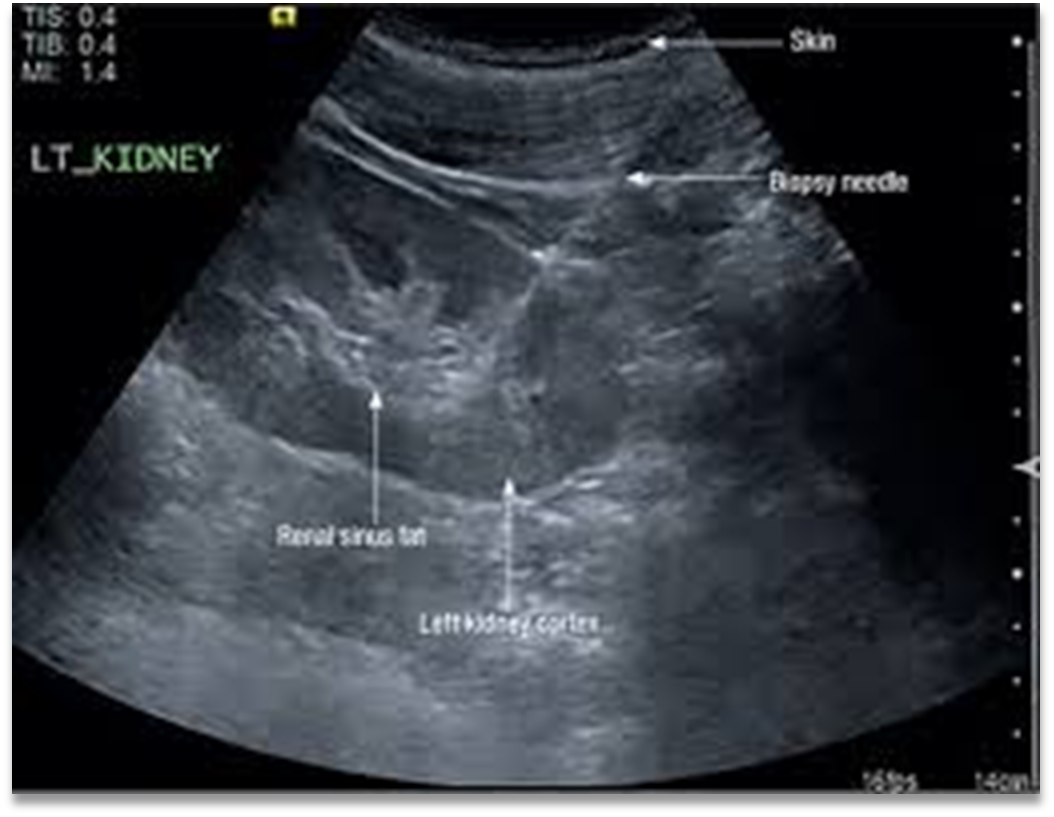
What is this image showing?
Biopsy of the left kidney
What are the types of rejection?
Hyperacute
Acute
Immunologic
Chronic
When does a Hyperacute rejection occur?
Within hours of the transplant
When does an Acute rejection occur?
Within days to months after transplant
What are the causes of an Immunologic rejection?
Performed antibodies
Immune complexes
Cell-mediated responses
When does a Chronic rejection occur?
Months after transplant with gradual onset
US is very important in the diagnosis of rejection, what should be observed?
Size
Shape
Appearance of pyramids, cortex, & parenchyma
Fluid collections
RI’s
Rejection Pattern #1:
Enlargement & decreased echogenicity of pyramids
Not uniform
Rejection Pattern #2:
Hyperechoic cortex
Rejection Pattern #3:
Localized area of renal parenchyma with anechoic area in polar areas
Rejection Pattern #4:
Distortion of renal outline
Localized- involving both cortex & pyramids
Sinus may appear compressed & displaced
Rejection Pattern #5:
Patchy sonolucent areas - both cortex & medulla
Follow-up becomes extensive affecting a large portion of the renal parechyma
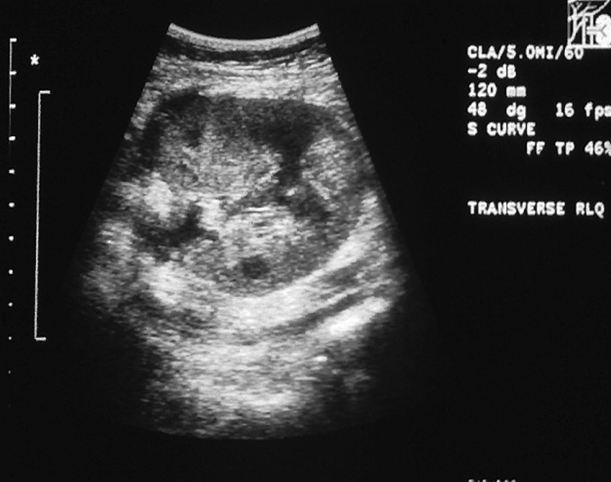
What is this image showing?
Chronic renal transplant rejection
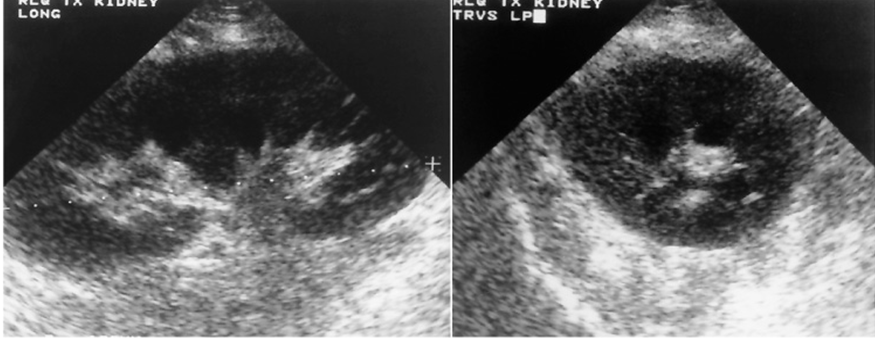
What is this image showing?
Distortion of the renal outline
Localized areas of swelling involving both the cortex & pyramids
Renal sinus echoes may appear compressed and displaced
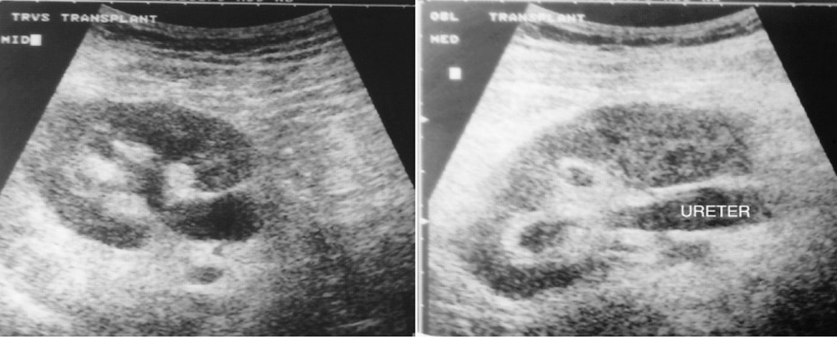
What is this image showing?
Hyperechoic cortex appears as swollen sonolucent pyramids
W/ background of ^ echogenicity of the outer and interpyramidal cortex
Mild dilation of the renal pelvis and ureter
RP ~ Long-Standing Rejection: A normal-size transplanted kidney has...
Very little differentiation between parenchymal & renal sinus echoes
RP ~ Long-Standing Rejection: A small transplanted kidney has…
Irregular margins
Parenchymal echo pattern
RP ~ Physiology: A hypoechoic appearance, can be a sign of what diseases?
Edema
Congestion
Hemorrhage of interstitium
RP ~ Physiology: A hyperechoic appearance, can be a sign of what diseases?
Ischemia
Cellular infiltration
Infarction & necrosis
RP ~ Physiology: A irregular parenchymal echo pattern appearance, can be a sign of what diseases?
Parenchymal atrophy
Fibrosis
Shrinkage
From long-standing rejection
When does a graft rupture usually occur?
In the first 2 weeks of post-op
What are the symptoms of a graft rupture?
Abrupt onset of pain
Swelling
Oliguria
Shock
What is the sonographic appearance of graft rupture?
Gross distortion of graft contour
Perinephric or paranephric hematoma
RI Relevance Post Op: Immediately
Patency of renal vein
RAS
Extrarenal compression
Adult allograft in a child
ATN
Biopsy to confirm
RI Relevance Post Op: Within a Few Days
Obstructive uropathy
Hydronephrosis
Pyelonephritis
Pyuria
Extrarenal compression
Extrarenal fluid collections
RI Relevance Post Op: Second Week
Rejection
(Especially with elevated Creatinine levels)
Biopsy to confirm
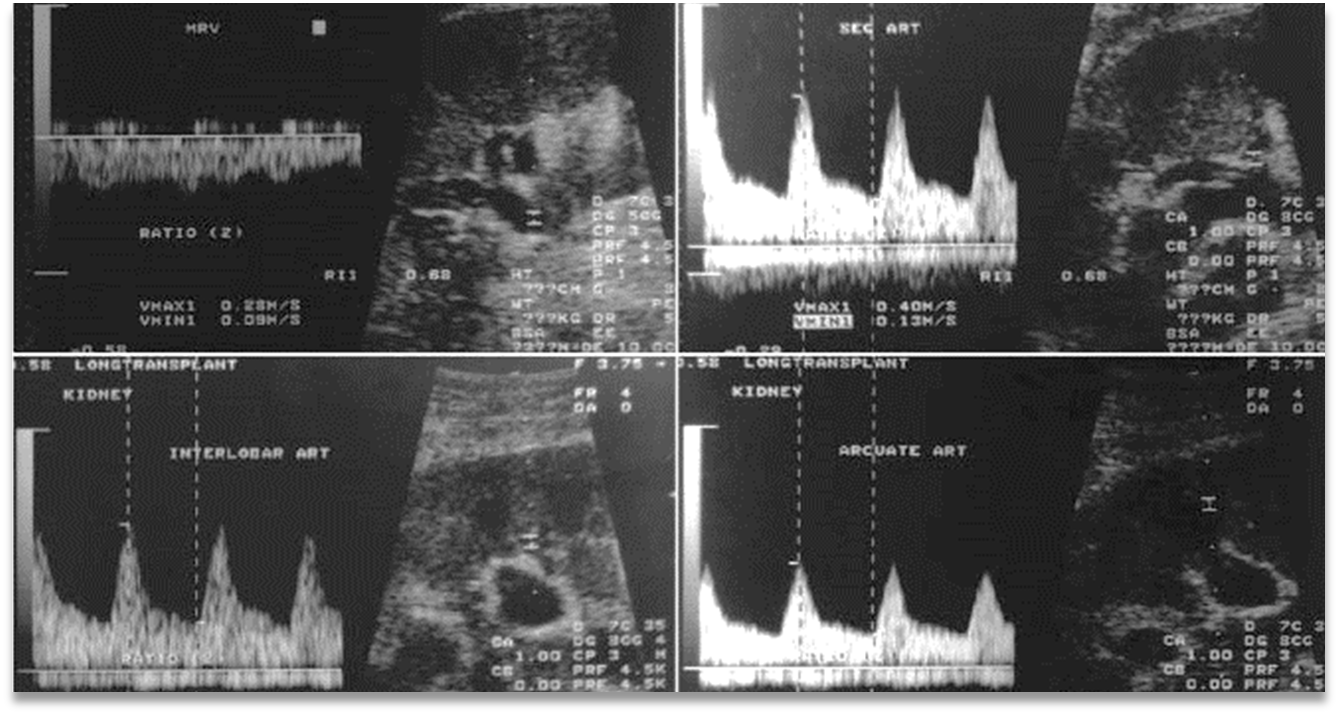
What are these images showing?
Normal Flow Patterns Post-Transplant
What are the different types of flow patterns considered abnormal?
Tardus parvus @ inferior segmental (RAS)
Elevated RI (ATN)
Elevated RA – Acute Rejection by biopsy
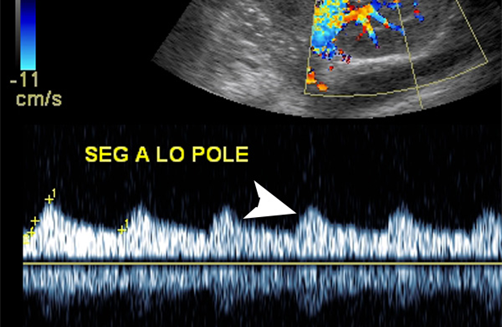
What is this image showing?
Abnormal Flow Patterns (Tardus parvus)
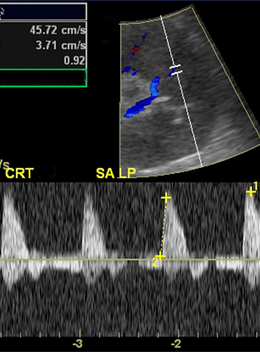
What is this image showing?
Abnormal Flow Patterns (increased RI)
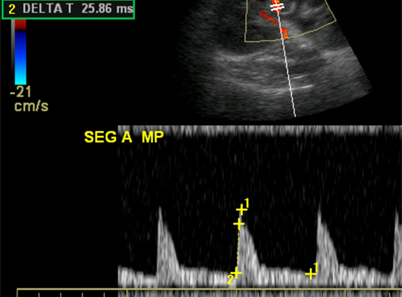
What is this image showing?
Abnormal Flow Patterns (increased velocity)
With an increased RI Relevance, what are the significant consisderations?
Postoperative time
Patient history
Donor history
Clinical findings
What does AVM stand for?
Arteriovenous malformation
What are the different types of AVM that can occur after a biopsy?
Pseudoaneurysms
Show “to-fro” flow
Arteriovenous fistula
Show turbulent flow in area
An increase in Heart Rate =
A decrease in RI
Contrast agents are not yet approved by the ____ for the kidney.
FDA
What does research show about using contrast agents in the kidneys?
Encouraging results
Increase in visualization of RAs
Decrease scanning time
What does CEUS stand for?
Continuing Education Units