Chapter 1 Theorems/info - Matrix Algebra
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This covers all the important ideas and theorems in chapter 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Theorem 1: Echelon Form
A matrix is in echelon form if:
1) All nonzero rows are above zero rows
2) Each leading entry is to the right of the one above
3) All entries below each leading entry are zero
This lets you identify pivot positions and reveals basic vs free variables.
We use it to determine consistency and counting pivots
Theorem 2 - Reduced Echelon Form
An echelon matrix is in reduced echelon form if:
4) Each leading entry is 1
5) Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in its column
System solutions can be read directly
Uniqueness of RREF
Every matrix is now equivalent to one and only one reduced echelon matrix.
RREF does not depend on row operation order
Two matrices are row equivalent - same RREF
“Is the RREF unique?” - YES
Pivot Position & Pivot Column
A pivot position is the location of a leading 1 in the RREF of a matrix
A pivot column is a column containing a pivot position
Pivot columns - basic variables
Non-pivot columns - free variables
Vector Equality
Two vectors are equal if their corresponding entries are equal
Converts vector equations to systems of equations
Linear Combination
A vector y is a linear combination of v1,…,vp if:
y = c1v1+,…,+cpvp
Core idea behind span, Ax=b, column space
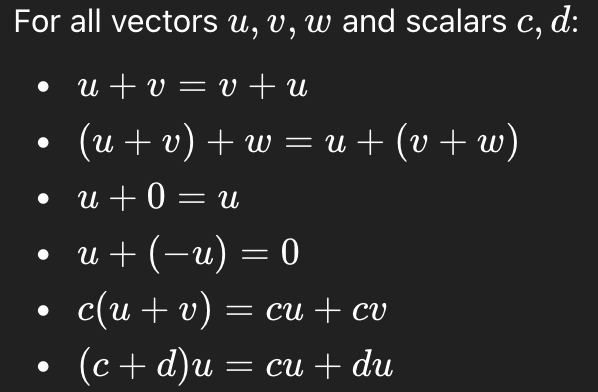
Algebraic Properties of Rn
These justify legal vector manipulations
Matrix - Vector Product
This connects matrix equations - linear combinations
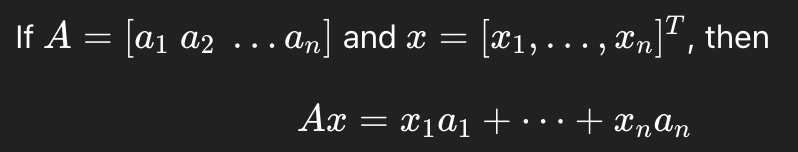
Theorem 3 - Equivalence of System Forms
The following have the same solution set:
Ax = b
x1a1+…+xnan = b
The augemented matrix [A b]
We can use any method
Theorem 4 - Existence of Solutions
For an m x n matrix A, The following are equivalent:
Ax = b has a solution for all b ∈ Rm
Columns of A span Rm
Every b is a linear combination of columns of A
A has a pivot in every row
Fast consistency test and no row by row solving needed.
Homogeneous Systems
A homogeneous system Ax = 0 always has the trivial solution.
Nontrivial solutions exist = free variables exists
Parametric Vector Form
When free variables exists, solutions can be written as:
Required final form on many problems
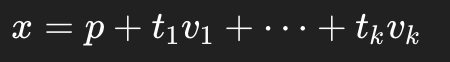
General Solution of Ax = b
If Ax = b is consistent, then:
solutions = particular solution + solutions of Ax = 0
“Describe all solutions” - use this
Linear Independence
{v1,…,vp} is linearly independent if:
x1a1+…+xpap = 0
has only the trivial solution
Columns of a Matrix
Columns of A are linearly independent if Ax = 0 has only the trivial solution
Independence = no free variables
Sets of One or Two vectors
One vector: independent - not zero
Two vectors: independent - neither is a scalar multiple of the other.
Theorem 7 - characterization of Dependence
A set of ≥ 2 vectors is linearly dependent if one vector is a linear combination of the others.
Lets you conclude dependence without row reducing