QUIZ 1- GYNO
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
fundus
top portion of the uterus
transabdominal
imaging through the abdomen
electronic medial record (EMR)
electronic database containing all the patient information
picture archiving and communication system (PACS)
database that stores radiologic images
transvaginal/endocavity
within the vagina
scanning protocol
list of images required for a complete exam
bioeffects
biophysical results of the interaction of sound waves and tissue
perivascular
around the vessels
ascites
fluid within the abdominal or pelvic cavity
transducer footprint
area of the transducer that comes in contact with the patient and emits ultrasound
adnexa
area around an organ
modality worklist (MWL)
electronic list of patients entered into a modality such as ultrasound which helps reduce data entry errors
lithotomy position
position of the patient with the feet in stirrups often used during delivery
endocavity
inside a cavity such as the abdomen or pelvis
radiology information system (RIS)
physical or electronic system designed to manage radiology data such as billing reports and images
nongravid
nonpregnant
hospital information system (HIS)
paper-based or computerized system designed to manage hospital data such as billing and patient records
A method used to classify the embryo, placing the embryo into categories depending on age, size, and morphologic characteristics is called
carnegie staging
fetal period genitourinary anomalies include all except
pre-embryonic fusion
cloacal anomalies can result in
hydrometrocolpos
an ultrasound exam of a patient with hematocolpos should include imaging of the
kidneys
the most common mast lesions in neonates are of
renal orgin
often development abnormalities in the female pelvis become apparent
at the onset of puberty
the pre embryonic phase, also known as the first carnegie stage last into the
3rd week
if the male gamete, which is capable of contributing either an X or Y chromosome, contributes an X to the ovum, the result is
a female zygote
precursors to the female ovaries and to the male testes are
gonadal ridges
diploid chromosomes are a result of fertilization and result in a count of
46 chromosomes
what cells produce a gender appearance
primordial germ cells
at birth that are approx ______ oogonia in the female newborn
1 million
the vaginal fornices surround the end of the
cervix
which would be an inaccurate diagnosis for the finding of a hypoechoic structure in the fetal pelvis
hemangioma
gender is determined at approx ______ days
44-49
mullerian ducts fuse to develop the uterus and
fallopian tubes
the normal male chromosome configuration is
46XY
what hormone is absent in female fetus that causes regression of the mesonephric ducts
Male inducer substance
what system develop in tandem in the embryo and are still closely associated in the adult
reproductive and urinary
hydronephrosis and hydroureter can display as a mass in the fetal
pelvis
complications fro uterine and vaginal malformations do not occur from
distal ductal regression
germ cells that migrate from the yolk sac to the gonadal region form the
genital ridges becoming sex cords
apoptosis is related to
regression of the uterine septum
sonography is useful in imaging______ a combination of menstrual blood, fluid and secretions in the distended vagina and uterus caused by imperforate hymen
hematometrocolpos
arrested development of the bilateral mullerian ducts causes
hypoplasia of both the uterus and vagina
MRKH and MURCS are related to
fetal renal and spinal anomalies
the wolffian duct forms the sinovaginal bulbs which the mullerian tubercle finally becomes:
lower one-fifth of the vagina
uterine agenesis is imaged best in the
sagital plane
defects of vertical vaginal fusion can result in the formation of a transverse vaginal septum, which can cause
obstruction and hematocolpos
initially a transverse vaginal septum requires all but
laparoscopy for endometriosis
the easiest vaginal anomaly to view sonographically is
complete absence of the vagina
which imaging modality is extremely helpful if hematometrocolpos or hematometra distorts the reproductive organs causing limited imaging capability using ultrasound
MRI
Sonohysterography is also known as
saline infused sonography (SIS)
choose the most effective diagnositc method for determining uterus unicornis
HSG
Bicornuate uterus is related to
cervical incompetence
Choose a definite method for distinguishing bicornuate uterus from septate anomalies
MRI, 3D endovaginal sonpgrpahy
complete midline failure of mullerian ducts fusion results in
uterine didelphys
the uterine septum consists of
poorly vascularized fibromuscular tissue
uterus didelphys more than any other mullerian anomaly is associated with
renal agensis
anomalies of the fallopian tubes include
luminal atresia, absent muscular layer and absent ampulla
Gravida
number of pregnancies
Para
number of pregnancies over 36 weeks
Abortion
number of failed pregnancies
Term
number of live births
Patient prep for transabdominal exam
Drink at least 32 oz to be finished at least one hour prior to the exam
Patient prep for transvaginal exam
empty bladder and give formal consent
To evaluate cervix during a transvaginal exam
pull probe out slightly and angle posteriorly
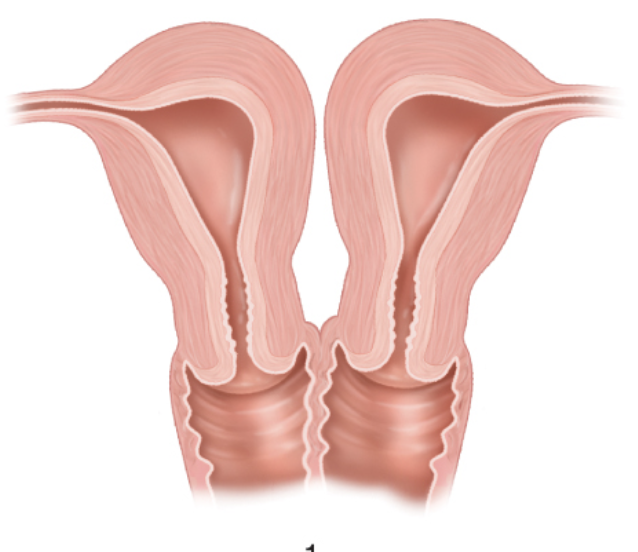
What anomaly is this
didelphys
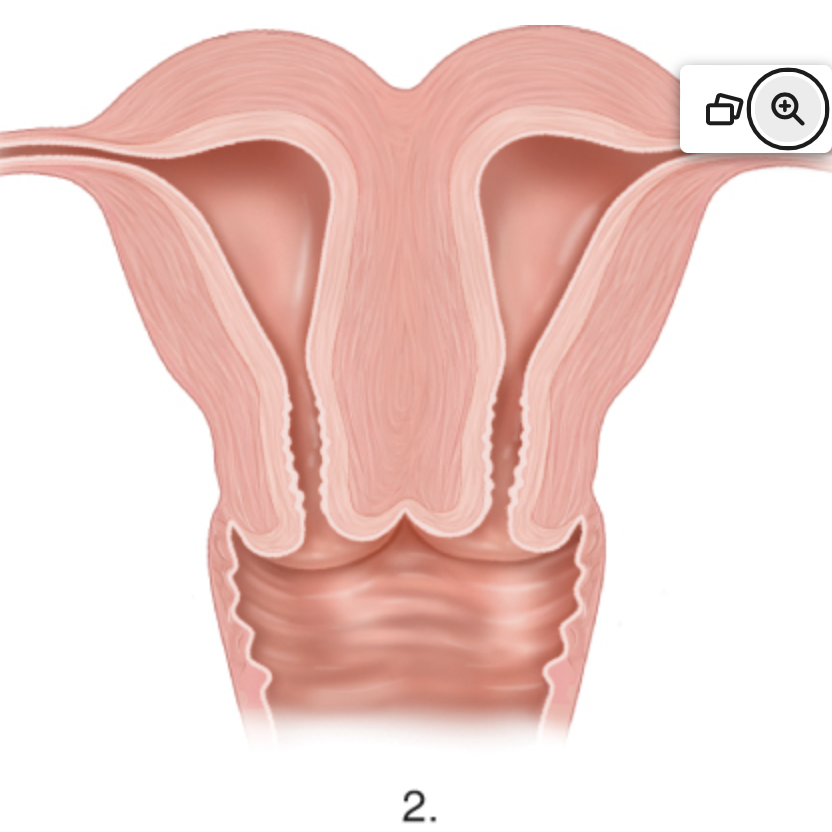
what anomaly is this
uterus duplex bicornis
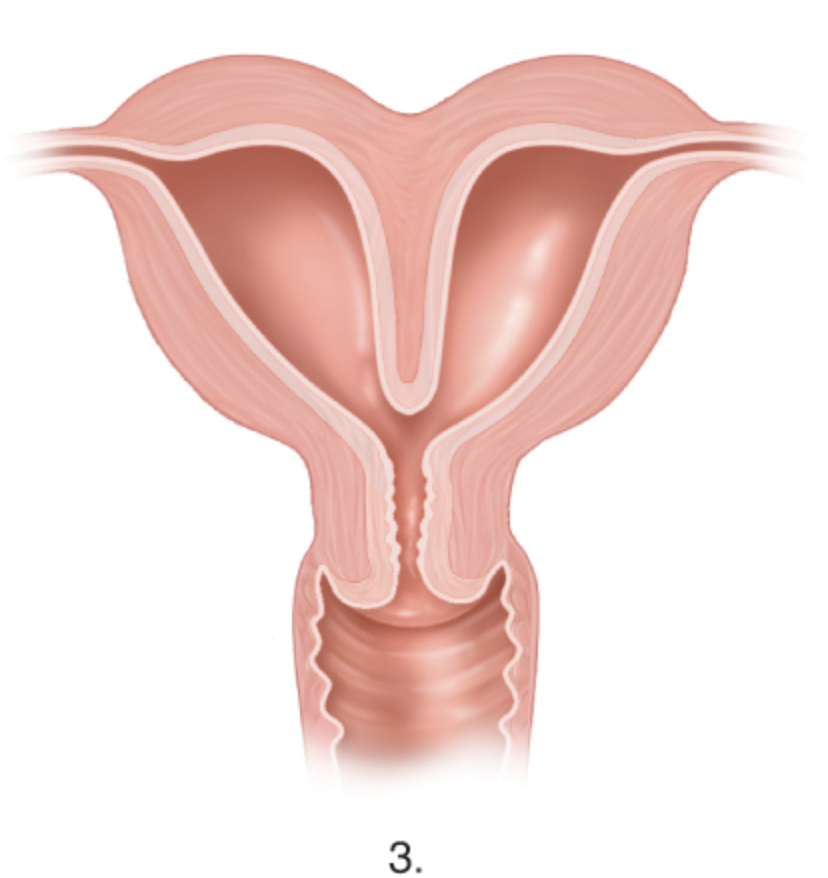
what anomaly is this
uterus bicornuate
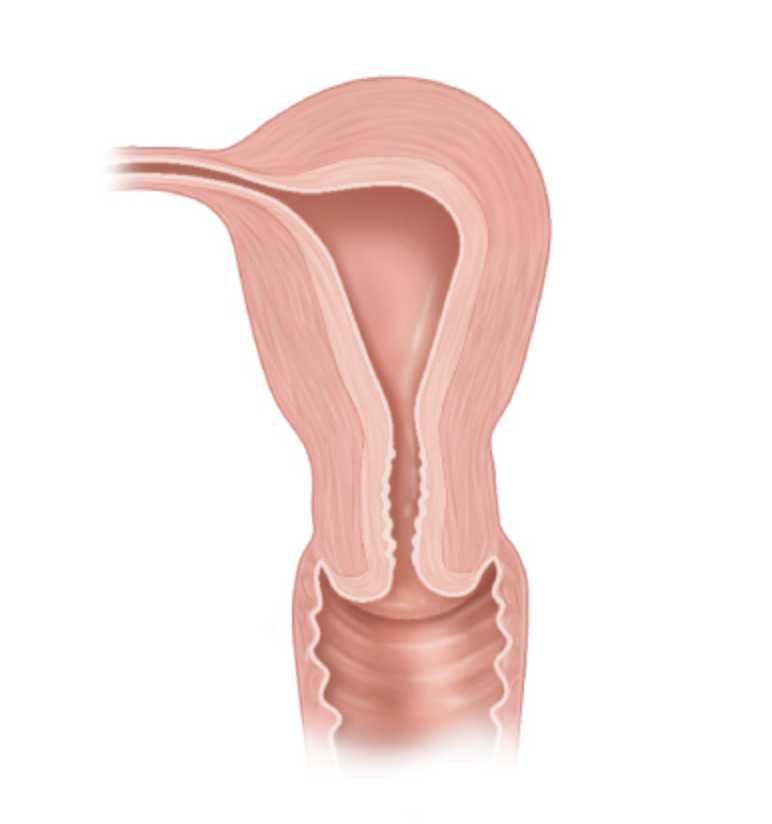
what anomaly is this
uterus unicornuate
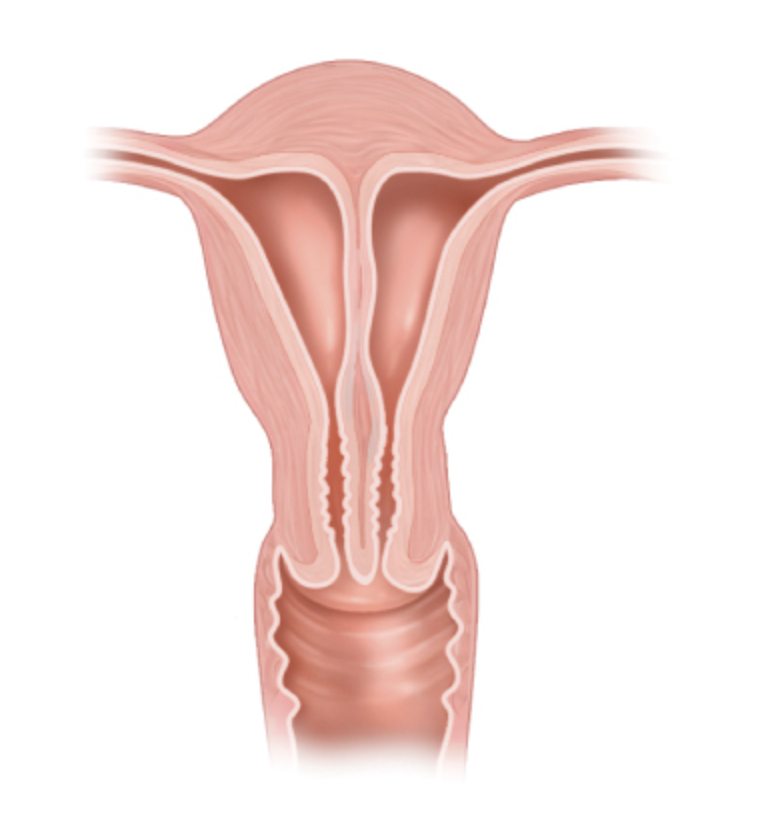
what anomaly is this
complete septate uterus
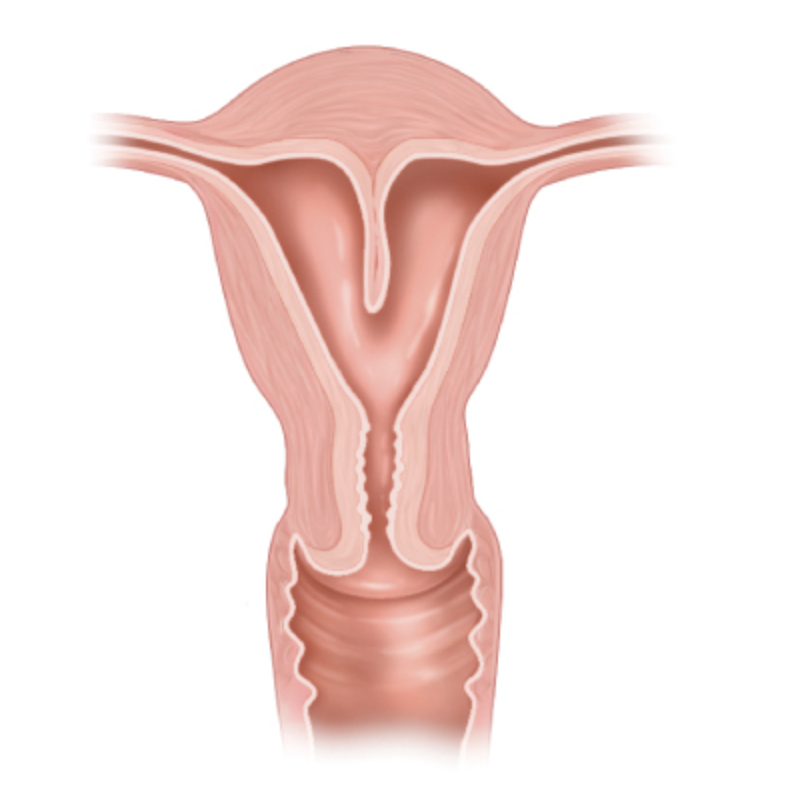
what anomaly is this
subseptate uterus
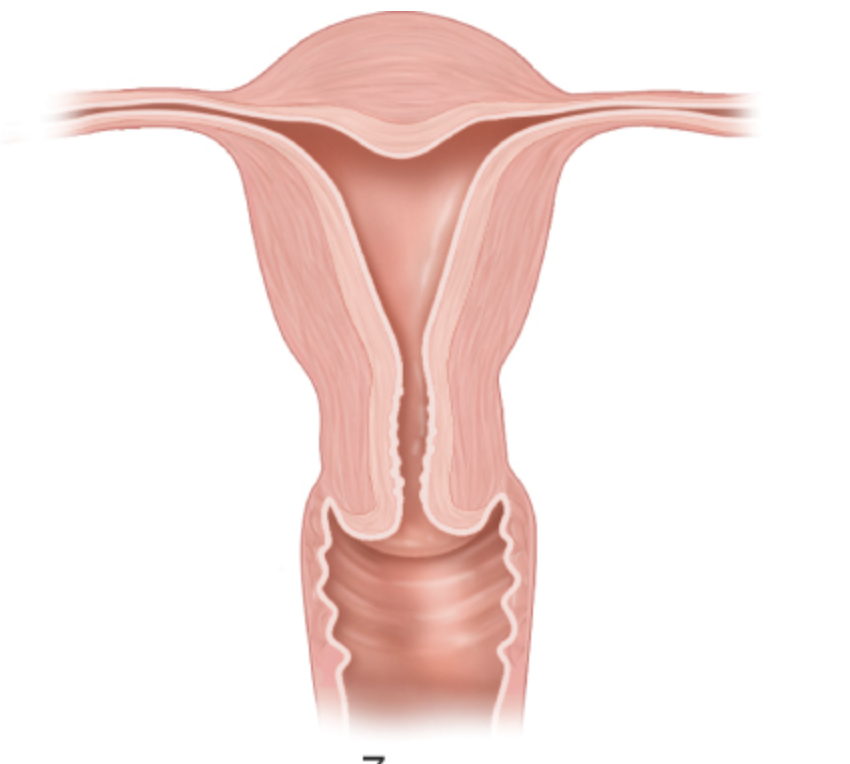
what anomaly is this
arcuate uterus
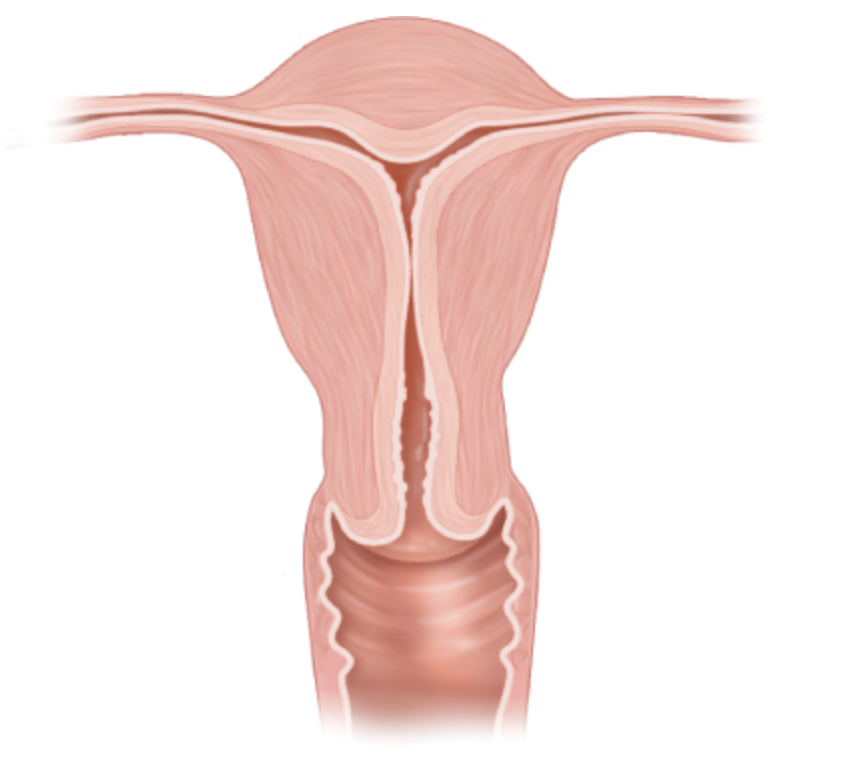
what anomaly is this
DES- T shaped
Carnegie stages classify the embryo by what
by age, size, and appearance of structures in the first 8 weeks of development
What systems develop simultaneously, resulting in coexisting malformations
reproductive and urinary
When does the determination of chromosomal gender or sex occur?
The time of conception (fertilization)
Where are gonadal ridges located (mesoderm)
anteriomedial sides of the mesonephros
what are the gonadal ridges precursors to
female ovaries and male testes
The first stage kidney is called _____ and forms in _____
pronephros, during 5th week
Second stages kidneys are called _____ and form during
mesonephros, during 6th week
the migration of what cells results in the development of the gonads?
primordial germ cells into the gonadal ridge
What do fused mullerian ducts develop
normal uterus, fallopian tubes, and the broad ligmanet
the broad ligament is a fold of what structure
peritoneum
How does vaginal formation occur
development of the urogenital sinus and the primitive cloaca
Body folding
period before embryonic disc folds into tube
Just before and as the primordial germ cells invade the genital ridge, epithelial tissue grows into the mesoderm, forming the _______
primitive sex cords
Primitive sex cords connect to:
mesonephric duct
Indifferent gonad
gonad cannot be distinguished as male or female
SRY Gene
sex determining region on Y
determines gonad will be testes
Sertoli cells secrete Mullerian Inhibiting Substance (MIS)
causes paramesonephric ducts to degenerate
Leydig cells secrete
testosterone
some gets converted to dihydrotesterone which leads to differentiation of male genitalia
Tunica albuginea
forms, separates testis from surface epithelium
Medullary cords eventually form
rete testis
Testis cords remain solid until the male reaches puberty when they hollow out to form
seminiferous tubules
Mesonephric ducts form
epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory duct
appendix epididymis is a remnant of the
paramesonephric ducts
What forms on each side of the urethral folds
genital swellings
What makes up a primordial follicle
primary oocyte and surrounding follicular cells
In all embryos, the paramesonephric orginates from the
urogenital ridge
What divides the pelvis into anterior and posterior regions
the uterus and broad ligament
Eopoophoron
remnant of mesonephric duct
found in broad ligament between fallopian tube and ovary