Q3 GENERAL PHYSICS 2 (copy)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
The branch of physics that deals with the study of stationary electric charges and their interactions.
Electrostatics
The branch of physics that deals with the study of moving electric charges and their interactions.
Electrodynamics
A hardened translucent yellowish tree resin – when vigorously rubbed with a piece of cloth, could attract nearby objects.
Discovered by the Greeks (600 BC)
Amber - From the Greek “electron”
Substance: Electrics
Ability to attract:
Electricity
In 1600, William Gilbert called substances that possess the same ability as that of amber when rubbed against another substance as _____.
electrics
A fundamental property of matter, either positive or negative, arising from the presence of protons and electrons.
Electric charge
What is the SI unit of charge?
Coulombs (q)
What is the charge of a proton?
1.602×10-19 coulombs
What is the charge of an electron?
-1.602×10-19 coulombs
What is the charge of a neutron?
0
What is the mass of a proton?
1.673×10-27 kg
What is the mass of a neutron?
1.675×10-27 kg
What is the mass of an electron?
9.109×10-31 kg
It is denoted by e, the constant electric charge carried by a single proton or a single electron.
Elementary Charge
It is the measure of the ease at which an electric charge moves through a material.
Conductivity
These are materials that allow an electric current to flow through them easily.
Conductors
These are materials that inhibit the flow of electric charge.
Insulators
These materials are intermediate between conductors and insulators. They are not as conductive as metal, but they are more conductive than insulators.
Semi-Conductors
These materials offer practically no resistance to the flow of charges below some critical temperatures
Superconductors
If the atom gains electrons, it becomes ______ charged; if it loses electrons, it becomes _____ charged.
Negatively; Positively
This involves rubbing two objects together, transferring electrons from one object to another.
Friction
A list of materials ranked according to their tendency to gain or lose electrons when rubbed against each other. It helps predict the direction of charge transfer during charging by friction.
Triboelectric Series
It is a measure of the attraction of an atom to an electron, or the tendency of an atom to become negatively charged
Electron Affinity
This involves bringing a charged object near a neutral object, causing charge redistribution in the neutral object without direct contact between them.
Induction
This involves the direct transfer of electric charge between objects through physical contact.
Conduction
In Induction, the side of the neutral body nearest to the charged body acquires a charge opposite to that of the charged body, while the side farthest from the charged body acquires a charge of the same sign causing bodies to experience repulsive forces.
This is called what?
Polarization
This principle states that electric charge cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred from one object to another or redistributed within a system.
In other words, the total electric charge in a closed or isolated system remains constant over time.
Conservation Of Charge
A metal sphere (A) that has a net charge of +6.O C was brought near to a neutral metal sphere (B). If their radii are the same, how would the charges redistribute?
6 C/2 = 3 C per sphere
Since the spheres have equal radii, the charge distributes equally between them (Conservation Of Charge)
A metal sphere (A) that has a net charge of +6.O C was brought near to a neutral metal sphere (B). If the radius of the neutral sphere (B) is twice that of the charged sphere (A), how would the charges redistribute?
With the ratio of 1:2 therefore, 6/2 =3
qA= 1/3 x 6.0 C = 2.0 C
qB= 2/3 x 6.0 C = 4.0 C
This states that the force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Coulomb's law
What is the unit of Coulomb's constant (k)?
Nm2/C2
If two charges have the same sign, what is the nature of the force between them according to Coulomb's law?
Repulsive
Coulomb's law predicts that as the electrostatic force decreases, distance ____ between the charges.
Increases
What is the value of Coulomb's constant (k)?
9×109 Nm2/C2
What happens to the electrostatic force if the distance between two charges is halved?
4F - The electrostatic force multiplies by 4
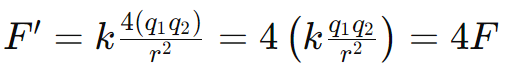
How does Coulomb's law describe the force between two charges if they have opposite signs?
Attractive
It is a vector field that surrounds a charged object and extends throughout the space surrounding it.
Electric field
What is the direction of the electric field lines produced by a positive charge?
Away from the charge
How are electric field lines arranged around two positive point charges?
(A) Repel each other and Curved Away
(B) Directed toward each other
Repel each other and Curved Away
True/False: Lines of force neither intersect nor break as they pass from one charge to another.
True
The greater the number of lines of force, the ___ the electric field.
Stronger
What is the relationship between the electric field strength (E) and the magnitude of the point charge (∣q∣)?
Directly proportional
What happens to the electric field strength (E) when you double the magnitude of the point charge?
Will also double - Direct proportionality
What is the SI unit of electric field strength?
Newtons per coulomb (N/C)
Refers to the Force that a test charge will experience when placed at that point
Electric Field Strength (E)
True/False: If a negative test charge is placed at a point in the electric field, it will experience a force opposite to the direction of the electric field.
True
True/False: If a positive test charge is placed at a point in the electric field, it will experience a force in the direction of the electric field.
True
They provide a visual representation of the direction of the electric field.
Electric Field Lines
True/False: Adding absolute values to the equation of Electrostatic Force leaves the direction and/or behavior of the force/s be figured out manually by simply looking at the point charges given.
True
What is the formula for electric field intensity (E) that involves the distribution of charge over a uniformly charged sphere.
where
E is the electric field intensity
k is Coulomb's constant
Q is the total charge of the sphere (in coulombs),
r is the distance
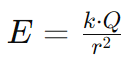
It is defined as the total potential energy a unit charge will possess if located at any point in outer space.
Electric Potential Energy
The electric potential energy is in a higher state when the charges have the same sign due to what forces?
Repulsive Forces
The electric potential energy between two point charges _________ as the distance between them increases, following an inverse relationship.
Decreases - Inverse proportionality
What is the formula for Electric Potential Energy (U)?
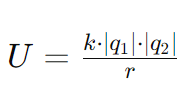
Refers to the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from a reference point to a specific point against an electric field.
Electric Potential
What is the SI unit of electric potential?
J/C
Electric Potential is related to electric field intensity (E) by what equation?
V = Ed
The potential difference (ΔV) when work is provided can be calculated using the formula: ___
ΔV = W/q
1 microcoulomb (µC) is equivalent to what in Coulomb?
1x10-6 C
It is a measure of the electric field lines passing through a given surface area.
Electric Flux
What is the SI Unit for Electric Flux (Φ)?
Nm2/C
Coulomb Constant (k) : Nm2/C2
Electric Flux (Φ) : _____
Nm2/C
How is electric flux calculated?
Φ = E⋅A⋅cos(θ)
Where:
E = Electric Field Intensity
A = Surface Area
θ = angle (ignore if none)
A larger surface area results in _______ electric flux if the electric field remains constant.
Greater - Direct proportionality
What is the relationship between electric flux and the number of field lines passing through a surface?
Directly proportional