cell structure and function unit 2
1/403
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
404 Terms
most integral membrane proteins have one or more ____ segments that span the lipid bilayer
hydrophobic
there fluid mosaic model
is thought to be a description of the structure of cell membranes, depicting a flexible matrix of lipids and proteins.
membranes are not
homogeneous - they randomly mix structures
membranes are ordered through dynamic micro domains called
lipids rafts
membrane lipids are important components of the ___ part of the fluid mosaic model
fluid
the different types of lipids that membranes contain
phospholipids, glycolipids, sterols
the most abundant lipids in membranes are
phospholipids
if you have a surface area of red blood cells and put them into a membrane how do you find the new surface area
multiply by two because bilayer
phospholipids have two diff types called
phosphglycerides (glycerol based) and sphingosine-based sphingolipids
phospholipid composition varies in
membranes from different sources
glycolipids are from by
the addition of carbohydrates to lipids
glycolipids are based with
glycerol or sphingosine
glycolipids are usually found on
the outside of the membrane
the membranes of eukaryotes contain significant amounts of
sterols
the main sterol in animal cell membranes is
cholesterol
cholesterol is needed to
stabilize and maintain membranes
membrane asymmetry is the difference between
the monolayers regarding the kind of lipids present and the degree of saturation of fatty acids in the phospholipids
most glycolipids in the plasma membrane of animal cells are in the
outer layer
membrane asymmetry is established
during the synthesis of the membrane
lipids move ___ within their monolayer
freely
rotation and lateral diffusion of lipids
are rapid and random
FRAP
fluorescent recovery after photobleaching
frap process
investigators label lipid molecules in a membrane with fluorescent dye
a laser beam is used to bleach the dye in a small area creating a dark spot on the membrane
the membrane is observed afterward to determine how long it takes for the dark spot to disappear, measure of how quickly new fluorescent lipids move in
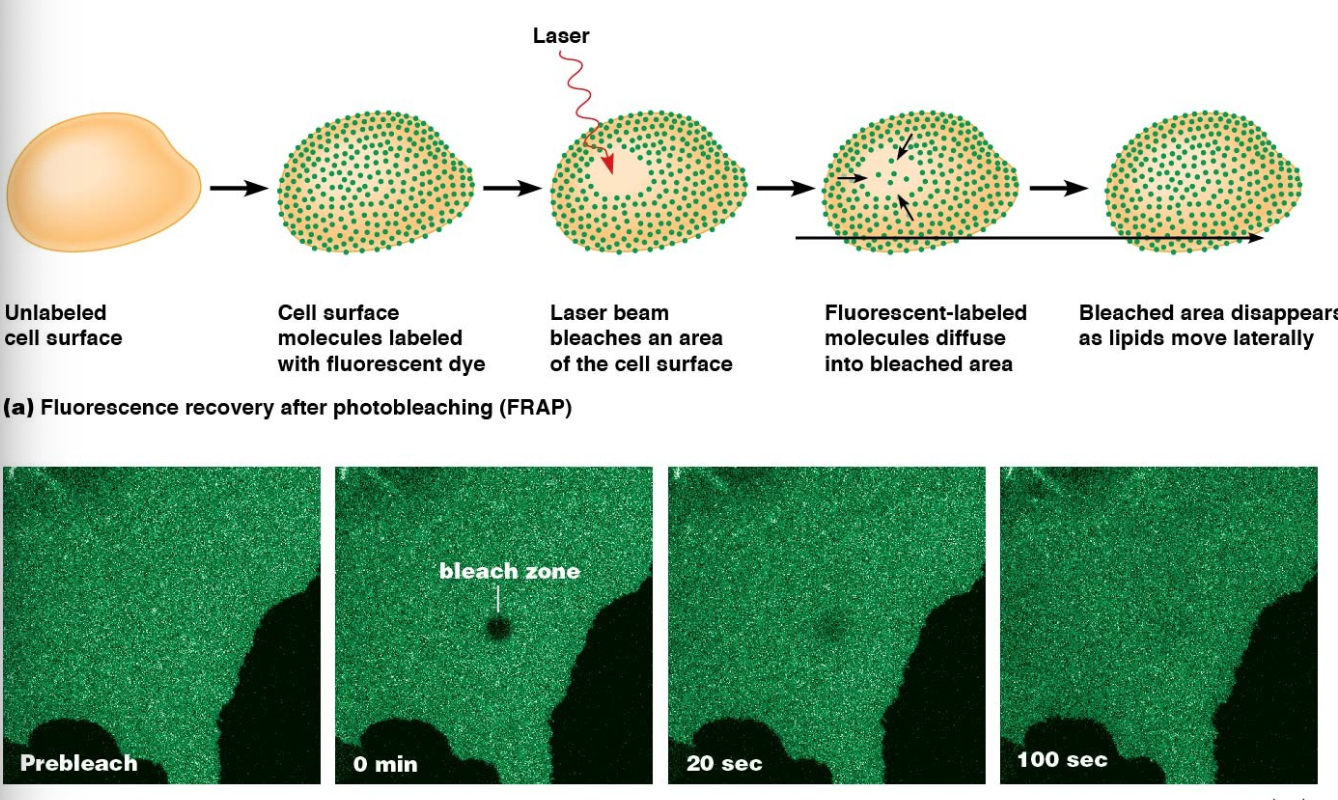
example of FRAP
membrane asymmetry tends to be
maintained
transverse diffusion
also known as flip flop
relatively rare
requires hydrophilic head group to pass through the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
when transverse diffusion does occur
phospholipid flip-flop does occur in natural membranes
inn some membranes the smooth ER membrane have proteins that catalyze the flip flop of membrane lipids
the proteins in phospholipids that allow for transverses diffusion
phospholipid translocators, flippases
membranes fluidity must be
maintained
factors that regulate membrane fluidity
temperatyre, fatty acid structure, incorporation for sterols
how does temperature affect fluidity
temp increases and fluidity increases
fatty acid structure and fluidity
saturation - unsaturated fatty acids increase membrane fluidity
length of hydrocarbon tail, fluidity increases when hydrocarbon length decreases
incorporation of sterols and fluidity
rigidity of sterol structure reduces membrane fluidity at higher temps
rigidity of sterol structure also prevents phospholipids from 0packing too close together and reduces the tendency to gel at cooler temps
membrane fluidity is characterized by tm value aka
temperature at which membrane changes from gel to fluid
lipids with saturated fatty acids pack
tight = less fluid
lipids with unsaturated fatty acids pack
loose = more fluid
the number of double bonds has a ___ effect on membrane fluidity than hydrocarbon chain
much greater
cholesterol iso found on
both inner and outer layers aka leaflets of plasma membrane
cholesterol acts as a ____ decreasing membrane fluidity at temperatures above the Tm and increasing fluidity when temperatures drop below the tm
fluidity buffer
sterols decrease ___
the permeability of the membrane
lipids rafts are
localized regions of membrane lipids that are involved in cell signaling
lipid rafts in the outer monolayer of animal cells have
elevated levels of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids and are less fluid than the rest of the membrane
lipid rafts bind to and concentrate
proteins at certain positions on the plasma membrane
the most prominent lipids in the animal cell membranes are
phospholipids
the mosaic part of the fluid mosaic model includes ____ however ___ are the main components
lipid rafts and other lipid domains
membrane proteins
freeze fracture method
splits a membrane into its two layers, particles the size and shape of globular proteins can be seen
the protein/lipid ratio
varies among cell types
the classes of membrane proteins
integral membrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins and lipid-anchored proteins.
integral membrane proteins
embedded in the lipid bilayer because of their hydrophobic regions
peripheral membrane proteins are
hydrophilic and locate on the surface of the bilayer. they interact with integral membrane proteins and membrane through weak electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding
lipid anchored membrane proteins are
hydrophilic and attached to the bilayer by covalent attachments to lipid molecules embedded in the bilayer
lipid anchored membrane proteins require
covalent medication of the proteins
lipid anchored membrane protein anchor types
fatty acids, isoprenoid and GPI
membrane proteins are oriented ____ across the lipid bilayer
asymmetrically
onice in place in or on one of the monolayers proteins
cannot move across the membrane from one surface to the other
all the molecules of a particular protein are oriented in the ____ way in the membrane
same
many membrane proteins are _____
glycosylated
glycoproteins are
membrane proteins with carbohydrate chains covalently linked to amino acid side chains
the addition of a carbohydrate side chain to a protein is called
glycosylation
glycosylation occurs in ____
the er and Golgi compartments
glycosylation involves the linkage of the carbohydrate to
the nitrogen atom of the amino group
n linked glycosylation ex. asparagine residue
the oxygen group of an atom of a hydroxyl group
O-linked glycosylation of serine, threonine, or modified lysine or proline residue
the easiest membrane protein to dissociate from membranes
peripheral membrane proteins bc non covalent bonds
membrane proteins are more variable than lipids because of
ability to move freely within the membrane
some proteins can move freely whereas others are constrained because
they are anchored to protein complexes
reasons for restricted protein mobility in membranes
anchoring cytoskeleton components (actin)
anchoring to extracellular structures or neighboring cells
large protein complexes that can only move sluggishly in the membrane
incorporation into lipid rafts
Frye and Edidin fused human and mouse cells and used two _____ fluorescent antibodies each with differently colored dye linked to it
fluorescent antibodies
the anti-mouse antibodies were linked to _____ a green dye
fluorescein
the antihuman antibodies were linked to _____, a red dye
rhodamine
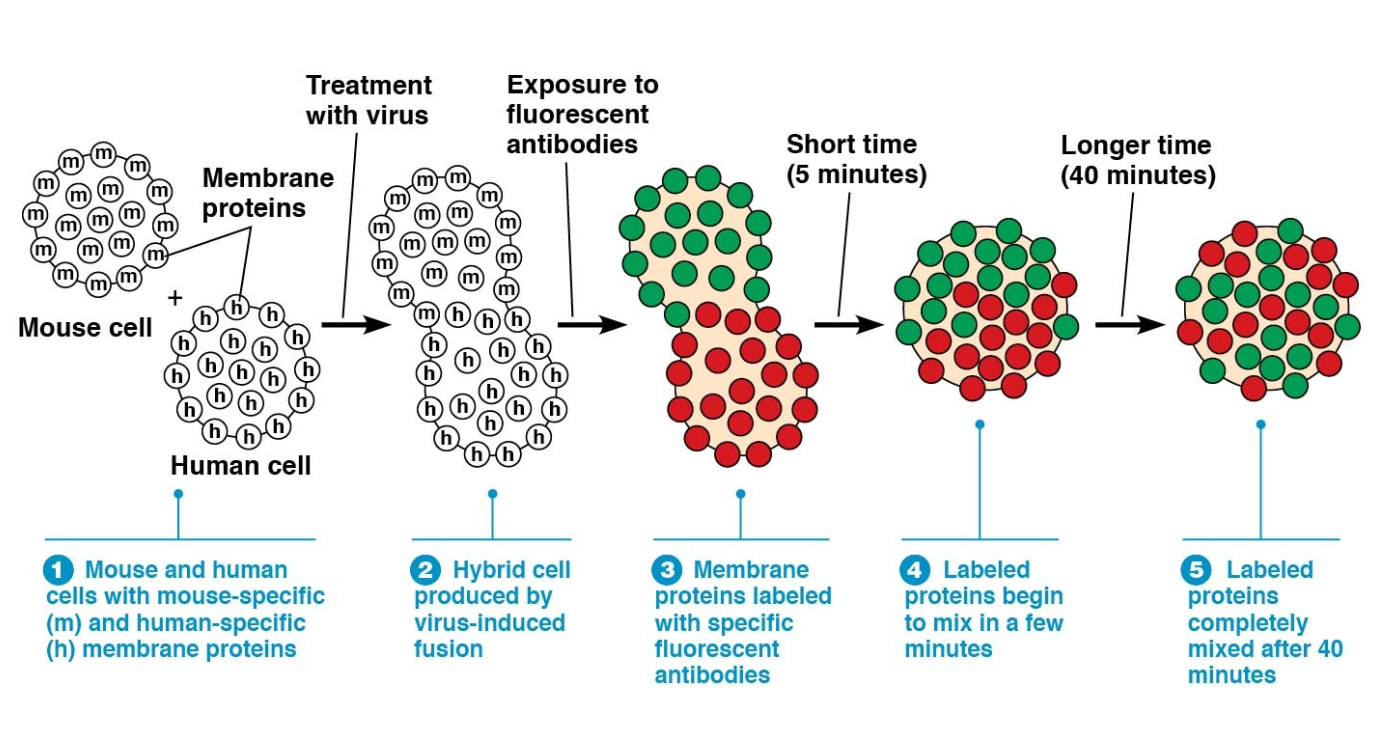
frye and edidion expirements
cholesterol acts as a ____
fluidity buffer
fluidity buffer and cholesterol
decreasing membrane fluidity at temperatures above the Tm and increasing fluidity when temperatures drop below the Tm
sterols ____ the permeability of the membrane
decrease
How are proteins inserted into the
phospholipid bilayer?
through covalently attached lipids and through transmembrane domain made of hydrophobic amino acids
sterols decrease the permeability of the membrane because
more rigid structure than other membrane lipids
passive transport
along a gradient - without net energy input
passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion
active transport
against the concentration gradient
important considerations for transport
solute properties
relative solute concentrations
availability of specific transmembrane proteins
availability of an appropriate energy source
The movement of a molecule that has no net charge
is determined by its
concentration gradient
simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion involve
exergonic movement down the concentration gradient - negative delta G
active transport involves
endergonic movement up the concentration graduate - positive delta G
the movement of an ion is determined by ____
its electrochemical potential
electrochemical potential is
the combined effect of its concentration gradient and the charge gradient across the membrane
the active transport of ions across a membrane creates a charge gradient or _____ across the membrane
membrane potential
abbreviation for membrane potential
Vm
simple diffusion molecules
small polar - h2o, glycerol
small nonpolar - o2 co2
large nonpolar (oils, steroids)
facilitated diffusion
small polar (h2o, glycerol)
large polar, glucose
ions (na, k , ca)
active transport molecules
large polar - glucose
9ions - na, k, ca2+
the best understood of all transport proteins
erythrocyte plasma membrane
the membrane potential is maintained by active transport of _______ inward and _____ outward
potassium ions, sodium ions
special pores or channels allow ______ to enter or leave the cell as rapidly as needed
water and ions
Simple Diffusion
unassisted net movement of a solute from a high to low concentration
only possible for gasses, nonpolar molecules, or small molecules such as water, glycerol, or ethanol
oxygen gas traverses the lipid bilayer readily by ____
simple diffusion
_____ take up oxygen in the lungs, where oxygen concentration is high and release it in the body tissues where oxygen concentration is low
erythrocytes
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
water molecules are not affected by the membrane potential because
they are not charged + small
If two solutions are separated by a selectively permeable membrane, permeable to the water but not the solutes, the water will move toward
the region of higher solute concentration
osmolarity
relative concentration of solutes between cytoplasm and extracellular solution
an animal cell in an isotonic solution
water will be removed
if an animal cell is put into a hypotonic solution
the cell will be lysed as water goes inward