Ch 15- Display & Image Storage
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Bistable images are composed of ____ shades: _____
two; black and white
Gray scale images display ____ levels of brightness
multiple
(white, light grey, medium grey, etc.)
The numerous levels of gray scale allow the system to assign different gray shades to different ____
echo amplitudes
What does contrast determine?
the range of brilliancies (brightness) within the displayed image
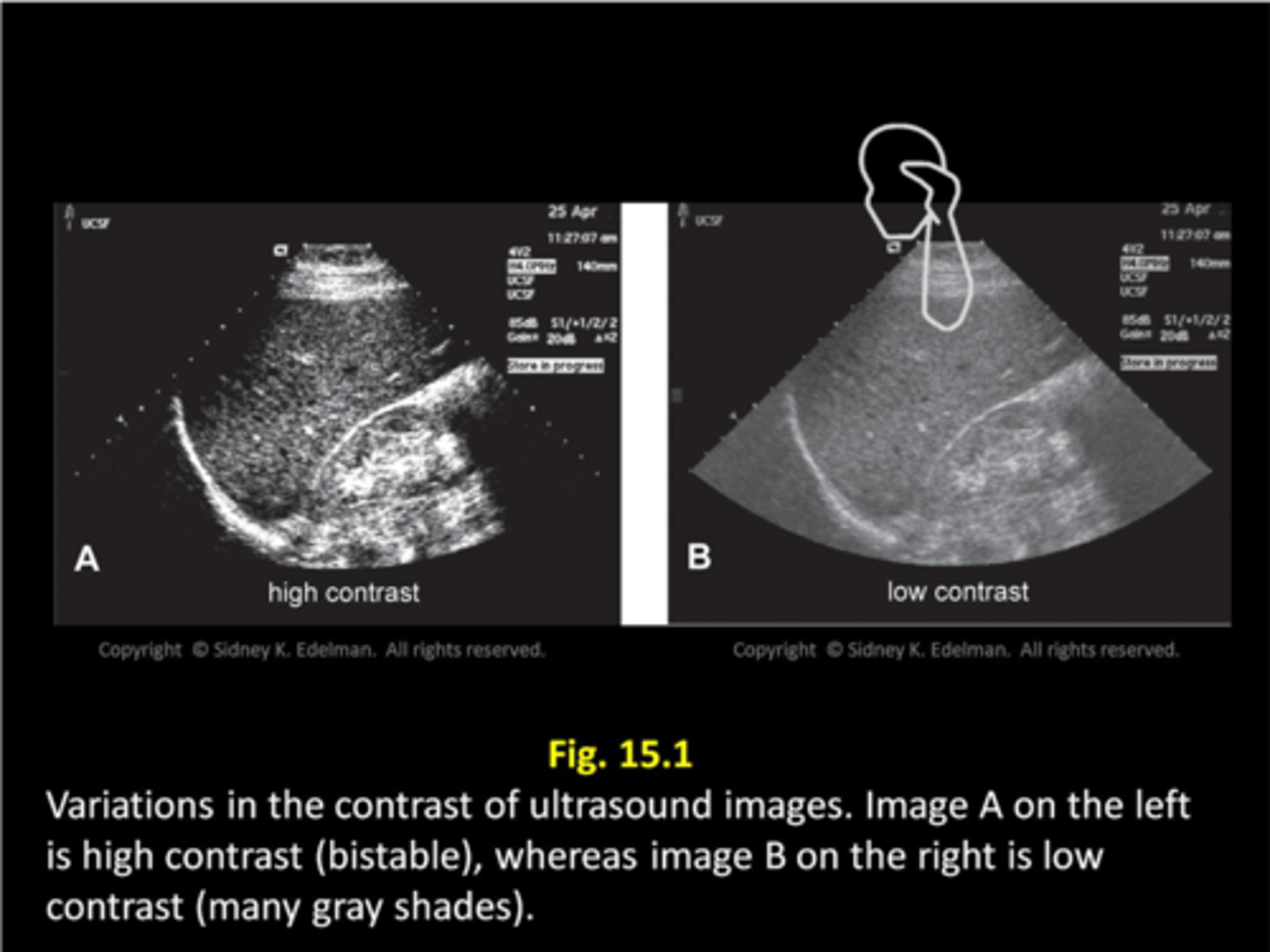
Bistable images are ____ contrast, gray scale images are ____ contrast
high; low
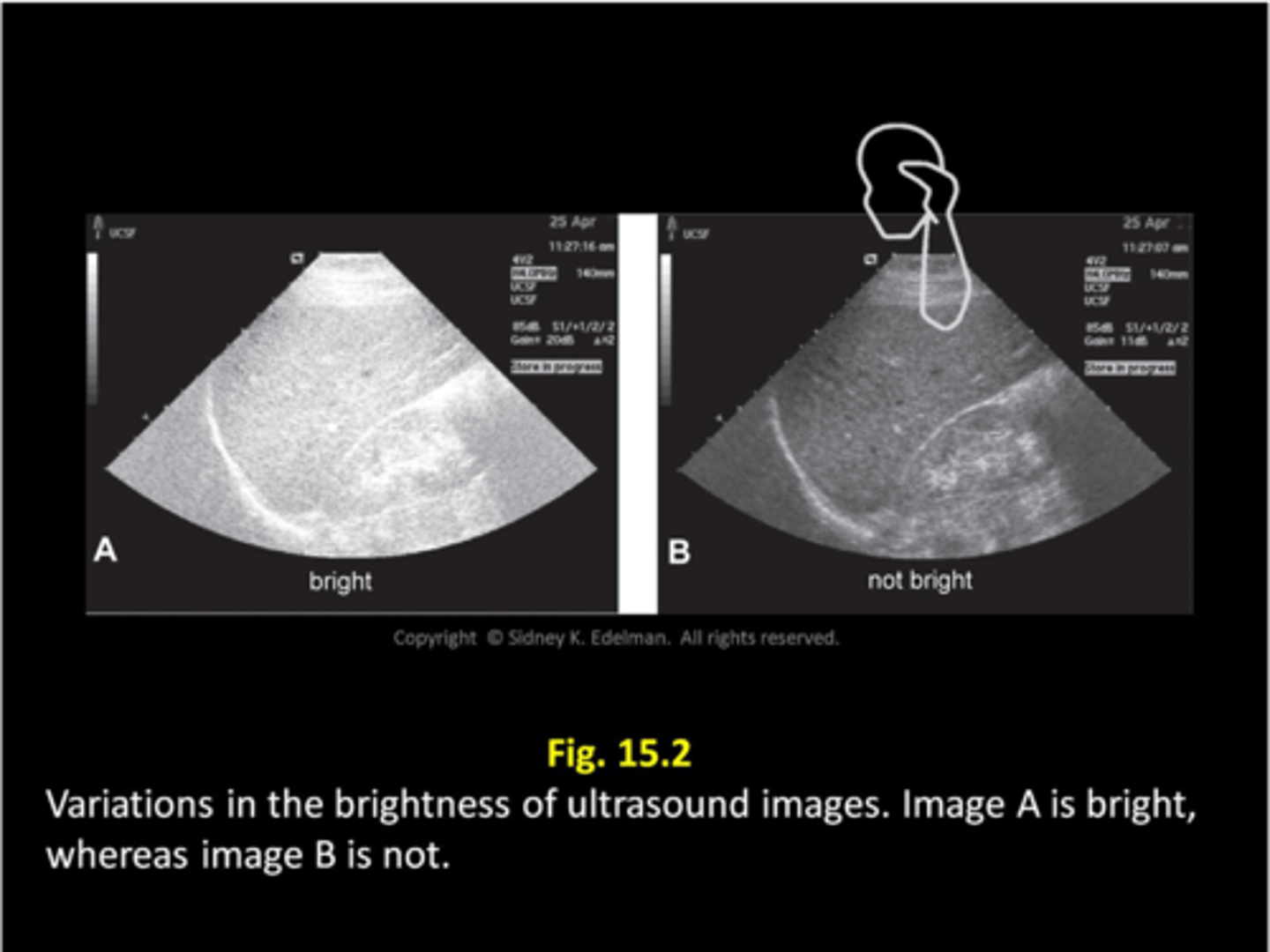
What does brightness determine?
the brilliance of the displayed image
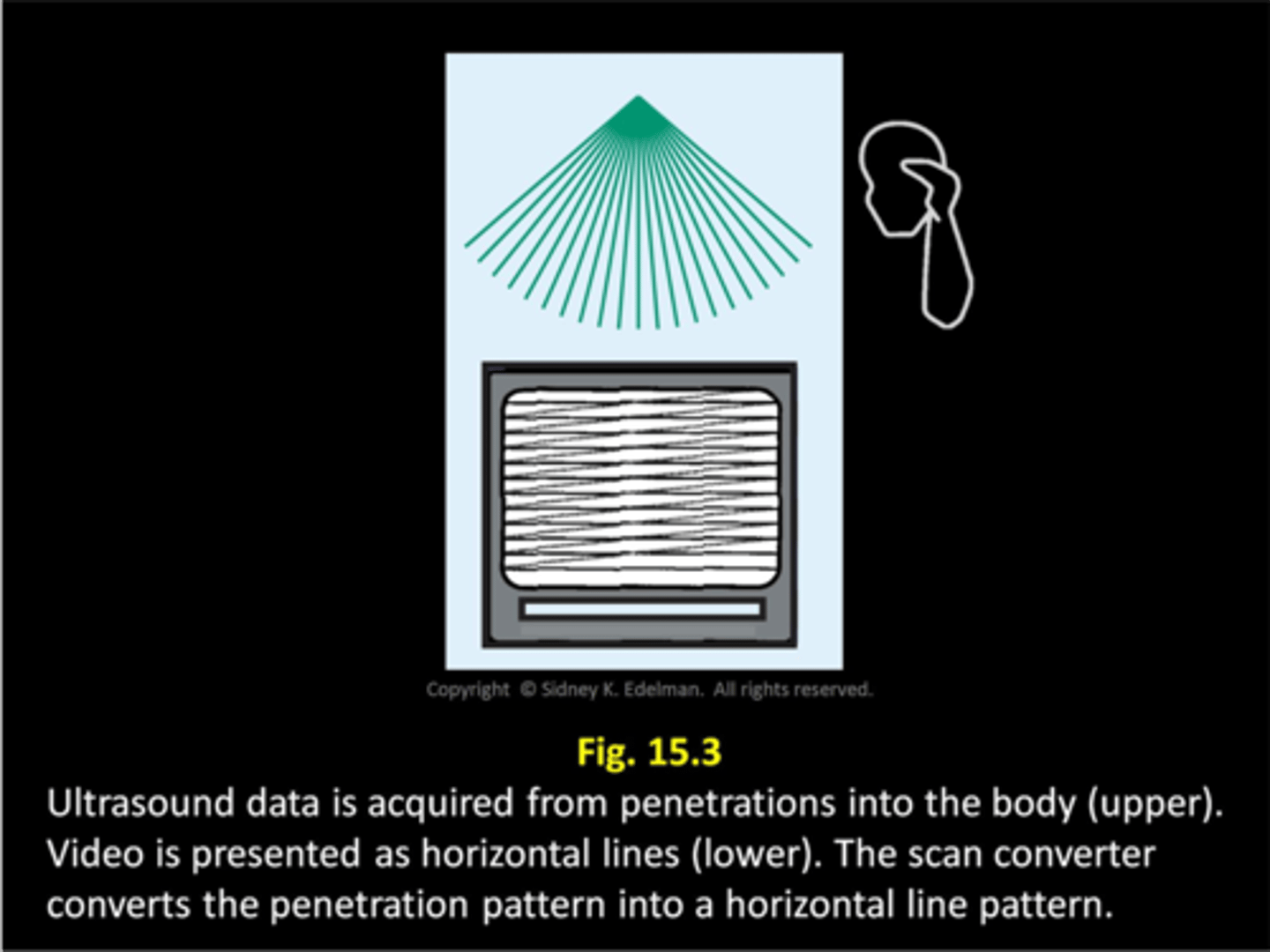
Gray scale imaging was first made possible with the use of ____
scan converters
Scan converters ____ information first, then ____ it later
store; display
Scan converters translate information from ____ format to ____ format
spoke; video
Modern digital scan converters use ____ technology
computer
Analog numbers are "real world" numbers that have ____ values with an ____ number of choices
continuous; unlimited
Ex. weight= 163.998
Digital numbers are "computer world" numbers that have ____ values with a ____ number of choices
discrete; limited
Ex. weight = 164
What type of scan converter is a funnel-shaped vacuum tube with an electron gun at its smaller end?
analog scan converter
In an analog scan converter, ____ are fired from the gun, then strike a ____ ____ where they are stored
electrons; dielectric matrix
The dielectric matrix may be thought of as what?
a picture divided into millions of tiny dots, each containing an electrical storage element (electron bucket)
Stored electrons in each bucket are ____ to retrieve information
read
Analog scan converters have excellent ____ ____
spatial resolution (image detail)
What limitations do analog scan converters have?
1. image fade
2. image flicker
3. instability
4. deterioration
(FFID)
What is digitizing?
using computers to convert images into numbers
How do digital scan converters work?
- digitize images
- images are stored in computer memory as a series of 0's and 1's
- numbers are retranslated into an image before display
What are the advantages of digital scan converters?
1. uniformity
2. stability
3. durability
4. speed
5. accuracy
(USDSA)
What are the two important elements of a digital scan converter?
1. pixel
2. bit
What is a pixel?
picture element; smallest building block of a digital picture

What is pixel density?
pixels per inch
High pixel density is achieved with ____ pixels
small

High pixel density requires ____ pixels per inch
many
Spatial resolution improves with ____ pixel density
high

What is a bit?
binary digit; smallest amount of computer memory
A bit is ____, having a value of either 0 or 1
bistable
What is a binary number?
group of bits
Ex. 01010100110011010
What is a byte?
8 bits
What is a word?
2 bytes or 16 bits
Fewer bits per pixel:
____ shades of gray
____ contrast resolution
fewer
degraded
More bits per pixel:
____ shades of gray
____ contrast resolution
more
improved

Pixels have better ____ resolution, bits have better ____ resolution
spatial; contrast

How many possible shades of gray are displayed with 5 bits of memory?
2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 32 shades of gray
During reception, a transducer produces ____ voltage electrical signals, making them susceptible to ____
low; noise
Digital information is ____ susceptible to noise
less
Translating image information from ____ to ____ and back again is a 5 step process
analog; digital
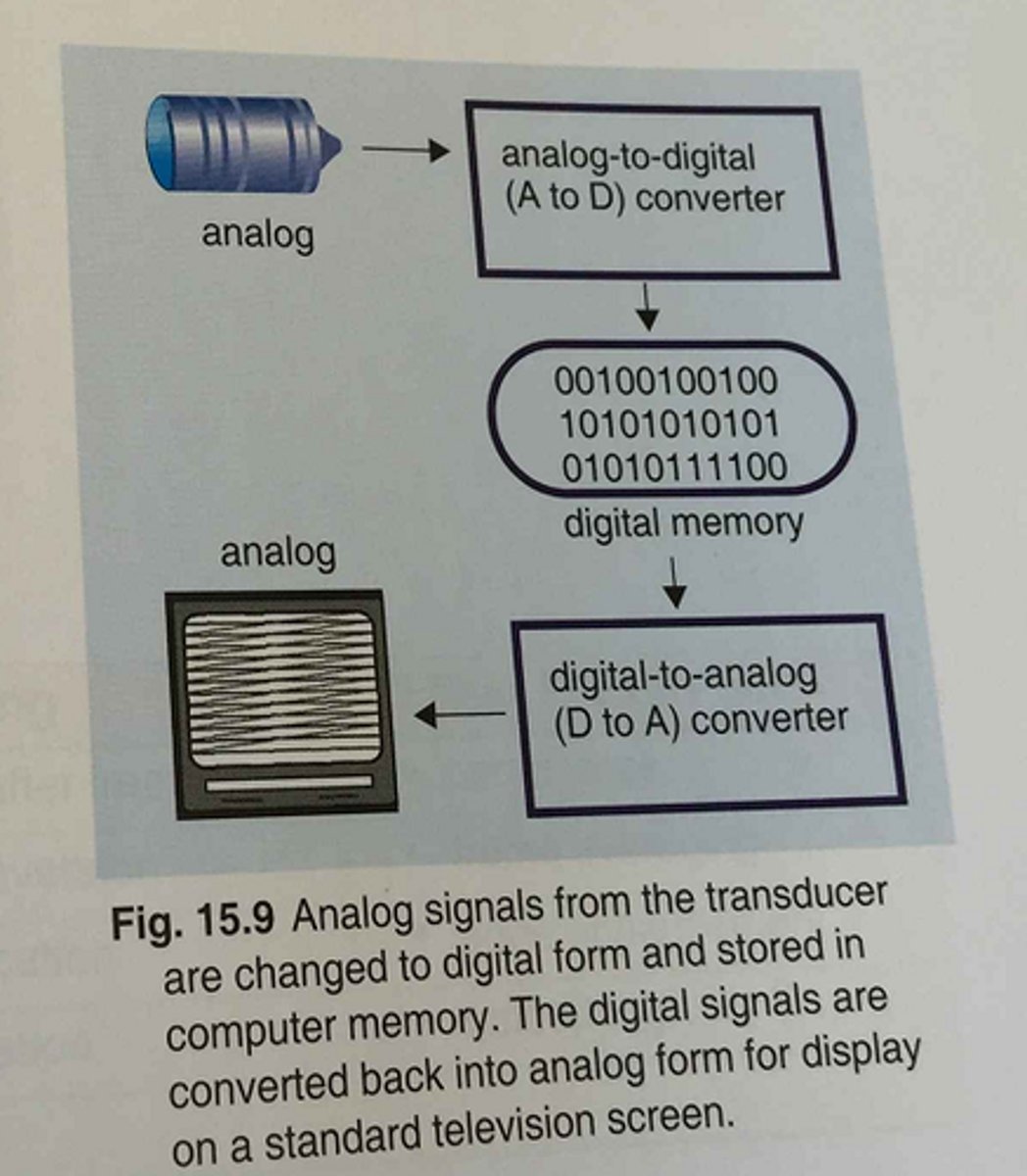
What are the 5 steps of translating image information from analog to digital and back again?
1. analog to digital (A-to-D)
2. preprocessing
3. post processing
4. digital to analog (D-to-A)
5. video display
Summarize the following:
1. analog to digital (A-to-D)
2. preprocessing
3. post processing
4. digital to analog (D-to-A)
5. video display
1. electrical signals created during reception are converted from analog to digital
2. digital information is stored in the scan converter
3. digital image information continues to be processed
4. digital signals in bistable form need to be converted back to analog
5. analog signal displayed on TV
What is pre-processing?
manipulation of image data BEFORE storage
Can pre-processing be reversed or undone?
no
What are examples of pre-processing?
1. TGC
2. log compression
3. write magnification
4. persistence
5. spatial compounding
6. edge enhancement
7. fill-in interpolation
What is post-processing?
manipulation of image data AFTER storage
What are examples of post-processing?
1. any change after freeze frame
2. black/white inversion
3. read magnification
4. contrast variation
5. 3D rendering
Magnification (zoom) enlarges a ____ of an image to fill the entire screen
portion
What is ROI?
region of interest; the selected part of the image

What is RES?
regional expansion selection
What are the 2 forms of magnification?
1. read magnification
2. write magnification
Read magnification occurs during ___
post-processing
What are the 3 steps of read magnification?
1. system scans anatomy
2. image is converted from analog to digital and stored
3. ROI is identified and system reads and displays original data, ROI is NOT rescanned

In read magnification, spatial resolution is ____ because number of pixels in ROI is ____
unchanged; unchanged
Write magnification occurs during ____
pre-processing
What are the 4 steps of write magnification?
1. system scans the anatomy and creates image
2. image is converted from analog to digital and stored
3. ROI is identified, old data is discarded
4. system rescans only the ROI and writes new data into scan converter

In write magnification, spatial resolution is ____ because there is a ____ number of pixels
improved; greater
With write magnification, temporal resolution may improve if bottom of ROI is ____ than the original depth
shallower
Backing material in transducers create ___ pulses but produce ___ intensity
short; high
- The FDA established ___ peak intensity levels for sound beams
- Imaging transducers cannot exceed these limits, which impacts ____
- What is the solution for this?
- maximum
- image quality
- coded excitation
Coded excitation creates ___ sound pulses containing a ___ range of frequencies
long; wide
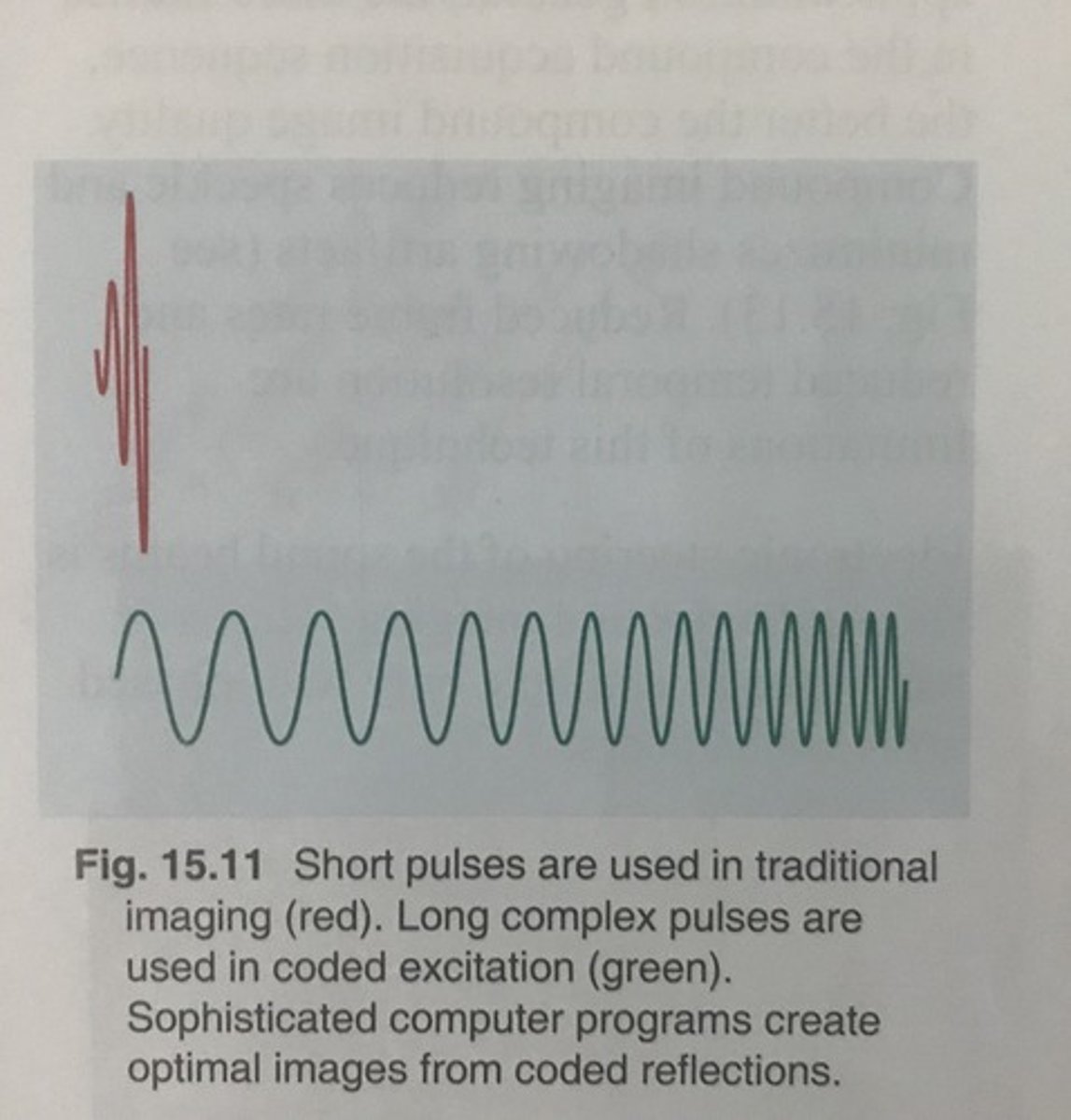
Coded excitation creates a ___ pulse but keeps intensity ___ FDA's limit, improving ___ and ___
strong; below; penetration; resolution
Coded excitation occurs in the ___
pulser
Coded excitation provides:
____ signal-to-noise ratio
____ axial resolution
____ spatial resolution
____ contrast resolution
____ penetration
higher
improved
improved
improved
deeper
Spatial compounding is a method of using sonographic info from several different ___ to produce a ___
angles; single image
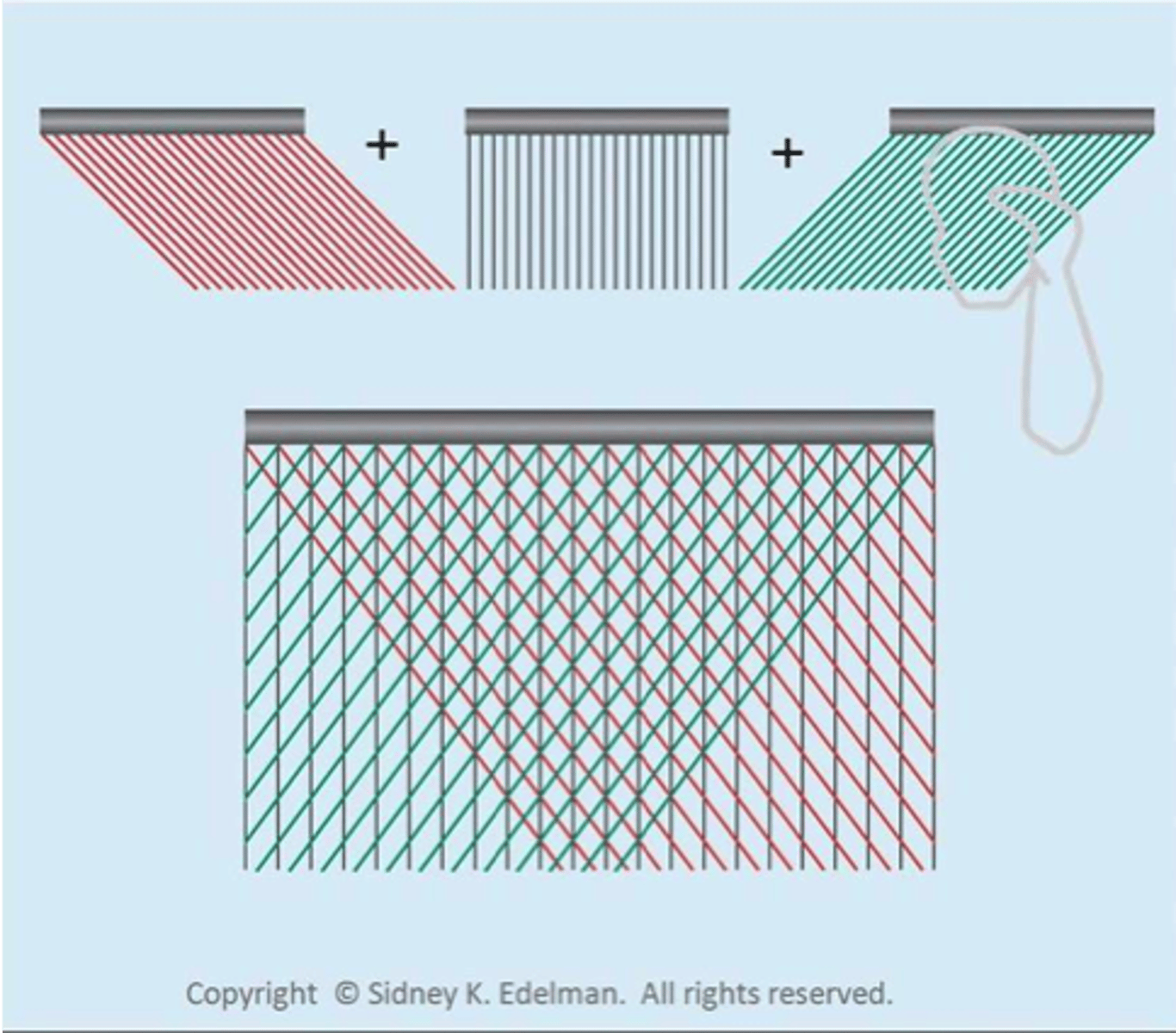
Spatial compounding starts by acquiring ___ frames from ___ views
multiple; different
- Spatial compounding starts by acquiring multiple frames from different views
- Frames are then ___ to form a ___
combined; single image
The more frames in the compound sequence, the ___ the compound image quality
better
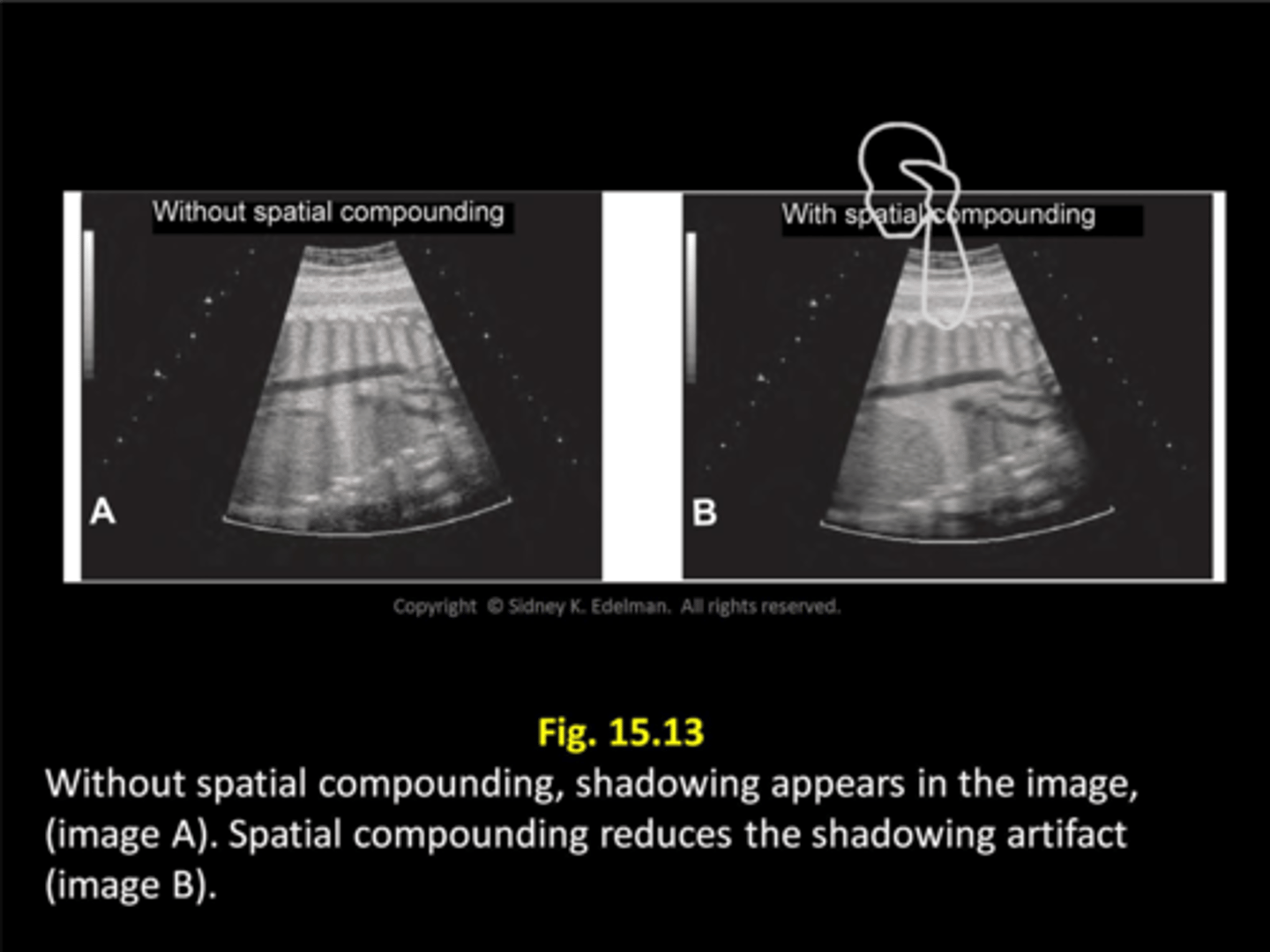
What are limitations of spatial compounding?
- reduced frame rates
- reduced temporal resolution
What type of steering is used in compounding imaging?
electronic
Electronic steering is only available with ___ transducers
phased array
Frequency compounding is an advanced technique that reduces ___ and ___
speckle; noise
With frequency compounding, instead of using a ___ range of frequencies to create an image, the reflected signal is divided into ___ of ___ frequencies
large; sub-bands; limited
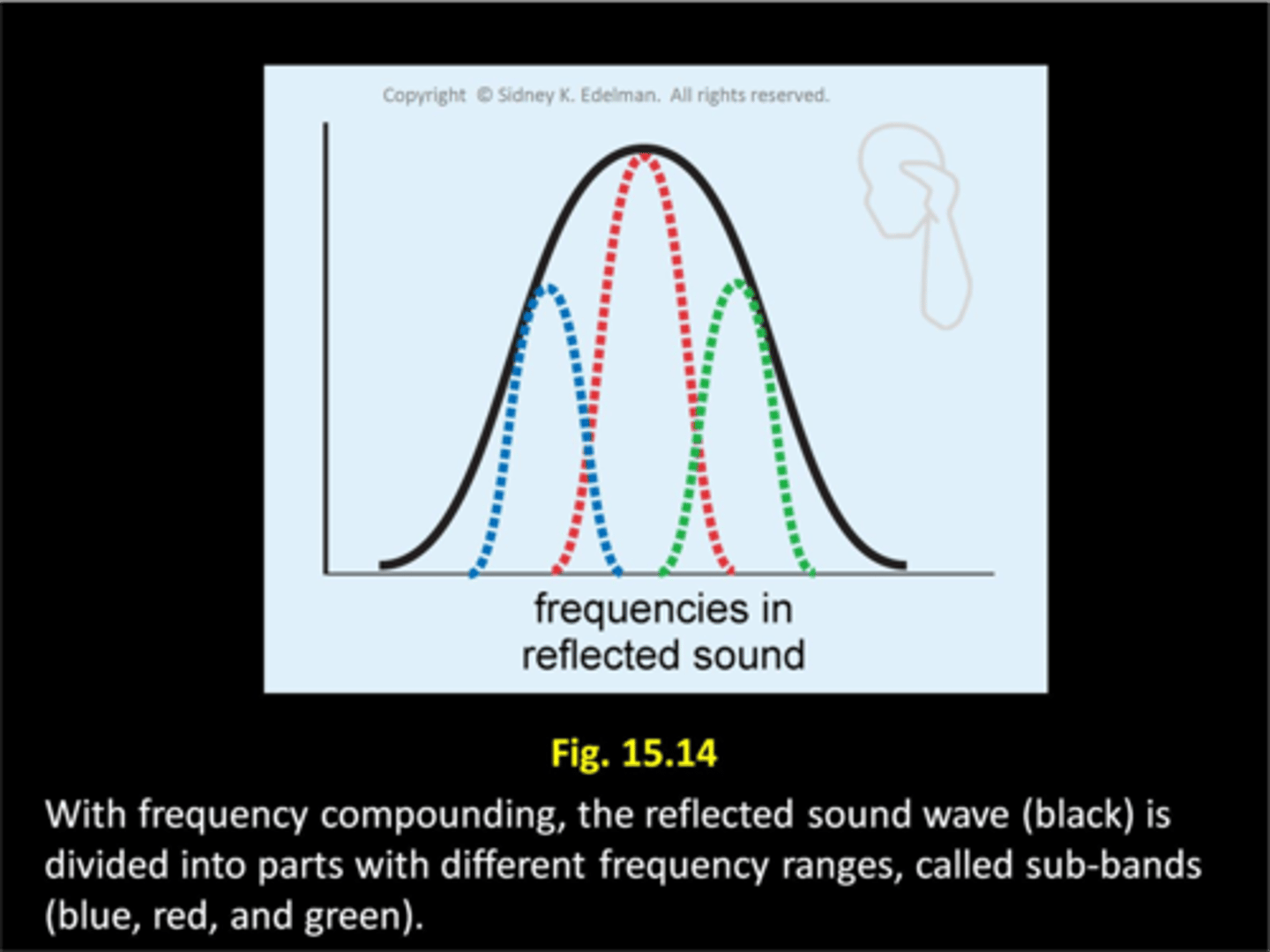
- With frequency compounding, instead of using a large range of frequencies to create an image, the reflected signal is divided into sub-bands of limited frequencies
- Images from sub-bands are then ___ to create a ___
combined; single image
Noise levels of reflections are different from each sub-band, and when combined, noise level is ___
reduced
What is an image processing method that makes pictures look sharper?
edge enhancement
Edge enhancement works by ___ image contrast around the edges
increasing

Edge enhancement creates subtle ___ and ___ highlights on either side of the boundaries to make them appear more ___
bright; dark; defined
Temporal compounding is an image processing technique that does what?
continues to display information from older images
What is temporal compounding also called?
persistence
temporal averaging
Temporal compounding produces a ___ image with:
___ noise
___ signal-to-noise ratio
___ image quality
smoother
reduced
higher
improved
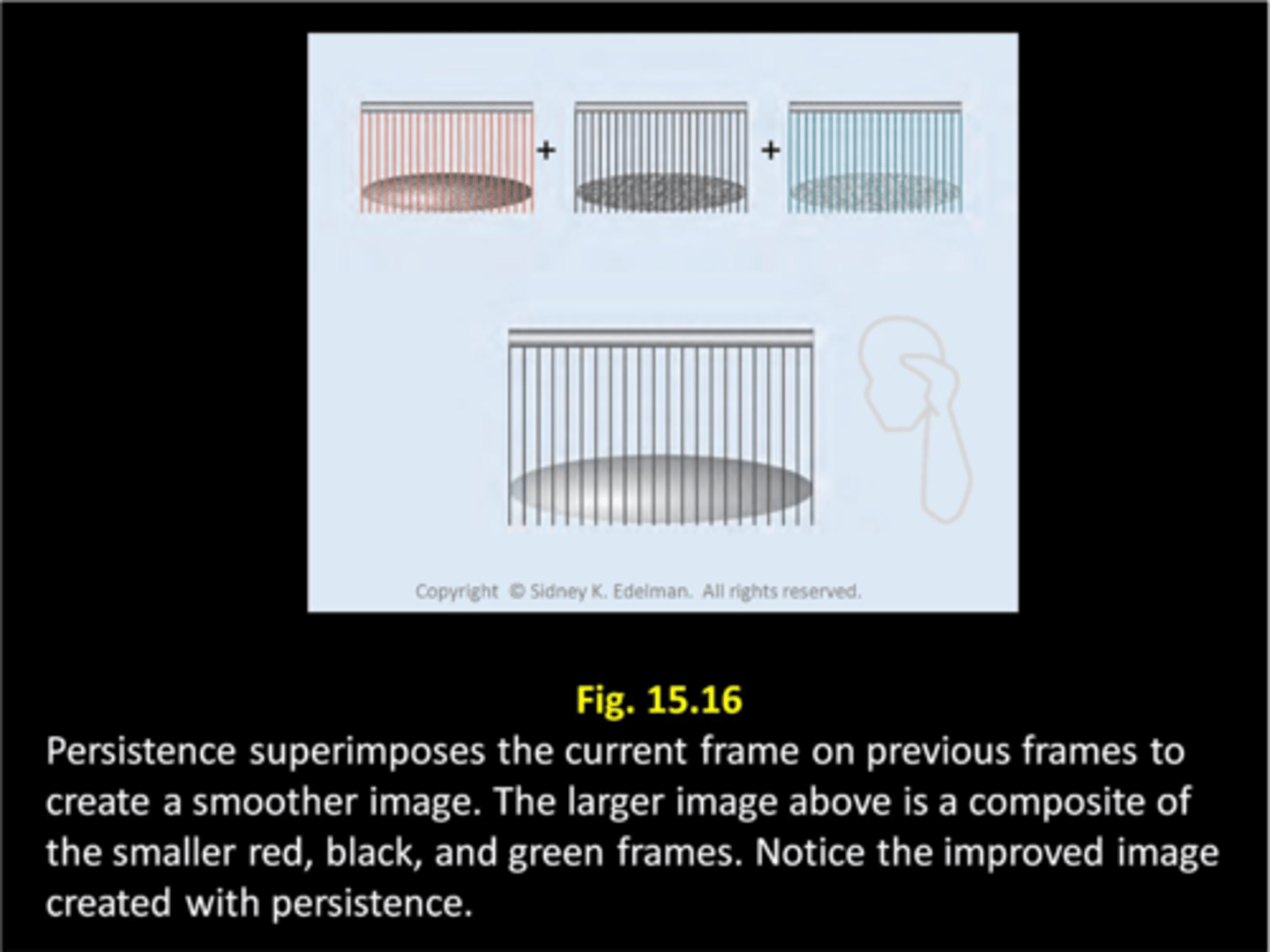
Temporal compounding is most effective with ___ moving structures
slow
What are limitations of temporal compounding?
reduced frame rate
reduced temporal resolution
Fill-in interpolation is a method of constructing what?
new simulated data points to fill in gaps between scan lines
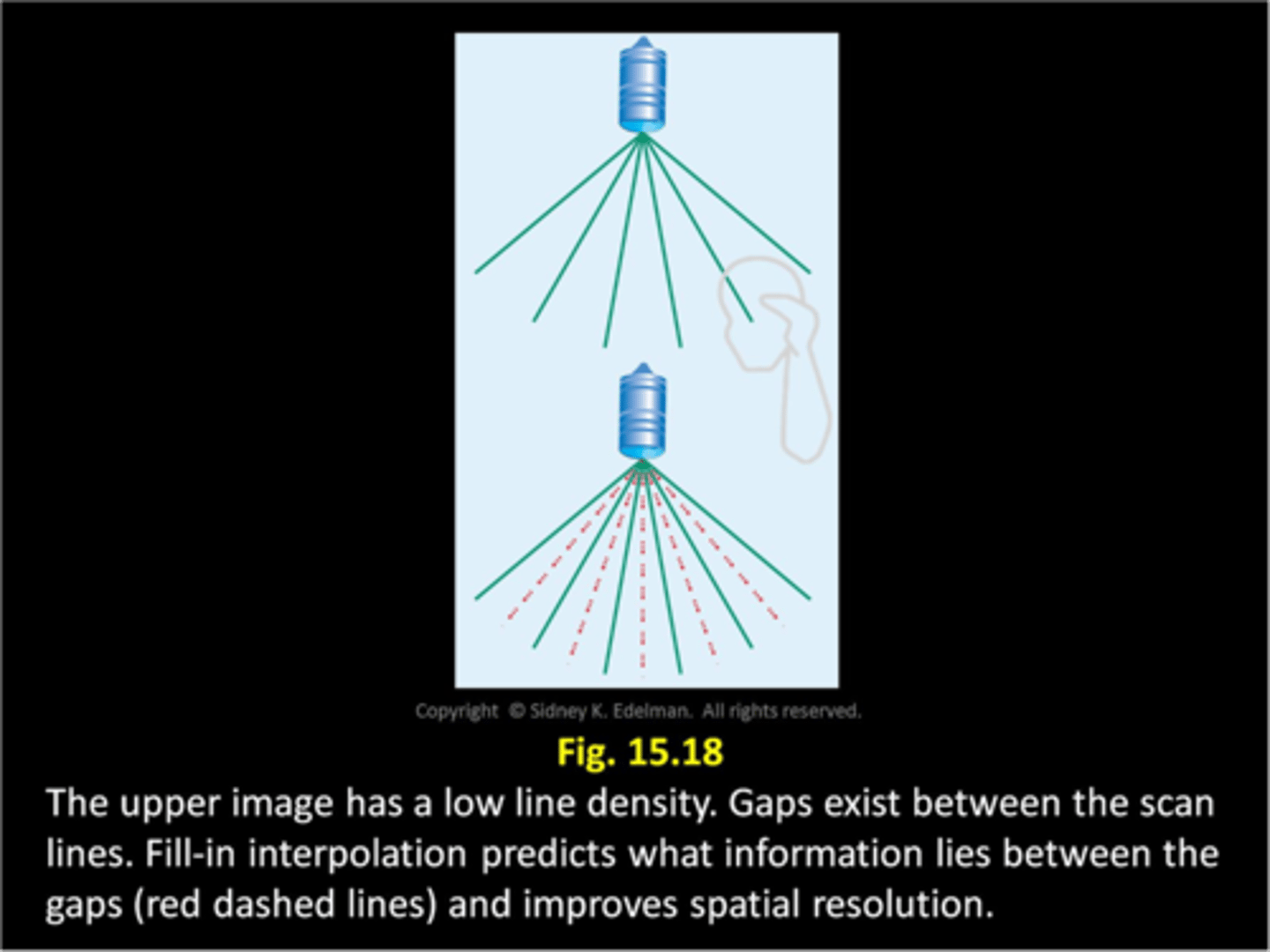
Is interpolation a form or pre or post processing?
pre-processing
As line density increases, spatial resolution is ___
improved
What is the theory that tissues will deform differently after applying force?
elastography
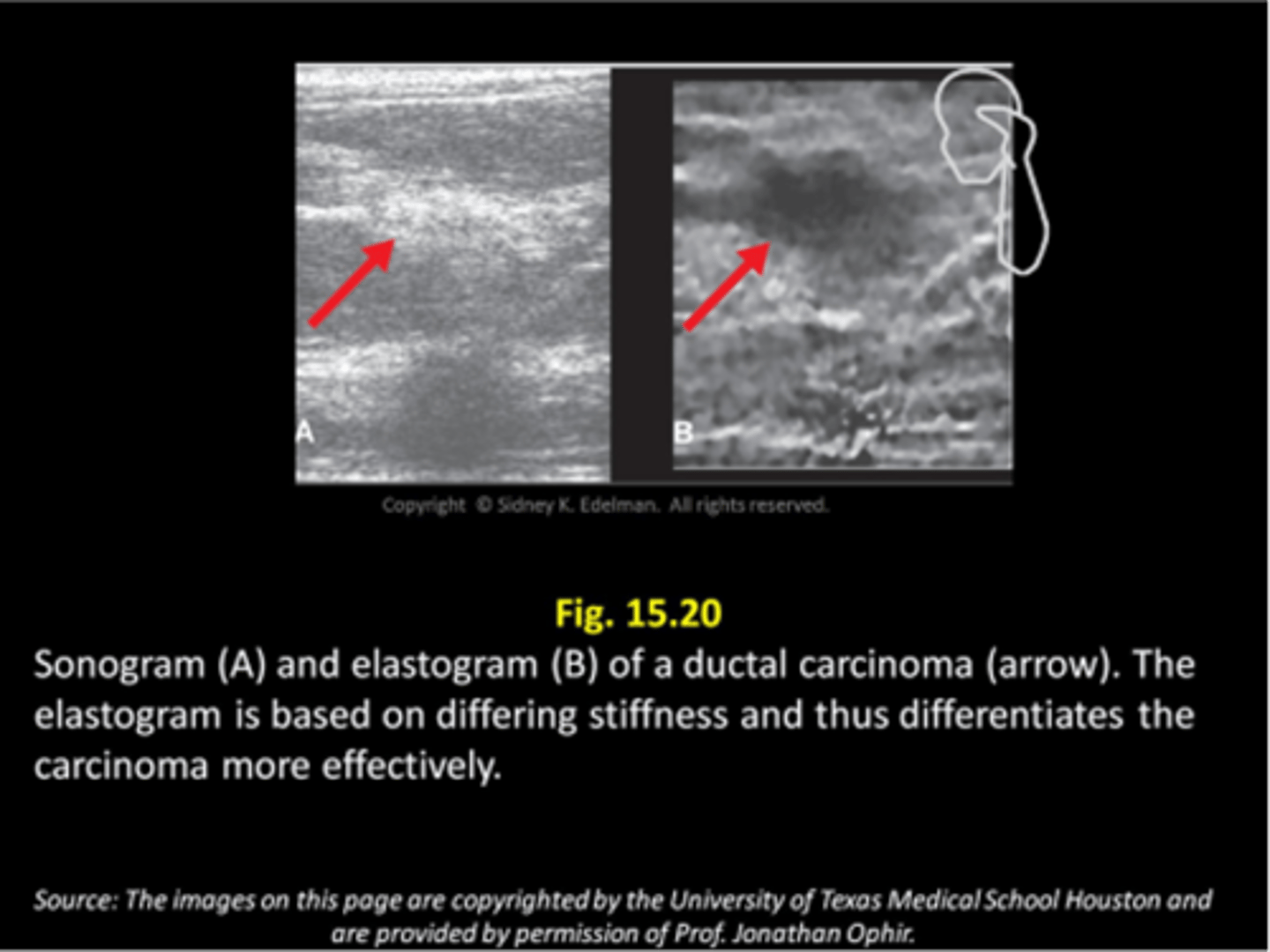
___ data and ultrasound ___ are combined into images called elastograms
stiffness; reflections
What is PACS?
Picture Archiving and Communications System
What are 3 advantages of PACS?
1. instant access
2. no degradation of data
3. "store and forward" technology
What are the primary digital storage devices used in PACS?
computer hard drives
What is DICOM?
Digital Imaging and Computers in Medicine
DICOM is a set of ___ that allows imaging systems to share information on a ___
rules; network
When a system adheres to ___ standards, the system, can connect to a ___ network
DICOM; PACS
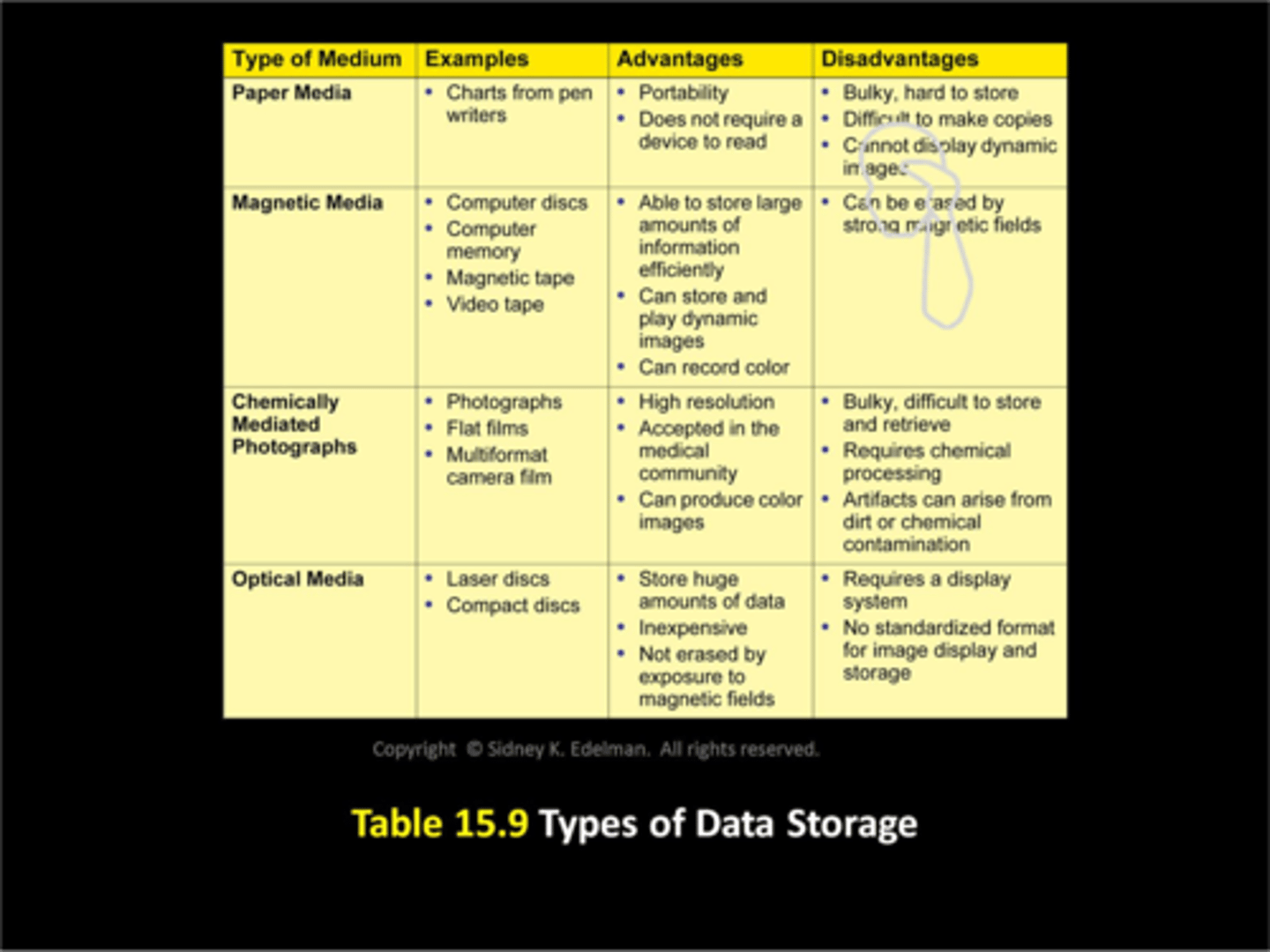
Types of data storage
- paper
- magnetic
- chemically mediated photographs
- optical