DS Exam 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Objective function, Decision variables, Constraints
All optimization problems have these three common elements:
.
.
.
Objective function
____ ____- What will be optimized (maximized or minimized)
Decision variables
____ ____- Values the decision maker is allowed to choose
Constraints
_____- Physical, logical, or economic restrictions or limitations that the decision variables must obey
solution
A ______ to an optimization problem defines a value for each decision variable
feasible solution
A ______ _____ is a solution that satisfies all of the constraints
optimal solution
An ____ ____ is a feasible solution that has the best possible objective function value. Some problems have multiple optimal solutions-different solutions that all achieve the same best objective function value.
feasible region
The ___ ____ is the set of all feasible solutions
possible solutions
The challenge is finding the optimal solution out of all ____ _____ in the feasible region.
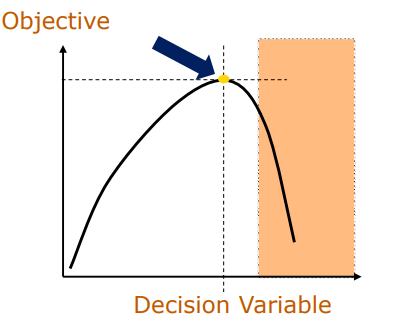
binding/active
Constraint ____/____
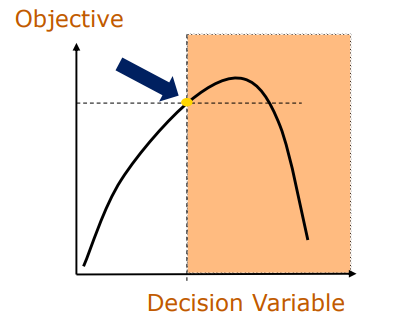
Constraint _____/_____
globally
Local optimum x global solution: Some points may be “Locally” optimal but are not “____” optimal
Define, identify, state, include
Defining a LP Problem:
_____ the function
_____ the decision variables
_____ the constraints
_____ the non-negativity restrictions
Linear programming
In ____ _____, the objective function is a linear function, and all constraints are linear.
Usually solved using the simplex method
Can solve problems with many decision variables and many constraints quickly
Guaranteed to find the global optimum
Can generate informative sensitivity reports
integer programs
In _____ _____, at least one decision variable must be an integer.
The objective and constraints are still linear, but the variable type has changed
Related to linear programs, but much harder to solve in general
There is no guarantee of finding the global optimal solution
Less informative sensitivity reports
Nonlinear programs
_____ _____ have nonlinear objective functions and/or constraints
Solved using a variety of techniques:
Slower than LPs
Stricter limitations on the number of variables or constraints
There may be local as well as global solutions
Sometimes there is no guarantee that you will find the best solution
Less informative sensitivity reports
continuous, integer, binary
Types of optimization problems: Types of variables
______ (decimal numbers)
_____ (whole numbers)
_____ (0 or 1)
Types of optimization problems: Types of functions
_____- the equation would plot as a straight line
____ ___-___- not a straight line, but differentiable
___-____ ___-___- not a straight line and not differentiable
Network Models
____ _____- are an important special case of linear optimization models
nodes, arcs
A network is a set of ____ that are connected by ____ (or “paths”).
objective constraint
____ _____- the cost (or profit) per each unit of variable in the objective function
Binding constraint
____ _____- a constraint that is exactly met at the optimal solution. It limits the solution.
Non-binding constraint.
____-_____ _____- a constraint that is not “tight”, there is slack. The solution could vary without violating it.
slack
_____- the amount by which the left-hand side of a constraint is less than or greater than the right hand side
shadow price
____ ____- change in objective value per 1-unit increase in the constraint RHS. only applies to binding constraints
reduced cost
____ ____- if variable >0, reduced cost = 0
allowable increase/decrease
____ ____/____- the range within the RHS can change without changing the shadow price or variable mix. Beyond this, the model must be resolved.
binding, nonzero shadow price
Is a constraint influencing the solution?
Check if the constraint is ____ and has a ____ shadow price
If yes, then the constraint is influencing the solution
binding
Will changing a constraint affect the mix of variables?
If the constraint is ____, changing it won’t affect the current mix
If it is binding, reducing or increasing the RHS will change the solution.
shadow price
What if I increase a requirement by 1 unit?
Multiple the ____ ____ by the 1-unit increase