Coordination Compounds PART TWO
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bonding Theories, Isomerism. I've skipped colour and organometallic complexes because I really can't lol. Check out my other flashcards too! Answer mode: Answer with Definition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What does Werner’s Theory postulate?
Each central metal ion/atom in a coordination sphere shows two types of valences: primary valency and secondary valency.
What does the primary valency of a central metal atom/ion represent?
the oxidation state of that metal atom/ion
What does the secondary valency of a central metal atom/ion represent
the coordination number of that metal atom/ion.
Is the primary valency of a central metal atom/ion directional or non-directional?
non-directional what the fuck even is this btw
Is the secondary valency of a central metal atom/ion directional or non-direction
directional
Which valency of the central metal atom/ion is ionisable? (primary/secondary valency)
primary
Which valency of the central metal atom/ion is NOT ionisable? (primary/secondary valency)
secondary
What is the coordination number of Fe^{2+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Fe^{3+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Co^{3+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Pt^{4+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Cr^{3+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Ru^{2+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Os^{3+}?
6
What is the coordination number of Pt^{2+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Ni^{2+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Cu^{2+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Zn^{2+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Au^{3+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Hg^{2+}?
4
What is the coordination number of Ag^{1+}?
2
What is the coordination number of Mo^{3+}?
8
What sort of molecules can satisfy a central metal atom’s primary valency?
(anions, cations, neutral molecules)
only anions
What sort of molecules can satisfy a central metal atom’s secondary valency?
(anions, cations, neutral molecules)
anions and neutral molecules
If a central metal atom has a coordination number of 2, what is its hybridisation?
sp
linear
If a central metal atom has a coordination number of 4, what are its possible hybridisations?
sp³ (tetrahedral)
dsp² (square planar)
If a central metal atom has a coordination number of 6, what are its possible hybridisations?
sp³d² (octahedral)
d²sp³ (octahedral)
If a central metal atom has a coordination number of h, what is its hybridisation?
dsp³ (trigonal bipyramidal)
What are inner orbital complexes / low spin complexes?
complexes where the central metal atom has its inner (n-1)d orbital participating in hybridisation
What are outer orbital complexes / high spin complexes?
complexes where the central metal atom has its outer nd orbital participating in hybridisation
What are Weak Field Ligands?
Ligands that cannot force electrons to pair up in the central metal atoms/ions.
What are the three main groups for donor atoms of Weak Field Ligands?
Sulphur
Halogens
Oxygen
What are the three main groups for donor atoms of Strong Field Ligands?
Nitrogen
Carbon
Phosphorus
What is the formula for calculating the magnetic moment of a complex?
\sqrt{n(n+2)}
where n is the number of unpaired electrons
What is the hybridisation of [Fe(CN)_6]^{3+}?
d²sp³
What is the hybridisation of [FeF_6]^{3-}?
sp³d²
What is the hybridisation of [Ni(CN)_4]^{2-}?
dsp²
What is the hybridisation of [NiCl_4]^{2-}?
sp³
What is the hybridisation of [Ni(CO)_4]?
(special case)
sp³
this is because the s orbital must be empty always for hybridisation.
What is the hybridisation of [Cu(NH_3)_4]^{2+}?
(special case)
dsp²
this is because dsp² is more stable than sp³ with one unpaired electron.
What does the Effective Atomic Number of a metal ion denote?
It tells us about the number of electrons in a central metal ion after making coordinate bonds with ligands.
What is EAN’s rule?
Complexes having an Effective Atomic Number equal to the atomic number of the next noble gas are found to be extra stable.
What is the formula for calculating Effective Atomic Number of a central metal ion/atom?
EAN=Z-OS+2CN
EAN = \text{atomic number of metal} - \text{oxidation state of metal} + \text{the number of electrons provided by ligands through coordinate bonds}.
What is the main postulate of Crystal Field Theory?
When a ligand approaches the central metal ion, the degenerate d orbitals of the metal ion undergo splitting into two sets (e_g and t_{2g}).
What is crystal field splitting energy?
The energy difference between the two split sets of d orbitals under Crystal Field Theory.
How does the Crystal Field strength of a ligand affect \Delta i.e. the Crystal Field Splitting Energy of a metal atom/ion’s d orbitals?
\Delta \propto \text{crystal field strength of ligand}.
What does the d_{xy} orbital look like?
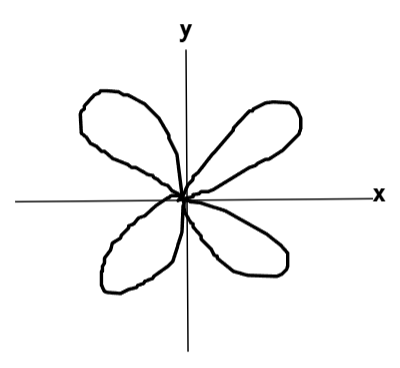
What does the d_{yz} orbital look like?
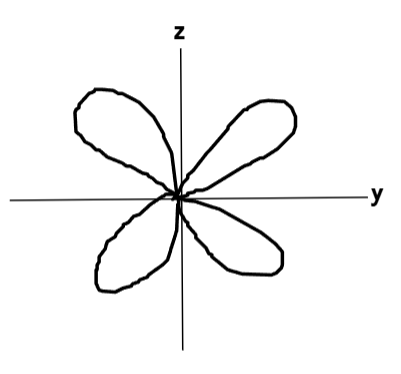
What does the d_{zx} orbital look like?
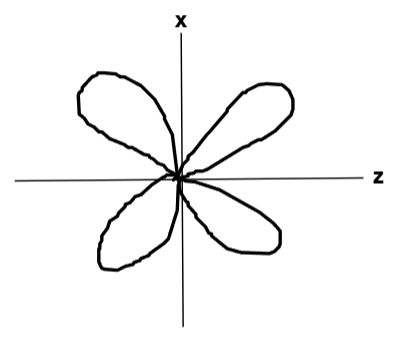
What does the d_{x²-y²} orbital look like?
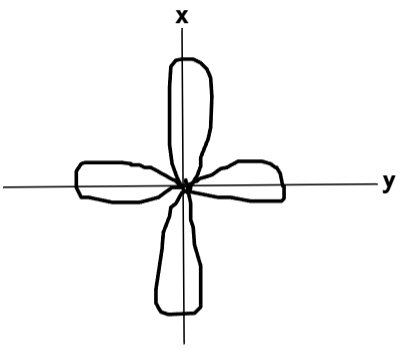
What does the d_{z²} orbital look like?
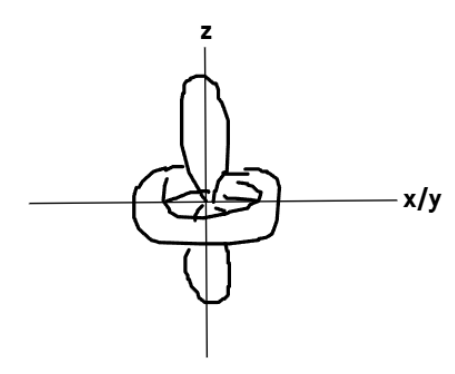
Which d orbitals are axial orbitals?
d_{x²-y²} and d_{z²}
Which d orbitals are non-axial orbitals?
d_{xy}, d_{yz} and d_{zx}
What are axial orbitals called?
(t_{2g} / e_g)
e_g
What are non-axial orbitals called?
(t_{2g} / e_g)
t_{2g}
How does the diagram of the splitting of d orbitals look in the presence of SFLs and WFLs in an octahedral complex?
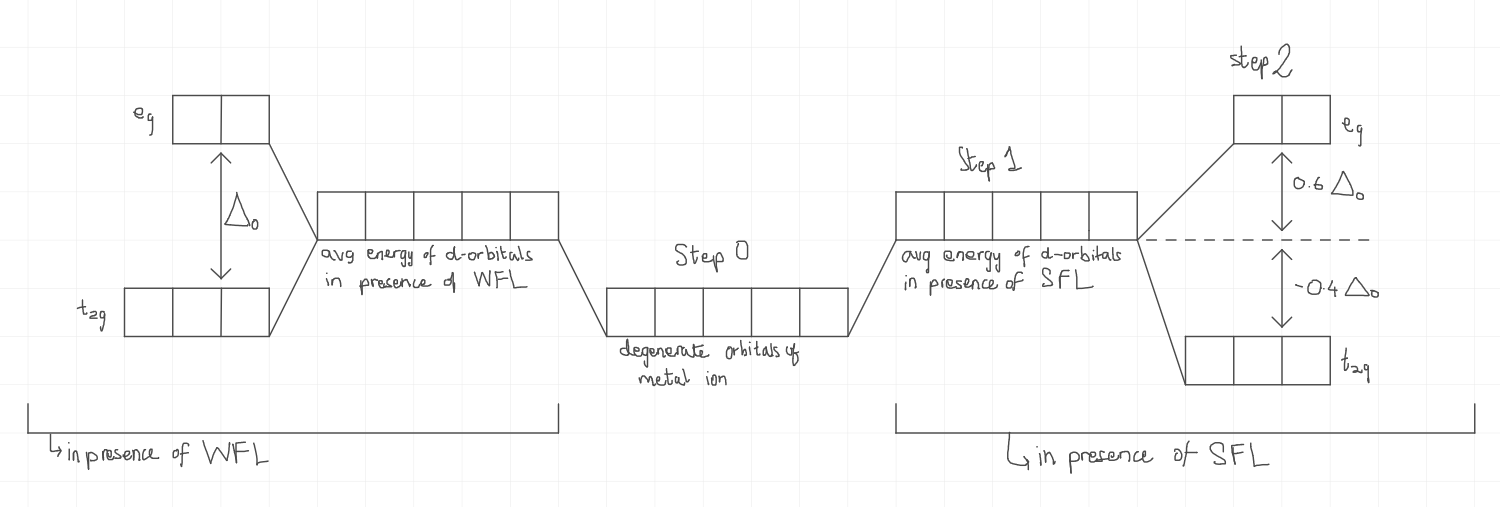
What is pairing energy?
The energy required to force two unpaired electrons into one orbital is called pairing energy.
In the presence of Strong Field Ligands, which one is greater; Crystal Field Splitting Energy or Pairing Energy?
Crystal Field Splitting Energy
In the presence of Weak Field Ligands, which one is greater; Crystal Field Splitting Energy or Pairing Energy?
Pairing Energy
What is Crystal Field Stabilisation Energy?
It is the energy by which complex compounds get stable due to the splitting of d orbitals.
What is the formula for calculating Crystal Field Stabilisation Energy in an octahedral complex?
CFSE = (0.6\times\Delta_o\times n_{e_g})+(-.04\times\Delta_o\times n_{t_{2g}})+np
Where:
\Delta_o is the crystal field splitting energy in an octahedral complex
n_{e_g} is the number of electrons in the e_g orbitals
n_{t_{2g}} is the number of electrons in the t_{2g} orbitals
n is the number of pairing done by SFLs (\therefore in WFLs this value is 0)
p is the pairing energy
The low spin complex of a d^6 cation in an octahedral complex will have what Crystal Field Stabilization Energy? (in terms of \Delta_o and p)
CFSE = (0.6\times\Delta_o\times0)+(-0.4\times\Delta_o\times6)+3p
CFSE = -2.4\Delta_o + 3p
In an octahedral complex, which orbitals have more energy, e_g or t_{2g}?
e_g
In a tetrahedral complex, which orbitals have more energy, e_g or t_{2g}?
t_{2g}
How does the diagram of the splitting of d orbitals look in the presence of SFLs and WFLs in a tetrahedral complex?
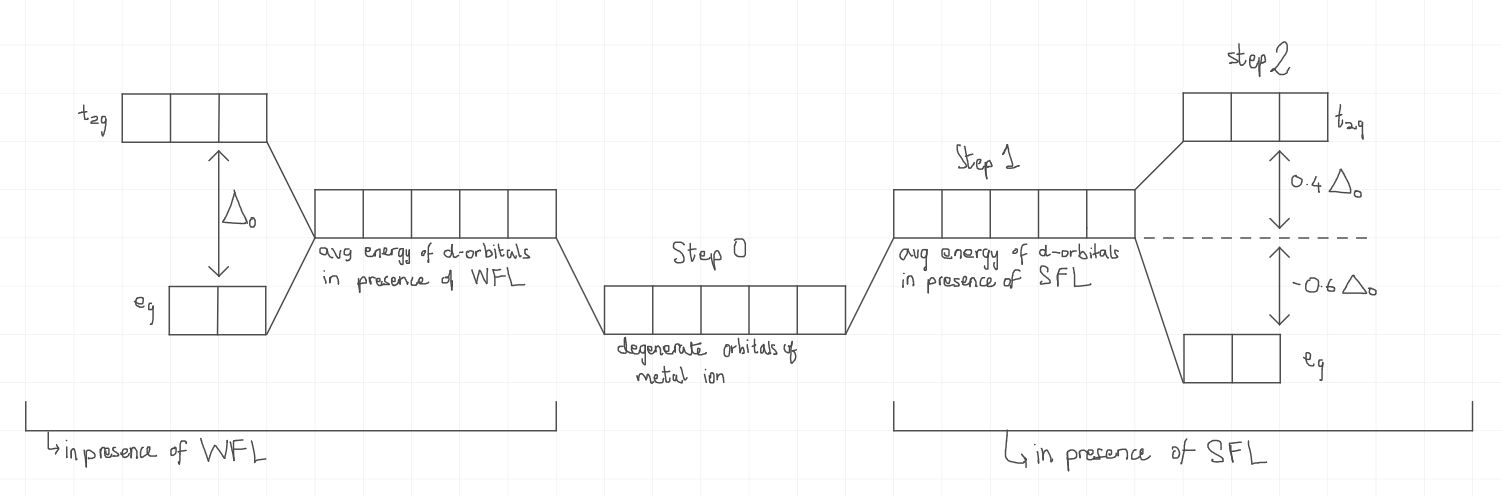
What is the formula for calculating Crystal Field Stabilisation Energy in an octahedral complex?
CFSE = (0.4\times\Delta_t\times n_{e_g})+(-0.6\times\Delta_t\times n_{t_{2g}})+np
Where:
\Delta_t is the crystal field splitting energy in an tetrahedral complex
n_{e_g} is the number of electrons in the e_g orbitals
n_{t_{2g}} is the number of electrons in the t_{2g} orbitals
n is the number of pairing done by SFLs (\therefore in WFLs this value is 0)
p is the pairing energy
What is the relationship between \Delta_o and \Delta_t?
\Delta_o is the crystal field splitting energy in an octahedral complex
\Delta_t is the crystal field splitting energy in an tetrahedral complex
\Delta_o=\dfrac94\Delta_t
\Delta_o is greater
List the spectrochemical series as best as you can.
(good luck 💀)
Weak Field Ligands:
I− < Br− < S2− < SCN− < Cl− < NO3− < N3− < F− < OH− < C2O42− < H2O
Strong Field Ligands:
NCS− < CH3CN < py < NH3 < en < bipy < phen < NO2− < PPh3 < CN− < CO
How does the oxidation state of the central metal ion affect the stability of the complex?
the greater the oxidation state, the more stable the complex
For a group complexes with the same oxidation number (of metal ion), same ligands, and same coordination number, how would you determine which one is more stable?
Greater the Z_{\text{eff}}, more stable the complex
How does chelation affect the stability of a complex?
Chelating ligands are more stable than non-chelating ligands.
Which ligands make the complex more stable; SFLs or WFLs?
SFLs
How does the number of rings in a complex affect the stability of the complex?
the more the number of rings, the more stable the complex.
What is Ionisation isomerism?
Coordination compounds that have the same composition but different ions in solution.
What sort of isomerism do these two show?
[Co(NH_3)_5Cl]Br
[Co(NH_3)_5Br]Cl
Ionisation isomerism
What is hydrate/solvate isomerism?
The coordination compounds that have the same composition but a different number of H_2O molecules present as ligands?
What sort of isomerism do these two show?
[Cr(H_2O)_5Cl]Cl_2\cdot H_2O
[Cr(H_2O)_4Cl_2]Cl\cdot 2H_2O
hydrate/solvate isomers
What sort of isomers give different confirmative tests?
ionisation isomers
What is coordination isomerism?
Isomerism caused by the interchange of ligands and metal ions between two complex ions of the same complex
(yeah both the anion and cation in the compound are complex)
What sort of isomerism do these two show?
[Pt(NH_3)_3Cl][CuCl_3(NH_3)]
[Pt(NH_3)_4][CuCl_4]
coordination isomerism
What is linkage isomerism?
The coordination compounds that have the same composition but differ in mode of attachment of ligand to metal ion.
(i.e. ambidentate ligands must be present)
What sort of isomerism do these two show?
[Co(NH_3)_5NO_2]Cl_2
[Co(NH_3)_5B(ONO)]Cl_2
linkage isomerism
What are stereoisomers?
Isomers that have the same formula, same composition, but differ in the orientation of ligands around the metal atom.
What are geometrical isomers?
Isomers of compounds where ligands occupy different positions around the central metal ion.
What are cis-isomers?
Isomers where two identical ligands are coordinated to the central metal ion from the same side.
What are trans-isomers?
Isomers where two identical ligands are coordinated to the central metal ion from opposite sides.
What is the characteristic of optically active isomers?
Isomers are due to lack of center/plane of symmetry
What is the characteristic of optically inactive isomers?
Isomers are due to existence of center/plane of symmetry
What sort of geometry must a 4-coordinated complex have for it to definitely not show geometrical isomerism?
tetrahedral geometry
Under what condition can 4-coordinated tetrahedral complexes show optical isomerism?
If all 4 ligands are different, it can show optical isomerism.
Depict the cis and trans isomers of a complex with the general formula [Ma_2b_2].
(a and b are both monodentate)

Depict the cis and trans isomers of a complex with the general formula [Ma_2bc].
(a and b and c are both monodentate)

Can a complex with the general formula [Ma_4] show geometrical isomerism?
no
Can a complex with the general formula [Ma_2b_2] show geometrical isomerism?
yes
Can a complex with the general formula [Ma_2bc] show geometrical isomerism?
yes
Can a complex with the general formula [Ma_3b] show geometrical isomerism?
no
Depict the geometrical isomers of a complex with the general formula [Mabcd].
(a and b and c and d are both monodentate)
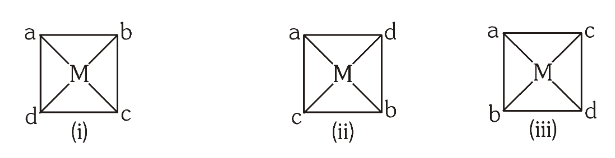
Can a complex with the general formula [M(AA)bc] show geometrical isomerism?
(AA is bidentate with the same donor atom, b and c are monodentate)
no
Can a complex with the general formula [M(AB)cd] show geometrical isomerism?
(AB is bidentate with different donor atoms, c and d are monodentate)
yes
Can a complex with the general formula [M(AA)_2] show geometrical isomerism?
(AA is bidentate with the same donor atom)
no