Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Structure, Function, and Transport Mechanisms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
The nucleus encloses DNA within a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, dividing the cell into cytoplasm and nucleoplasm.
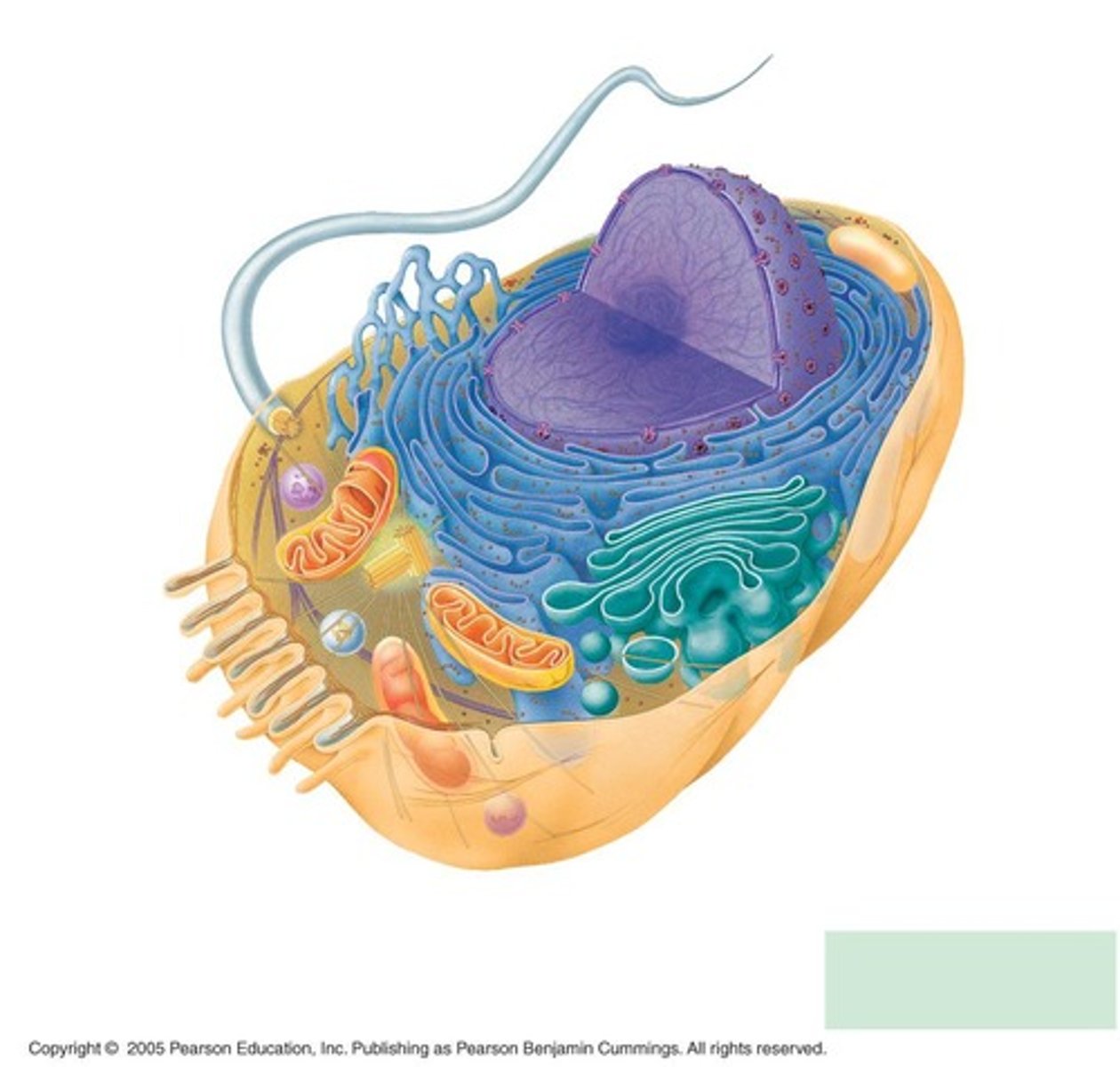
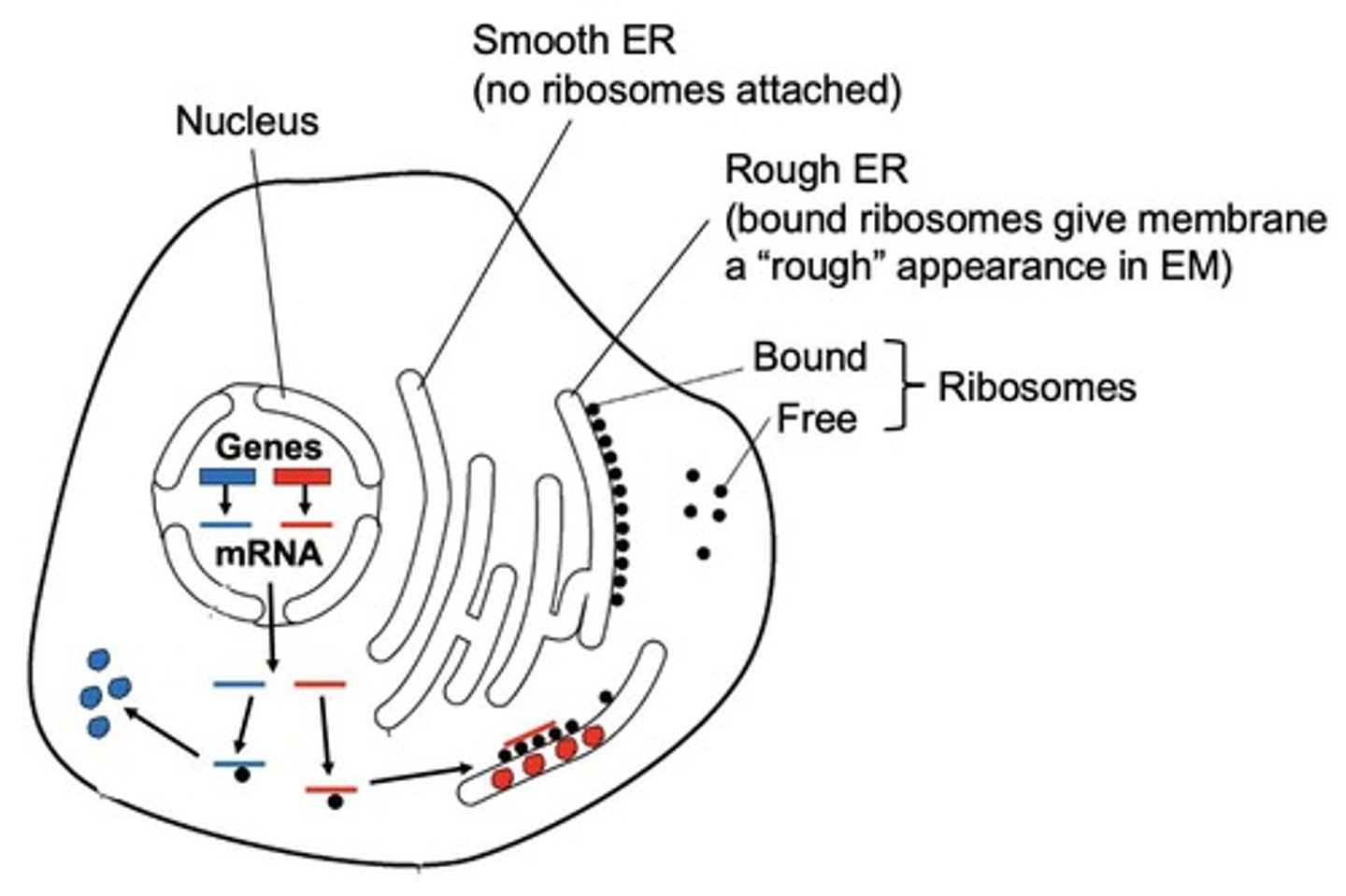
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and their main features?
Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and synthesizes lipids, while Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface and is involved in protein synthesis and processing.
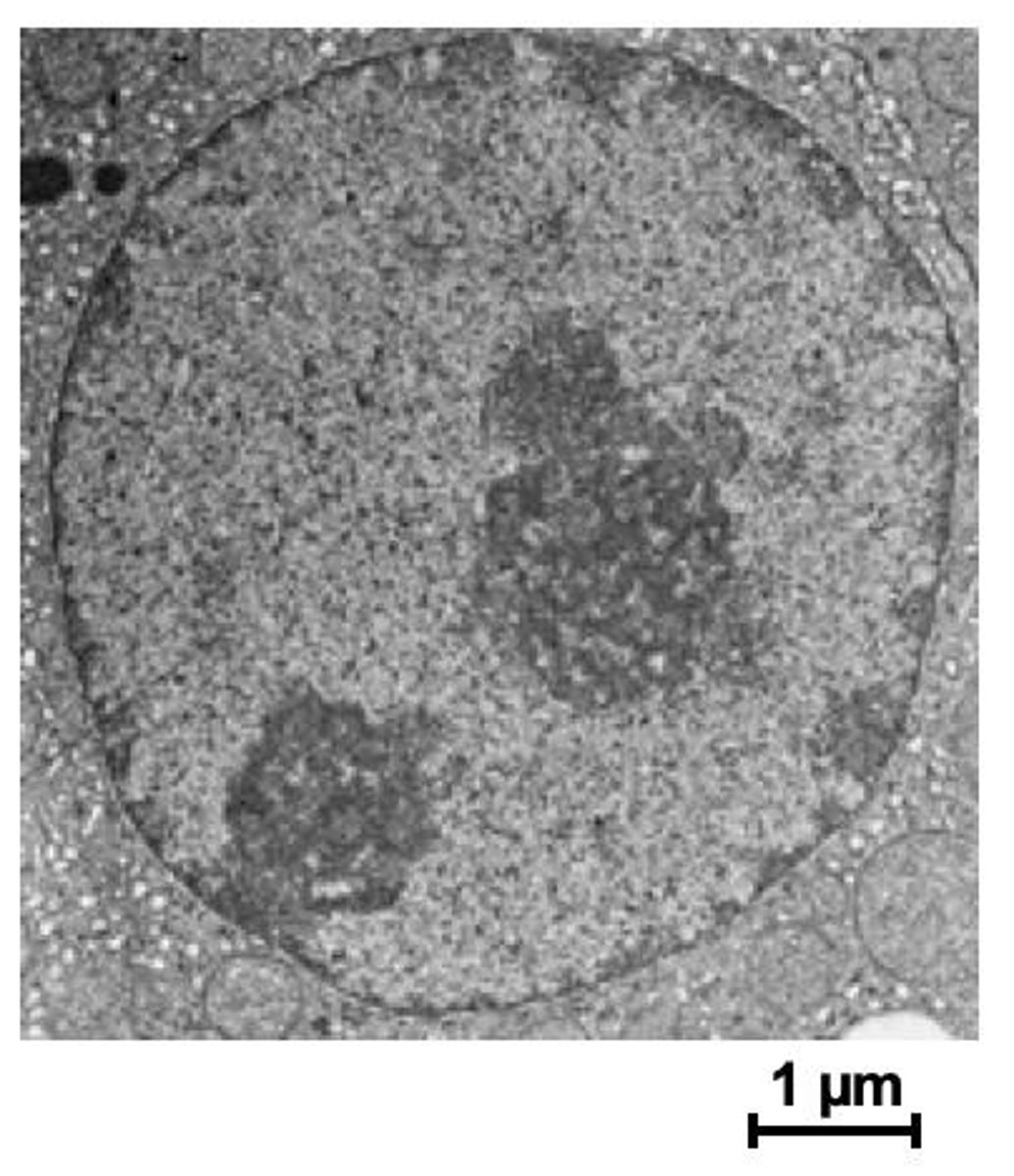
What is the role of the nucleolus?
The nucleolus is a dense region in the nucleus where ribosome assembly occurs.
What is the endomembrane system?
The endomembrane system consists of interconnected compartments that transport materials via vesicles, including the nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
How do secretory proteins exit the cell?
Secretory proteins are synthesized on ribosomes bound to the Rough ER, processed in the Golgi apparatus, and then transported to the plasma membrane for secretion.
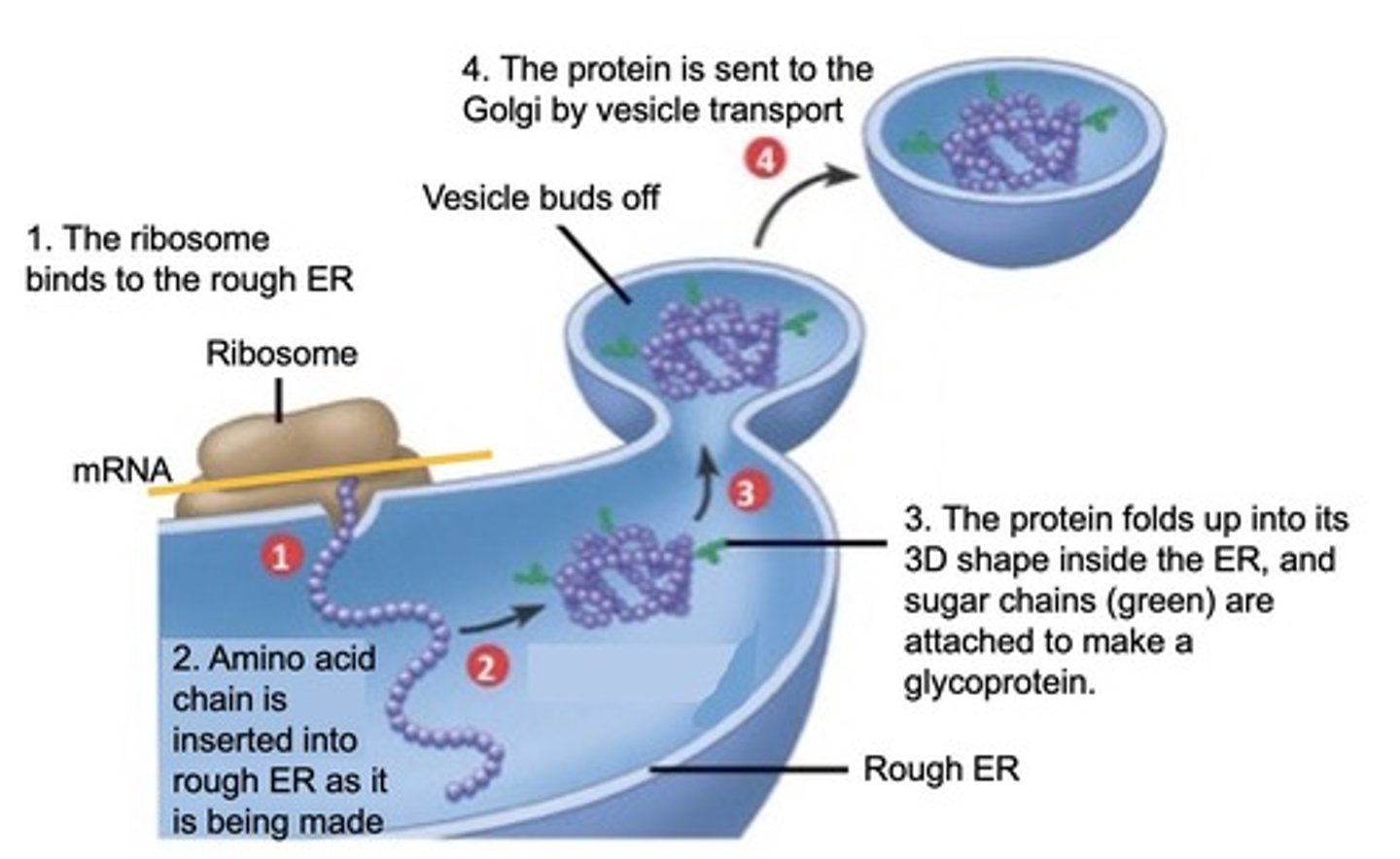
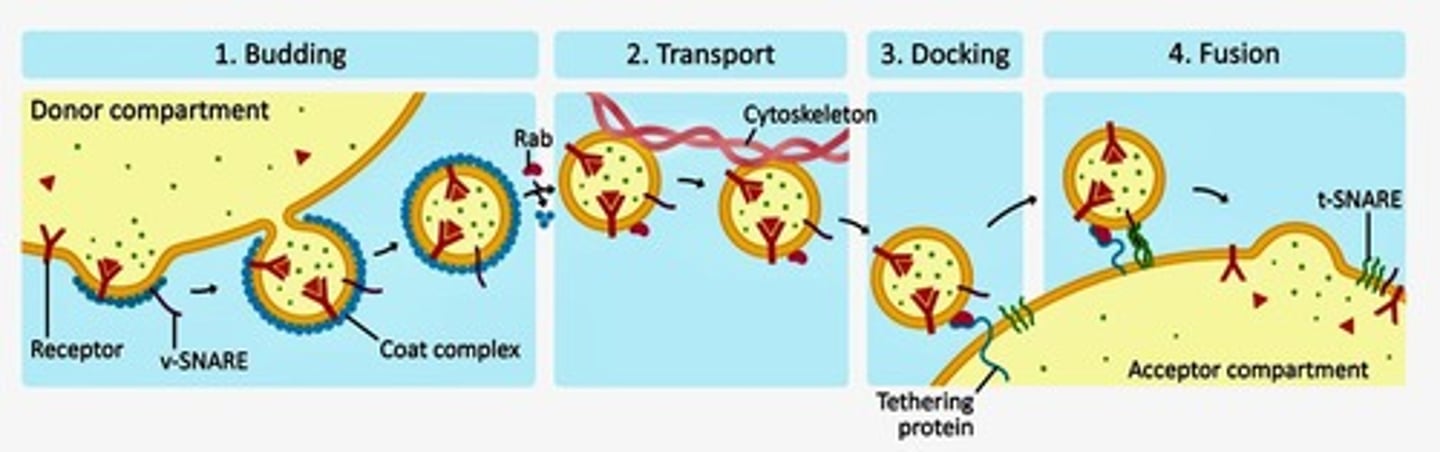
What is vesicle transport?
Vesicle transport is the process where a membrane bud from one organelle forms a transport vesicle that fuses with another organelle to transfer materials.
What are SNAREs?
SNAREs are proteins that act as address labels to ensure vesicles fuse with the correct target compartment.
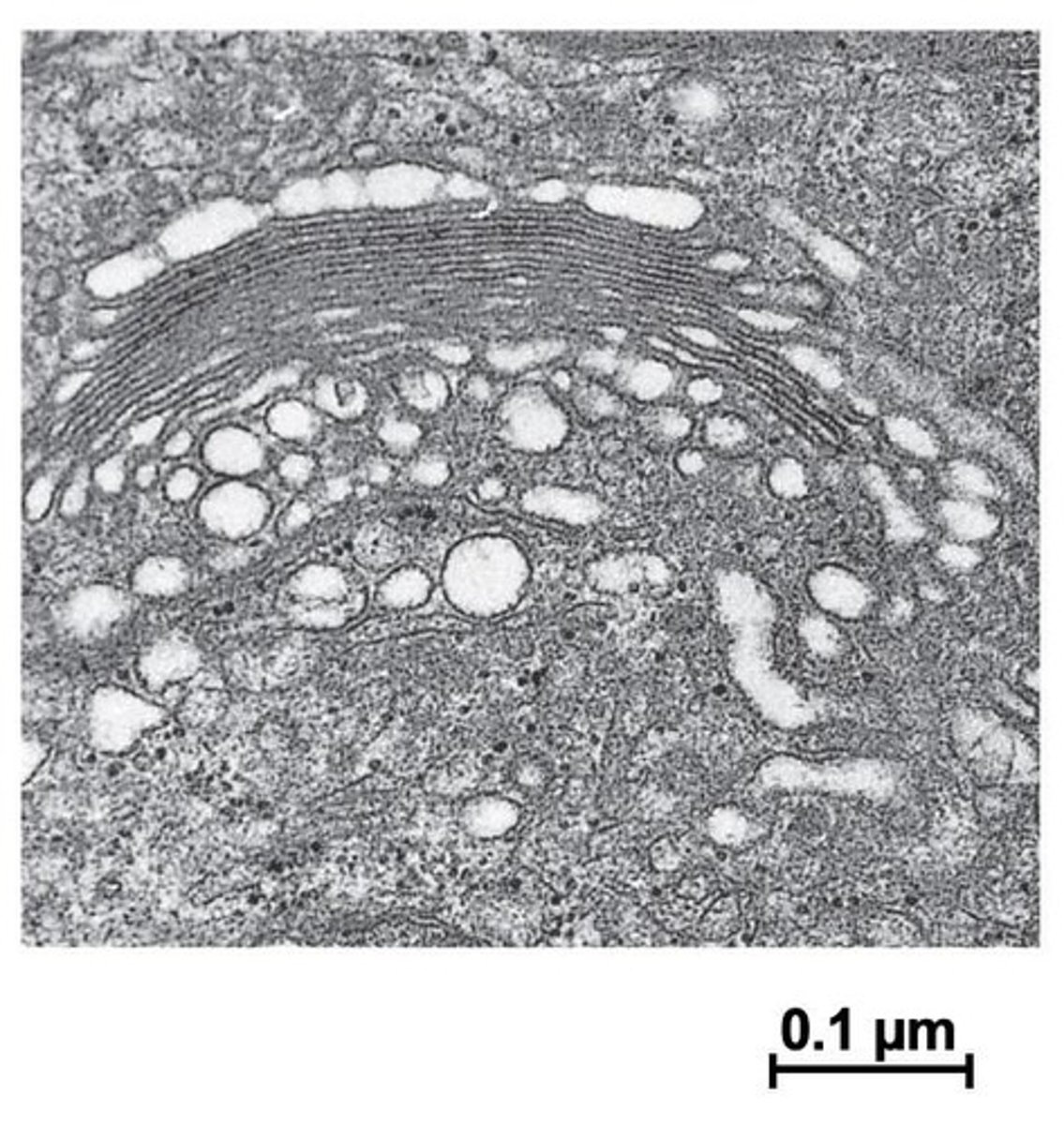
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus sorts, packages, and ships newly synthesized proteins to their correct destinations.
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis?
Exocytosis is the process of transporting materials out of the cell, while endocytosis is the process of internalizing materials into the cell.
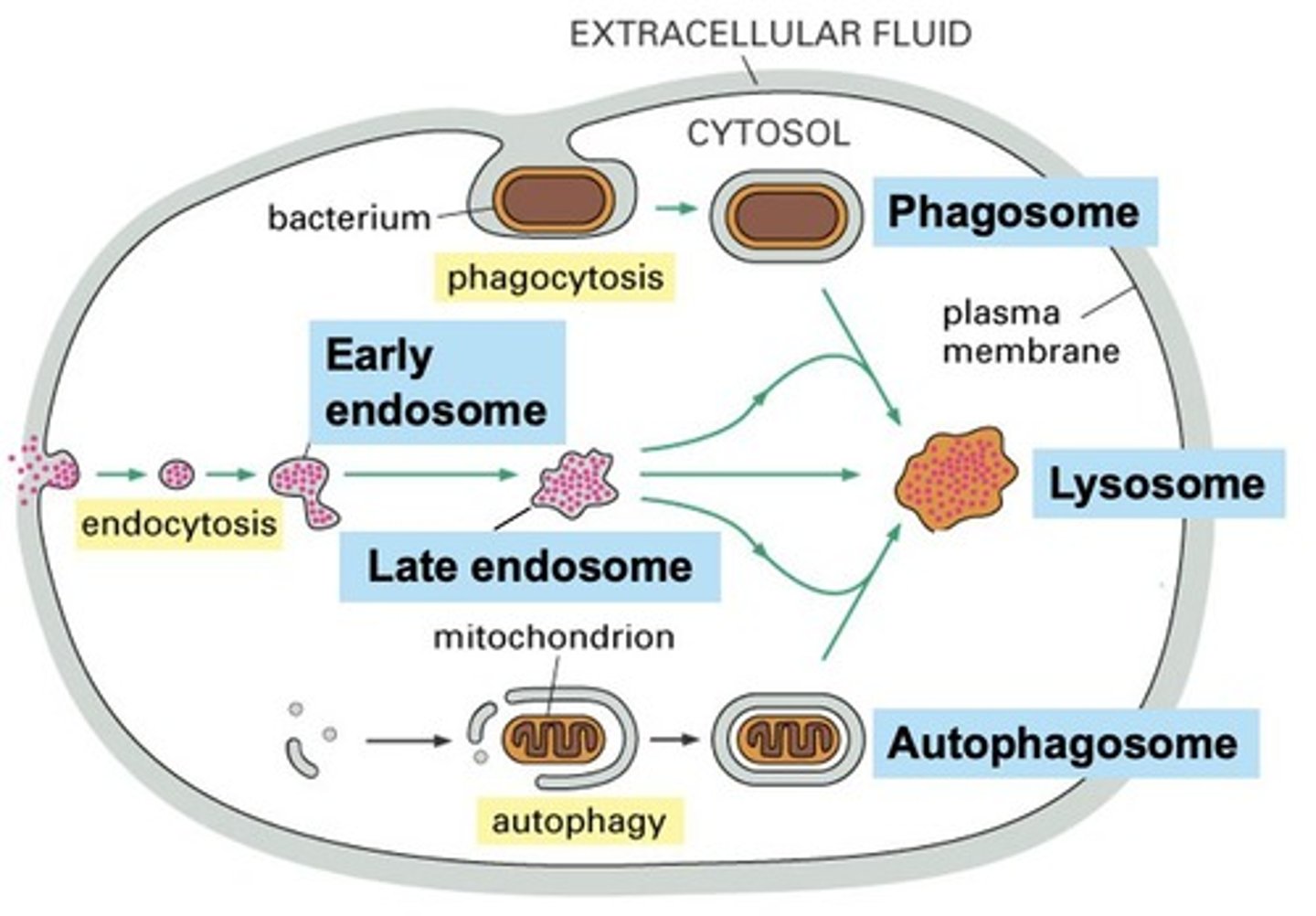
What is phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis that involves the internalization of large particles.
What is the structure of the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes that are continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is chromatin?
Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins (histones) that packages DNA in the nucleus.
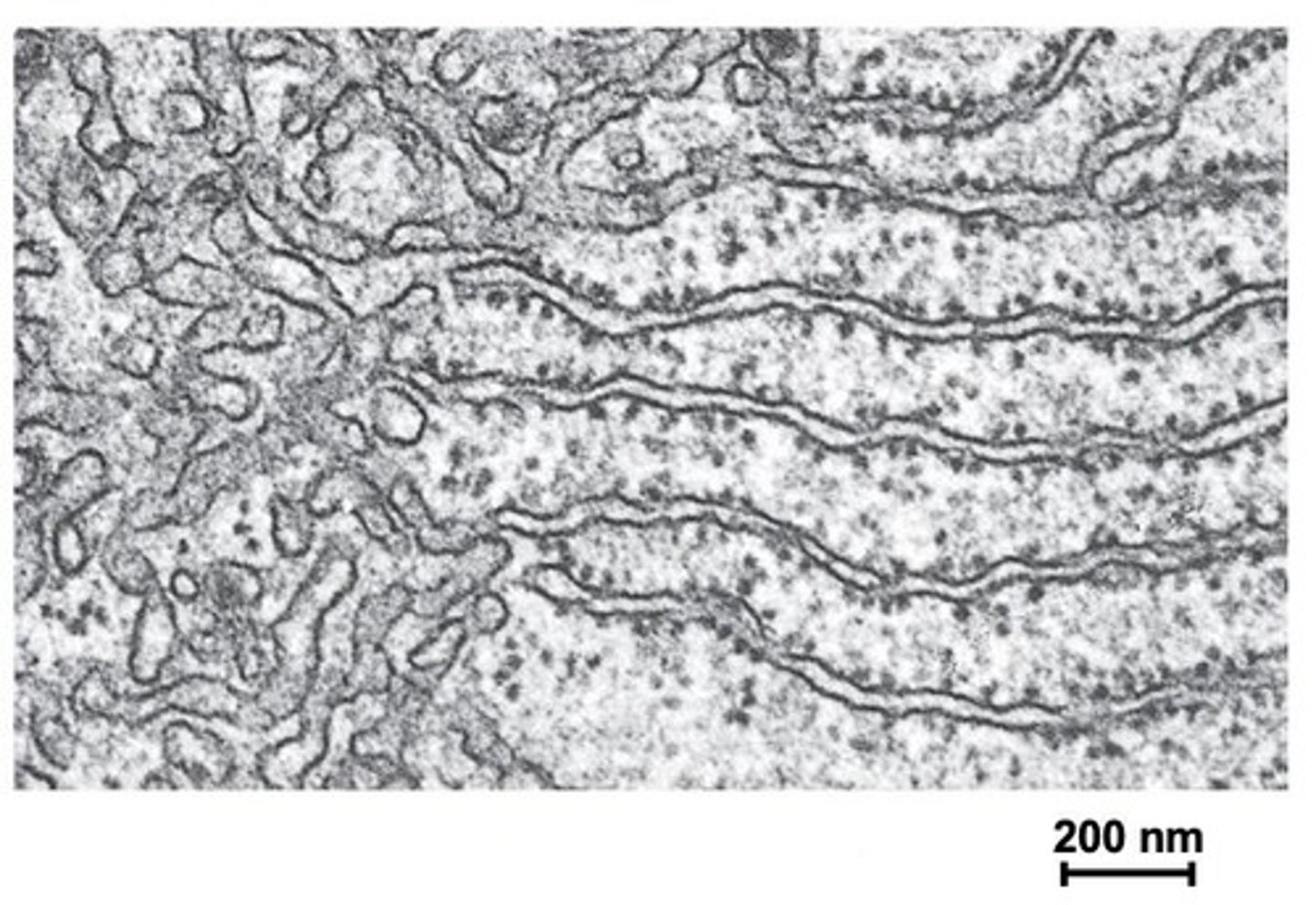
What is the significance of the rough ER's ribosomes?
Ribosomes on the rough ER are essential for synthesizing proteins that are secreted from the cell.
What occurs during the transcription process?
During transcription, DNA is transcribed into mRNA within the nucleus.
What happens during translation?
During translation, mRNA is translated into proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
What is the lumen of the rough ER?
The lumen is the interior space of the rough ER where proteins are folded and processed.
What are the main functions of the smooth ER?
The smooth ER synthesizes lipids, breaks down glycogen to glucose, and detoxifies toxins.
How do newly synthesized proteins get to the Golgi apparatus?
Newly synthesized proteins are transported from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus via vesicle transport.
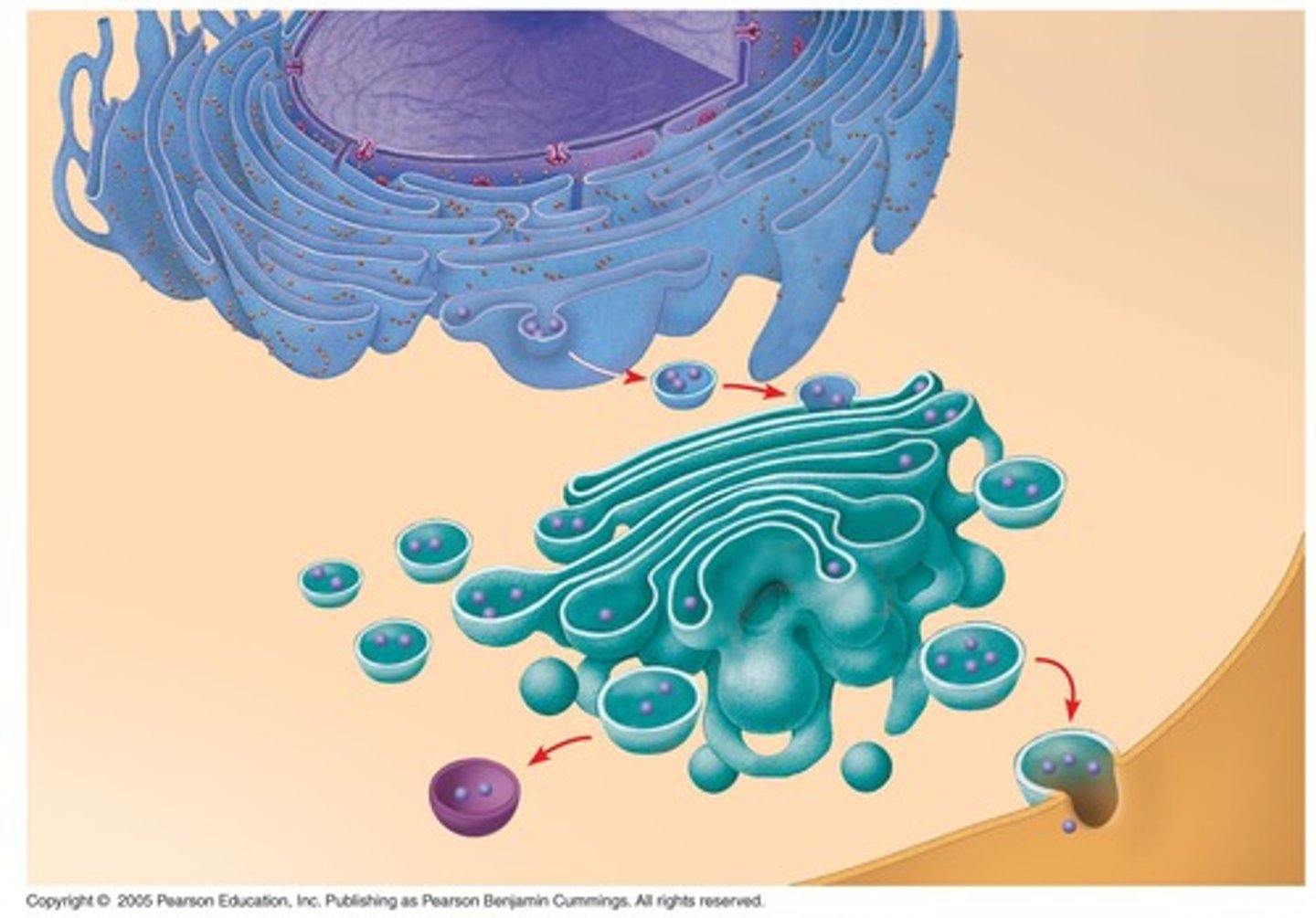
What is the role of the plasma membrane in vesicle transport?
The plasma membrane facilitates exocytosis and endocytosis, allowing material to be transported in and out of the cell.
What is the process of protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis involves transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, followed by translation of mRNA to protein on ribosomes.
What is the function of macrophages in the immune system?
Macrophages internalize and destroy bacteria, playing a crucial role in fighting infections.
What is pinocytosis?
A non-specific form of endocytosis where the cell engulfs extracellular fluid.
What triggers receptor-mediated endocytosis?
The binding of specific molecules to receptors in the plasma membrane.
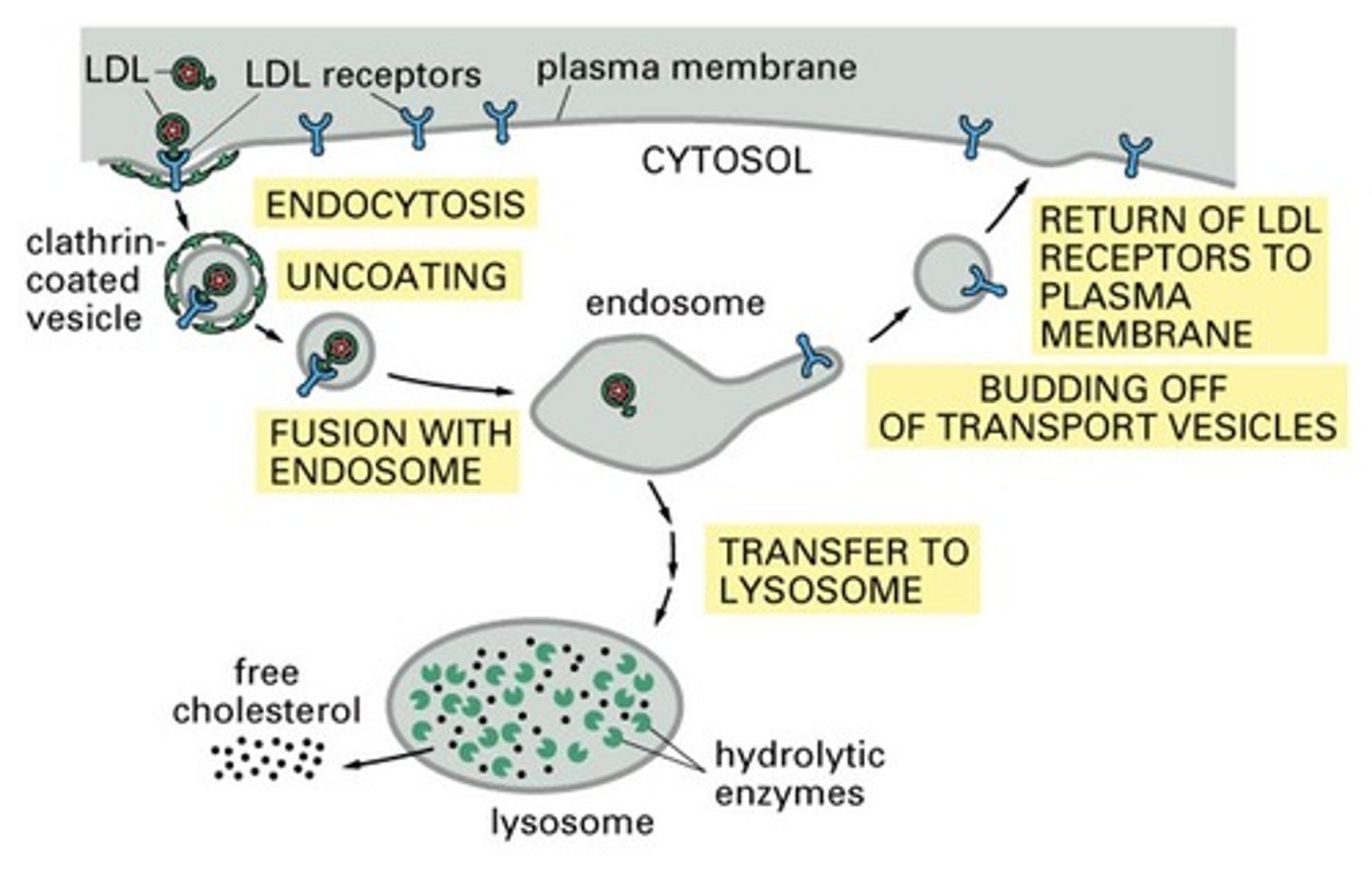
What is the primary function of endosomes?
Endosomes receive material internalized by endocytosis and sort it to the correct destination.
What role do lysosomes play in the cell?
Lysosomes function as waste disposal and recycling centers, digesting macromolecules and recycling worn-out cell parts.
What are lysosomal storage diseases?
Genetic disorders caused by the lack of certain lysosomal enzymes, leading to the accumulation of undigested materials in cells.
What is Tay-Sachs disease?
A lysosomal storage disease caused by a missing lipid-digesting enzyme, leading to brain impairment and often fatal outcomes in early childhood.
What causes familial hypercholesterolemia (FHC)?
A genetic defect in the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor, leading to high blood cholesterol levels and increased risk of heart disease.
How does receptor-mediated endocytosis work?
LDL binds to its receptor on the plasma membrane, triggering endocytosis, where LDL is degraded in lysosomes and its components are utilized by the cell.
What is the role of clathrin in endocytosis?
Clathrin is a coat protein that mediates the formation of endocytic vesicles.
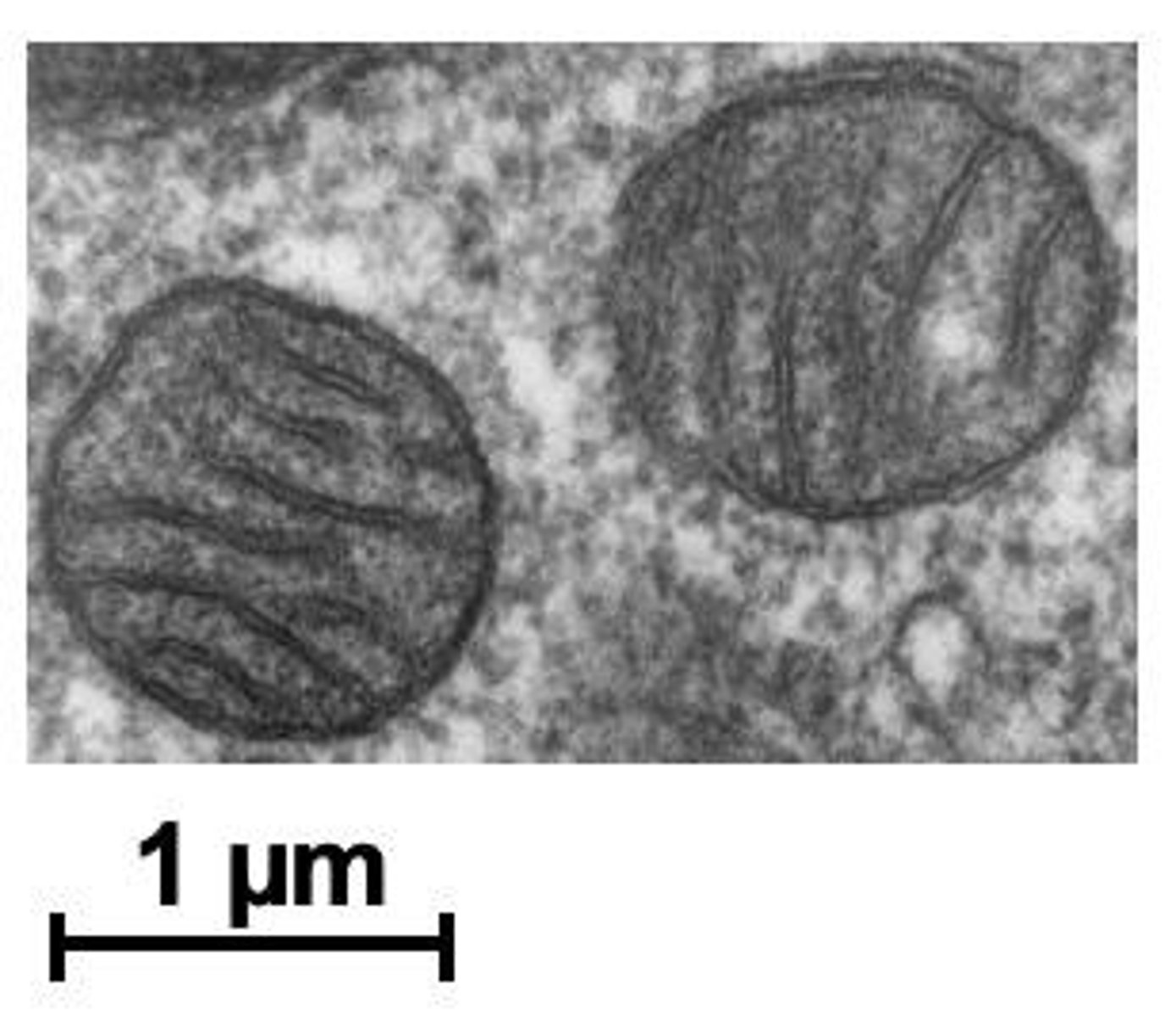
What are the two main functions of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration and ATP production, acting as the energy transformers of the cell.
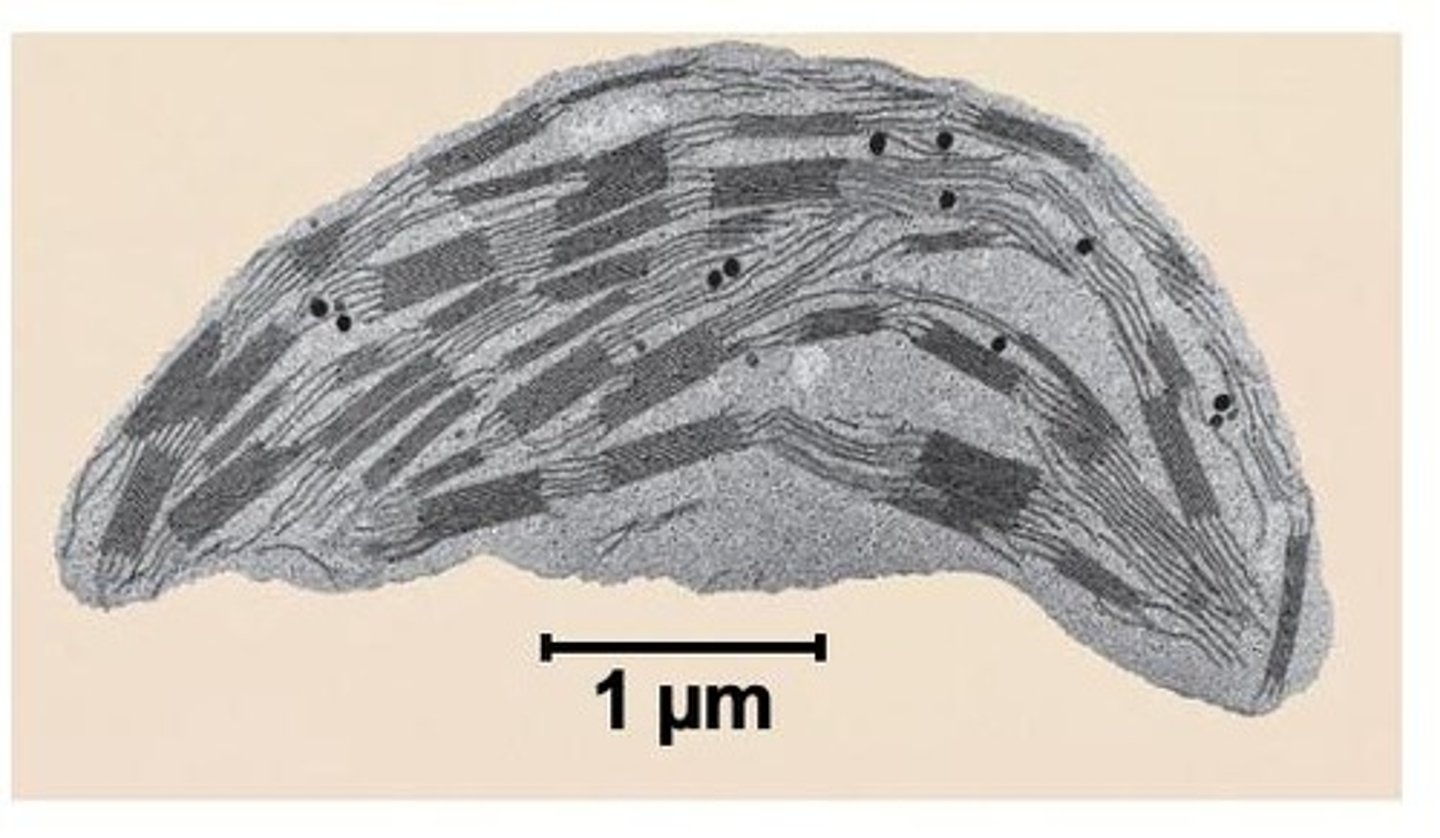
What is the primary function of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, harnessing sunlight to produce food for the plant.
What is the significance of the central vacuole in plant cells?
The central vacuole can occupy up to 90% of a plant cell's volume, playing a key role in storage and maintaining turgor pressure.
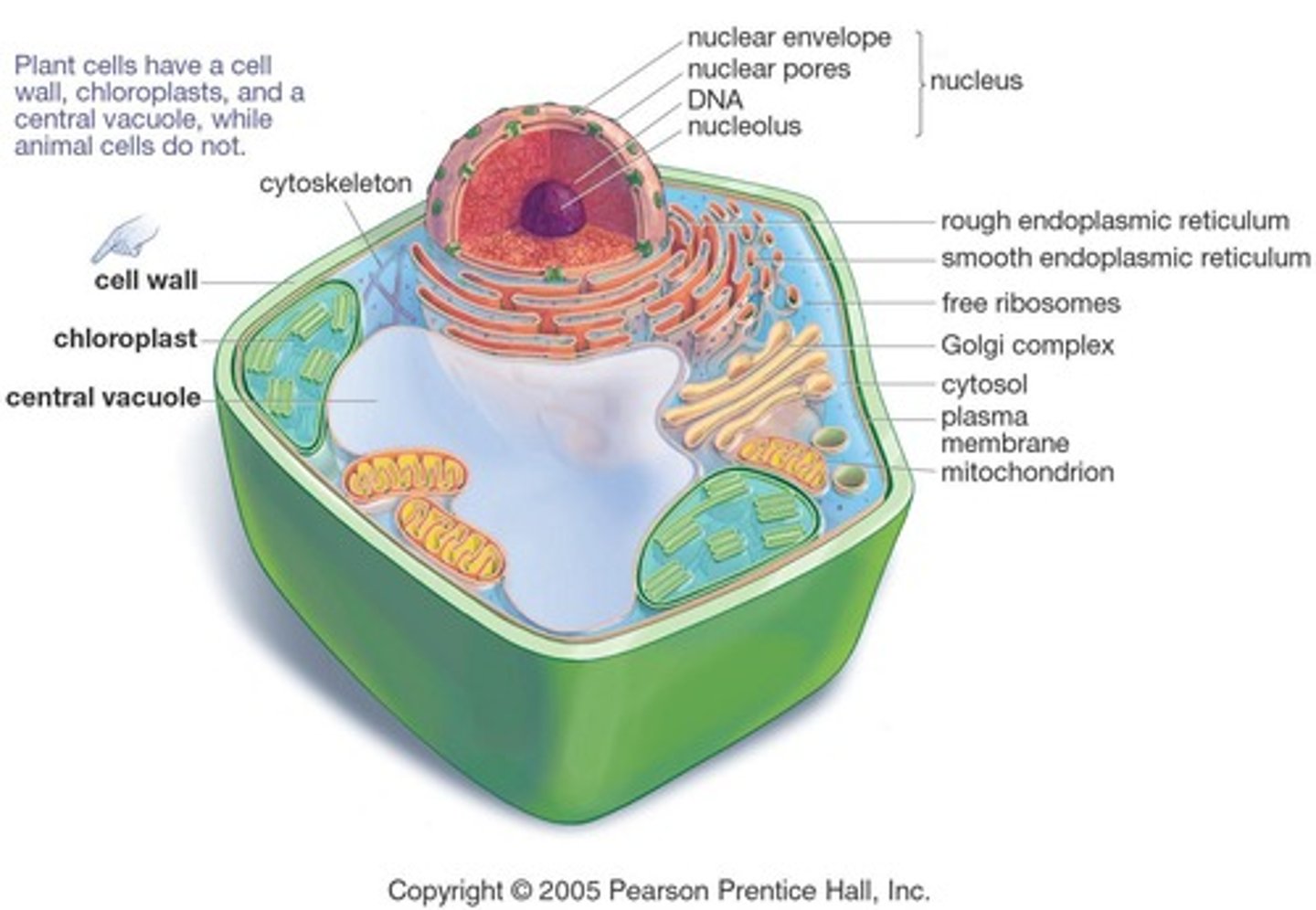
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER)?
The Rough ER is involved in the synthesis and processing of secretory and membrane proteins.
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
The Golgi functions like a post office, sorting and packaging newly synthesized proteins from the Rough ER for their final destinations.
What is cell fractionation?
A technique used to isolate cell organelles based on size and density for biochemical and functional analysis.
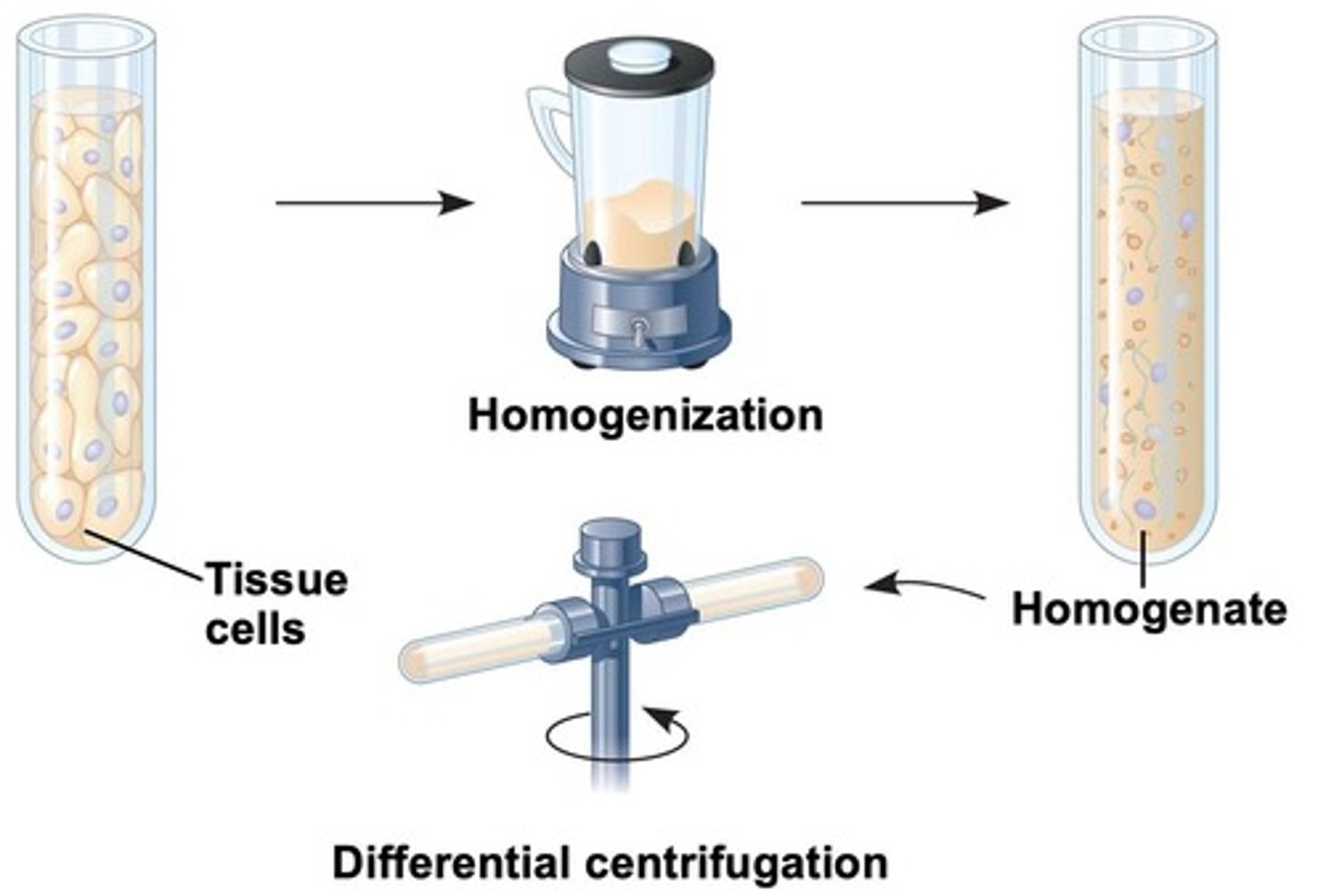
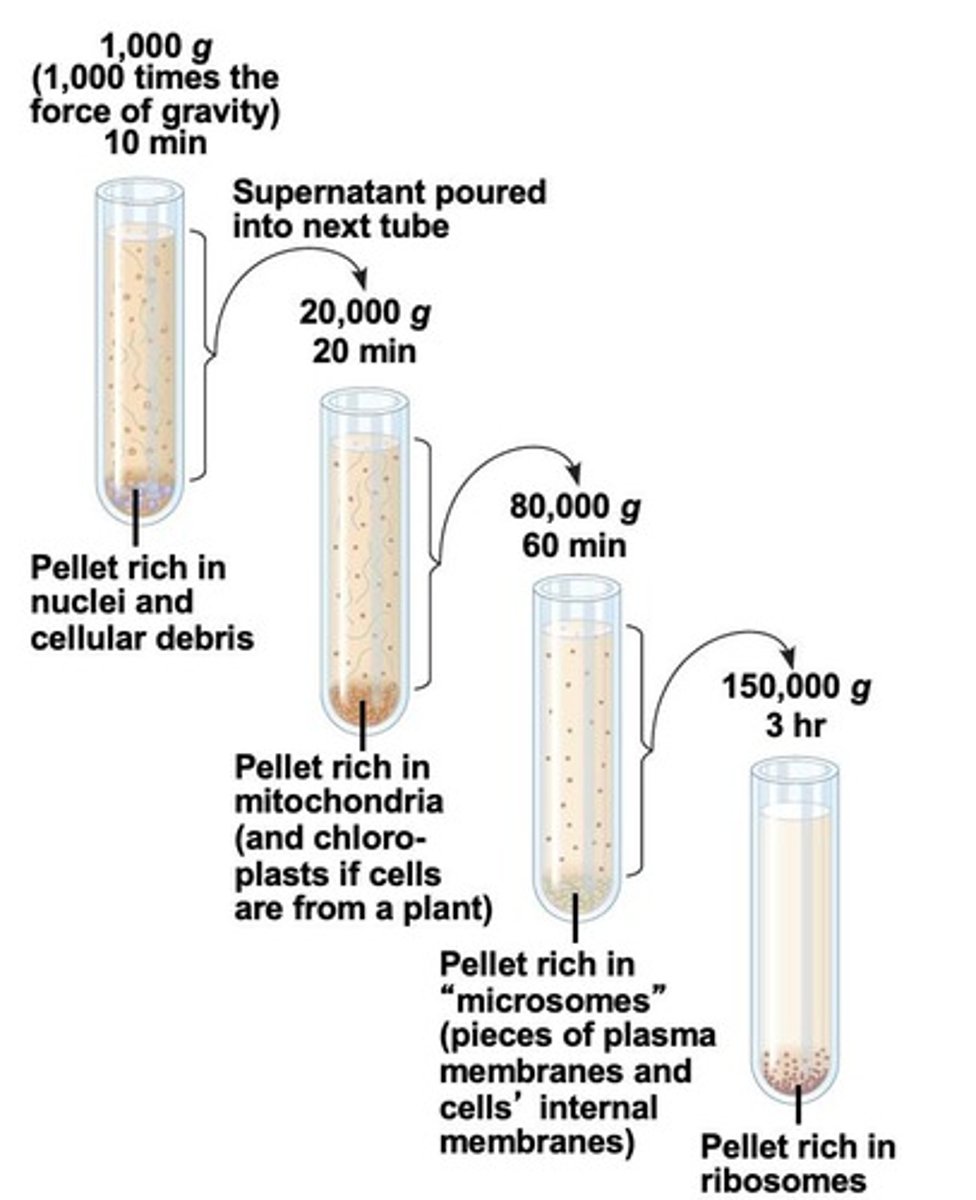
How does centrifugation work in cell fractionation?
Cells are homogenized and spun at high speeds; larger components like nuclei form a pellet at lower speeds, while smaller components are pelleted at progressively higher speeds.
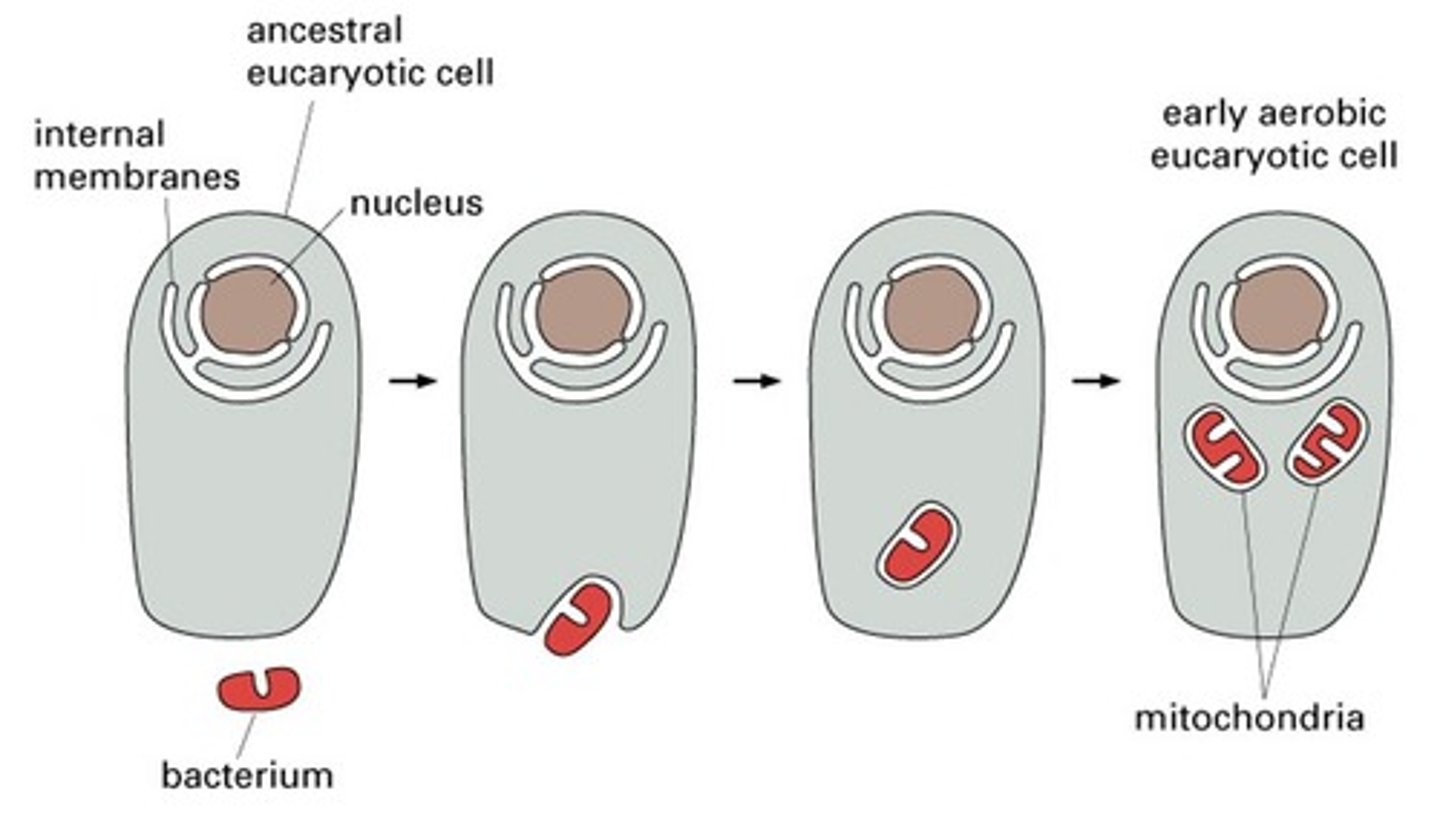
Why are mitochondria and chloroplasts not part of the endomembrane system?
They do not exchange membranes with other organelles via vesicle transport and are thought to have originated from free-living bacteria.
What is the role of lysosomes in autophagy?
Lysosomes digest and recycle worn-out parts of the cell through the process of autophagy.
What is the significance of the low pH in endosomes?
The low pH in endosomes helps to uncouple ligands like LDL from their receptors, allowing receptors to be recycled back to the plasma membrane.