Grade 8 Science
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
A heterogeneous mixture consists of visibly different substances, while a homogeneous mixture you cannot from a human’s perspective tell the difference between the substances. It appears as it is composed uniformly throughout.
What is the difference between a heterogeneous and a homogeneous mixture?
To flow refers to the movement of a liquid or gas, allowing it to change shape and fill the space of its container. To move continuously and smoothly.
What does the term “to flow” mean?
Solid: Definite shape and volume
Liquid: No definite shape but a definite volume
Gas: No definite shape or volume
Each form of matter either has or doesn’t have a definite shape or volume. State which each one has.
Vaporization
What is the term use from going from a liquid to a gas?
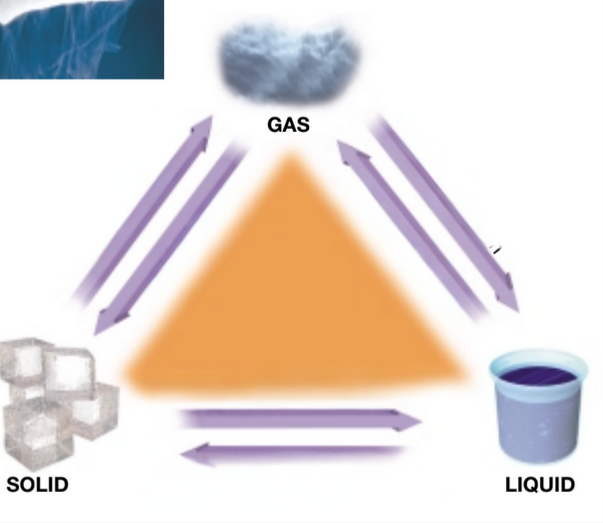
Freezing or solidification
What is the term used from going to a liquid to a solid?
1. All substances are made of tiny
particles.
2. All particles in a pure substance are
the same.
3. The particles have spaces between
them.
4. The particles are always in motion —
vibrating, rotating, moving from place to place.
The speed of the particles increases/
decreases when the temperature
increases/decreases.
5. The particles in a substance are
attracted to one another.
What are the five rules of the particle model of matter?
A pure substance consists of only one type of particle, while a mixture contains two or more pure substances or particles.
What’s the difference between a pure substance and a mixture?
Elements and compounds.
Pure substances have two categories, what are they?
A homogeneous mixture where there is no settling and that the solutes are distributed equally throughout the solvent.
What does a solution mean?
Solute: The substance being dissolved
Solvent: The substance that dissolves the solute
Soluble: A solute that is able to be dissolved in a solvent
What does solute, solvent, and soluble mean?
Suspension: A heterogeneous mixture in which the particles settle slowly after mixing
Colloid: A heterogeneous mixture in which the particles do not settle
What is a suspension and a colloid?
Solubility refers to the amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given
amount of solvent to form a saturated solution.
What does solubility mean?
When the solute mixes with the solvent and breaks down into smaller particles to form a solution.
What is dissolving?
Two-thirds of Earth’s surface is covered with water. Water has been
called the “universal solvent” because it can dissolve so many materials.
Why is water called the universal solvent?
When we measure how fast a solute dissolves in a solvent.
What does the rate of dissolving mean?
-Agitation
-Temperature
-Pressure
What factors affect the rate of dissolving?
Unsaturated: When more of the solute could dissolve in a amount of solvent.
Saturated: When no more solute can dissolve in the solvent.
What is the difference between a saturated solution and an unsaturated solution?
A solution that contains more solute than would normally dissolve in the solvent.
What is a supersaturated solution?
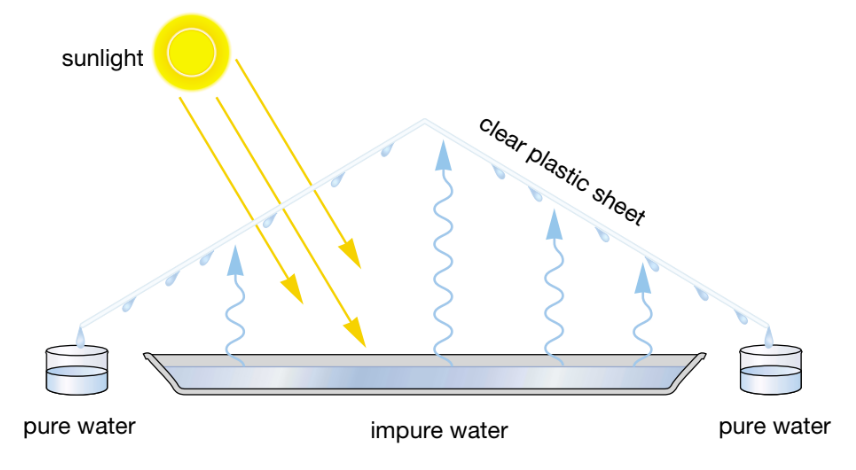
Removing the salt from salty water.
What does desalination mean?
The desert tent method.
What is this method called?
Dehydration.
The process of removing water from a solution. What is it called?
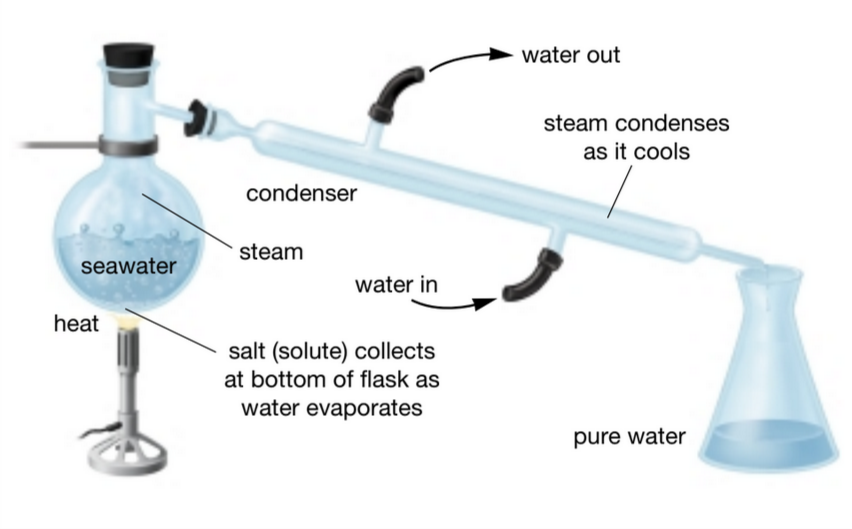
Distillation is a separation method that allows all liquid fractions of a
mixture to be separated from each other and collected in different
containers.
What is distillation?
How thick or thin a liquid is.
What’s viscosity?
More thick.
If a liquid is more viscous it is..?
You could measure the time it takes for the fluid to flow from one point to another point.
How would you measure a liquid’s flow rate?
Therefore, the viscosity of a liquid DECREASES as it is HEATED, and
INCREASES as it is COOLED.
Therefore, the viscosity of a liquid ______ as it is HEATED, and
______ as it is COOLED.
Therefore, the viscosity of a
gas INCREASES as it is HEATED, and DECREASES as it is COOLED.
Therefore, the viscosity of a
gas _______as it is HEATED, and _______as it is COOLED.
Density is mass per unit volume of a substance.
What is density?
Mass is the amount of
matter in a substance. Volume is a measurement of the amount of space occupied by the substance.
What is mass and volume?
Weight is the force of gravity exerted on an object.
What is weight?
A force is a push or pull or change of motion in an object. Gravity is the ongoing force that pulls everything to the center of the earth.
What is a force? What is gravity?
Density = Mass/Volume or D = M/V
In calculating density, what does density equal?
The tendency for materials to rise or float in a fluid.
What is buoyancy?
The upward force exerted on objects submerged in fluids.
What is the buoyant force?
The total mass of all substances on board divided by the total volume.
What is average density?
The buoyant force acting on an object equals the weight (force of gravity) of the fluid displaced by the object.
What is Archimedes principle?
When gravity = buoyancy.
What is neutral buoyancy?
An instrument used to measure the density or specific gravity of a liquid. It works by observing how much a weighted device floats within the liquid, with a lower float level indicating a denser liquid.
What is a hydrometer?
Gas
Which state of matter is compressible?
An instrument measuring atmospheric pressure, used especially in forecasting the weather and determining altitude.
What is a barometer?
• living organisms need energy
• living organisms respond and adapt to their environment
• living organisms reproduce
• living organisms grow
• living organisms produce wastes
There are five things all living organisms need. What are they?
The basic unit of every system. Everything is made up of cells.
What is a cell?
Eyepiece or ocular lens
Tube
Coarse-adjustment knob
Fine-adjustment knob
Arm
Revolving nosepiece
Objective lens
Stage
Condenser lens
Diaphragm
Light source
Starting from the top name each part of the microscope.

What did Anton Van Leeuwenhoek do?
He created a microscope that was way more powerful then any of his time. He was also the first to observe and describe many micro-organisms.
What did Robert Hooke do?
Was the first to discover and name cells.
What was the hypothesis that Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann came up with?
That all organisms are composed of cells and that a cell is the basic unit of life.