3C5 Lagrangian & Hamiltonian
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
How many generalised coordinates are required to fully describe a system with N degrees of freedom?
N
Energy method for single DOF?
T + V = const
Which systems require Lagrange & Hamilton?
And what do these methods lead to?
Many DOFs
Multiple coupled differential equations
All 3 Lagrangian relationship?
p = dL/dq dot
F = dL/ dq
d/dt (p) = F
Differentiate e_r and e_theta (taking note of direction)
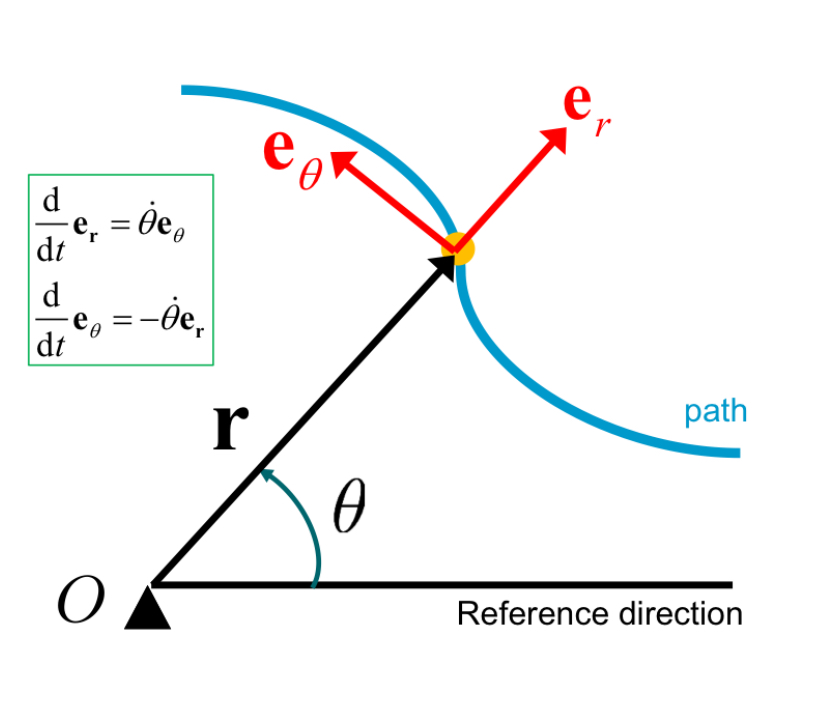
Holonomic vs Non-holonomic?
Holonomic: current state of system fully described by instantaneous displacements and velocities
Non-holonomic: system depends on current displacements & velocities AND path taken by system to reach current state (won’t come up on exams)
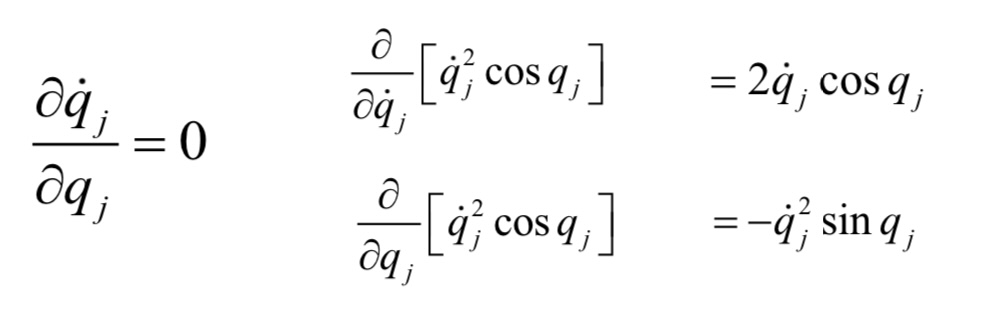
Work done by applied generalised, external forces equation?
δW = ∑j Qj δqj
Steps to find generalised forces?
not made FC yet :(
What to remember to include in T and V?
T = ½ m v²
T = ½ I ω² (include whenever there’s rotation NOT accounted for by generalised coordinates)
V = mgh
V = ½ k x²
What form should you get T into to find mass matrix?
T = ½ m [ α x² + β y² + (2 γ xy) ]
M = m |α γ|
|γ β|
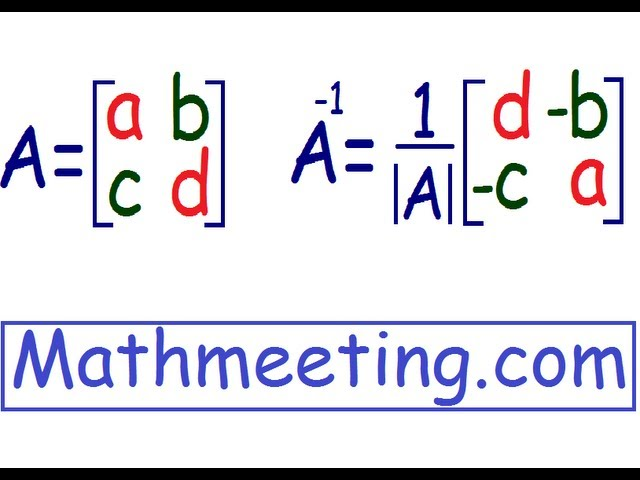
Invert 2×2 matrix?
When is Kamiltonian equal to Hamiltonian?
When G has no explicit time-dependence