Introduction to Organic Chemistry; Quantum mechanics and bonding
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
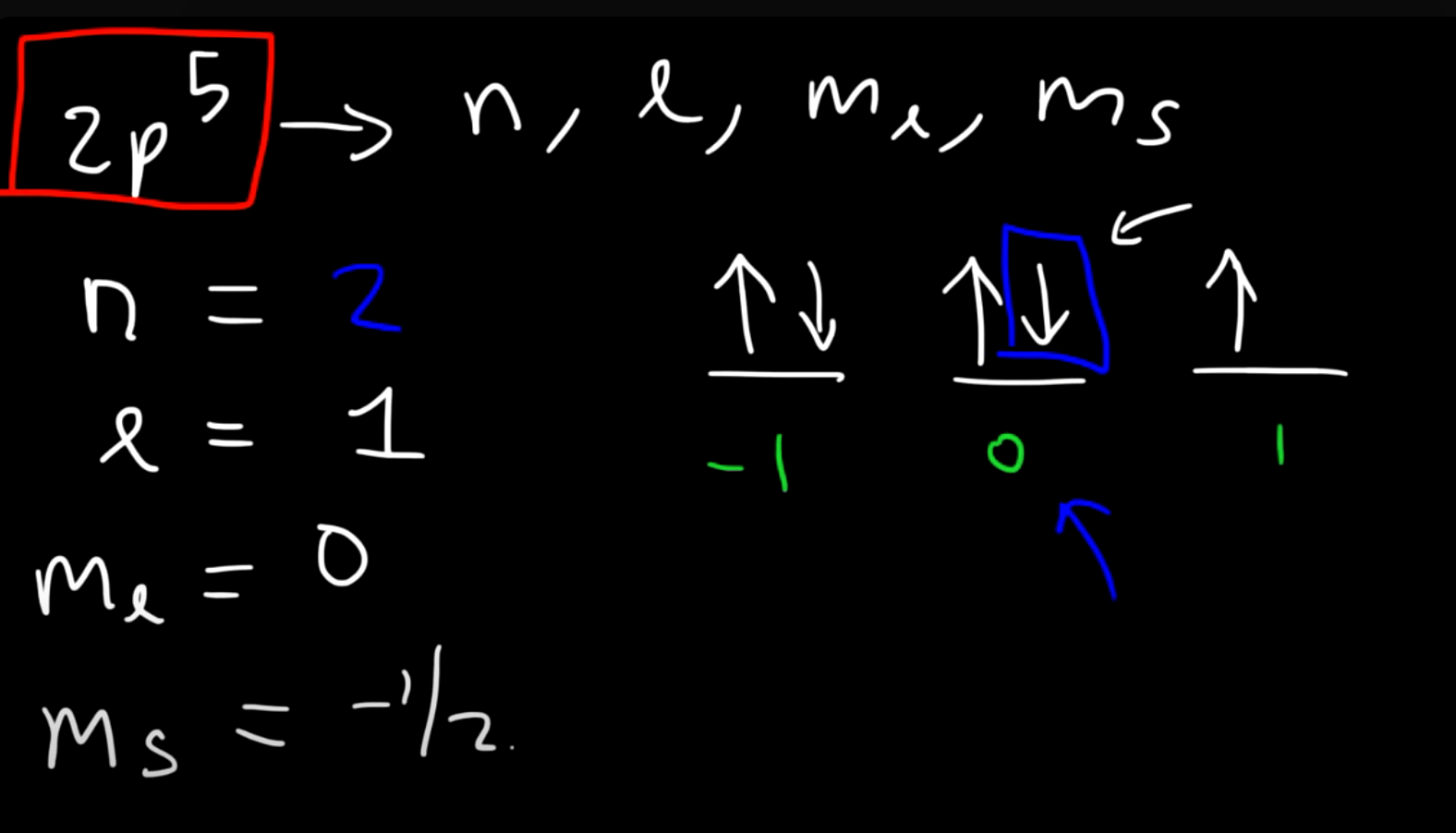
What are the four quantum numbers and what do they represent? What do quantum numbers N and L tell us??
Represents the most probable location and properties of an electron
n (principal quantum number) = energy level
higher n = greater distance from nucleus (and thus a greater energy level)
Orbitals start at 1 and increase…
L = Angular momentum or shape of the orbital
The numerical value of L cooresponds to a shape. For our scope, we are only focused on L = 0 and L = 1
When L = 0, we have a standard circular shape, also known as an S orbital
When L = 1, we have a dumbell shape, also known as a P orbital.
by the way, S = the shape of the orbit
but ALSO S = a sublevel
Same with P. P = the shape (Dumbell) and is also, a sublevel
Now how about quantum numbers Ml. and Ms?
ML = magnetic quantum number, or the oritentation of the orbital.
You will now notice; that the numerical value of L is actually relevant to ML.
know that -L < ML < L (greater than or equal to
For instance, S = 0. This makes sense because because there is only one S orbital, so per energy level there is only one orbital the electron could be
P = 1 makes sense as well because there are indeed three orbitals per energy level, Px Py and Pz, so the electron must be in -1, 0, or 1.
Px doesnt neccesairly coorespond with -1. We don’t really have any way of telling where the electron is, anyways.
Thankfuly, l=2 and L=3 are beyond the scope of our class. For now.
MS is extrodinarily simple. MS is simply up spin or down spin. Ms is either +1/2 or -1/2. All you need to know is that you must place them firstly with parallel spins, and then pair them with the opposite spins.
Example of how you can use the quantum numbers to find the electron
It is not that hard.
For any give n energy level, what is higher; The P orbital or the S orbital? And, because of this, where is the orbital in relation to the nucleus?
The P orbital. The P orbital is farther from the nucleus compared to the S orbital.
Explain hybrydization
Hybrydization comes into play when standard orbitals cannot explain the location of the electron.
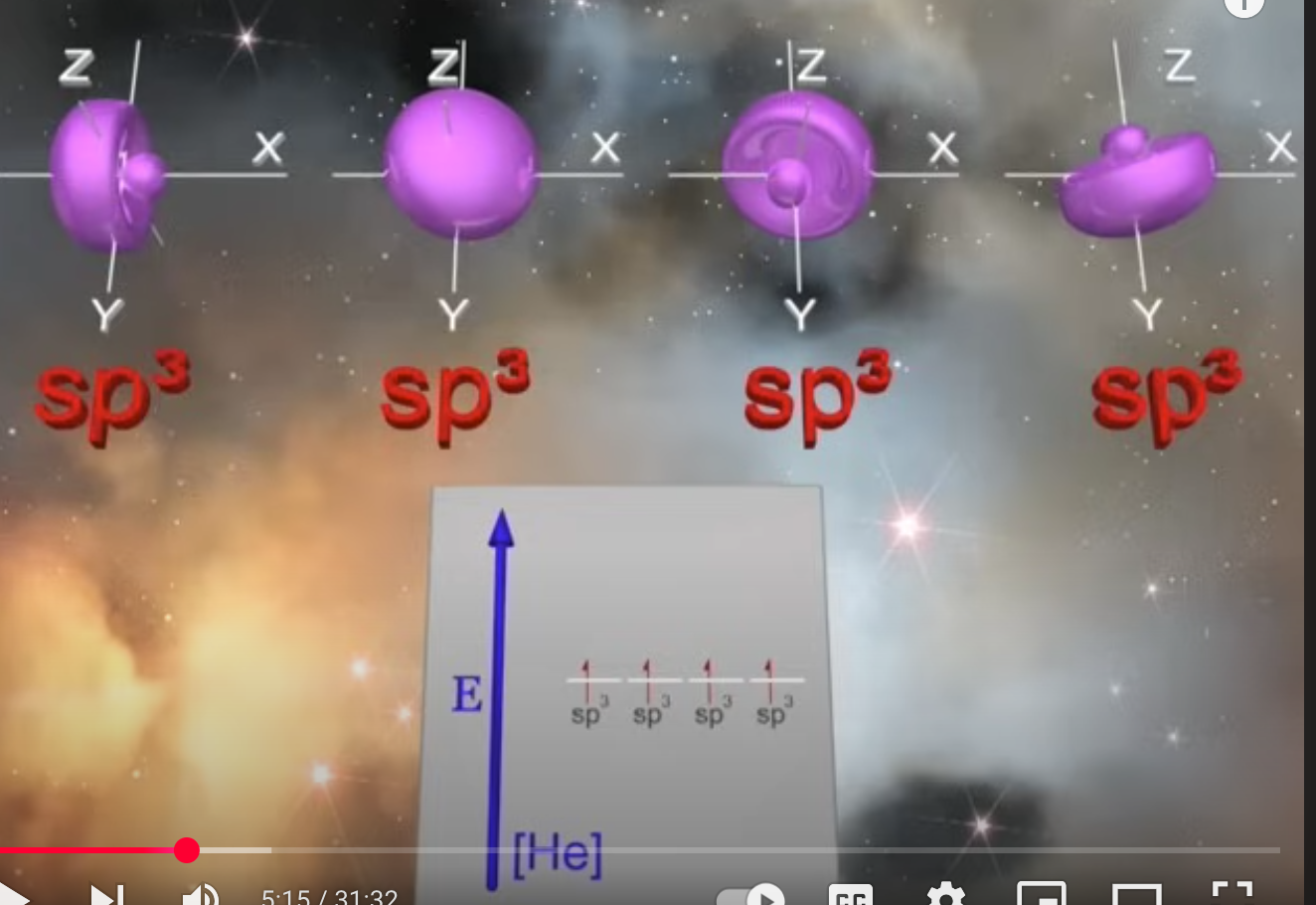
What are orbitals basically doing?
estimating electron density with 90-95% accuracy. Orbitals are clouds of electron density
What exactly occurs during a sigma bond? what kind of interference is this?
Direct overlap of orbitals. The electrons are essentially on top of each other. This is constructive inferference
What are the positive and negative phases of an electron’s wave function?
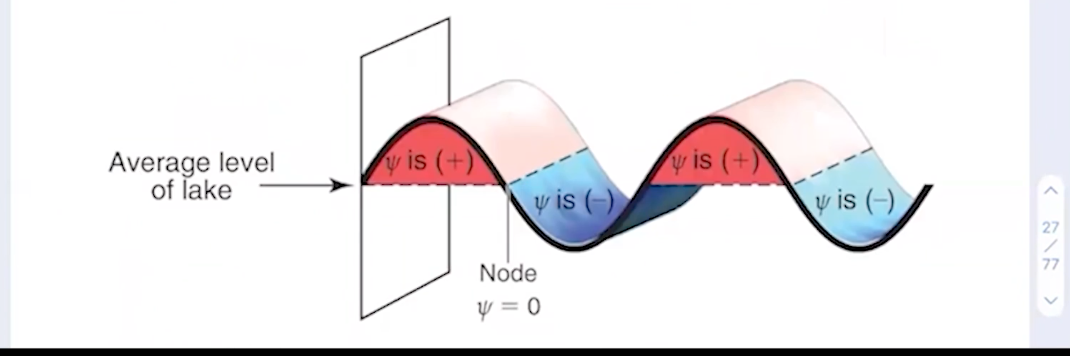
Basically; it’s positive on one side of the node and negative on the other.
Bonding at its core…
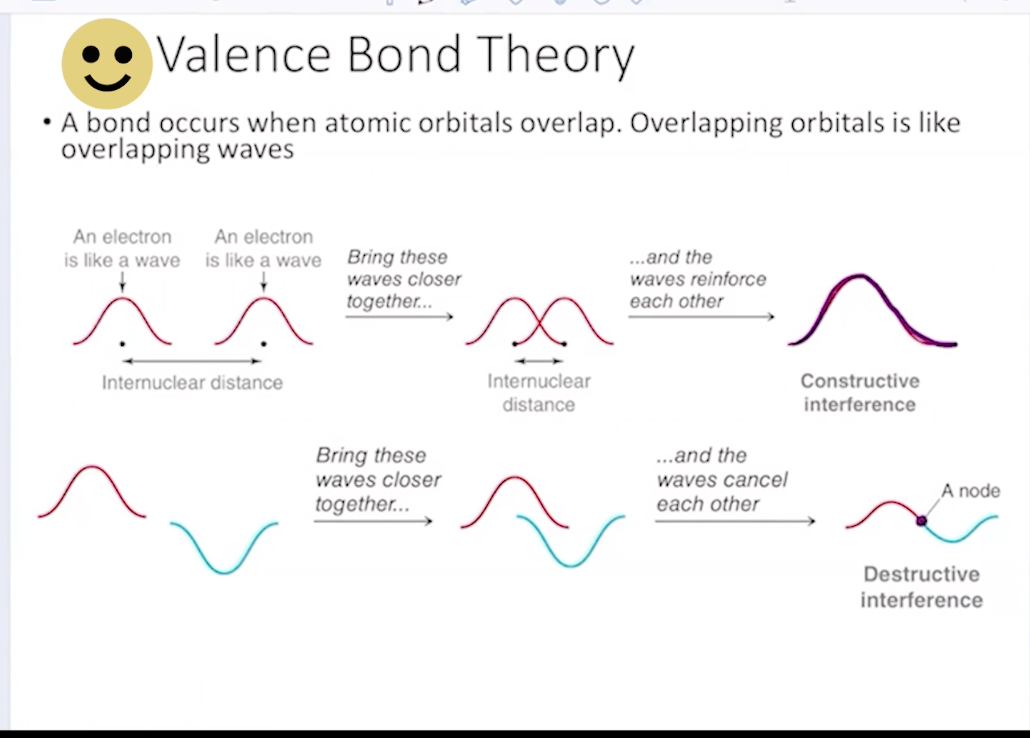
Sigma bonds result in…. what for energy?
A lower energy level, as bonding is energetically favorable
With every sigma bond, there is a…
constructive and deconstructive molecular orbit establisbed. the deconstructive is inidcated as sigma star, or an antibonding MO.
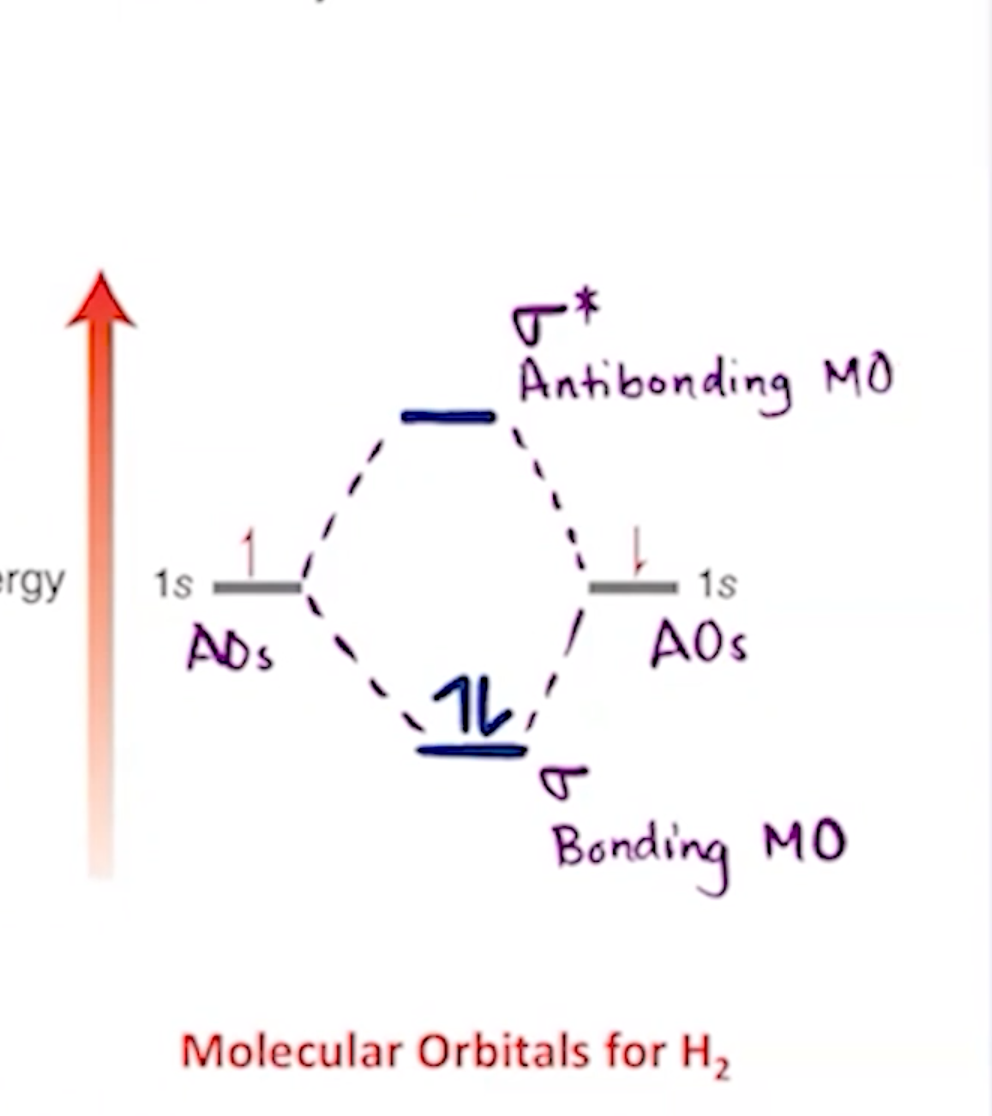
Antibonding is _____
Bonding is ______
__ Is Higher energy
__ Is lower energy
unstable/destructive
Stable/constructive
Antibonding
Bonding/ Sigma bonds