All Euro Units 1-3 Topics
1/274
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
275 Terms
English Civil War
a conflict, lasting from 1642 to 1649, in which Puritan supporters of Parliament battled supporters of England's monarchy
Absolute Monarchy
A government in which the king or queen has TOTAL control over the country's institutions.
James I
Stuart monarch who ignored constitutional principles and asserted the divine right of kings.
Charles I
Stuart king who brought conflict with Parliament to a head and was subsequently executed.
Parliamentarians
Supporters of Parliament, who fought the Royalists during the English Civil War.
Royalists
supporters of the king during the English Civil War (synonym of Cavalier)
Oliver Cromwell
English military, political, and religious figure who led the Parliamentarian victory in the English Civil War and called for the execution of Charles I. As lord protector of England he ruled as a virtual dictator.
Restoration
the period of Charles II's rule over England, after the collapse of Oliver Cromwell's government
William and Mary
Became King and Queen of England in 1688 as part of the Glorious Revolution.
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange without the use of violence.
Long Parliament
(1640 - 1660) English Parliament which met off and on for twenty years due to religious and civil problems. Occurs during the English Civil War.
English Bill of Rights
1689 laws protecting the rights of English subjects and Parliament
Parliamentary Sovereignty
Belief that Parliament is supreme in all matters, rather than the monarch.
Constitutional Monarchy
A system of governing in which the monarch's power is limited by law.
Divine Right of Kings
the belief that kings receive their power from God and are responsible only to God
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
mixed farming
growing crops and feed and livestock all on the same farm
seed drill
created by Jethro Tull, it allowed farmers to plant seeds in well-spaced rows at specific depths; this boosted crop yields
mechanical hoe
removed weeds from between the seed rows
thresher
Machines that separate grains and seeds from plants
enclosure movement
practice of fencing or enclosing common lands into individual holdings
yeomen farmer
a freeman who owned his own land, usually small farms
internal tariffs
taxes on items or properties sold WITHIN a country, which hurt the average person by raising the price of goods.
customs barrier
Taxes and restrictions on imports designed to protect a country's trade
external tariff
taxes on items coming in to a country with the goal of protecting that country's industries
water meadow
A meadow that is artificially created and maintained, with flooding controlled. Produces efficient grazing for livestock
cottage industry
Merchants
employed people such as spinners and weavers to work from home making
finished products, and the workers were paid per item made. (also known as the putting out system)
putting out system
Merchants
employed people such as spinners and weavers to work from home making
finished products, and the workers were paid per item made. (also known as Cottage Industry)
proto-industrialization
the first industry, before the development of factories. (example cottage industry)
self-sustaining growth
an economic cycle in which a nation produces products that then drive more economic activity
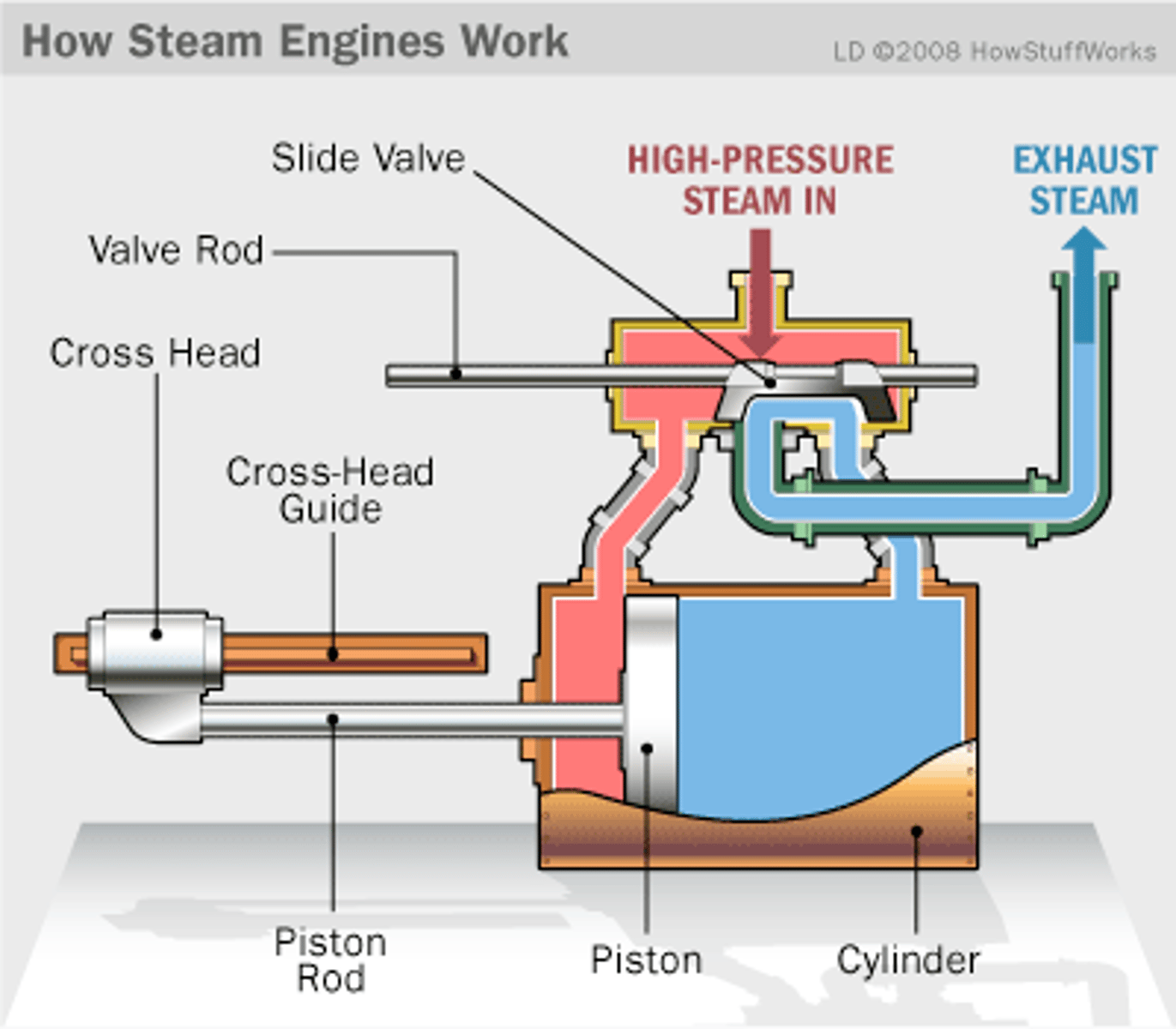
steam engine
A machine that turns the energy released by burning fuel into motion by using the expansion or rapid condensation of steam to generate power.
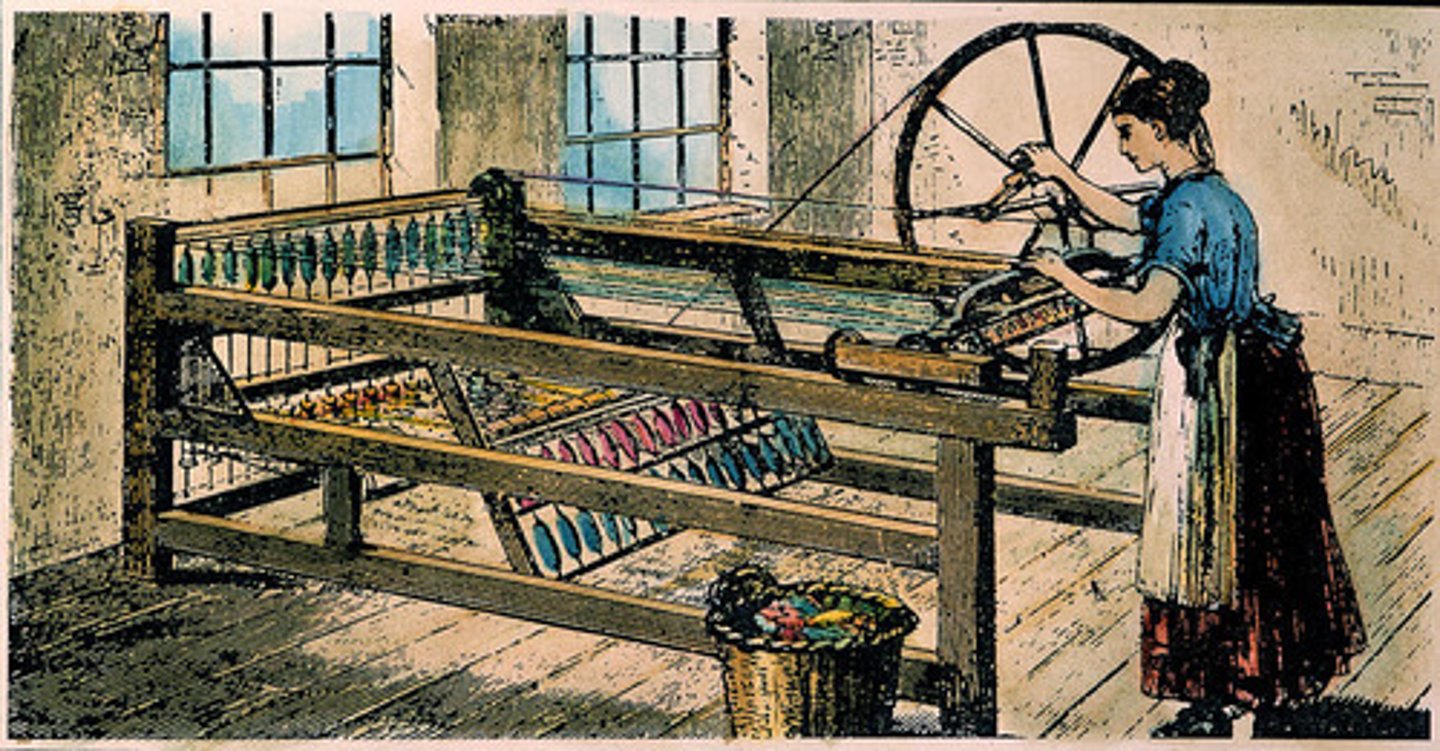
spinning jenny
A machine that could spin several threads at once to make cloth.
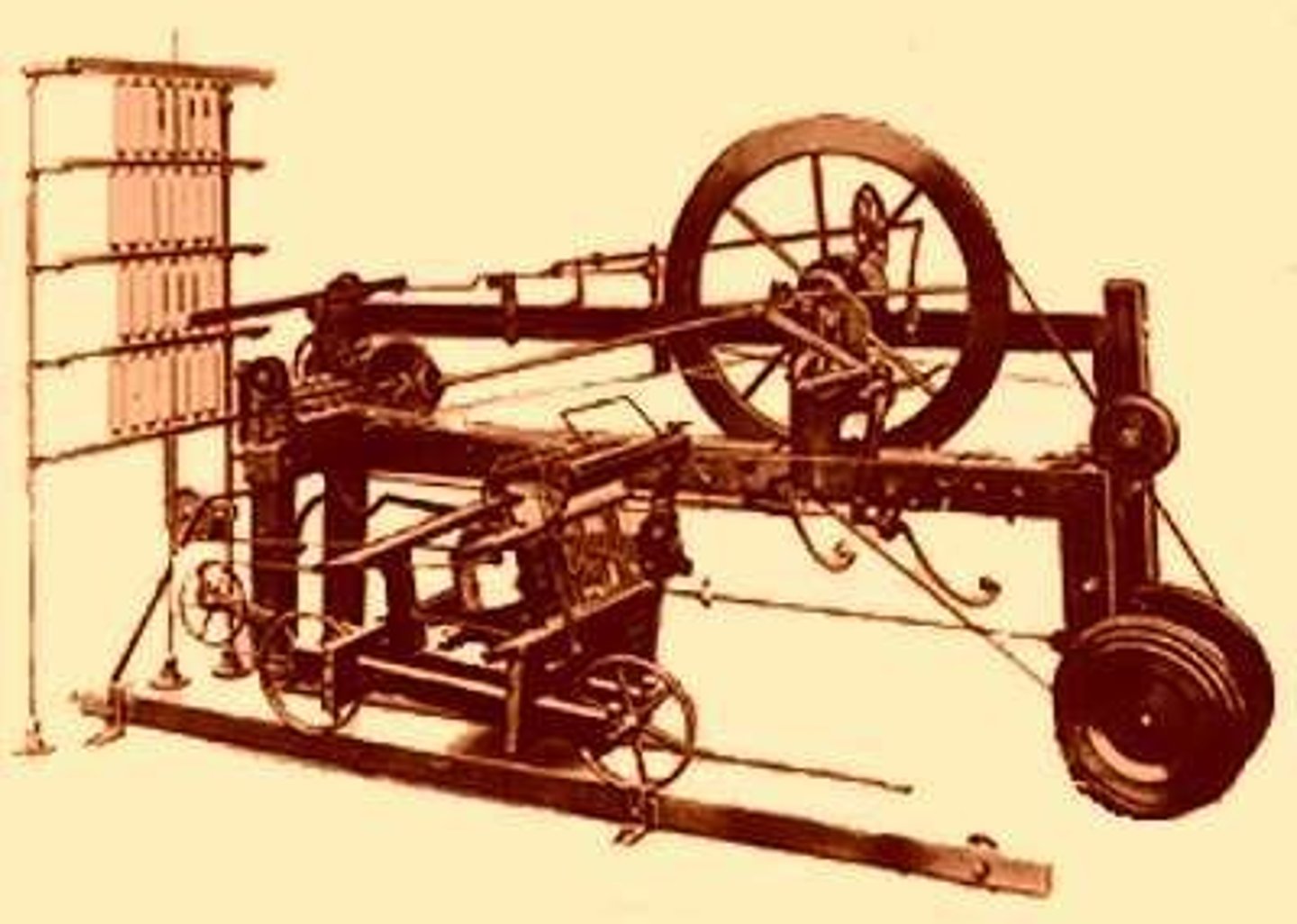
water frame
Invention that allowed factories to use the moving water to power machines.

spinning mule
combined the spinning jenny and the water frame to create a machine which produced a thread which was stronger, finer and more consistent
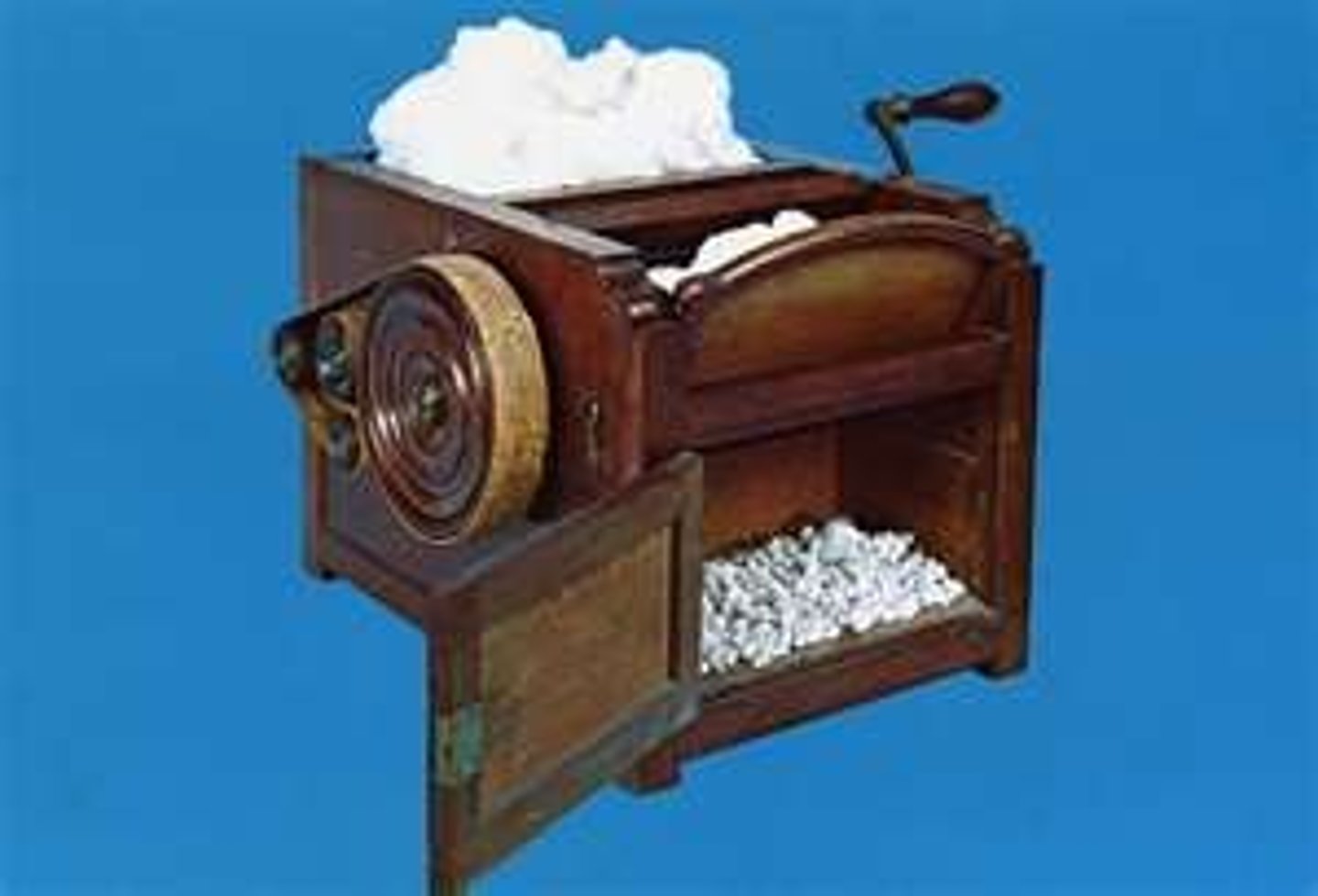
cotton gin
a machine that removed seeds from cotton fiber making cotton cloth production more efficient and less costly.

Le Chapelier Law
In June of 1791 this law made guilds and all trade union illegal in France. Made it illegal for workers to strike.
Bank of England
created in England 1694 to ensure a stable money supply and to lay the foundation for a network of lending institutions. Allowed Britain to be very powerful
Limited-Liability Corporation
made investment safer by making investors not responsible for a company's debts, but only for the amount they originally invested in it.
Triangle Trade
the extensive exchange of slaves, sugar, cotton, and furs between Europe, Africa, and the Americas that transformed economic, political, and social life on both sides of the Atlantic
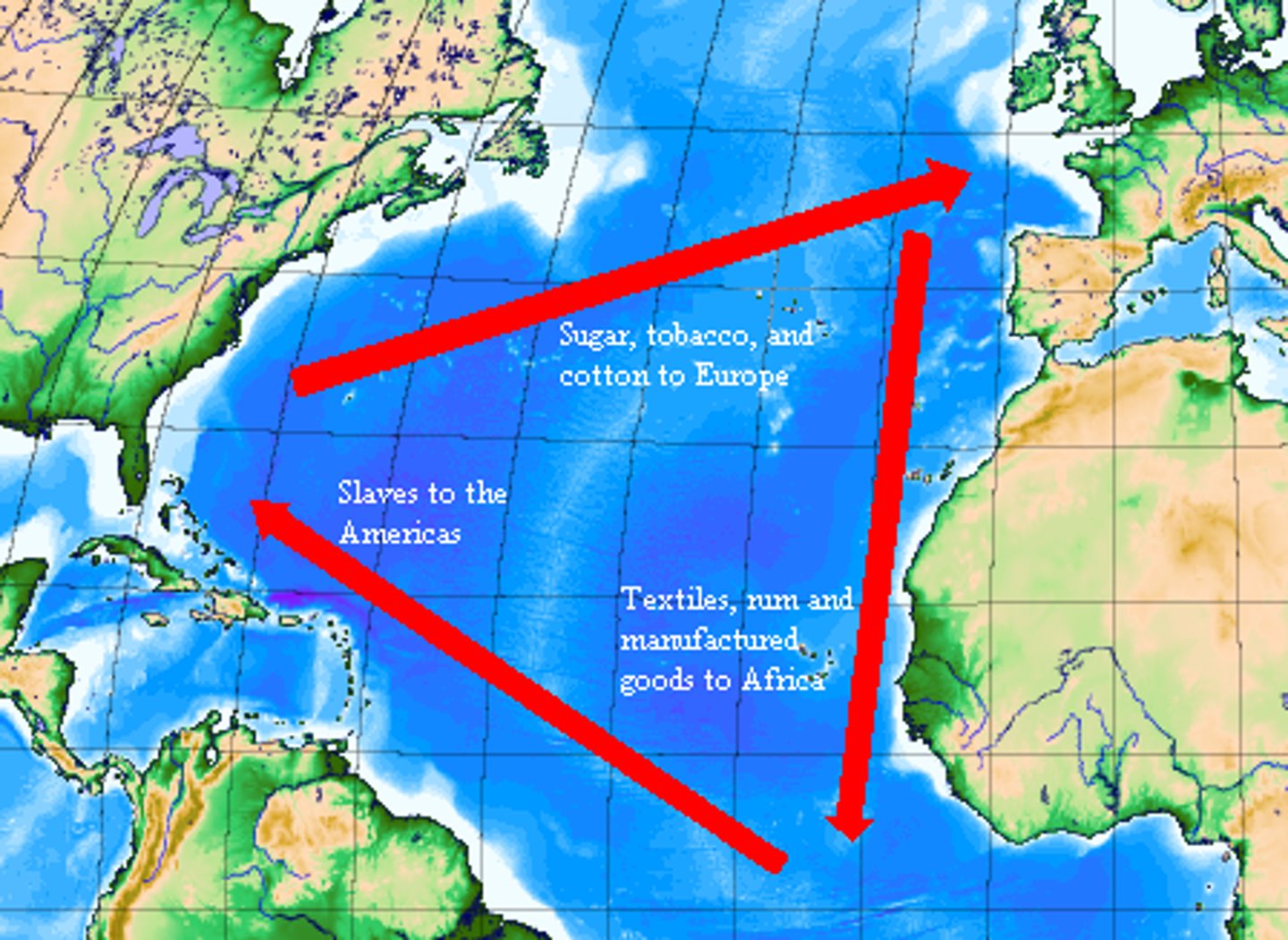
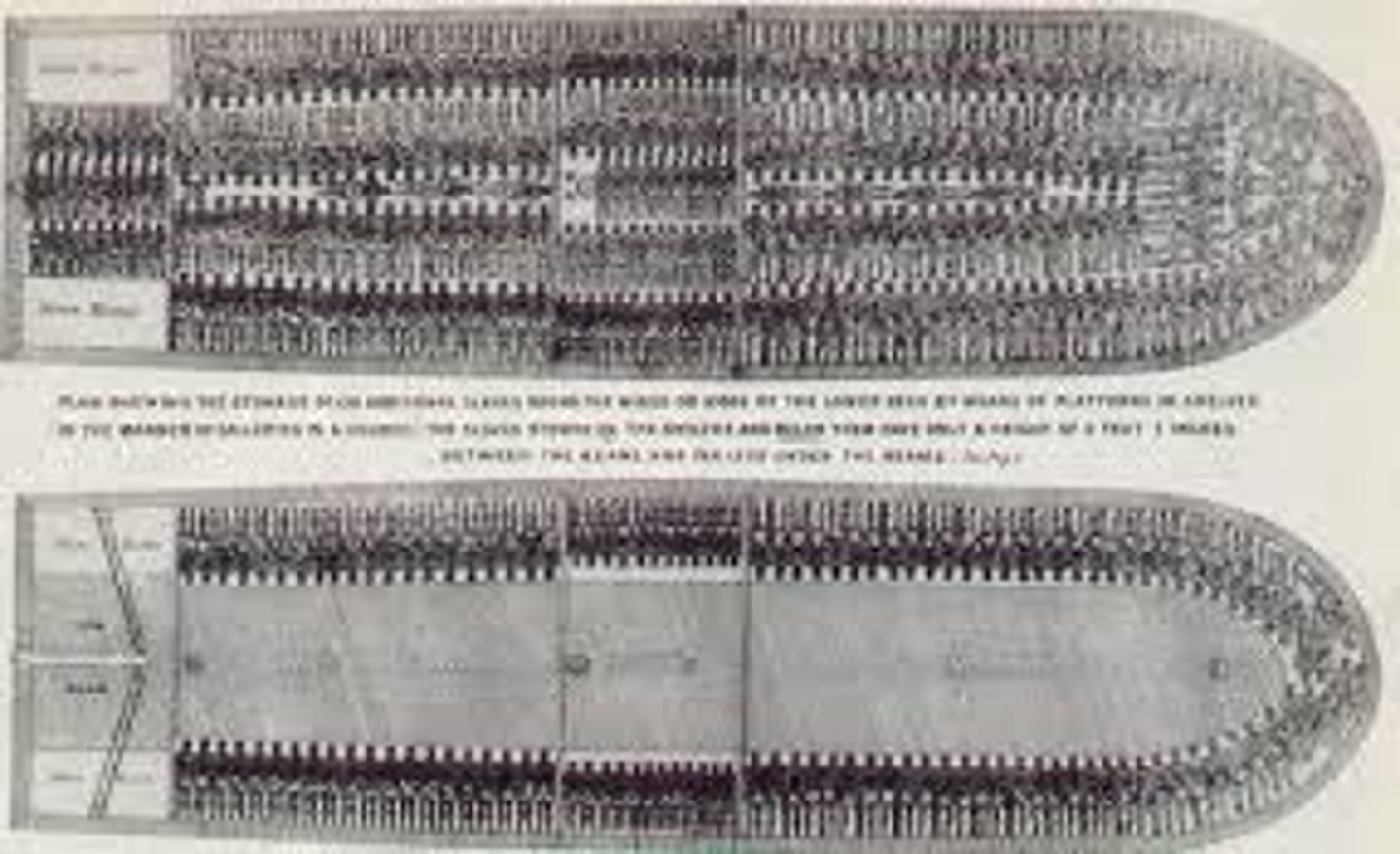
Middle Passage
the horrific sea journey undertaken by slave ships from West Africa to the West Indies.
Commercial Revolution
A dramatic change in the economy of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages. It is characterized by an increase in towns and trade, the use of banks and credit, and the establishment of guilds to regulate quality and price.
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
colonization
The expansion of countries into other countries where they establish settlements and control the people
Plantation
A large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two crops for sale, usually to a more developed country.
Navigation Acts
Laws that governed trade between England and its colonies. Colonists were required to ship certain products exclusively to England.
Joseph Marie Jacquard
French inventor of a loom that could automatically weave complicated patterns (1752-1834)
John Rolfe
Jamestown colony leader who showed that tobacco could be grown successfully in Virginia
Eighty Years' War
Dutch War of Independence from Spain (1568-1648), began as a revolt of the Seventeen Provinces against the political and religious oppression by Philip II of Spain.
Union of Utrecht
The alliance of seven northern provinces of the Netherlands (led by Holland) that declared its independence from Spain and formed the United Provinces of the Netherlands.
oligarchy
A government ruled by a few powerful people
urban gentry
The rich upper class of Holland that ruled in an oligarchy
Dutch East India Company
A company founded by the Dutch in the early 17th century to establish and direct trade throughout Asia.
Joint-Stock Company
A business, often backed by a government charter, that sold shares to individuals to raise money for its trading enterprises and to spread the risks (and profits) among many investors.
Balance of Power
system that prevents any one country from dominating the others
Absolutism
A political system in which a ruler holds total power over all institutions in a country.
Peace of Westphalia
the peace treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War in 1648, changing the system of diplomacy in Europe.
Gustavus Adolphus
Swedish Lutheran king who stabilized the Swedish government, modernized its military, and won victories for the German Protestants in the Thirty Years' War.
Dutch Revolt
This was the revolt by the Netherland against the Spanish in order to create their independent state (also known a the 80 Years' War).
Catalan Revolt
Revolt in Spain, due to Philip IV's Court Favorite, Count Olivares's attempt to gain access to that region's people and resources to fight the French
Parlements
French regional courts dominated by hereditary nobles. The one in Paris claimed the right to register royal decrees before they could become law in attempts to limit the power of the king.
Battle of Vienna
This battle in 1683 freed Europe from the threat of the Ottoman Turks as it stopped their expansion into Europe.
Dutch War
(1672-1678) Louis XIV's war against William of Orange to obtain territory in the Spanish Netherlands (modern day Belgium) ended with treaty of Nijmegen
Nine Years' War
1688 - 1697 (War of the League of Augsburg) Result of Louis XIV trying to extend French territory to the Rhine. France fought against England, the Netherlands, Spain, Austria, and the Holy Roman Empire.
Philip V
Grandson of Louis XIV who became the first Bourbon king of Spain after the War of the Spanish Succession.
War of the Spanish Succession
a conflict, lasting from 1701 to 1713, in which a number of European states fought to prevent the Bourbon family from controlling Spain as well as France.
Peace of Utrecht
A series of treaties, from 1713 to 1715, that ended the War of the Spanish Succession, ended French expansion in Europe, and marked the rise of the British Empire.
Frederick William I
Prussian king responsible for Prussian absolutism and continuing militarization. Grew it into an efficient state with a strong military.
Frederick the Great
(1712-1786), King of Prussia from 1740 to 1786. Enlightened despot who enlarged Prussia by gaining land by war from Austria
Maria Theresa
Empress of Austria whose main enemy was Prussia
Seven Years War
worldwide struggle between France and Great Britain for power and control of land (called the French and Indian War in the United States)
Sejm
The legislative assembly of the Polish nobility.
partition
divide into parts (as Poland was in the last 20 years of the 18th Century).
Philip II
(1527-1598) Absolute monarch of Spain at the height of its power. Obsessively Catholic and obsessively mistrusting of everyone.
Louis XIV
(1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
Cardinal Mazarin
Regent for Louis XIV until he was declared of age. The Fronde was actually a rebellion against his policies.
Cardinal Richelieu
Regent for Louis XIII, set in place the cornerstone of French absolutism. Attempted to break the power of nobility by creating the intendant system
Fronde
A series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV triggered by growing royal control and increased taxation--frightened Louis into becoming paranoid about control.
courtier
An attendant at a royal court, wealthy powerful nobles.
Palace of Versailles
Lavish palace constructed by Louis XIV to reflect his power and might and to control his nobles.
Jean Baptiste Colbert
An economic advisor to Louis XIV; he supported mercantilism and tried to make France economically self-sufficient. Brought prosperity to France.
tsar
A Russian emperor
Peter the Great
The tsar of Russia that Westernized Russia and built up a massive Russian army.
Grand Embassy
Peter the Great's long visit to Western Europe to learn Western technology economics and culture so he could Westernize Russia.
Great Northern War
War between Russia and Sweden that got Peter the Great a port on the Baltic Sea.
Russian Academy of Sciences
founded by Peter the Great as part of Russia's westernization and attempt to modernize Russia's intellectual community
boyar
Russian landed nobility.
Holy Synod
The replacement Peter the Great created for the office of Patriarch of the Russian Orthodox Church. It was a "bureaucracy of laymen under his supervision." and they were loyal to him
Catherine the Great
Empress of Russia who greatly increased the territory of the empire and attempted (but failed at) creating enlightened reforms in Russia.
vernacular bibles
Bibles written in the common language of the people, rather than Latin.
Puritans
Protestant sect in England hoping to "purify" the Anglican church by getting rid of of Roman Catholic traces in practice and organization.
Huguenots
French Protestants influenced by John Calvin
Concordat of Bologna
Treaty under which the French Crown recognized the supremacy of the pope and obtained the right for the government to nominate all French bishops and abbots (1516)
indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. It was common practice when the church needed to raise money.
Reformation
a 16th century movement for religious reform, leading to the founding of Christian churches that rejected the pope's authority
Martin Luther
a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief questioning some church practices.
95 Theses
Martin Luther's ideas that he posted on the church door at Wittenberg which questioned some Roman Catholic Church practices.
Diet of Worms
This was the conference that Charles V called to question/prosecute Martin Luther
Charles V
This was the Holy Roman Emperor that called for the Diet of Worms. He was a supporter of Catholicism.
Sola Scriptura
Belief that the Bible is the sole source of religious truth
Sola Fide
Belief in Justification by faith alone--faith alone is needed to get to heaven.