Mental Health 🪴
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Conduct Disorder
-Disregard for laws/rights of others leading to aggression and criminal behaviors
Behavioral FOR
-Idea that behavior is learned and can be unlearned
-Practice assertiveness through role playing
-Shape client’s behavior in safe environment
-Use relaxation/breathing activities for anxiety
mild intellectual disability
-can acquire ADL, IADL, vocational skills to be independent
-min support needed, some support for new things (moving, job)
moderate intellectual disability
-independence in routine daily skills, when provided with support
-supervised living required
-mod support for specific occupations (meal prep, use of public transport)
severe intellectual disability
-acquires communication skills, some health habits (brush teeth)
-impairment to motor and physical development
-assistance for most tasks
Selective Attention
Blocking out anxiety-inducing things
Immediate Memory
-aka short-term memory
-recalling material w/i seconds-minutes
-ex: putting in verification code to login
Working Memory
-aka recent memory
-recalling events of past few days
-ex: remembering where you parked your car at the airport after a short trip
Long-Term Memory
-aka remote memory
-recalling events of distant past
-ex: answering security question about high school mascot
Procedural Memory
-automatic sequence of behavior ~conditioned response
-ex: performing morning routine tasks
Declarative Memory
-fact recall
-OT student naming cranial nerves
Semantic Memory
-knowing meaning of words and being able to classify info
Episodic Memory
-knowledge of one’s personal experiences
-ex: remembering where you celebrated your birthday last year
Prospective Memory
-remembering to carry out actions in the future
*clinically important because it relates to a person’s ability to live safely and independently
-ex: person remember to turn stove off before leaving kitchen; paying bills by due date; remembering scheduled doctor’s appointments
Retrograde Amnesia
-inability to remember events that happened before the amnesia set in
OT mental health eval
-determine values, interests, roles, and goals
-identification of strengths and deficits
-identification of coping skills, stressors, and supports
OT MH intervention acute hospital
-during acute hospitalization, management of behaviors that threaten safety, stabilization of behaviors with activities that are brief and structured
-relax/stress management techniques, activities to inc communication
OT MH intervention long term hospital
-create self determined plan for goal achievement
-graded activities that inc ADL, IADL, social, leisure, work
-develop skills/external supports for post discharge roles
OT MH intervention for community setting
-facilitation of recovery, maintain skills
-skills needed for community living, social participation
-skills for ongoing recovery
-skills to get practical resources (SSI, afforable housing)
-individualized
-empowerment
-nonlinear
-peer support
-hope
-family
Wellness recovery action plan (WRAP):
Developmental Group Overarching Purpose
get skills for group interactions
Evaluation Group Overarching Purpose
gather info on persons task and group interaction to make goals and interventions
Instrumental Group Overarching Concern
-concerned with meeting health needs and maintaining function through socialization and participation in activities
-not about skill development or expressing emotions
Model of Human Occupation (MOHO)
Three Main Elements
volition
habituation
performance capacity
Environment
physical and social components
environment impacts individuals with opportunities, demands, resources, constraints
PEO model
-occ performance is dynamic in nature
-transactional relationship of the 3 elements
-eval emphasizes the occupational performance issue, environment
-OT intervention should involve improving fit between person, environment, and occupation
Cognitive Disabilities Model
-Based on cog development from Piaget
-Cognition is based on biological factors, and if it cannot change, adaptations the activity provides opportunity for success
-Use client’s strengths to allow for function
-When max level reached, compensation must be made to person, or environment
-Train caregiver to provide appropriate environmental supports for the client
Ecology of Human Performance (EHP)
-emphasis on the role of the person’s contexts (culture, physical, social) and its impact on performance
-ecology: interaction of person and environs
-person+task+context= performance
-skills can be inc/dec d/t illness
-contexts are dynamic
-roles are made up of tasks
-people are empowered by inc self-determination
5 Strategies of Ecology of Human Performance (EHP)
⚡️Elves wear A CAPE (EHP goes with a. c.a.p.e.)
alter: change the context the person is trying to perform in (environ mods)
create: supporting optimal performance without assuming there is a disability; designing new environs, contexts, tasks (workspace layout, new program)
adapt/mod: changes to the context and task for better performance (AE, simplifying tasks)
prevent: minimize problems that may develop by changing the client, context or task; assumes there is a disability or one is likely to occur
establish/restore: teaching skills lost d/t illness; improve ability and function
Occupational Adaptation (OA)
-focused on the process person goes thorough internally to adapt to environment
-person consists of cognitive, psych social components- desires mastery
-occ environment is physical, social, cultural systems- demands mastery
-outcome of interaction of those two is the occ response
-Expected improvements through OT are improved self-initiation, generalization, and relative mastery
Role acquisition
-person uses tasks and social skills to meet demands of roles
-performance addressed through task skill, interpersonal skill, family interaction, ADL, school, work, play
-focus on getting skills to function in environs
Lifestyle performance model
-match the environment and the persons needs
4 hypotheses
-competency in valued/prioritized occupations-society cares about having greater meaning and social efficacy
-activity has symbolic and reality-based meaning
-activites that mesh well with our neuro/psychological structures make us feel better
-competence is more easily seen with end products
-the use of sensory modalities or activities to prepare someone for therapy/occupation
-such as snoezelen rooms, multisensory environs, weighted blankets, self-soothing toys, sensory diets
-includes brushing patterns for sensory defensiveness (avoidance pattern)
Sensory avoiding
Sensory sensitivity
Poor registration
Psychodynamic FOR
-behavior determined by unconscious forces, resolved when brought to conscious thought
-behavior patterns begin in early childhood, and early childhood experiences can affect clients in the future
-interventions include open ended/ unstructured/ task oriented groups to explore the inner psyche (discussion, journaling, painting, etc.)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
-effective for depression,schizo, anxiety, bipolar, OCD, eating disorders
-works to alter negative thoughts about self, life by correcting misinterpretations
-changes in cognitive processes to facilitate behavior and emotional changes
OT Interventions:
-learn to manage anxiety with relaxation skills
-systematic desensitization- exposure to anxiety producing stimulus with graded contact, reframing & relaxation, until trigger no longer produces anxiety (NEED specialized training for this approach)
-assist in identifying current problem/solution
-identify distorted/unhelpful thinking
-scheduled activities to inc mastery
-cognitive rehearsal/ role playing
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
-focuses on helping people accept the reality of their lives/behaviors & help them learn to change their lives
-good for clients with difficulty managing and regulating emotions (borderline personality disorder)
-talk based therapy
OT Interventions
Assertiveness, coping skills, distress tolerance, interpersonal skills
Mindfulness, emotional regulation
Recovery Model
-fostering ppls intrinsic motivation for hope
-focus on improving QOL
-recovery from illness as a journey of healing
-self-direction: ppl identify their own goals
-person-centered: recovery is unique to each person
-empowerment: people take control over lives and recovery
-peer support: reciprocal relations with others with lived experiences
-should be community-based where ppl live
-vocation focused: work is healing
Reasons to use one-to-one interventions in lieu of group
-refusal of group, inability to tolerate group, disruptive behavior, suicide precautions/danger to self/others
Developmental Group Levels of Interaction
parallel: individual tasks with no required interaction with others; OT is directive and supportive
project: common, short term activity, some interaction is required to complete task; OT chooses activity
egocentric-cooperative: joint interaction on long term task; clients choose task rather than OT; OT acts more as role model
cooperative: learning to work together, to enjoy company, gain sense of fulfillment; completion of task is secondary to sharing emotions/expressing ideas/self-expression; OT acts as an advisor
mature: carrying out task and meeting needs of people in the community; completion of project and group interaction are equally important; OT acts as peer
Task-Oriented Groups Purpose
-purpose is not to complete a task, tasks are used as a means of exploring feelings, thoughts, and needs
-ex: painting, journaling
-aligns with psychodynamic FOR
Thematic Group Overarching Purpose
-learning a specific skill with a structured/simulated activity that can be graded
-ex: making a birdhouse
⚡️thrive with thematic
Topical Groups Overarching Purpose & Two Types
-focus on discussion of activities and issues of the group
-Concurrent Topical Group- talking about current events
ex: parents talking about raising child with SCI
-Anticipatory Topical Group- talking about topic that has not yet happened but will happen in the future
ex: retirement planning; caregiver support group about supporting loved one after hospital discharge
Managing Difficult Behaviors
(Hallucinations, delusions, akathisia, offensive physical/verbal acts, lack of initiation, manic/monopolizing behaviors, escalating behavior, kids acting out)
Hallucinations: make environs free of distractions, highly structured, concrete activities, redirect to reality-based thinking
Delusions: dont refute the delusion, redirect to reality, avoid discussions that validate the belief
Akathisia (cant sit still, restless, shaky legs, hand tremors): allow to move w/out disruption, select gross motor activities
Offensive physical/verbal: set limits and immediately address behavior, reasons its not accepted should be explained, needs of entire group should be first thought
Lack of initiation: id reason for lack, make interaction w/i area of interest, success/fun is motivator, curiosity/food is motivator
Manic/monopolizing: highly structured activities, redirect attention to others
Escalating behavior: avoid challenging them (direct eye contact), actively listen, calm voice, clearly present what you want them to do
Acting out kids: put words to why the kid is behaving that way, redirect to assignment, limit setting, time out
Attention disturbances
- Ability to focus on various aspects of an activity
- Distractability is inability to concentrate one's attention without being drawn to irrelevant stimulus
- selective inattention is blocking out those activities that produce anxiety
- Hypervigilance is excessive attention to guard against danger
Disturbances of Consciousness
- Disorientation- changes to orientation of person, place, or time
- Delirium- acute/ reversible marked by confusion liability and disturbances in behavior
- Confusion- inappropriate reactions to environmental stimuli
- Sundowner syndrome- happens in the late afternoon with people with dementia. Drowsiness confusion agitation and aggression
Emotional Disturbances
- Physiological disturbances associated with mood are autonomic in nature
-Inappropriate affect- inconsistent with accompanying thoughts or ideas
- Blunted Affect- lack of affect and does not change
- Flat Affect- absence of signs of emotion
- Labile Affect- rapid and abrupt changes in emotion
Disturbances in Motor Behavior (echopraxia, catatonia, psychomotor agitation, hyperactivity, psychomotor retardation)
Echopraxia- imitation of other person’s movements
Catatonia- immobility or rigidity
Stereotypy- repetition of fixed patterns of movement
Psychomotor Agitation- excessive motor and cognitive activity
Hyperactivity- restless sometimes aggressive activity
Psychomotor Retardation- decreased/slowed movement
Hallucinations vs. Illusions
- hallucinations are false sensory perceptions not linked to external stimulus (just responding to internal stimuli ~voices in head)
- illusions are misperceptions or misinterpretations of real sensory events
Disturbances of Perception (agnosia, astereognosis, apraxia, adiadochokinesia)
Agnosia is inability to understand and interpret sensory input
visual agnosia- inability to recognize people and objects
prosopagnosia- face blindness
Astereognosis- inability to identify objects through touch
Apraxia- inability to carry out specific motor tasks
Adiadochokinesia- inability to perform rapidly alternating movements
Disturbances of Conversion and Dissociative Phenomena (derealization, depersonalization, dissociation)
- Derealization- sense that the environment is unreal
- Depersonalization- sense of unreality about one's self
Fugue- state of serious depersonalization involving travel where they take on a new identity with amnesia about former identity
- Dissociation- separation of a group of mental/behavorial processes from rest of persons brain activity ~doing activity while being totally zoned out
Disturbances of Speech (pressured, poverty, poverty of content, non-spontaneous, stuttering, perseveration)
- Pressured speech- rapid and increased in amount
- Poverty of speech- limited in amount
- Poverty of content and speech- does not give information
- Non spontaneous speech- responses that are given only when spoken to
- Stuttering- repetition of sounds or syllables
- Perseveration in speech- continued repetition of word or phrases
Disturbances of Thought (circumstantiality, tangentiality, flight of ideas, loosening of associations, perseveration, thought blocking, delusions, compulsions, obsession, concrete thinking)
Form:
-Circumstantiality- speech that is delayed in reaching the point
- Tangentiality- abrupt change of focus or loosely associated topic
- Flight of ideas- rapid change in thoughts
- Loosening of associations- ideas shift from one subject to another with no obvious connection
-Perseveration- persistent focus on previous topic/behavior after a new topic/behavior has been introduced
-Thought Blocking- interruption of a thought before it is carried through to completion
Content:
- Delusions- false beliefs about external reality
- Compulsions- need to act on a specific impulse to relieve anxiety
-Obsession- persistent thought or feeling that cannot be eliminated by thought
-Concrete Thinking- inability to think abstractly (difficulty understanding idioms/jokes)
Schizophrenia Diagnosis & OT Interventions
- Two or more of the following symptoms
delusions
hallucinations
disorganized speech
catatonic behavior
- Negative symptoms
flat affect
anhedonia (difficulty in experiencing pleasure)
alogia (decreased thought/speech),
anergia (lack of energy)
DON’T mistake for lack of motivation
inability to relate to others
-disturbances in work, relations, self care
-ongoing signs of illness 6 month
-other things have been ruled out
-not caused by illness or drugs
OT Interventions for Schizophrenia & Related Psychotic Disorders
Communicate clearly/simply/concretely
Provide external structure/consistency to help organize thinking
Ensure activities are simple and structured
Provide supports/tools for recovery like a Wellness & Recovery Action Plan (WRAP)
Common Short Assessments of Mental Status
-Mini-Mental State Examination aka Folstein Mini-Mental
-Short Portable Mental
-MoCA
assesses orientation, short-term memory, executive function, language, abstraction, animal naming, and attention
-SLUMS
Schizoaffective Diagnosis
- Uninterrupted period of illness which there is major depressive/manic episode concurrent with positive or negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia
Schizophreniform Disorder
- person meets criteria for schizophrenia however lasts less than six months
Delusional Disorder
- Presence of one or more delusions for the duration of a month or longer and the criteria for schizophrenia has not been met
Brief Psychotic Disorder
- presence of one or more sensory behavioral cognitive or psychomotor symptoms
- Symptoms range from one day to one month
Side Effects & Complications of Traditional Antipsychotic Medications
Common Meds: Haldol, Thorazine
Side Effects
Photosensitivity- teach sunburn precautions
Orthostatic Hypotension- watch for increased fall risk
Dystonia
Dry mouth, blurry vision, constipation, cardiovascular disorders
Complications
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome- autonomic emergency leading to increased blood pressure, tachycardia, convulsions, coma
Tardive dyskinesia- abnormal involuntary irregular, slow, rhythmic movements of the head, tongue, fingers that results from long-term use of antipsychotic meds
OT should use Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale to measure uncontrollable movements during every intervention session to monitor symptoms & side effects
Neuroleptic Induced Parkinsonism- muscle stiffness, cogwheel rigidity, shuffling gait (usually no pill rolling tremor)
Side Effects & Complications of Second Generation Antipsychotic Medications
Common Meds: Clozaril, Risperdal, Seroquel, Abilify
Generally much less side-effects/complications than first gen
Side effects
Vary between each med
Clozaril can cause agranulocytosis where WBCs to decrease to fatal level; need close monitoring
Complications
Metabolic Syndrome- high blood glucose, low good cholesterol, high level of triglycerides, high BP. Increases risk of heart attack & stroke
Bipolar I
- One or more manic episodes, may be combined with major depressive episode
Bipolar II
- One or more major depressive episodes, must be at least one hypomanic episode
- No history of manic episode
Manic Episode
-3 or more symptoms for a week
- Mood is uncharacteristically and inconsistently elevated/irritable
- increase in targeted goal directed behavior or restless purposes behavior (psychomotor agitation)
- inflated self esteem or thoughts of grandeur
- decreased need for sleep
- pressured or quick speech
- increased engagement and subjectively pleasurable HIGH-RISK activities
-marked impairment in daily functioning
-Suggestive dressing, gambling, promiscuity, irritable, suicidal
-Lithium commonly used for mood stabilizing, as well as anti psychotics
side effects: excessive thirst, tremors, excessive urination, weight gain, nausea, diarrhea, cognitive impacts
*high levels of lithium can cause nerve damage and death- blood levels should be carefully monitored to ensure lithium levels are in therapeutic window
*early symptoms of toxicity include motor disturbances
-Anticonvulsants are another medical treatment
Tegretol, Depakote, Lamictal
Side effects can lead to increased risk of falls (drowsiness, ataxia, dizziness)
-Antipsychotic meds are also commonly prescribed
Seroquel, Risperdal, Zyprexa, Abilify
OT int: Limit setting to improve boundaries/promote safety, engagement in structured activities to release energy, period between episodes should be used to educate about symptom management
Major Depressive Episode Diagnosis, Meds & OT Intervention
- Five or more symptoms must be present for two weeks
- Depressed mood or loss of interest
- fluctuations in weight
- changes in thinking or behavior such as slowing down and thinking
- fatigue or loss of energy
- changes in mood or self perception including feelings of worthlessness
- decrease the ability to concentrate on tasks
- Suicidal thoughts
- difficulty falling asleep
- Behavior is either irritable, anxious, difficulty with social interactions
-SSRIs- Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, Celexa, Lexapro
Side effects increased HR, dysrhythmias, seizures, disturbed balance/OH can increase fall risk
-MAOIs- Nardil, Parnate
Interaction with tyramine can cause stroke/serious cardiac issues
Must avoid various “picnic” items: aged cheese, pickled foods, processed meats, fermented foods, fruits that ripen to eat (bananas, avocados), chocolate, beer, red wine, soy products
Must also avoid cold, sinus, and hay fever medications, nasal decongestants, inhalers, and appetite suppresants
STOP MED & NOTIFY DOC IMMEDIATELY if pt complains of severe headache or palpitations (first signs of hypertensive crisis)
OT Interventions
Provide safe environment and manage behaviors that threaten safety/well-being
Look out for suicidal behavior
*Most dangerous time for this is when signs of depression seem to vanish, ex just before discharge from inpatient
Use cognitive approaches to therapy (CBT)
Can still use therapy after pt has received electro convulsive therapy (ECT) just keep in mind that they may have temporary memory loss/confusion and may need a simpler task to complete
Persistent Depressive Disorder
- At least two years of depressive mood most days with depressive symptoms
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
- Severe and recurrent verbal behavioral episodes, uncharacteristic for expectations consistent with developmental level
- Diagnosis may be made between the ages of six and 18
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
- Marked affective lability, irritability, increased personal conflict, depressed mood, anxiety during PMS period
Substance Related Disorders
- Diagnosed on taking the drug, the side effects, the exposure to toxins
- use: consumption that causes impairments that affects daily functioning
- Intoxication: causes problems both behaviorally and mentally
- withdrawal: stopping significant consumption causes physical symptoms
Substance Use Disorder & OT Considerations
- Two of the following symptoms must be present within a 12 month.
- Substance reviews in large quantities which may develop to a tolerance for the substance
- Significant amount of time is dedicated to the use of the substance
- Desired use substance is stronger throughout the day, behavior continues despite the physical harm, attempts to cease fail
- Ongoing substance use causes disruption in social, occupational, educational, and daily life
OT Considerations
Try to avoid overestimating client’s abilities d/t their survival skills
Rely on observation and assessment of actual skills
Help pt to ID reasons for substance use
Help pt to develop healthy coping skills for life stressors
Communication/social skills to support substance free social participation and advocate for needed services
Skills for work/school/home management
Leisure exploration
Refer to support groups for sustained recovery (ex: AA, NA, halfway house)
Gambling Disorder
- Thoughts of gambling occupied the mind
- multiple unsuccessful attempts usually irritable and unhappy
- gambling increases with stress
- serious financial trouble
- gambling behavior continues even after loss
- lies to downplay the frequency of gambling
Panic Attacks
-Just a symptom not a diagnosis
- Discrete period of fear/discomfort with four or more symptoms developed within minutes
Heart palpitations, sweating/chills, trembling, shortness of breath, nausea/vomiting, dizziness
Derealization feelings of loss of control, fear of dying, paresthesia
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Six months of persistent and excessive unfocused anxiety
Panic Disorder
- Recurrent panic attacks with concern for recurrence
Selective Mutism
- Consistent inability to speak in social situations when expected, despite being able to speak in other circumstances (i.e. being totally silent at school, but talking at home)
- must be present for at least one month and not attributable to a communication disorder
Separation Anxiety Disorder
- excessively attached to another individual, the level of anxiety is considered developmentally inappropriate and unwarranted
OT Considerations for Anxiety Disorders
- Skills training and using cognitive behavioral approaches may reduce anxiety
- Relaxation and stress management skills
- graded activities designed to promote self efficacy
- systematic desensitization which involves incremental exposure to specific fears with imagery and relaxation and then contact with the image/actual object (used with phobias) *requires special training
Personality Disorder Clusters & General OT Considerations
-Skills training and cognitive behavioral approaches (CBT/DBT)
-Relaxation and stress management skills
-Graded activities to promote self-efficacy
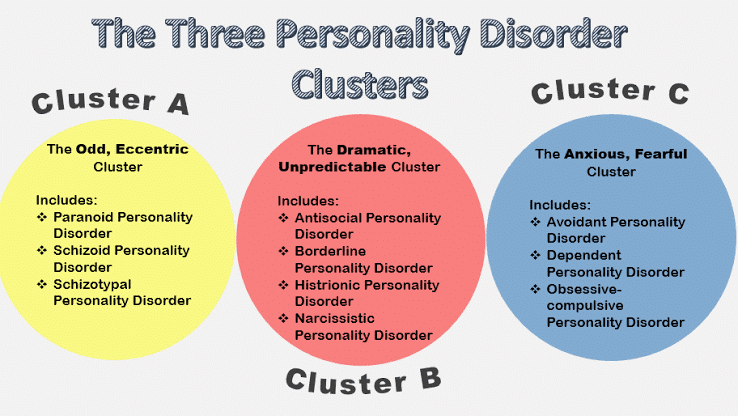
Antisocial Personality Disorder
-fka sociopathy
- Characterized by continual antisocial or criminal acts
- and ability to conform to social norms
- no regard for the safety or feelings of others
-no remorse
-Conduct disorder is often a precursor diagnosis to antisocial personality disorder
Avoidant Personality Disorder
- Extreme sensitivity to rejection which may lead to social withdrawal
- Show great desire for companionship but think of themselves unworthy
- unusually strong need for uncritical acceptance
~inferiority complex
Borderline Personality Disorder
- Recurrent self destructive/ self mutilating behavior
- fear of abandonment
- Extraordinarily unstable affect, mood, behavior
-History of trauma (physical, sexual, emotional abuse) is common
- intense interpersonal relationships with alternating extremes of idealization and evaluation
- Chronic feelings of emptiness
-DBT can help to increase functional/coping skills and decrease symptomatic behavior
Dependent Personality Disorder
- Excessive need for others to take care of their physical/emotional needs
- Lack self confidence
- Experience discomfort when alone for more than a brief period
Histrionic Personality Disorder
- Colorful dramatic extroverted behavior
- Inability to maintain deep long lasting attachments
Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Characterized by a heightened sense of self importance and grandiose feelings that they are special
Obsessive Compulsive Personality Disorder
- Emotional constriction, orderliness, perseverance, stubbornness
- Pervasive pattern of perfectionism and inflexibility
- NOT the same as obsessive compulsive disorder
Paranoid Personality Disorder
- Characterize my long standing suspicions and mistrust of people
- appear hostile irritable and angry
Schizoid Personality Disorder
- Lifelong patterns of social withdrawal
- discomfort with human interaction, bland/constricted affect
-often appear eccentric, isolated, or lonely
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
- Appear odd or strange in their thinking and behavior
- magical thinking, peculiar ideas, illusions, and derealization
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Obsessions are persistent thoughts or feelings that are unwanted intrusive and inappropriate
- Compulsions are irresistible urges that take on the form of repetitive behavior typically through strict or specific rules
- Obsessive thoughts and behaviors are time consuming and intrusive
-Individual realizes they are not rational
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Person is preoccupied with a perceived physical flaws
- repetitive thoughts or behaviors as an attempt to conceal these flaws
- can cause significant interruptions in social and occupational areas of functioning
Hoarding Disorder
- Perceive need to save items and difficulty or and difficulty or discarding possessions
- Accumulation of items results in cramped cluttery living conditions compromise safety
Trichotillomania
- Compulsive irresistible desire to pull out ones hair
Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD) of Infancy or Early Childhood
- Child is characterized by social neglect or instability of primary caregiver
- interactions are excessively inhibited hypervigilant
- Inability to exhibit appropriate selective attachments
- overly affectionate with strangers
-frequent lying, hoarding, gorging, denial of responsibility, projecting blame
-OT considerations: Ongoing collaboration with child's family, assist child to form sense of self, limit exposure to multiple caregivers, provide high level structure
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
- Child initiates active interactions with unfamiliar adults with little reservation when approaching unfamiliar people, child is willing to leave with unfamiliar adult without hesitation
- upbringing characters by social neglect, constantly changing caregiver
-Child has developmental age greater or equal to 9 months old
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
- Exposure to threats are actual events which can result in sexual bodily injury or death
- first hand witness to a traumatic event, or learning about traumatic events
- repeated exposure to visual explanation of adverse details
- intrusive symptoms for more than 1 month intrusive memories related to the event, physical or mental exposure to the traumatic event
- Changes in patterns of behavior to avoid external stimuli that reminds them of the event
Adjustment Disorders
- Clearly identifiable stressor causes emotional or behavioral symptoms within three months
- symptoms resolve and disappear within six months of the stressor
Delirium
- Brain dysfunction, medication, endocrine disorders, cardiac disorders, fever can cause delirium
Anorexia Nervosa
- Low body weight due to difficulty maintaining weight, with fear of gaining weight or becoming fat
- alterations and self perception of body weight or shape
- food restrictive or binge eating/purging type
-often accompanied with low self-esteem/feeling less capable than others
Bulimia Nervosa
- Ongoing binge eating of larger portions than would be expected
- use of laxatives or vomiting or exercise to reduce weight
- person’s self conception defined by body proportions
-*teens with bulimia have higher rates of suicidal ideation/attempt than teens with anorexia