Aortic insufficiency/regurgitation
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
Blood moves backward through the Av from the aort to the LV through diastole
Define aortic insufficiency
Diastole
When does AI occur
Determine etiology, understand Pathophysiology, recognize clinical history, assess LV size and function, measure aortic dimensions, estimate severity of AI
What are the 6 steps of the role of echo in AI
Cuspal abnormalities, aortic root dilation, loss of commissural support
What are the 3 groups of mechanism that can cause AI
Any congenital disorder or disease process that affects the AV cusps
What are cuspal abnormalitites limited to
Congenital abnormalities, rheumatic AV disease, AV prolapse, infective endocarditis
What does cuspal abnormalities include
Infective endocarditis
What is the most common "itis" in the heart
Bicuspid and quadricuspid AV
What are the two congenital abnormalities that can effect the AV
Bicuspid aortic valve
What does BAV stand for
True
T/F: quadricuspid AV is extremely rare
Anomalous coronary artery origin
What is quadricuspid AV associated with
Quadricuspid AV
What does this image represent
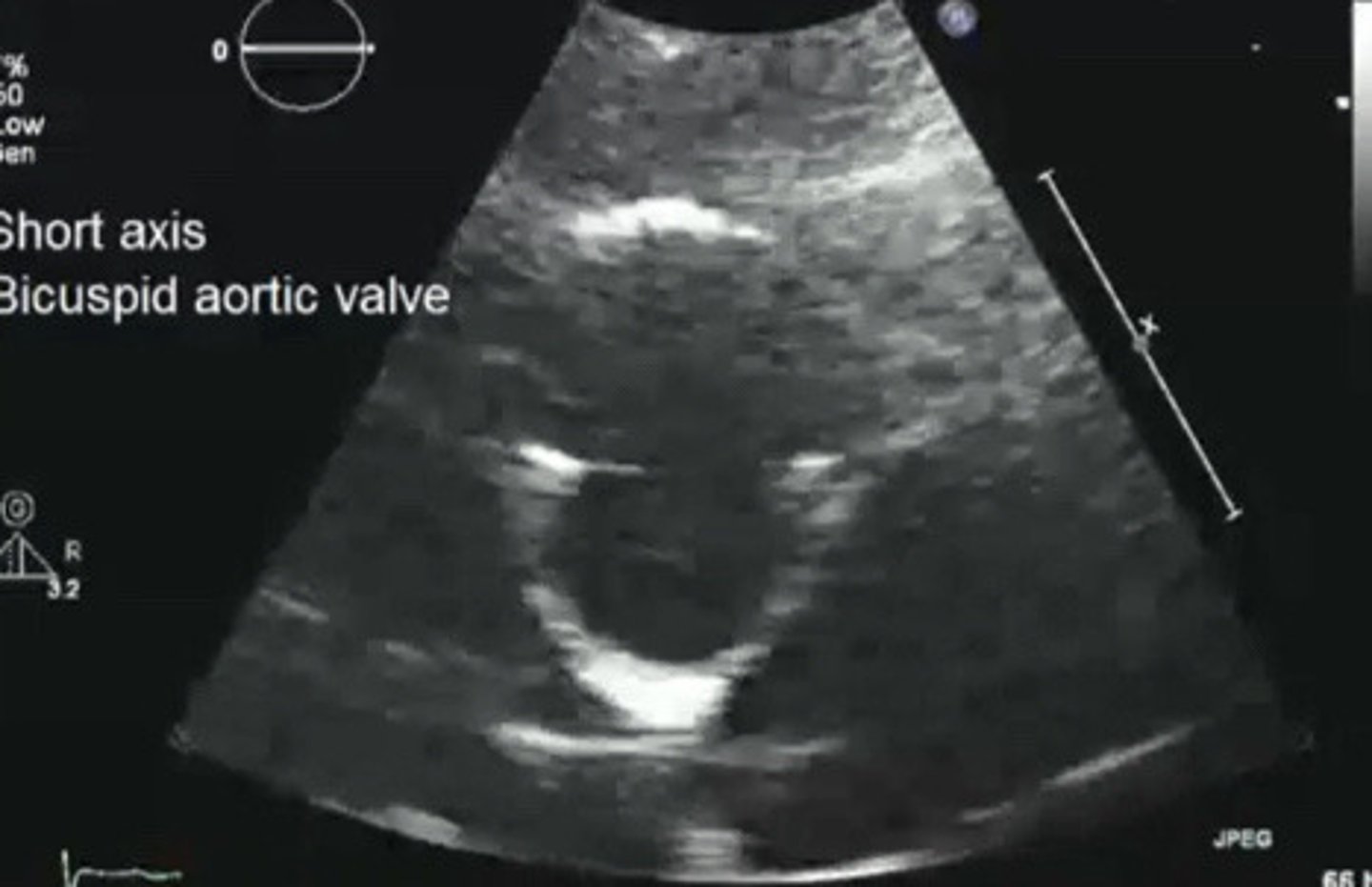
Bicuspid AV
What does this image represent
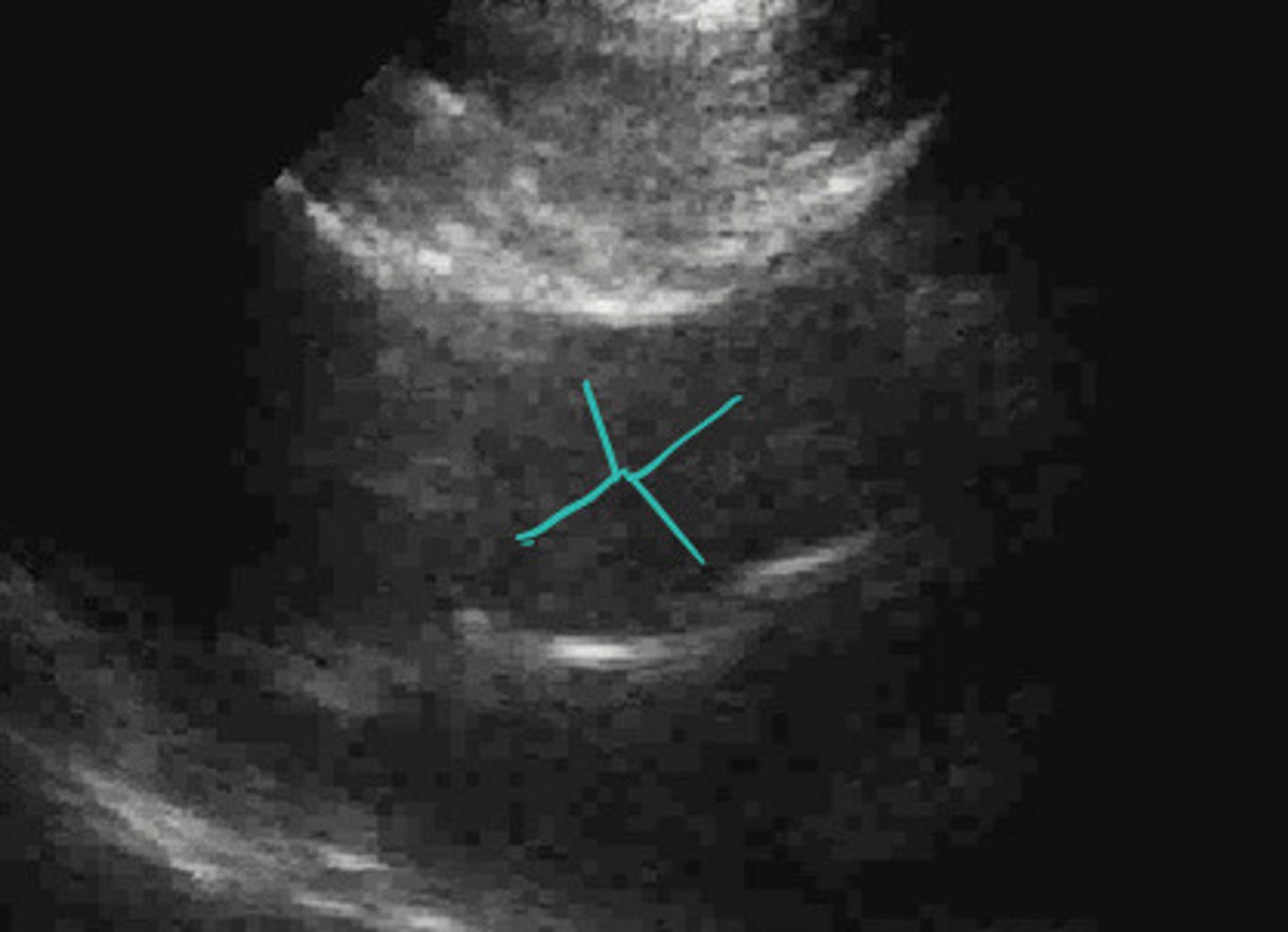
Eccentric closure line of AV suggesting BAV
What does this image represent
Small mass suggesting BAV
What does this image represent
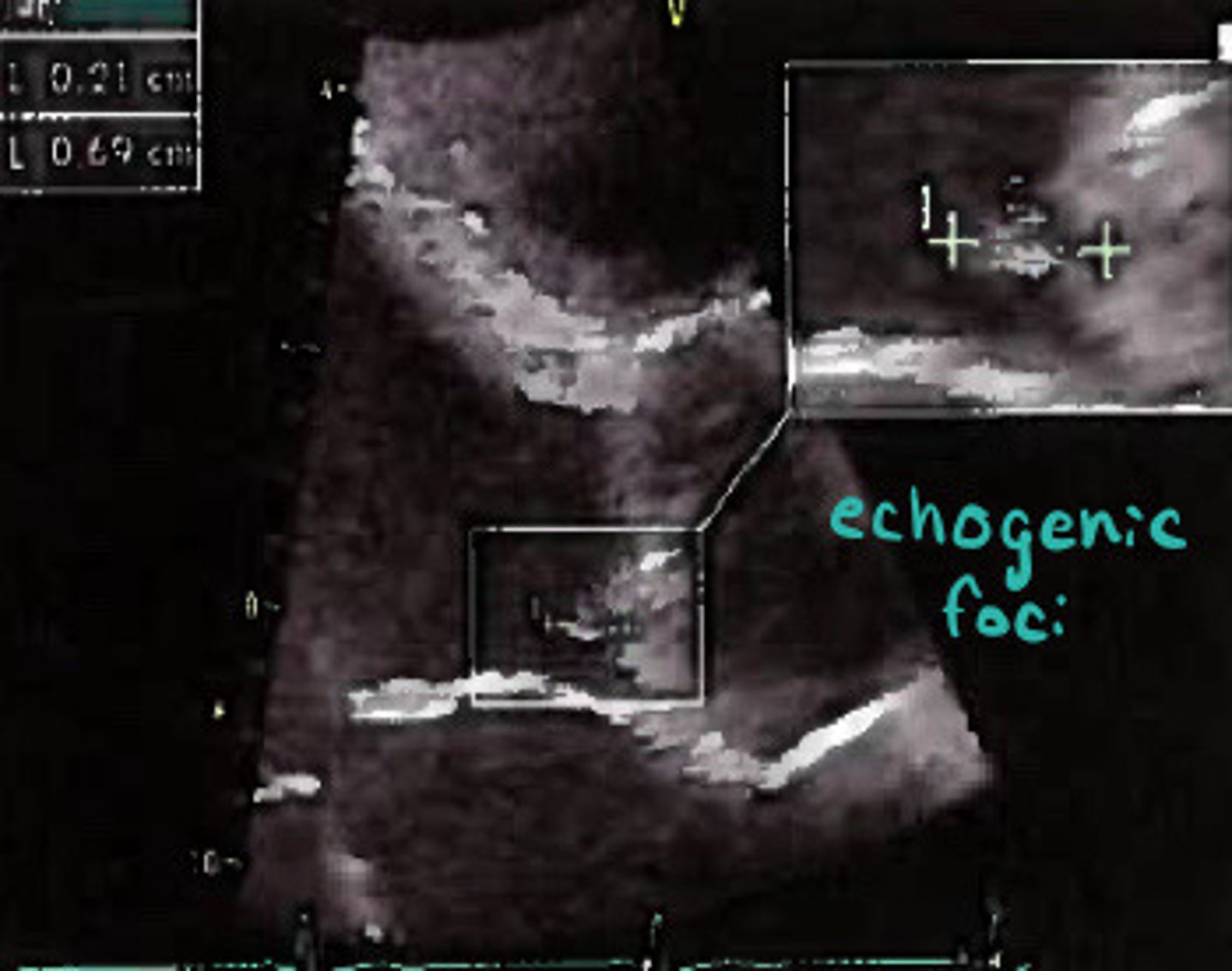
Eccentric AI jet suggesting AI
What does this image represent
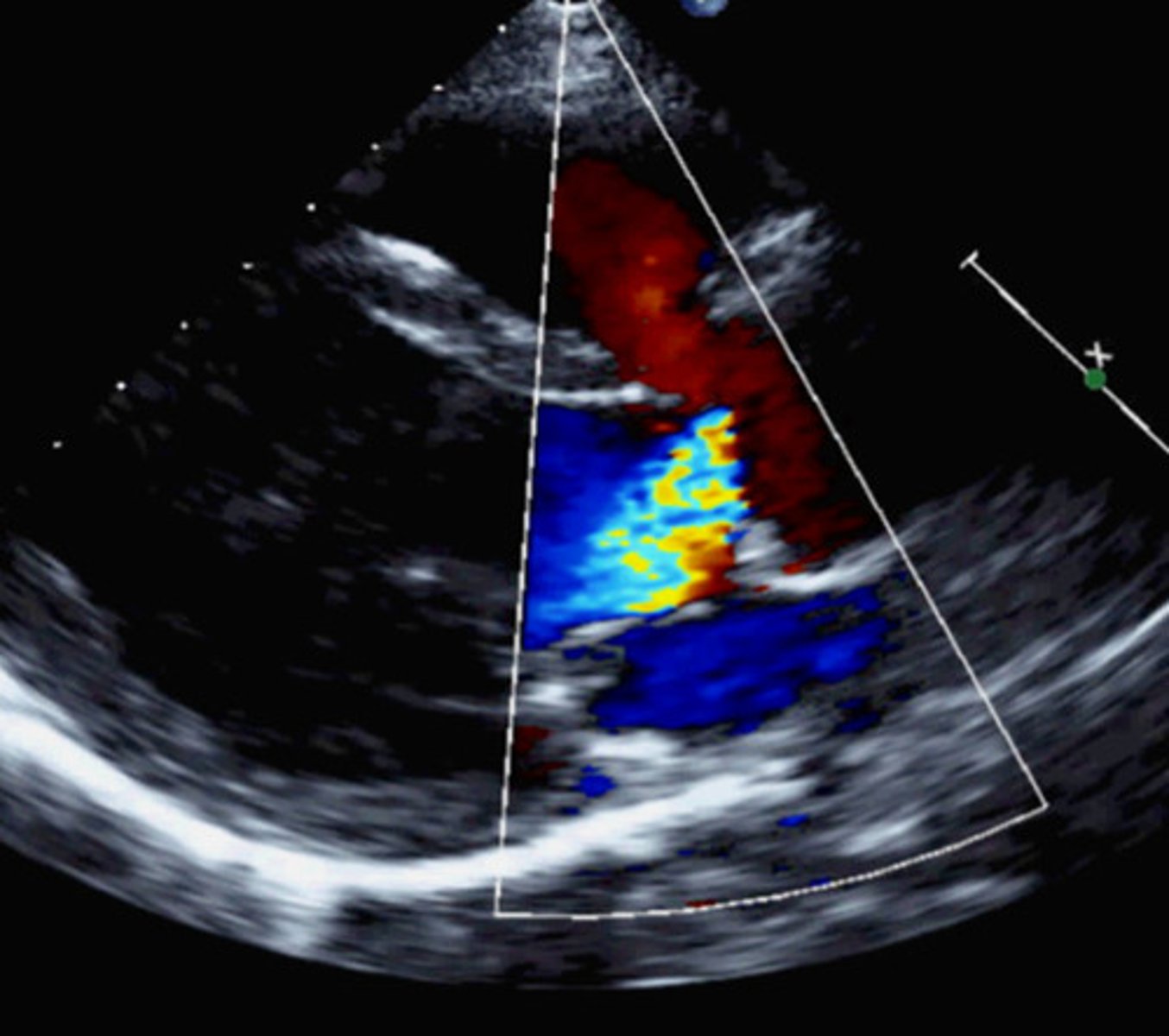
Dilated aortic root
What may also be see with a BAV
AI gets worse as patient ages and aortic root dilates
Describe how AI severity can progress
True
T/F: if a patient is born with a BAV it may coapt well when they are younger and not lead to any problems until they are older
Aliasing on the edges of the AV during diastole
Describe edge AI
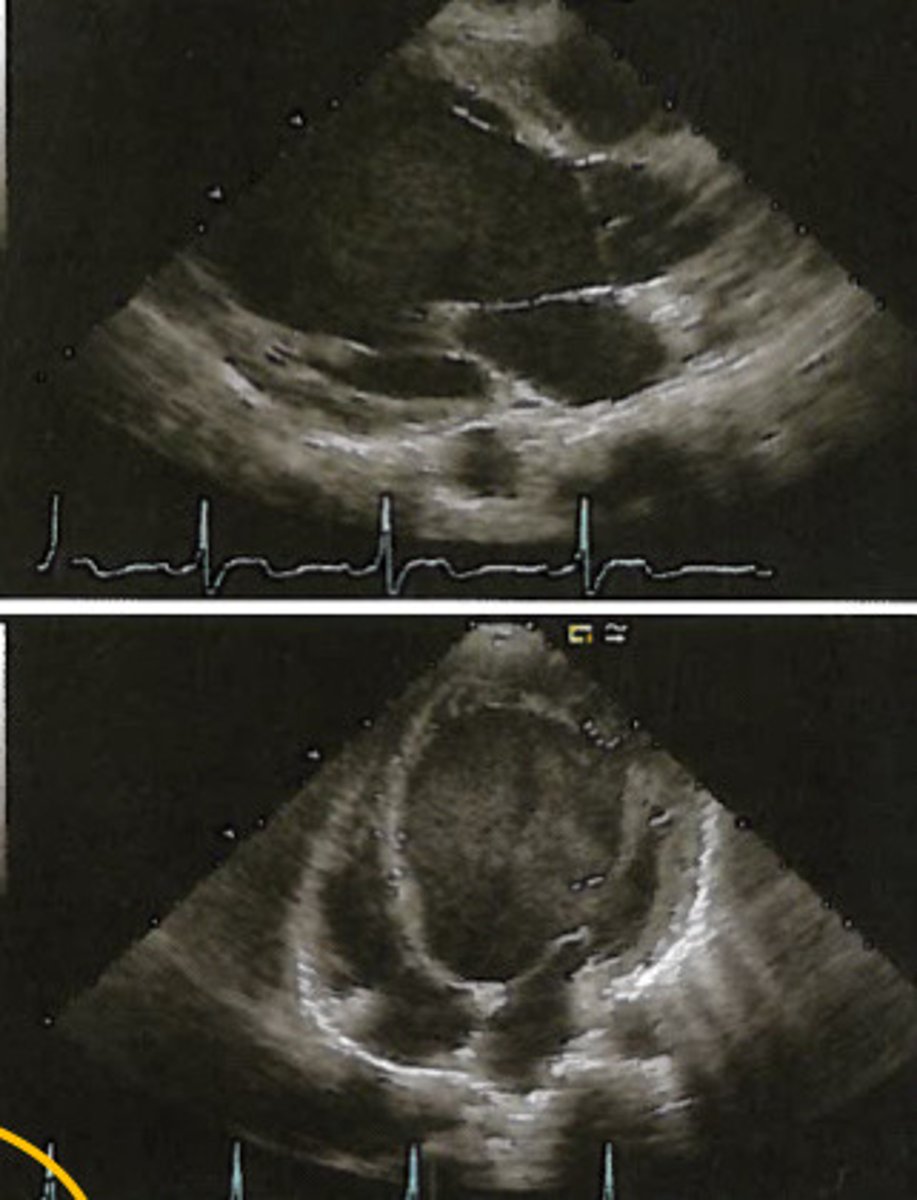
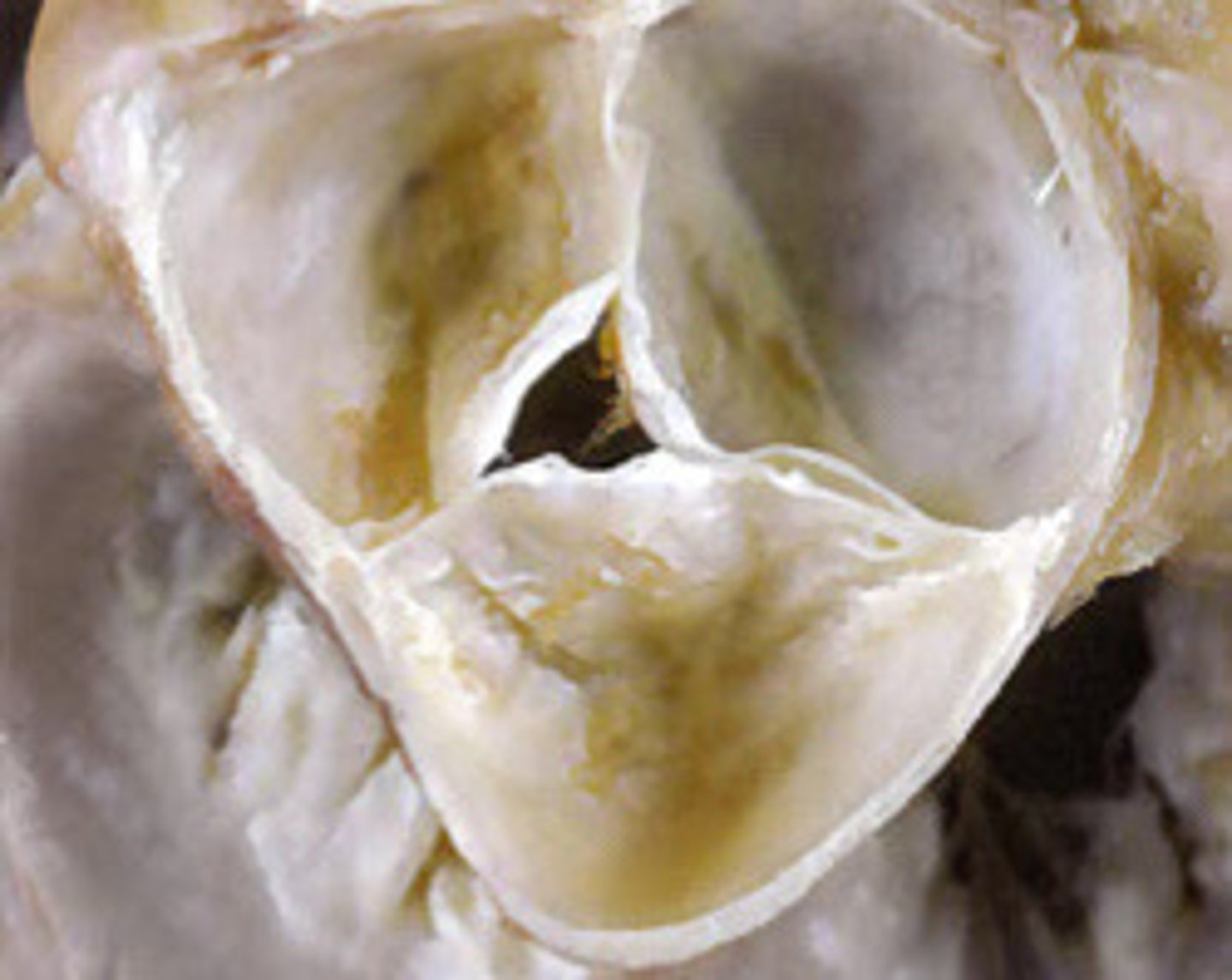
Quadricuspid AV
What does this image represent
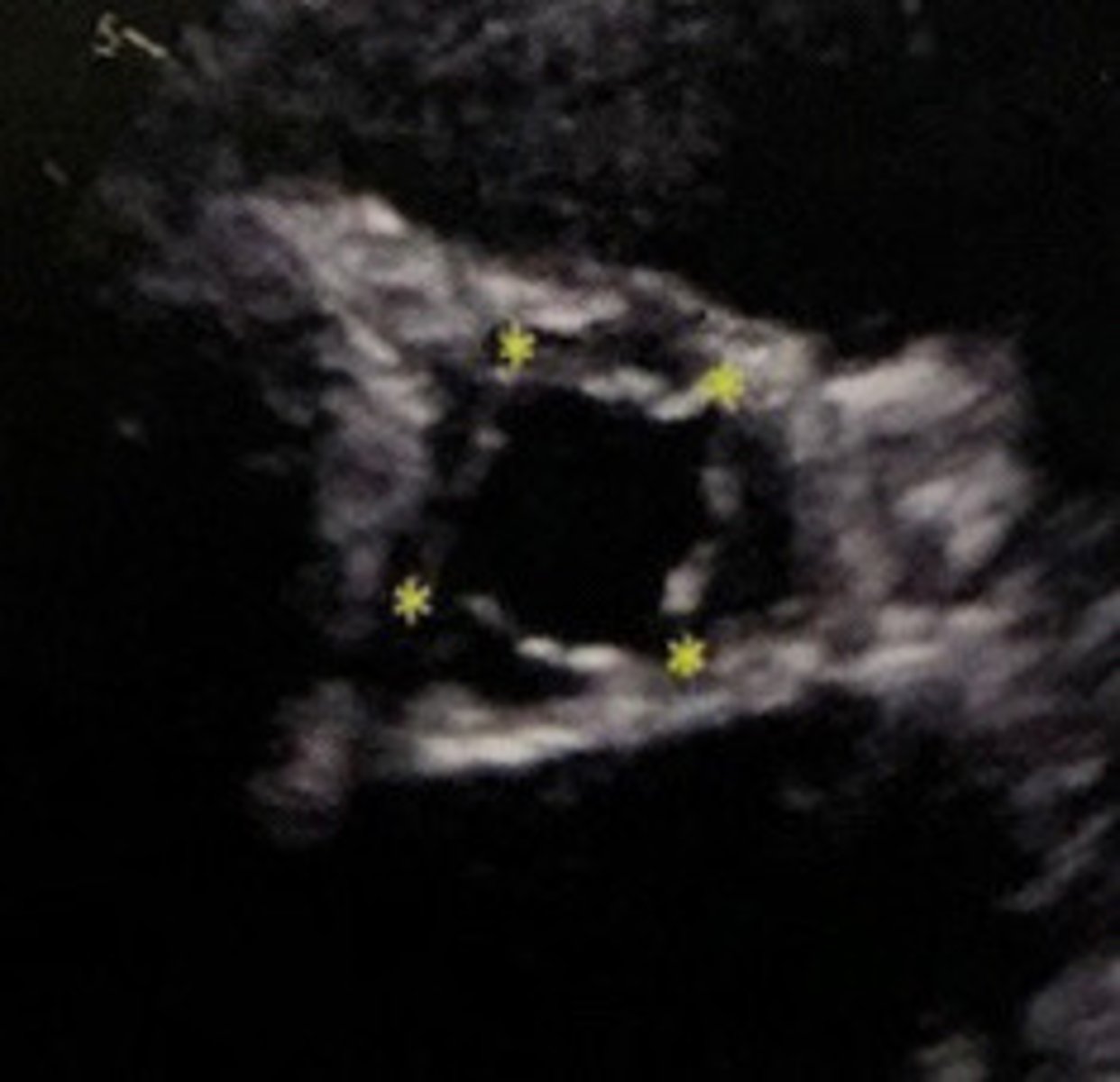
Quadricuspid AV
What does this image represent
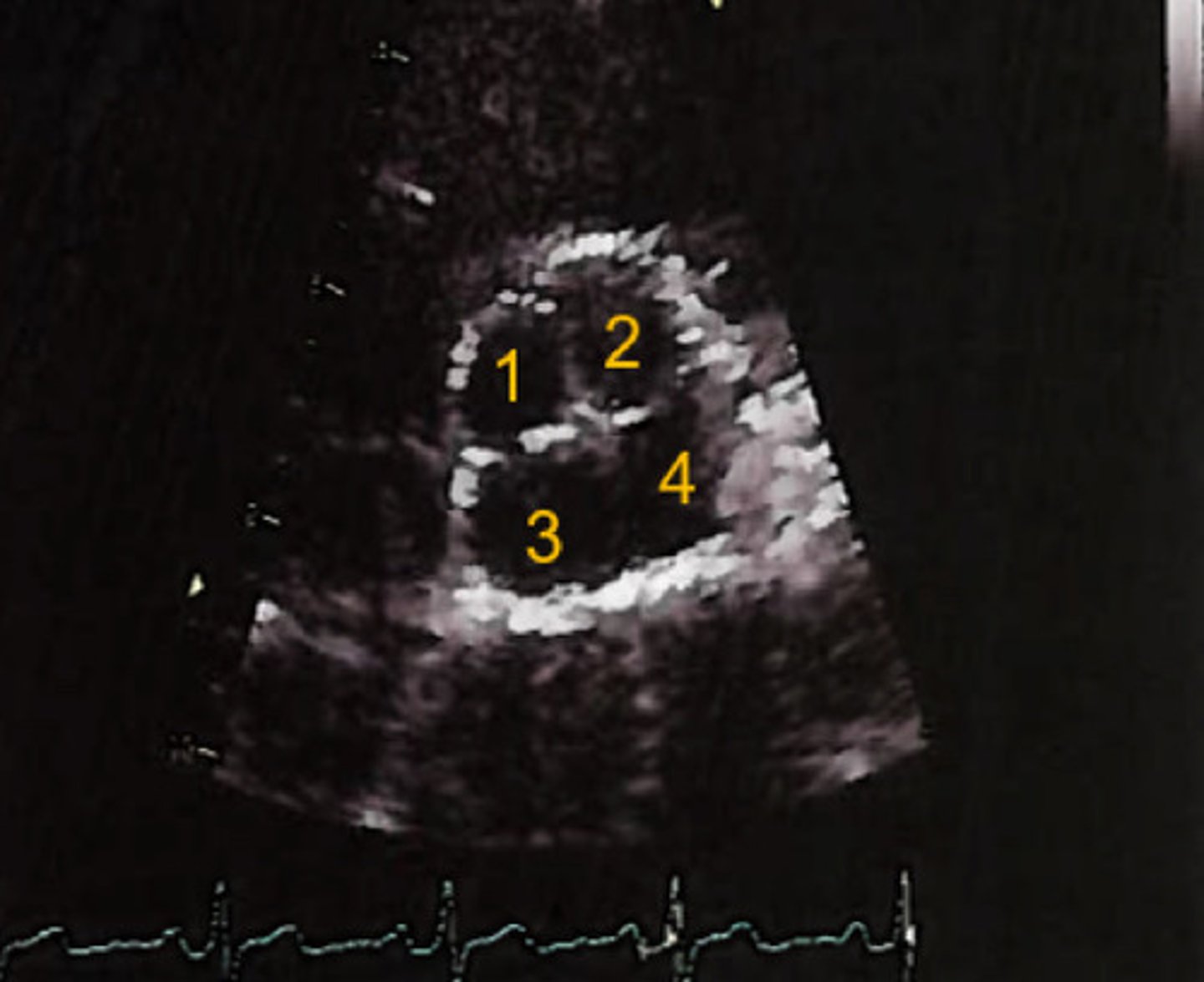
X or +
What shape does a quadricuspid usually take on
Bicuspid
Is quadricuspid or bicuspid AV more common
Cusp tissue is infiltrated with fibrous tissue causing them to shorten and retract
What is rheumatic AV disease
MV
What valve is most commonly affected by rheumatic disease
Cusps can no longer properly coapt
Why does rheumatic disease cause regurge or stenosis
True
T/F: rheumatic AV disease is usually associated with some degree or aortic stenosis as well
BAV
Aortic valve prolapse is more common in conjunction with ________
One leaflet slips down below the valve ring during diastole
What is AV prolapse
Aortic root dilation, trauma, rheumatic heart disease, or myxomatous
Besides BAV, what else can aortic valve prolapse be cause by
Vegetation (collection of bacteria cells) destroys the AV
What is aortic bacterial endocarditis
Infection that started somewhere else in the body and travelled to valve
Describe how aortic bacterial endocarditis infects the AV
Endocardial layer
What layer of the heart does bacterial endocarditis infect
Bacterial endocarditis eatin through the AV and abscess is formed
Describe what is happening in this image
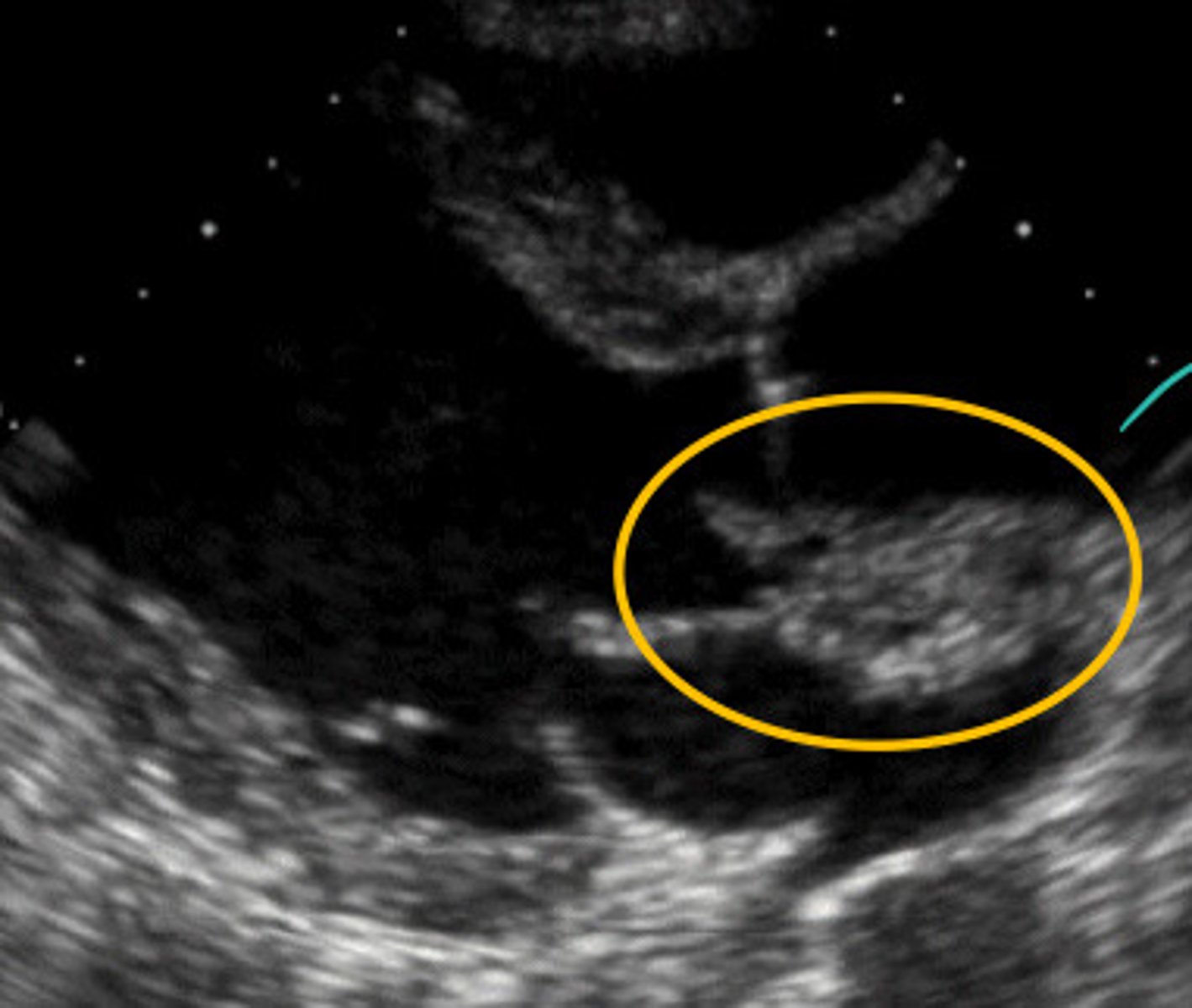
Forms "jellyfish strings" which are mobile and can break off and travel, thus leading to PE or stroke
Explain how bacterial endocarditis can lead to a PE or stroke
Hospital forms infections
Where is bacterial endocarditis commonly seen
Infective endocarditis (IE)
What is another term for bacterial endocarditis and its abbreviation
Acute severe
IE is a common cause of _______ __________ AI
Underside of AV (LV side)
What side of the valve is IE found
Destroying one or more cusps
How does IE cause AI
True
T/F: IE can also eat away at the valve and cause holes
Prevents normal leaflet coaptation because too far away
Why does aortic root dilation cause AI
HTN
What is the most notable cause of aortic dilation
Atherosclerosis, connective tissue disorders, bicuspid AV, sinus of valsalva aneurysms, idiopathic
What are some other causes of aorti root dilation
>3.4cm
What mmt of the aortic root indicates aneurysm
Dilated aortic root
What does this image represent
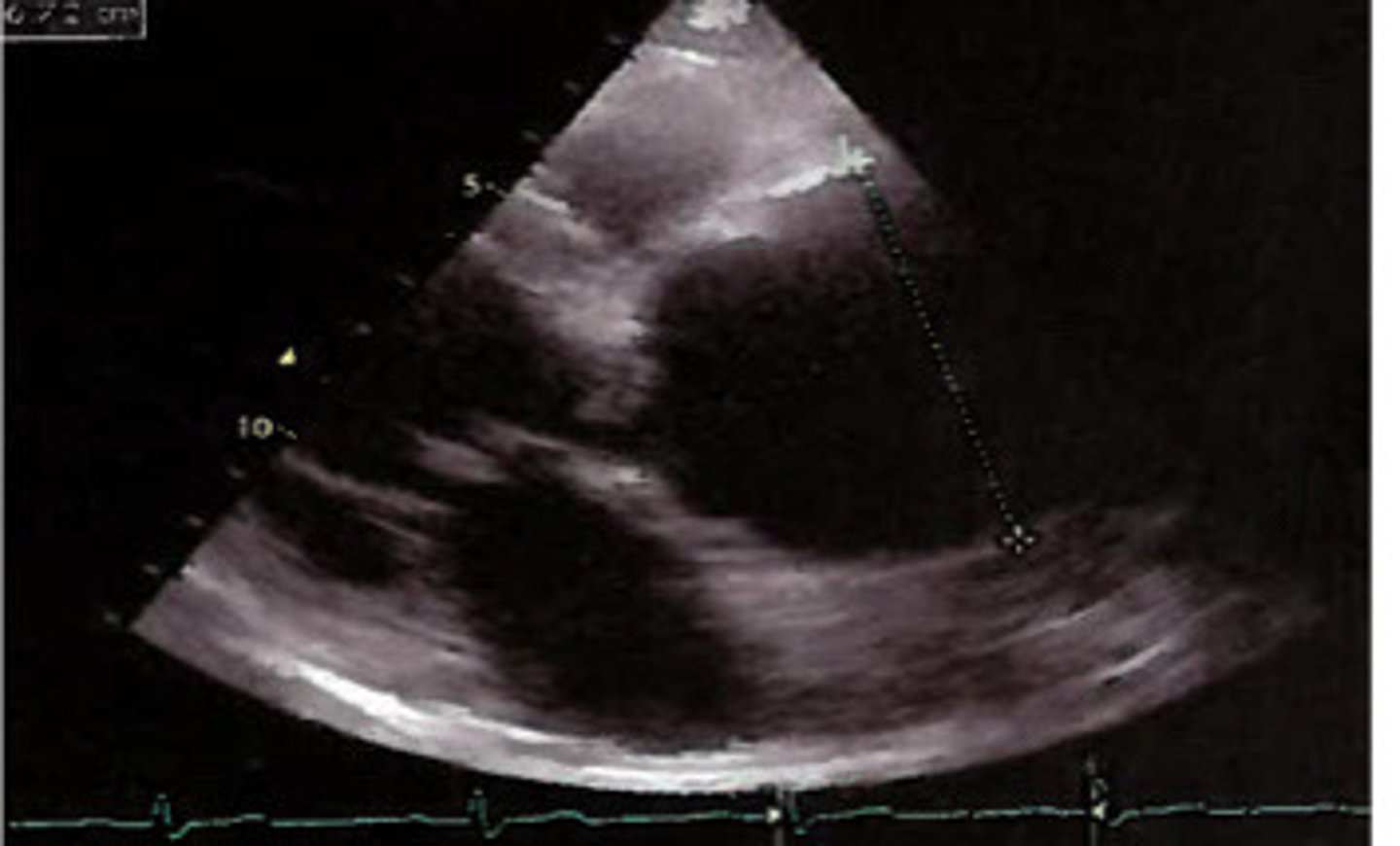
Aortic valves unable to coapt from aortic root dilation
What does this image represent
Layer of the aorta tears
What is an aortic dissection
If dissection occurs in the proximal portion of the aorta it can fall into the AV and prohibit the cusps from coapting
Explain how an aortic dissection can result in aortic regurge
Dissection flap prolapses into valve, causing AI
What does this image represent

Just on the LV side of the AV
Where are membranous VSDs located
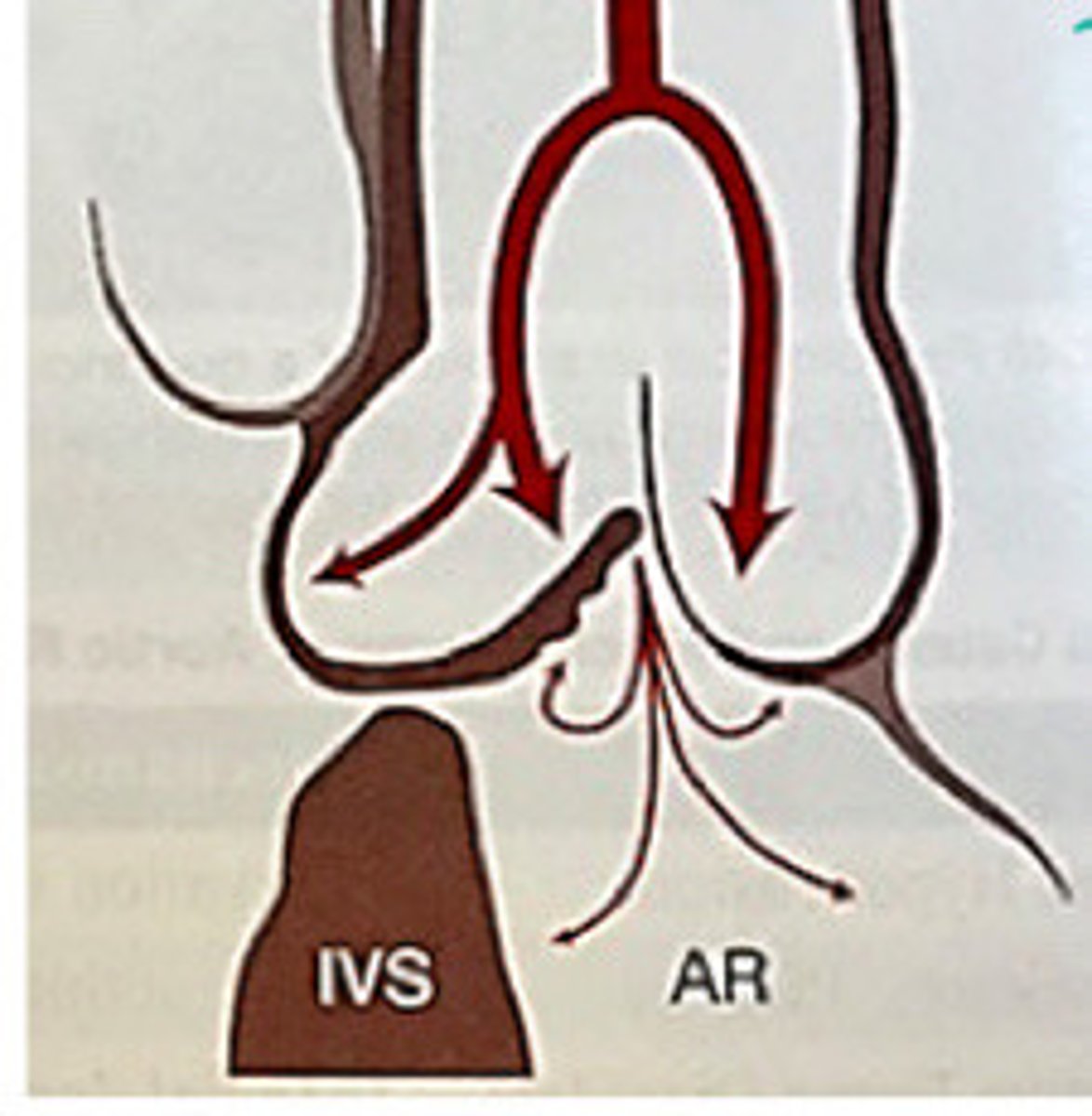
Weakens supporting structure of the aortic root and the AV flops into it, causing AI
Explain how VSD's can cause AI
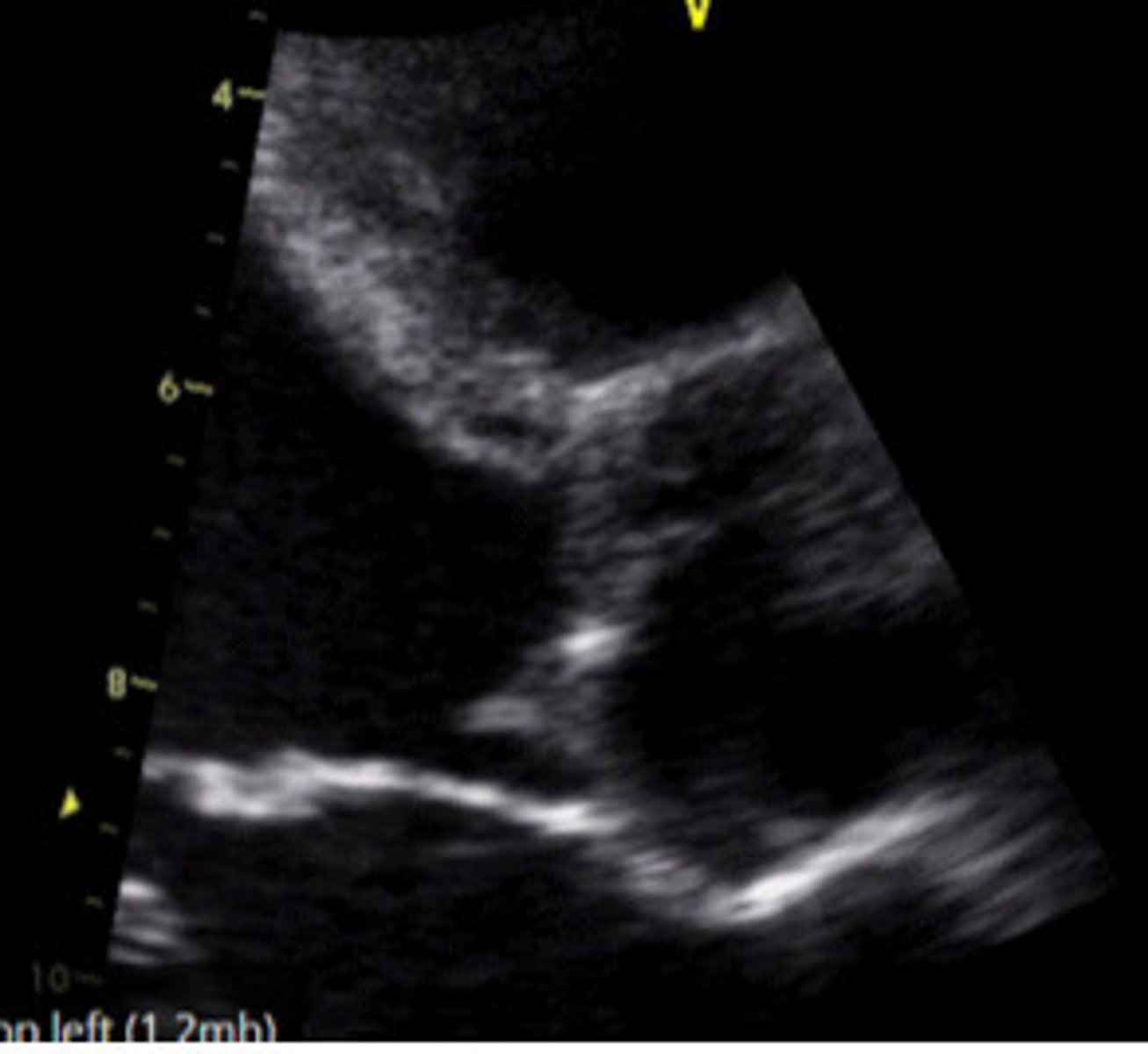
VSD causing AI
What does this image represent
In just a few days
How fast can the "goobers" from infective endocarditis develop
Trauma, infective endocarditis, aortic dissection
What can cause acute severe AI
No
Is there any LVH with acute AI
Filling pressures
Acute severe AI causes and increase in __________________________________
LVEDP
What pressure is most likely to be elevated with acute,severe AI
Because the heart hasn't had time to change shape or thicken in order to compensate for the increases pressure
What does acute, severe AI result in increases filling pressures
Pressure
Acute, severe AI causes a ________________ overload
During diastole, we have the normal inflow PLUS regurge flow from the AI
What does LVEDP increase with acute AI
When LV pressure exceeds LA pressure
When does the MV close (what is happening with the pressures)
LV pressure is increases for AI, so it does not take as long for it to exceed the LA
Why does AI sometimes leave to an early closure of the MV
Normal-slightly elevated
What are the filling pressures like in chronic sever AI
Volume
Chronic AI causes the LV _____________ to increases over time due to stretching
Increased forward flow through the AV
What may this increase in the LV volume result in
Frank starling law
What law predicts that there will be an increase of forward flow with an increase in LV chamber volume
Chamber dilates to try to accommodate it
Why does the LV chamber volume increase overtime with chronic AI
Volume
Chronic severe AI results in _______________ overload
Eccentric hypertrophy
What kind of LV geometry can chronic AI lead to
LV may start to fail at which the LVEDP will increase
Explain what can happen to the heart over a longggg time with chronic AI
Increase in LV and LA size and pressure overload
What is the main complication of AI
Pressure goes backwards from LV into the LA
Why can AI also cause increase in LA size
If pressure in LV very high during diastole, it can cause MR diastolic regurge
Explain what causes diastolic MR from
Will have E wave and might not have A wave
Describe what the waveform of the MR would look like if it has diastolic regurge
Still lets through flow but at some point in diastole the flow becomes regurge
Describe what is happening to the flow in the MV if it has diastolic MR as a result of AI
True
T/F: AI can also lead to pulmonary venous congestions
Pressure continues to back up from left heart into pulmonaries
Explain how AI can lead to pulmonary venous congestion
Pulmonary edema, rt heart failure, systemic venous congestion and edema, embolization
What can pulmonary venous congestion lead to
From the scattered and abnormla flow caused by pulmonary venous congestion
How can pulmonary venous congestion cause embolization
Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors
What are the medications associated with AI
Avoid heavy physical exertion, do not want to add workload
What lifestyle changes may someone with AI may make
Significant, chronic Ai
When is surgical intervention considered for AI
Repair or replacement
What are the two main types of surgeries done for AI
Dilation
What is a repair surgery usually used for
IE, structural problems
What is a replacement surgery used for
SOB, fatigue, edema
What are the general symtpoms of AI
Occasional chest pain
What symptoms is specific to chronic severe AI
Increases LV mass decreases myocardial perfusion causing ischemia
Why may chronic severe AI result in occasional chest pain
Pulmonary edema
What symptom is specific to acute AI
Austin flint
What murmur is specific to severe AI
S3 and S4 from LVH
What other noise may your hear on auscultation with AI
Ventricular arrhythmias, LVH
What findings on the ECG may indicate AI
Cardiomegaly
What finding on a CXR may indicate AI
LVID, LV mass, IVS, PW
What do we measure to assess the LV size
Eccentric
What type of hypertrophy are we looking for with AI
LV volume overload
What does LVVO stand for
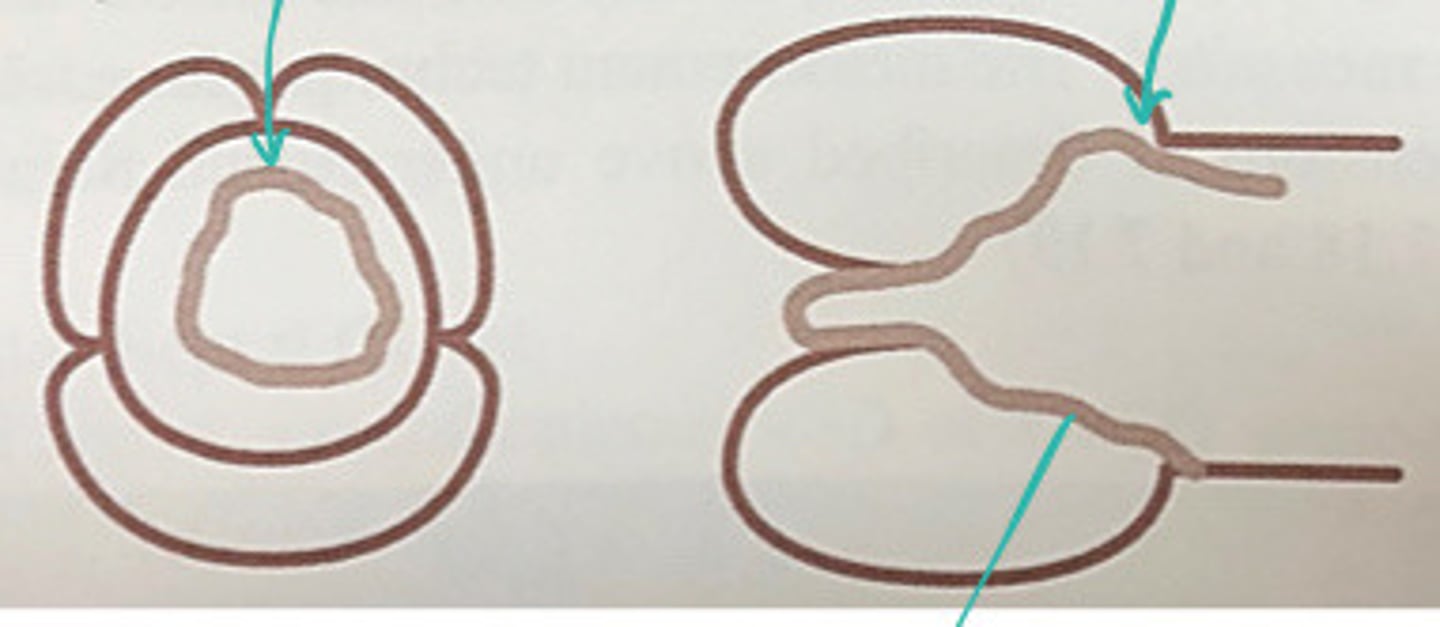
LV progressively dilates until it fails and takes on a more spherical shape
Describe what happens to the LV with LVVO from AI
LV more spherical shaped from LVVO
Describe what these images represent