PNB Lab Quiz Prep - Tissues
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is histology?
the study of tissues
What are the two types of lenses?
ocular and objective lenses
What is the ocular lens?
work to bring the image into focus for the eye. Magnification of 10x
What is the objective lens?
closest to the ‘object’ being viewed. ranges from 4x to 100x
What is the stage?
the platform on which the slide is placed
What is the coaxial stage controls?
can be moves in the X-Y plane to change which part of the slide is being viewed
What is the light source?
illuminates the specimen, and the dial on the side of the scope can control its intensity
What is the iris diaphragm?
can alter illumination and is controlled by the lever beneath the stage
What is the course focus control?
large knob on the side of the scope, allows you to adjust the stage height to bring the object into focus
What is the fine focus control?
can be used to make more precise focus adjustments
How is a microscope meant to be held?
two hands; one on the arm and the other under the base when moving it
How must a scope be cleaned?
with lens paper to avoid scratching the surface
What is epithelial tissue?
forms the surface layer of the body, lines body cavitites, hollow organs and structures, and constitutes most gland tissues
What are characteristics of epithelial tissue?
polar and avascular
What are intercellular junctions?
found in epithelial cells; between adjacent cells that vary with the unique structures and functions of various subtypes
What are the functions of intercellular junctions?
protect against dehydration and injury from physical, chemical, and biological agents, and regulating the passage of materials entering and leaving the body
How are epithelial cells classified?
based on their number of cell layers and apical cell shape
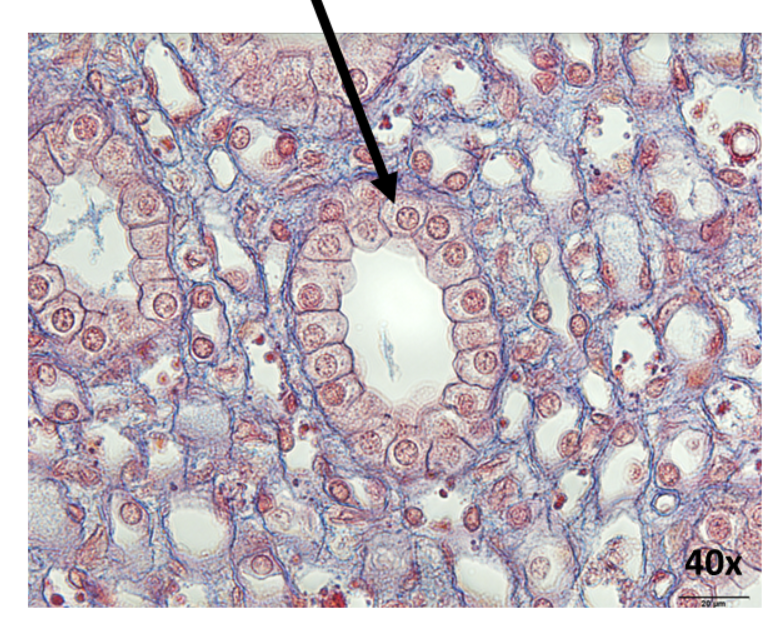
What is this epithelial tissue?
simple cuboidal epithelia
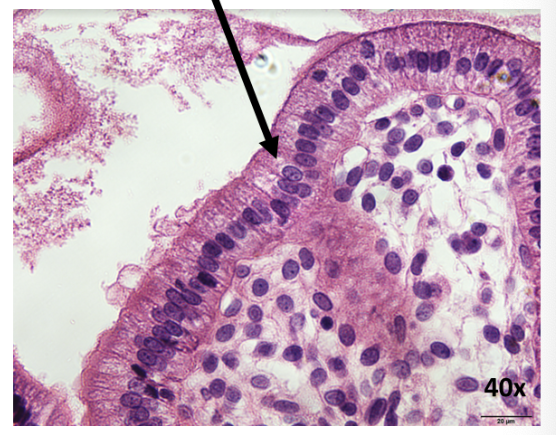
What is this epithelial tissue?
simple columnar epithelia
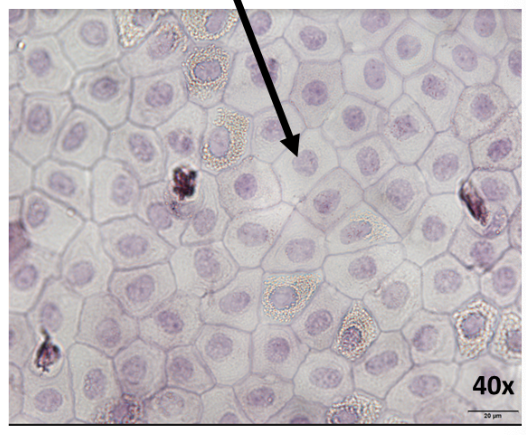
What is this epithelial tissue?
simple squamous epithelia
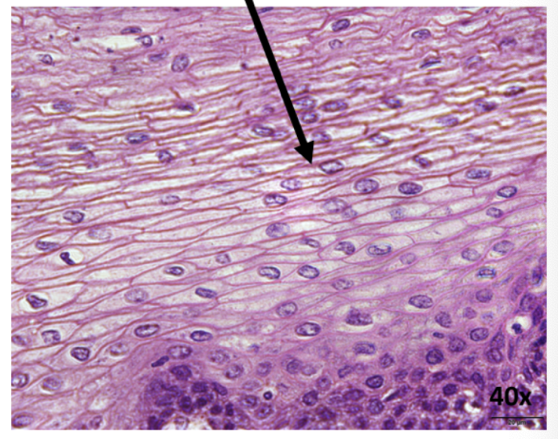
What is this epithelial tissue?
stratified epithelia
Where is transitional epithelia found?
in the bladder
Where is simple cuboidal epithelia found?
in the kidney
Where is simple columnar epithelia found?
in the intestines
Where is pseudostratified columnar found?
in the upper respiratory system
Where is stratified squamous epithelia found?
in the skin
What is connective tissue?
found in a variety of forms throughout the body, from rigid bone to flexible cartilage
What are the primary functions of connective tissue?
structural support, binding structures together, and protecting the less durable parts of the body.
What are the 3 components of connective tissue?
cells, protein fibers, and ground substance
What is connective tissue proper?
loose and dense tissue
What is loose tissue?
fibers create loose, open framework
What is fluid connective tissue?
blood and lymph
What is blood tissue?
contained in circulatory system
What is lymph tissue
contained in lymphatic system
What is supporting connective tissue?
cartilage and bone
What is cartilage tissue?
solid, rubbery matrix
What is the antomy of bone tissue?
solid, crystalline matrix
What are the main cells in loose and dense connective tissue?
fibroblasts and adipocytes
What are the main cells in dense connective tissue?
regular and irregular
What is regular dense connective tissue?
parallel protein fibers
What is irregular dense connective tissue?
protein fibers are in clumps arranged at scattered angles
What is hyaline cartilage?
most common, provides support through flexibility and resilience
What is fibrocartilage?
absorbs shock and resist compression of the vertebral column
What is elastic cartilage?
has extensive flexibility, characterized by abundance of elastic fibers around chondrocytes
What is bone tissue?
supportive tissue that provides levels from movement when muscles that are attached to them contract and protect soft tissues and vital organs
What is compact bone?
form the outer shell of the bone, and it is formed by concentric circles, called Haversian system, runs parallel to the shaft of the bone
What is spongy bone?
inside of the bones, and contains spaces and latticework structure of the bone tissue
What is not a type of connective tissue?
muscle
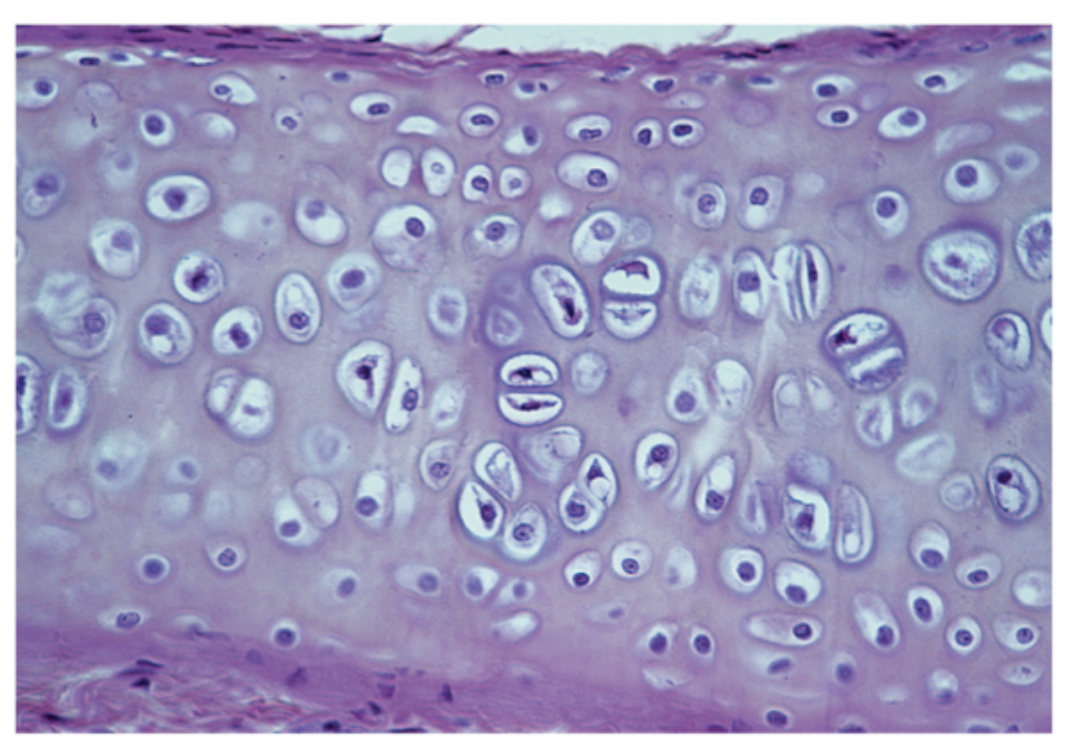
What cartilage is this?
hyaline
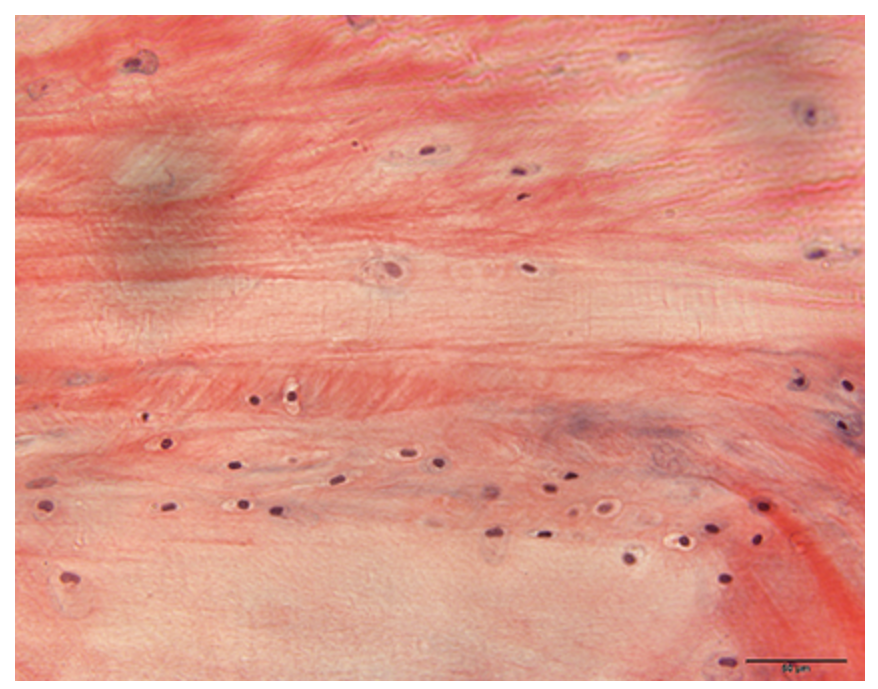
What cartilage is this?
fibrocartilage
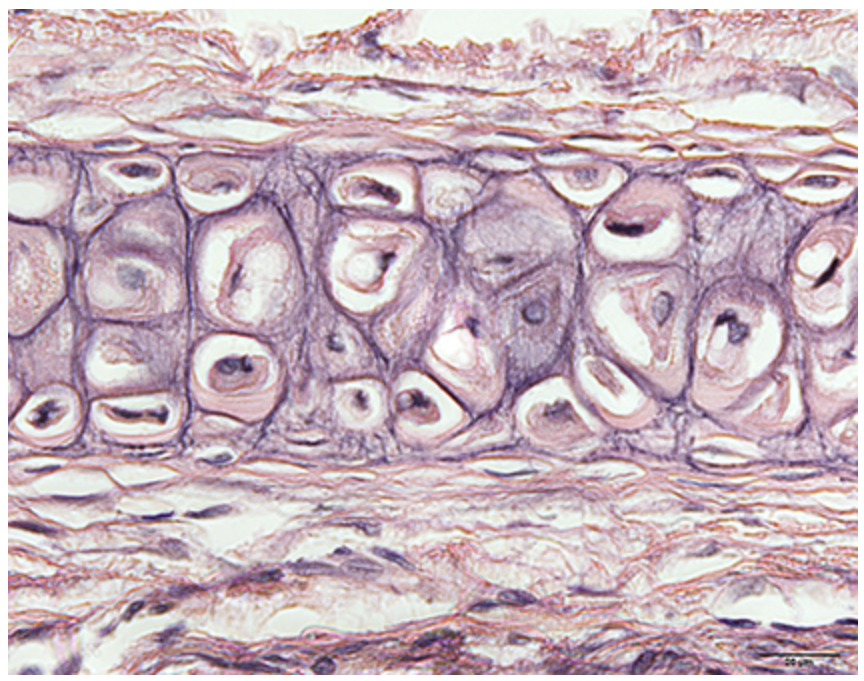
What cartilage is this?
elastic cartilage
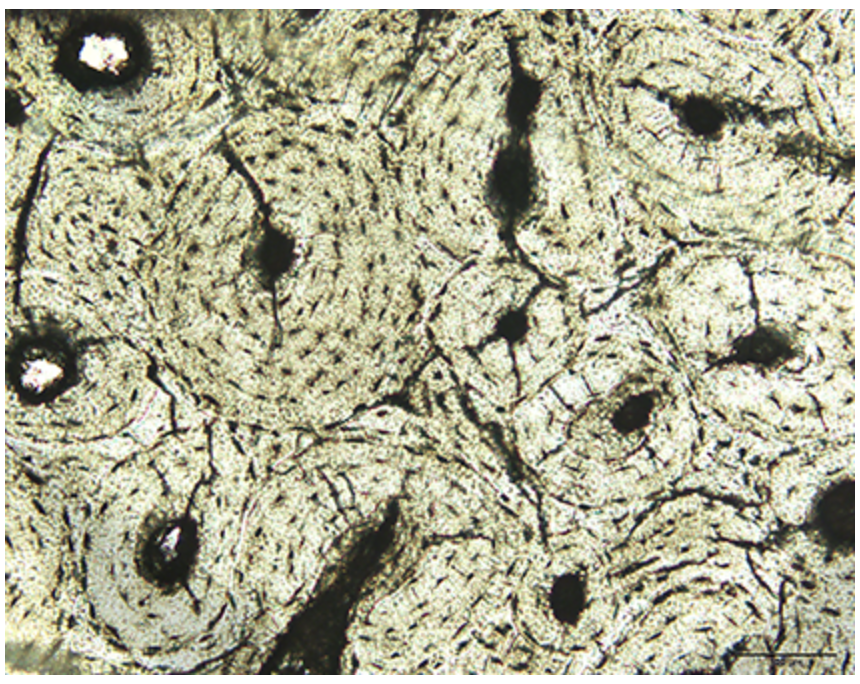
What is this diagram showing?
bone tissue
What is muscle tissue?
composed of specialized cells that respons to stimulation from the nervous system by undergoing internal changes that cause them to shorten
What are the three types of muscle?
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
What is cardiac muscle?
alternating dark and light bands that appear as striations, has intercalating disks, that enable commuication between cells and synchronicity of action
What is skeletal muscle?
have cylindrical, cardiac short and bifurcated, have many nuclei located at the periphery of the cell
What is smooth muscle?
have fusiform cells, have only 1 nucleus
Which muscle tissue displays a synchronized activity of cells?
cardiac muscle
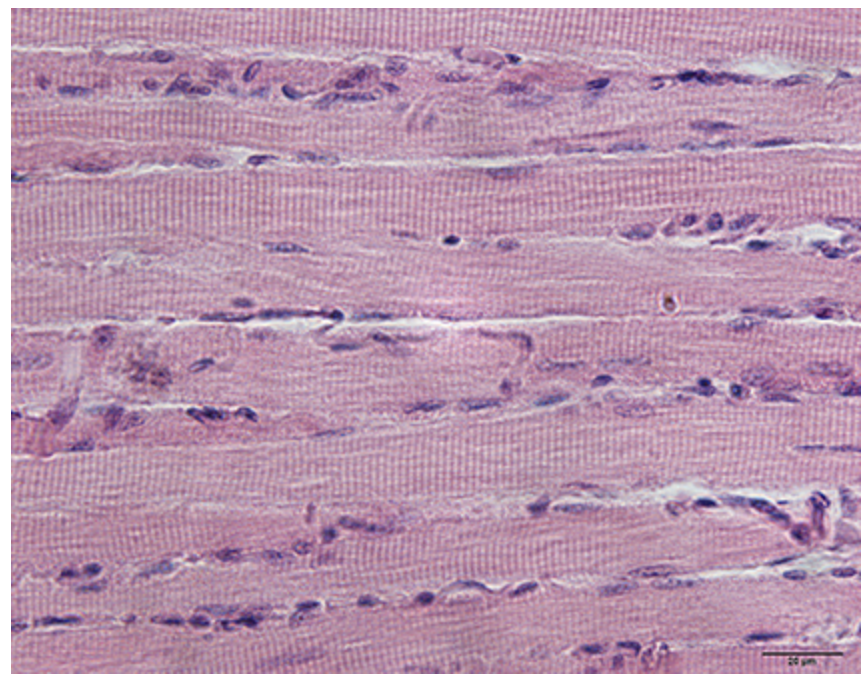
What muscle is this?
skeletal muscle
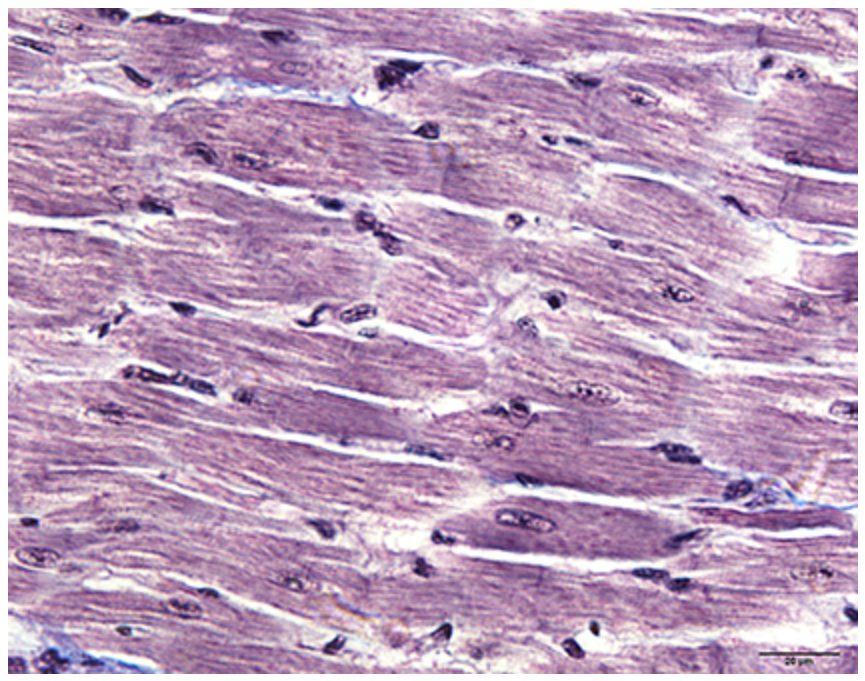
What muscle is this?
cardiac muscle
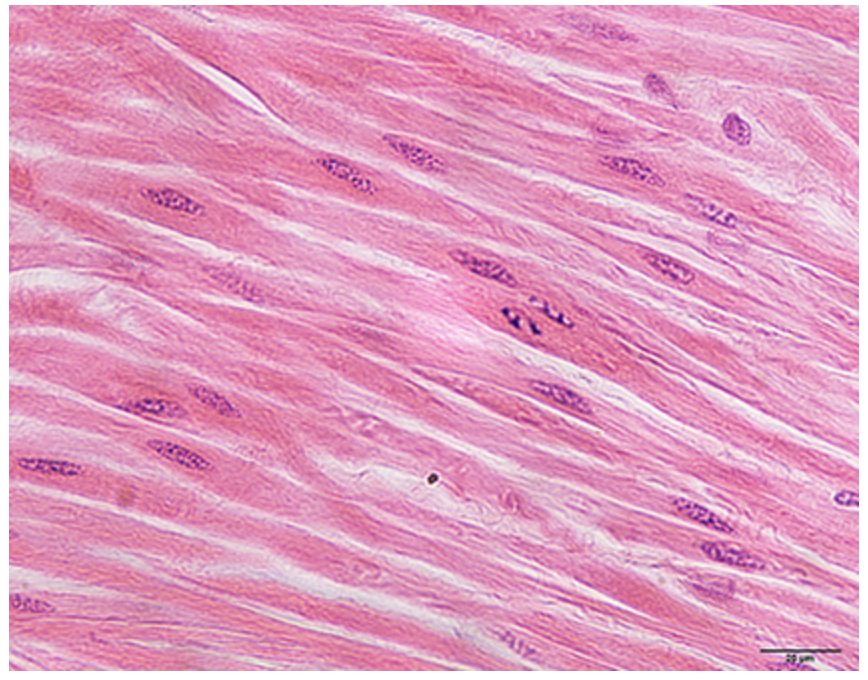
What muscle is this?
smooth muscle
What is the skin?
largest organ of the body, consists of several tissues
What are the 3 layers of skin?
epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
What is the epidermis?
stratified squamous epithelial cells, layers of keratinocytes, melanocytes, merkel cells, and langerhans cells
What is the dermis?
connective tissue of areolar and dense irregular type, composed of proteins, collagen and elastin, support the skin and make it flexible and strong
What is the hypodermis
connective tissue of adipose and areolar tissue, which serves as insulation and support
What are sweat glands?
excrete on the surface of the skin (merocrine gland), or in the hair follicle (apocrine gland)
What are oil glands?
open onto the hair follicle
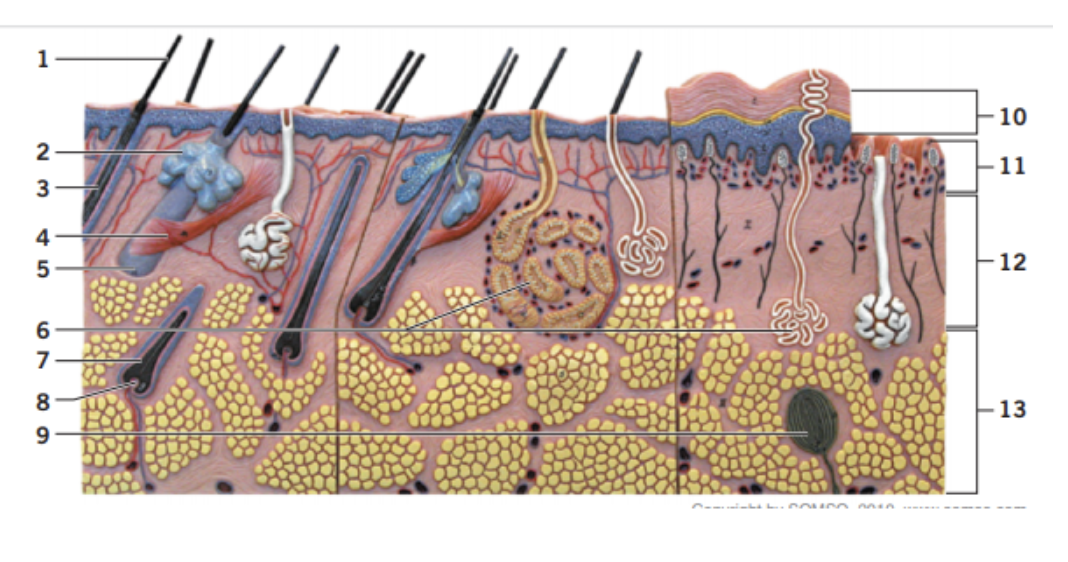
What number is the sebaceous gland?
2
Why is skin considered an organ?
it consists of several different tissues
What microscope is used in this course?
compound light microscope
What must be turned off on a microscope?
light source when not in use
What is the condenser?
located below the stage is a lens that condenses the light through the specimen on the slide above
What objective must be started with?
lowest power objective (4x)