1.3 Structures 💎
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Structure
how atoms are arranged once they are bonded together
Giant structure
3D network of atoms or ions
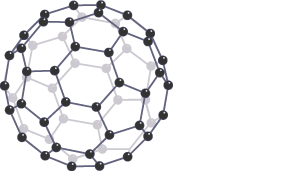
Lattice
Regular arrangement of particles
Type of structure
depends on its bonding
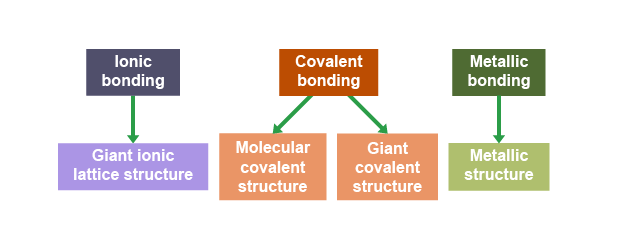
Metallic structure
regular lattice of positive metal ions, surrounded by sea of delocalised electrons
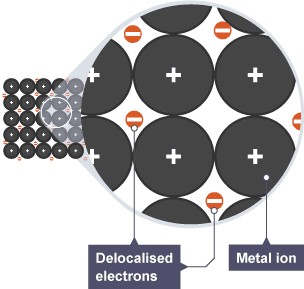
Examples of metallic structures
magnesium or sodium
Delocalised electrons
electron able to move freely and carry charge
Properties of metallic structures
high melting/ boiling points as large amount of energy needed to break strong electrostatic forces
good conductivity as delocalised electrons can move, carry charge and transfer heat energy quickly
layers of ions can slide over each other, but still held together by delocalised electrons so is both malleable and ductile
Malleable
can be hammered into shape
Ductile
can be drawn out into wires
Alloy
mixture of two or more elements, one of which a metal, and resulting mixture has metallic properties
Reason alloys are harder than pure metals
different sized atoms distort layers of ions in the structure, preventing them from sliding
Gold used in jewellery
usually an alloy with silver, copper and zinc
Proportion of gold in alloys
measured in carats, 24ct being pure and 18ct being 75%
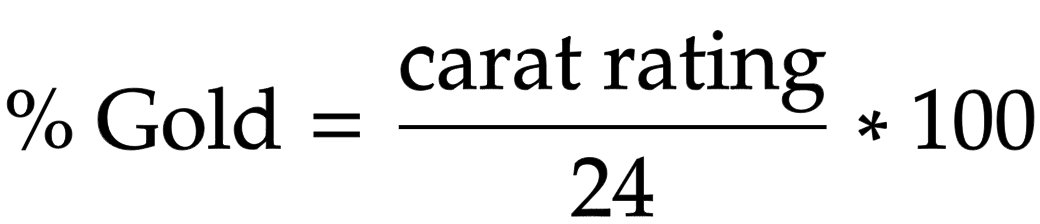
Molecular covalent structures (most common)
simple molecules held together by weak forces of attraction
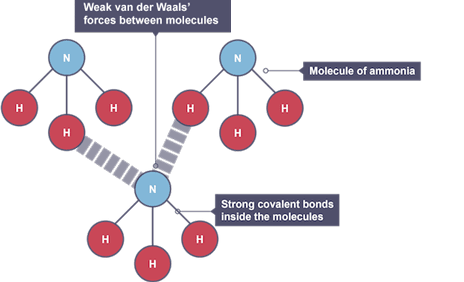
Examples of molecular covalent
iodine or carbon dioxide
Weak forces of attraction
Van der Waals’ forces, stronger the larger the molecule
Properties of molecular covalent substances
low melting and boiling points as small amount of energy is need to break weak forces between molecules
don’t conduct electricity as molecules are neutral so no ions/ delocalised electrons to carry charge
most are insoluble in water
Ammonia
molecular covalent structure, but is charged, so will form ionic bonds to non metals
Giant covalent structures
3D structure of atoms joined together by lots of strong covalent bonds
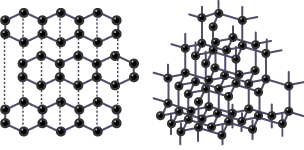
Examples of giant covalent structures
diamond, graphite or graphene
Allotropes
different forms of same element in the same physical state e.g diamond, graphite and graphene
Carbon atoms have
up to 4 covalent bonds (shares all outer electrons)
Diamond
each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 4 other in 3D tetrahedral structure
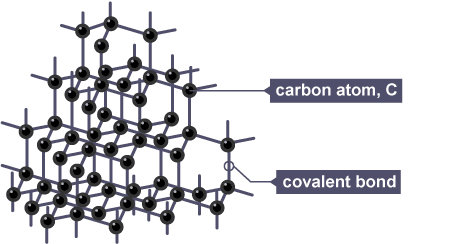
Properties of diamond
high melting and boiling points as large amount of energy needed to break many strong covalent bonds
doesn’t conduct electricity as no ions or delocalised electrons can carry charge
very hard due to strong covalent bonds in rigid tetrahedral structure
Uses of diamond
cutting tools for hard materials and jewellery
Graphite
carbon atom forms 3 covalent bonds with 1 delocalised electron, in layers of hexagonal rings, held by weak forces of attraction
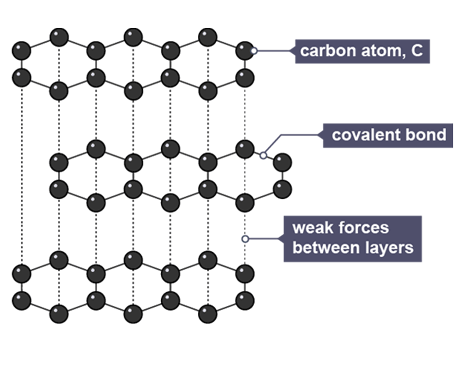
Properties of graphite
high melting and boiling points as large amount of energy needed to break many strong covalent bonds
conducts electricity as each atom has 1 delocalised electron that is free to move through layers and carry charge
soft due to weak forces between layers, allowing them to slide easily
Uses of graphite
lubricant and pencils as carbon layers slide
Graphene
single-atom thick layer of graphite with strong covalent bonds between each atom, arranged in hexagons
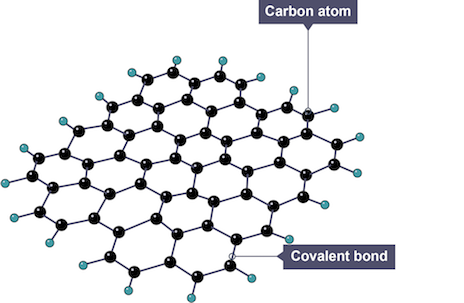
Properties of graphene
high melting and boiling points as large amount of energy needed to break many strong covalent bonds
excellent conductor of electricity and heat as each atom has 1 delocalised electron that is free to move through layers and carry charge
very strong (100x steel) due to many covalent bonds
low density and transparent as is only single atom thick
flexible and stretchy as layer of atoms can bend without breaking bonds
Uses of graphene
batteries and solar cells due to good electrical conductivity
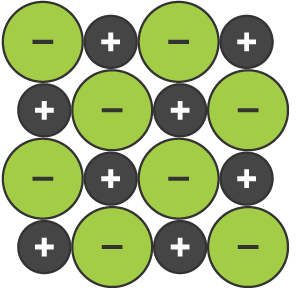
Giant ionic lattice
huge 3D regular structure held together by electrostatic forces of attraction between positive and negative ions
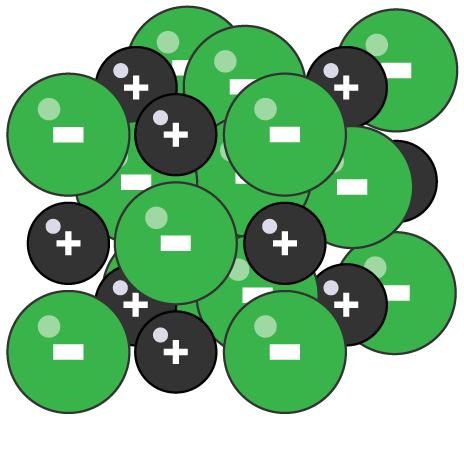
Examples of ionic compounds
sodium chloride or magnesium oxide
Properties of ionic compounds
high melting and boiling points as large amount of energy needed to break strong ionic bonds
do not conduct electricity when solid as ions are held in fixed positions, cannot move and carry charge
conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water as ions are free to move and carry charge
most are soluble in water
brittle as when struck layers of ions move beside one another, opposite charges repel, so shatters crystal structure
Ions when molten/ dissolved in solution
break free so can move and carry charge
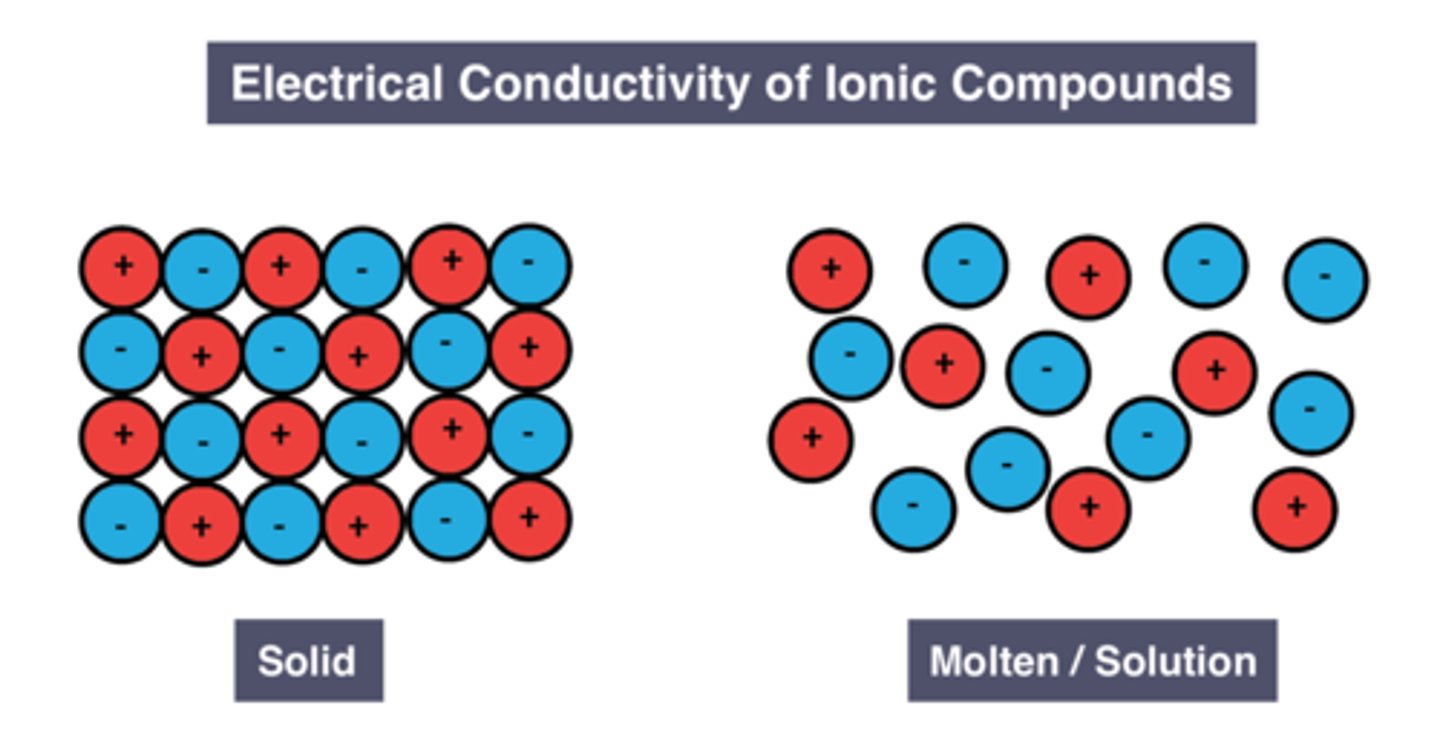
Electrostatic force of attraction
attractive force between oppositely charged particles
Reason some molecules are soluble
react with water, usually giant ionic structures but also acids
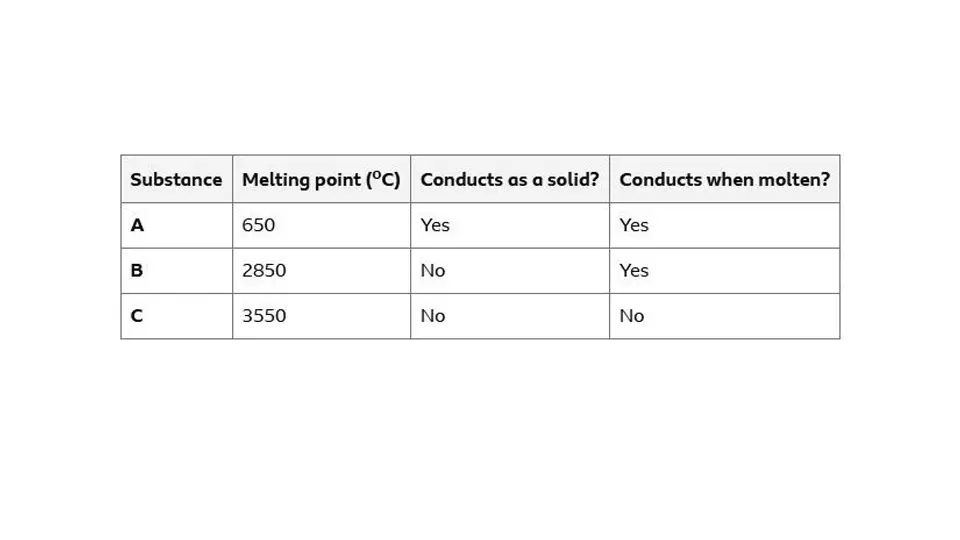
Classifying structures
Structure | Melting point | Solubility in water | Electrical conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
Giant ionic lattice | High | Soluble | Conductive when molten or dissolved |
Molecular covalent | Low | Insoluble | Not conductive |
Giant covalent | Very high | Insoluble | Not conductive (except graphite/ graphene) |
Metallic | Usually high | Insoluble | Conductive |
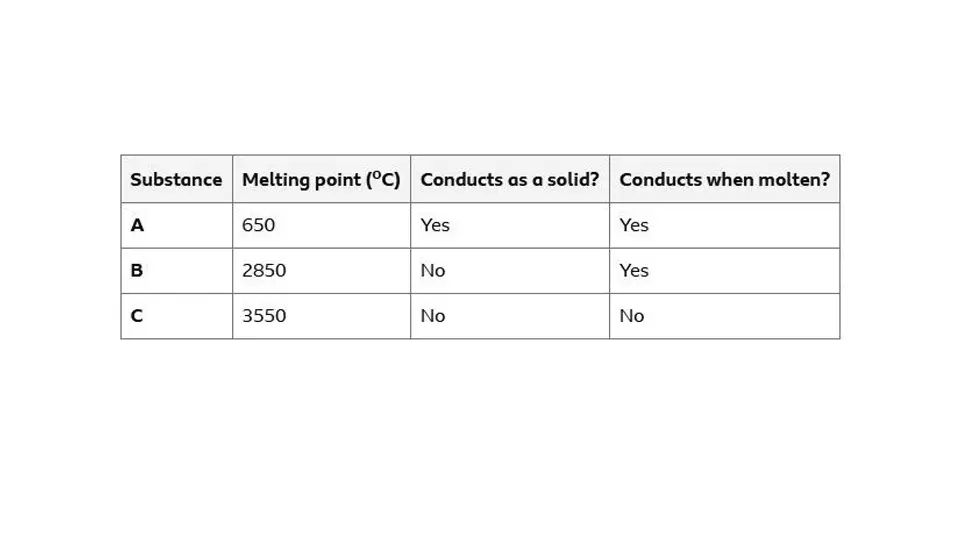
Classifying example
A is a metallic structure
B is a giant ionic lattice
C is a giant covalent structure