Detailed Exploration of the Skull
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
what are the important features of the anterior cranial fossa?
orbital plates of frontal bones, cribriform plates of ethmoid bones, crista galli
orbital plates of the frontal bones
convex elevations to either side of the cribriform plates, form the roof of the body orbit
crista galli
part of the ethmoid bone, projects upwards in the midline, provides attachment for the falx cererbi
cribriform plates of the ethmoid bone
perforated areas on either side of the crista galli, small perforations communicate with the roof of the nasal cavity below and transmit the olfactory nerve (CN I)
when looking at the anterior cranial fossa, where can the lesser wing of the sphenoid be found?
at the posterior aspect
anterior clinoid processes
part of the middle cranial fossa, extend posteriorly from the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and provide attachments for dura
squamous portion of temporal bone
part of the middle cranial fossa, flat region
petrous portion of the temporal bone
part of the middle cranial fossa, chunky/bulky region
sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
within the middle cranial fossa, turkish saddle
tuberculum sellae
within the middle cranial fossa, front of the saddle
hypophyseal (pituitary) fossa
within the middle cranial fossa, a concavity that resembles a riders seat in the saddle and accommodates the pituitary gland
dorsum sellae
within the middle cranial fossa, back of the saddle
posterior clinoid process
within the middle cranial fossa, extends posteriorly from either end of the dorsum sellae and provides dural attachments
optic canals
within the middle cranial fossa, pass forward to the orbits and transmit the optic nerves and the ophthalmic arteries
superior orbital fissure
within the middle cranial fossa, inverted, comma shaped gap between the greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone found under the cover of the lesser wing that communicates with the orbit anteriorly and through which the ophthalmic veins and cranial nerves III, IV, VI, and V1 pass
foramen rotundum
within the middle cranial fossa, round opening posterior to the inferior orbital fissure that transmits the maxillary nerve (CN V2)
foramen ovale
within the middle cranial fossa, an oval shaped opening posterior to the foramen rotundum that leads to the infratemporal region below the skull and transmits the mandibular nerve (CN V3)
foramen spinosum
within the middle cranial fossa, lies immediately behind and lateral to the foramen ovale, is a small, round opening leading from the infratemporal region below that transmits the middle meningeal artery
foramen lacerum
within the middle cranial fossa, provides and opening on either side of the hypophyseal fossa for the entrance of the internal carotid artery, occupied by cartilage in life
carotid canal
found at the junction of the greater wing of the sphenoid and the petrous portion of the temporal bone
hiatus for the greater petrous nerve
within the middle cranial fossa, exits from the anterior slope of the petrous temporal ridge (the groove can be followed to the foramen lacerum), transmits the greater petrosal nerve
hiatus and groove for the lesser petrosal nerve
within the middle cranial fossa, runs parallel and inferior to the greater hiatus and groove, and leads toward the foramen ovale and transmits the lesser petrosal nerve
what structures are part of the posterior cranial fossa?
clivus, foramen magnum, hypoglossal canal, internal auditory meatus, jugular foramen, internal occipital protuberance
clivus
the body of the sphenoid bone behind the dorsum sellae which becomes fused with a portion of the occipital bone anterior to the foramen magnum, slopes posteriorly and inferiorly to end as the anterior margin of the foramen magnum
foramen magnum
large, oval shaped opening through which the spinal cord is continuous with the brainstem above
hypoglossal canal
found on the lateral margin of the foramen magnum, anterior to the occipital condyle, runs obliquely anteriorly and laterally and transmits the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
internal auditory meatus
lies on the posterior slope of the petrous temporal ridge just above the jugular foramen, CN VII and VIII pass through this to the middle ear region within the temporal bone
jugular foramen
a large opening lateral to the foramen magnum that leads to the base of the skull below, transmits the internal jugular vein and CN IX, X, and XI
internal occipital protuberance
internal projection of bone at the posterior pole of the internal aspect of the skull
each side of the hard palate consists of ___ bones which are the ____ and they form the ____
2
palatine process of the maxilla, forms the anterior 2/3 of the palate
horizontal plate of the palatine bone, forms the posterior 1/3 of the palate, ending posteriorly as a double crescent shaped free border
where is the intermaxillary suture found?
in the midline of the palatine processes of the maxilla, aka median palatine suture
posterior nasal spine
midline posterior projection form the posterior border of the bony palate
incisive fossa
opening of the incisive canals behind the central incisor, is the common opening for the right and left incisive canals, transmits the nasopalatine nerve and vessels
what does the greater palatine canal open as?
the greater palatine foramen and the lesser palatine foramen
greater palatine foramen
on the palatal process of the palatine bone in line with the last maxillary molar, transmits the greater palatine nerve and vessels
lesser palatine foramen
posterior to the greater palatine foramen, transmits the lesser palatine nerve and vessels
posterior nasal apertures
the posterior limits of the nasal cavity
vomer
free edge of the bony nasal septum, divides the nasal cavity into right and left nasal cavities
lateral plate of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone
provides attachment for both lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
medial plate of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone
forms the posterior limit of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity
hamulus
small, slender hook, inferior ending to the medial plate of the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone
scaphoid fossa
canoe shaped shallow depression at the base of the medial pterygoid plate, tensor palatini muscle originates from this area
pharyngeal canal
aka palatovaginal canal, runs near the base of the vomer
pterygoid canal
passes through the base of the pterygoid process, mouth of the canal is immediately medial to the scaphoid fossa
mandibular fossa
accommodates the condyle of the mandible
tympanic plate
forms the anterior wall of the external auditory meatus and the posterior, nonfunctioning wall of the mandibular fossa
external auditory meatus
lies behind the mandibular fossa
squamotympanic fissure / petrotympanic fissure
transmits the chorda tympani nerve which is a branch of CN VII
spine of the sphenoid
a pointed projection medial to the mandibular fossa, the sphenomandibular ligament joins it to the lingula of the mandible
foramen spinosum from norma basalis
a small opening just anterior to the spine of the sphenoid, transmits the middle meningeal artery from the base of the skull to the interior of the skull
stylomastoid foramen
lies between the styloid and mastoid processes, allows passage of the facial nerve (CN VII) from within the temporal bone
styloid process
long, slender, needle-like process that points downward, forward, and medially and is joined to the lesser horn of the hyoid bone by the stylohyoid ligament, provides attachment for several muscles
entrance to the carotid canal from norma basalis
immediately anterior to the jugular foramen and separated from the jugular foramen only by a small wedge of bone
tympanic canaliculus
a small opening located inferiorly on the wedge of bone separating the carotid canal and the jugular foramen, transmits the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
what structure is labeled A?
orbital plates of the frontal bone
what structure is highlighted in orange?
crista galli
what structure is labeled B?
cribriform plate
what structure is labeled C?
lesser wing of sphenoid
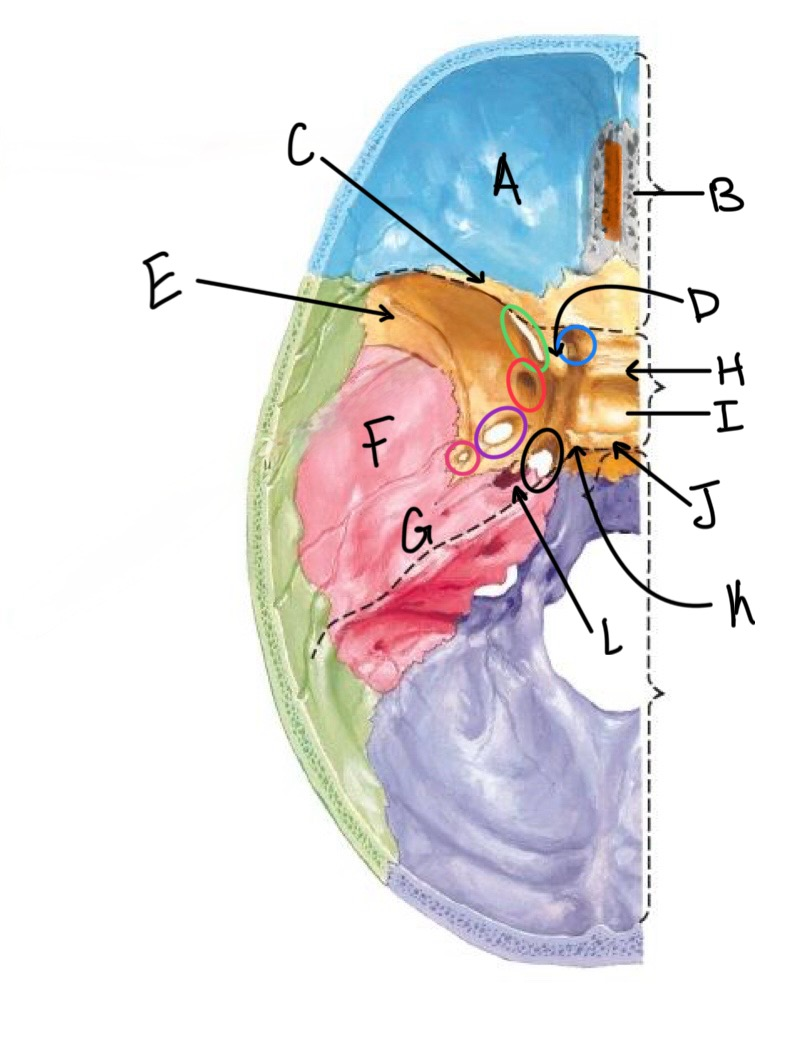
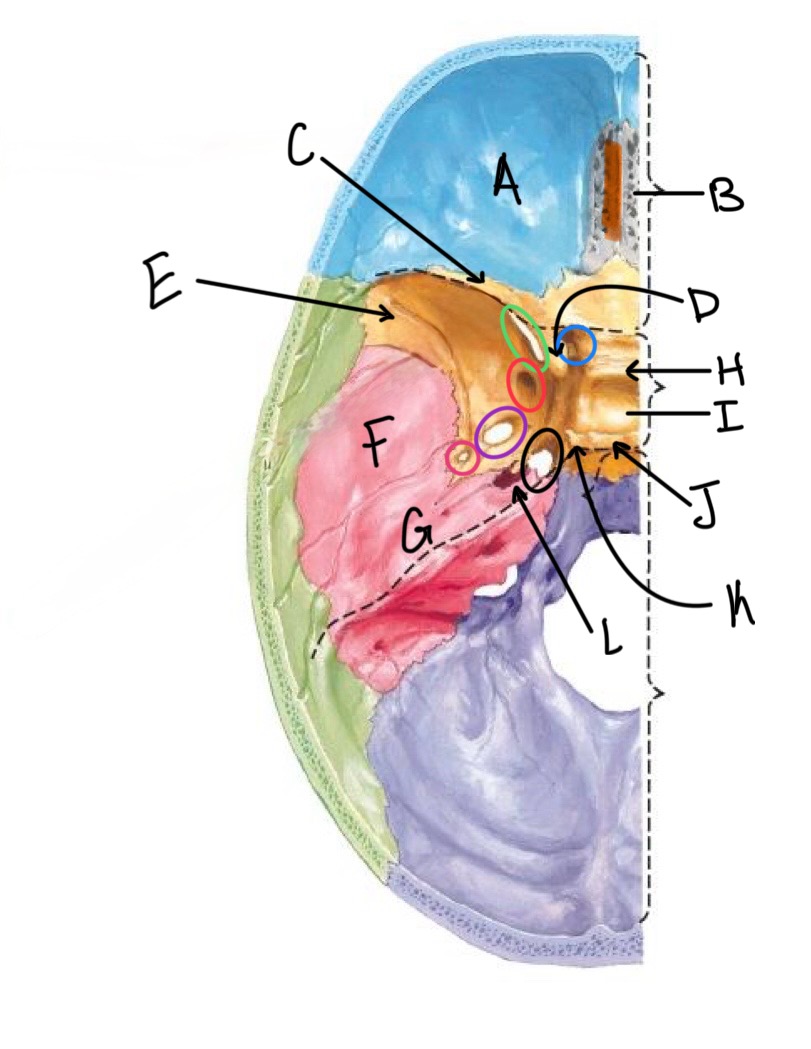
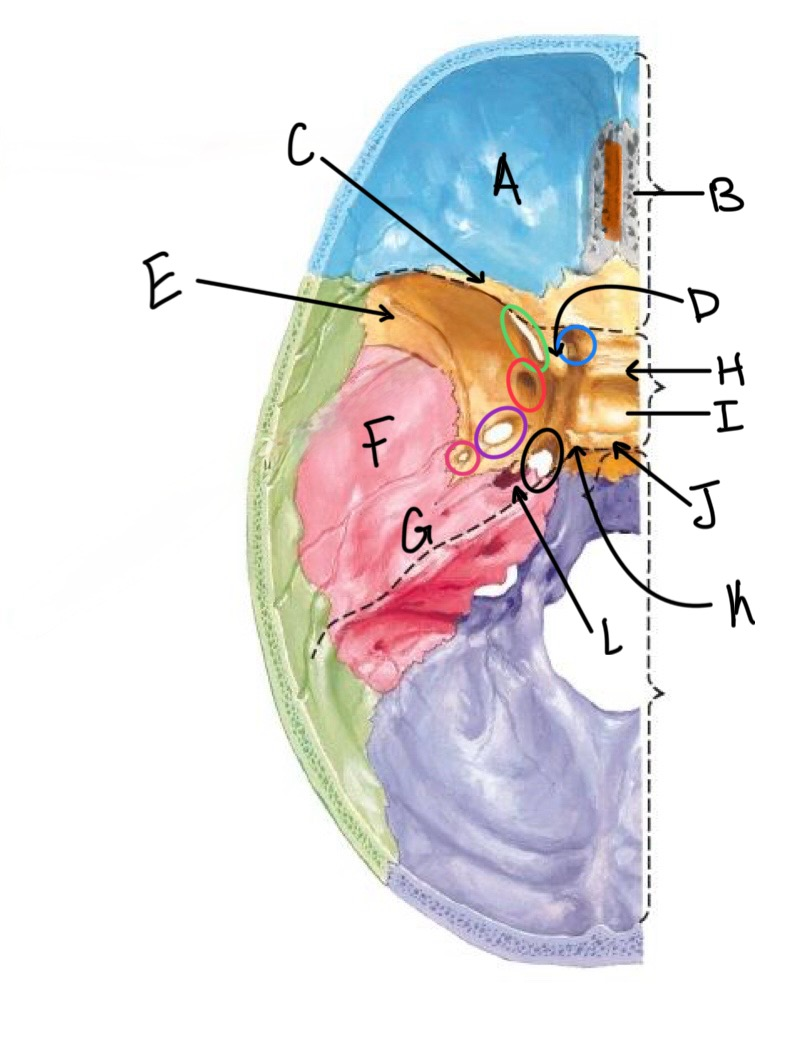
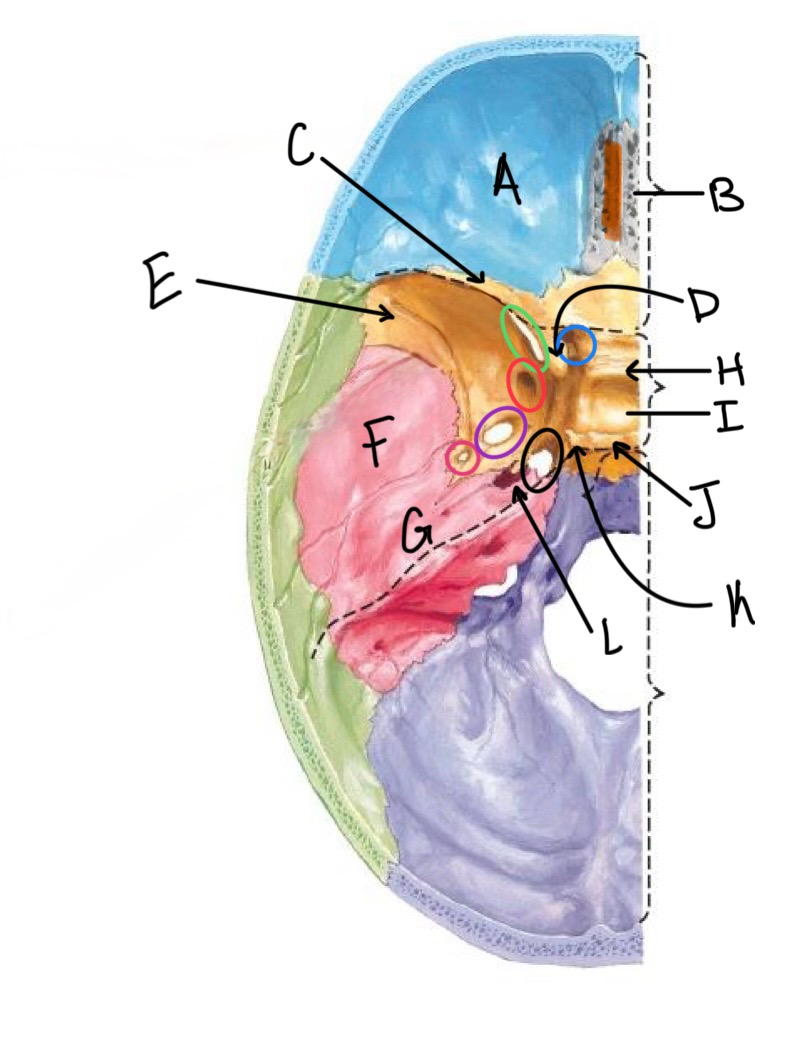
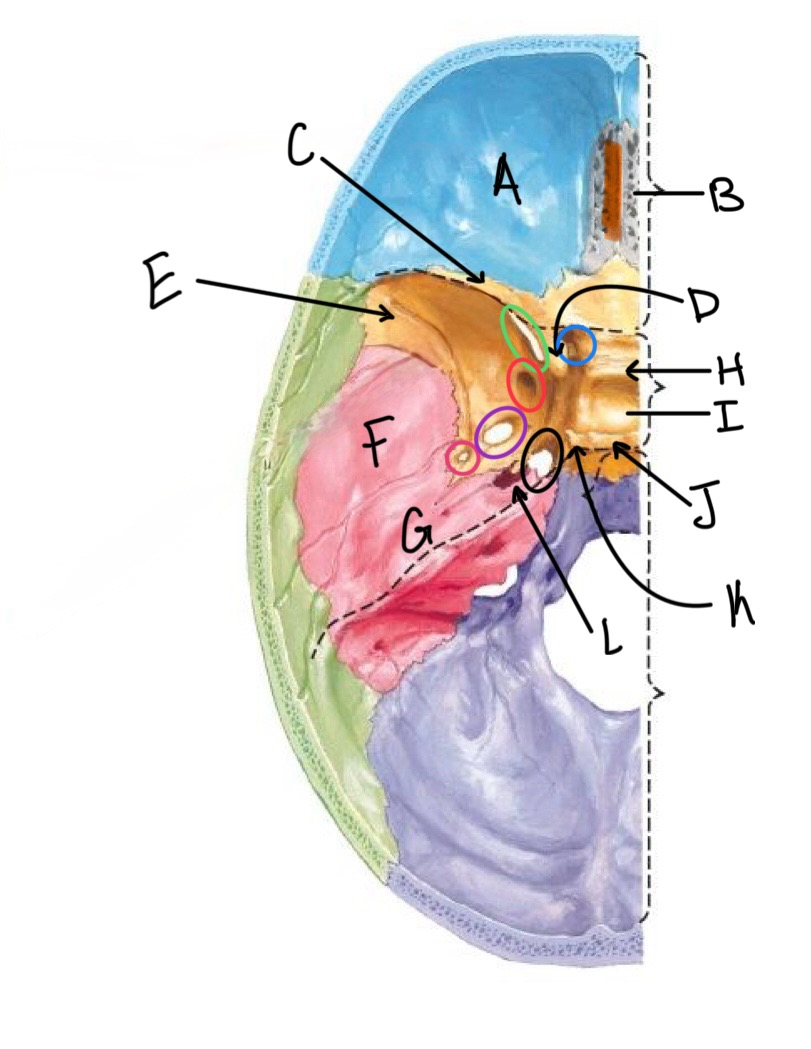
what structure is labeled D?
anterior clinoid process
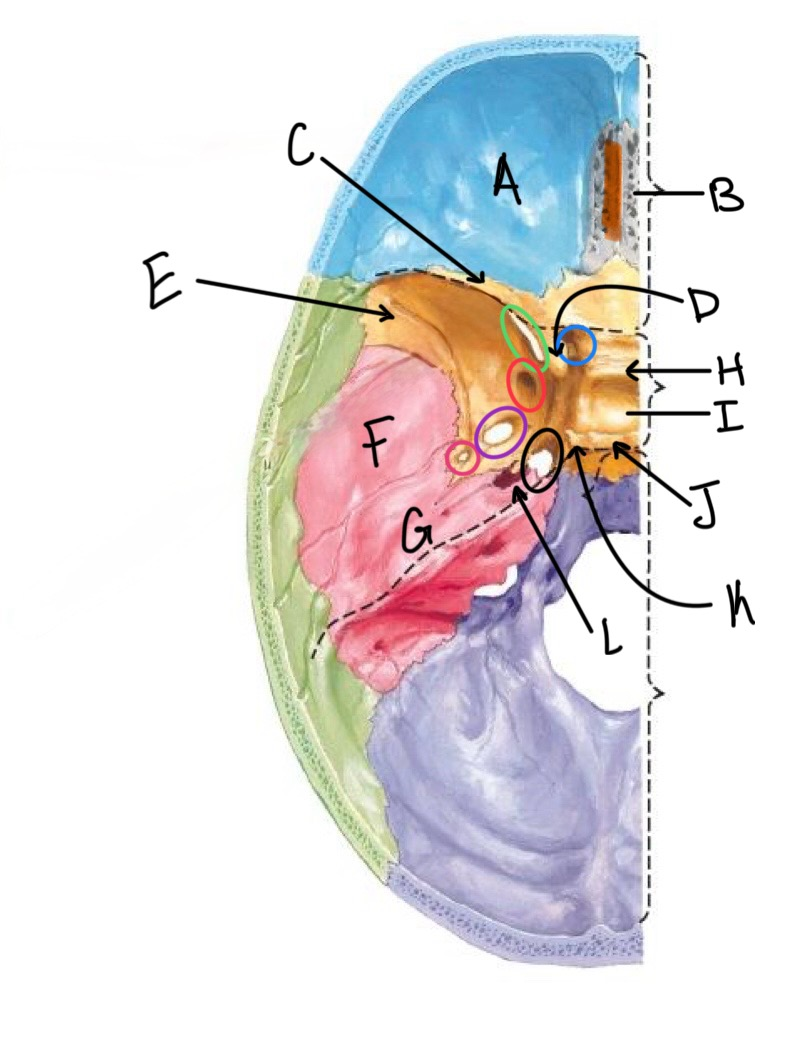
what structure is labeled E?
greater wing of the sphenoid
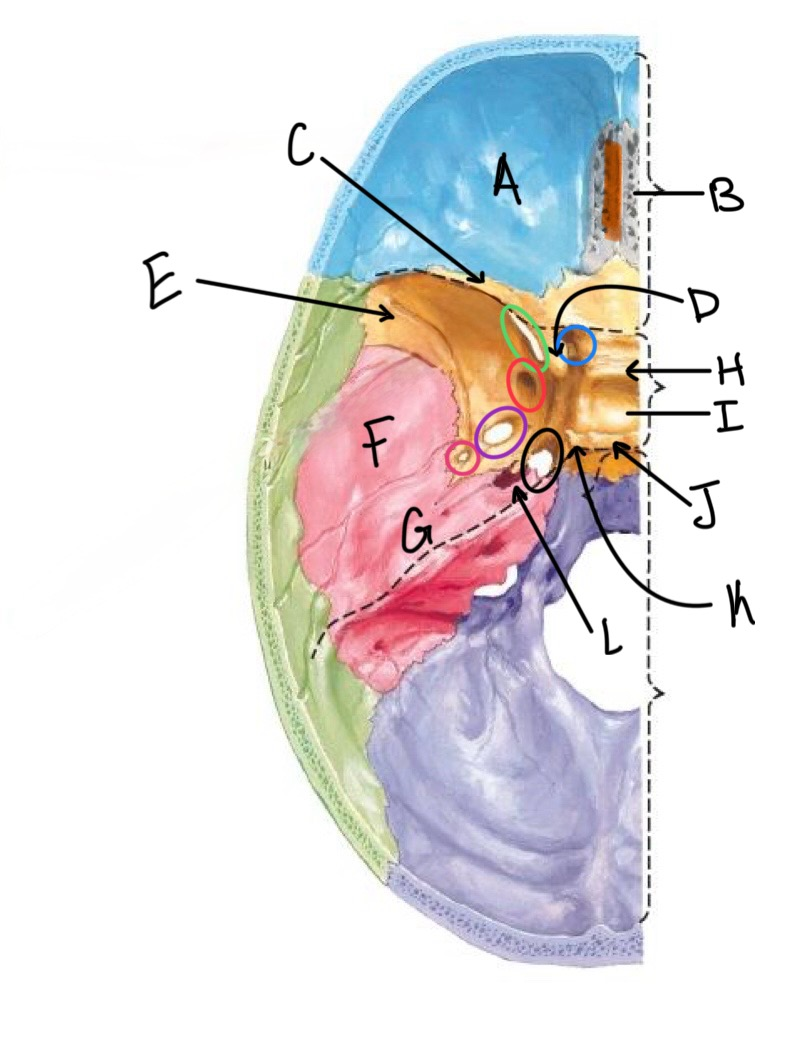
what structure is labeled F?
squamous portion of temporal bone
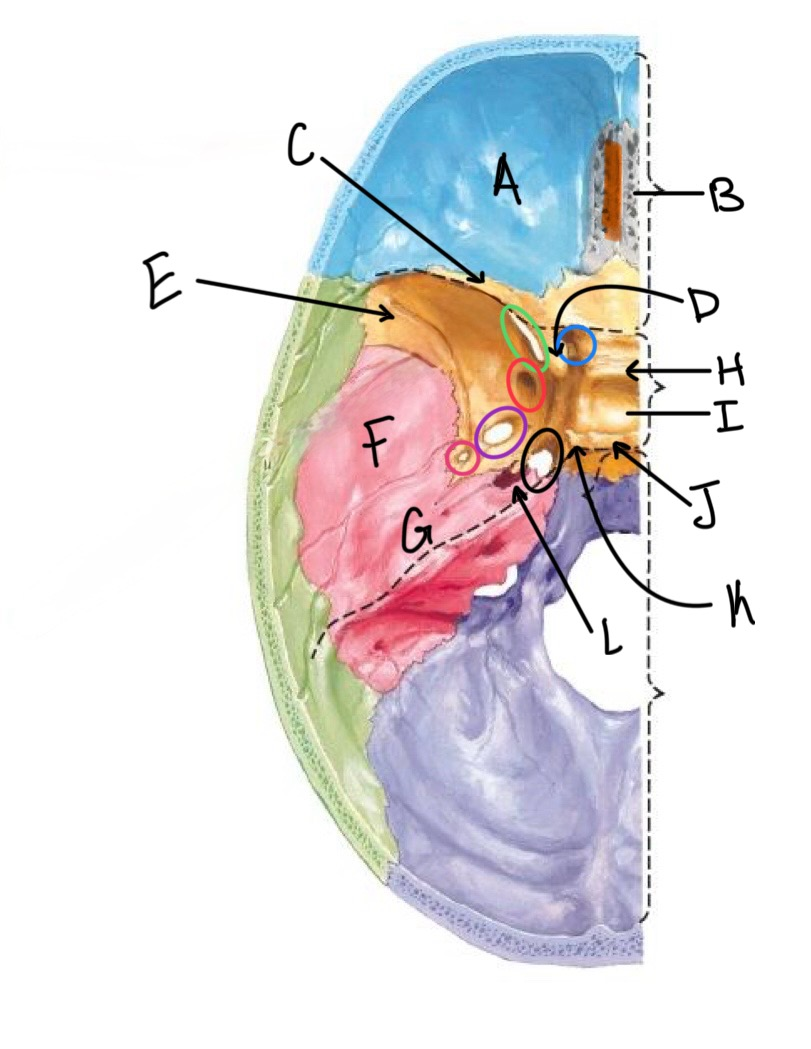
what structure is labeled G?
petrous portion of the temporal bone
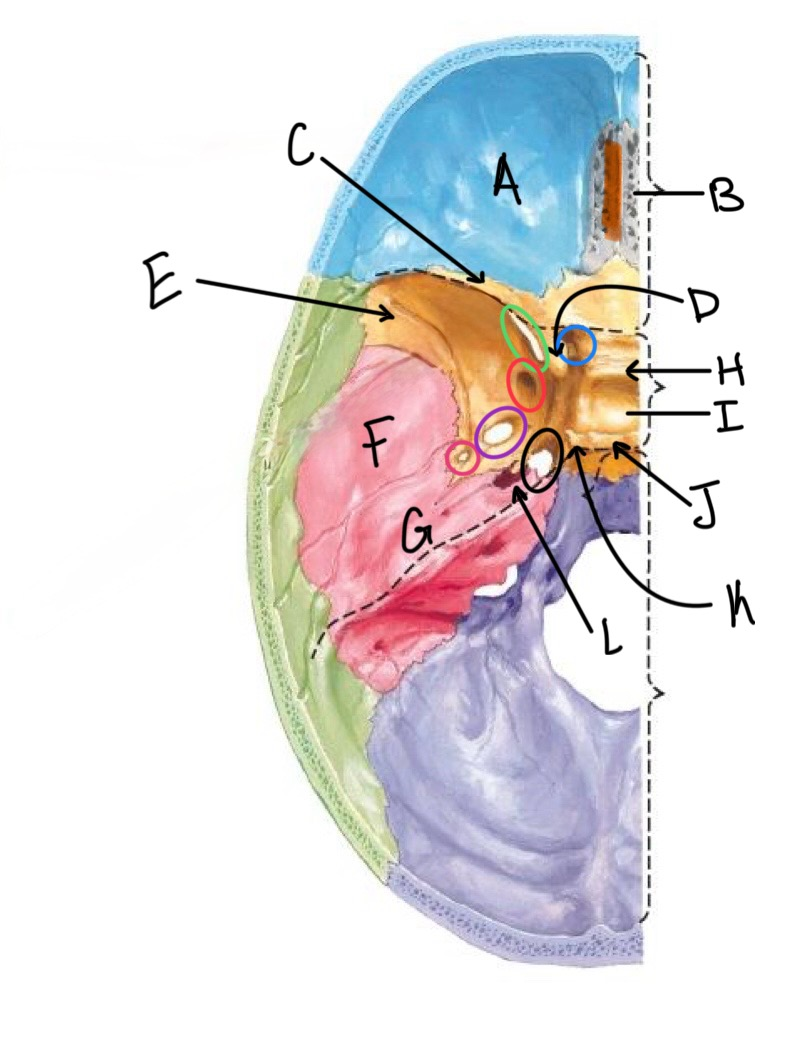
what structure is labeled H?
tuberculum sellae
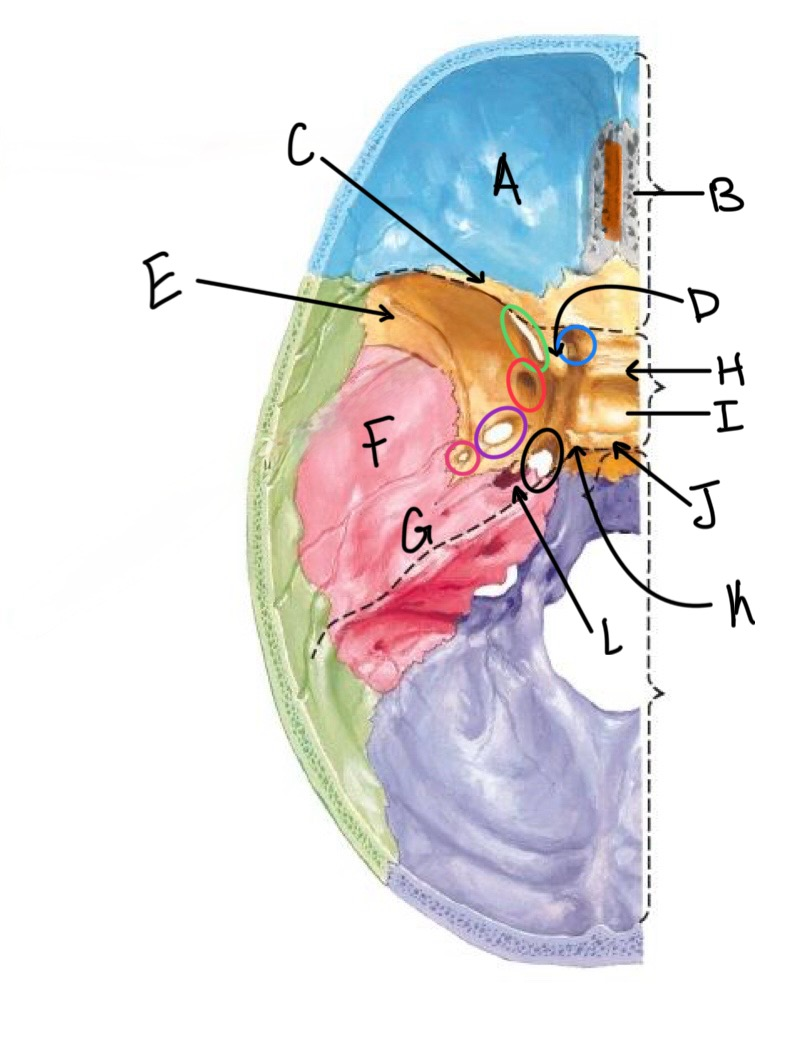
what structure is labeled I?
hypophyseal fossa
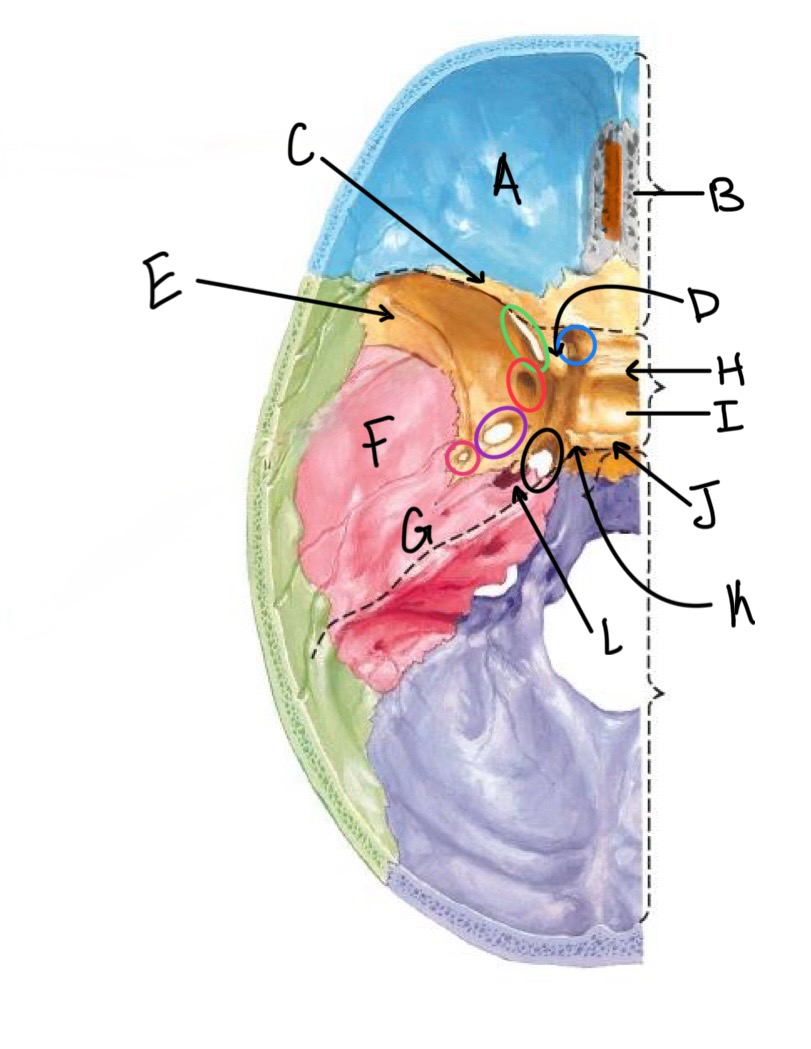
what structure is labeled J?
dorsum sellae
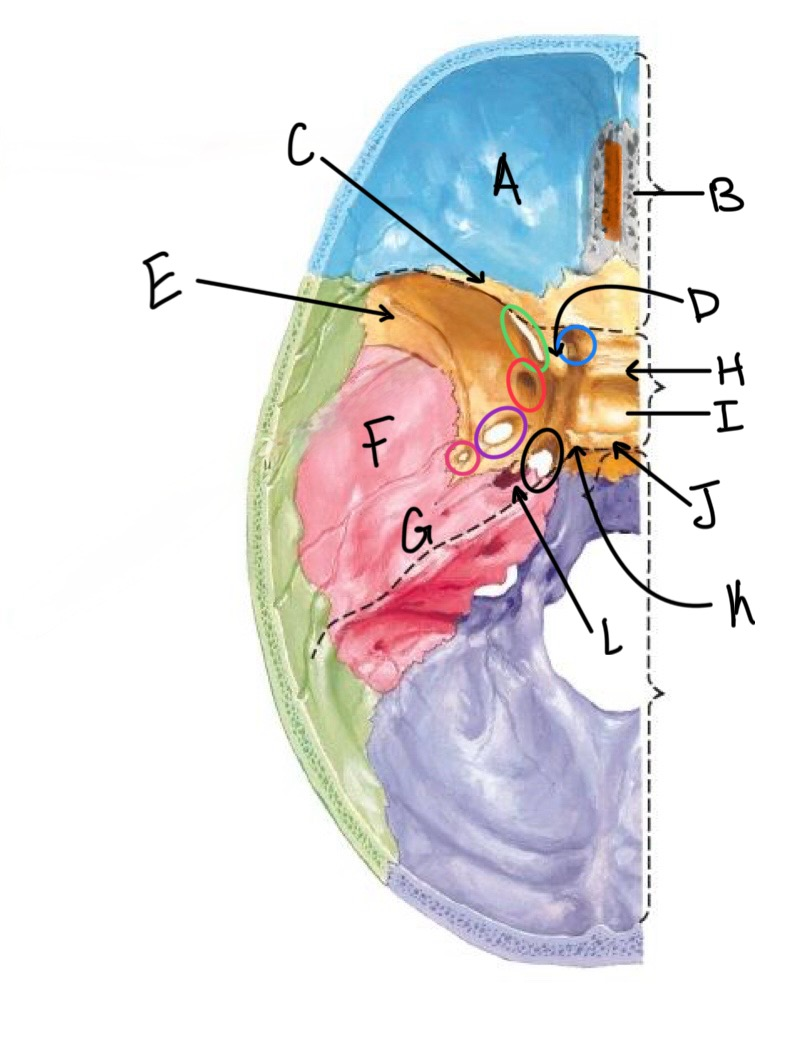
what structure is circled in blue?
optic canal
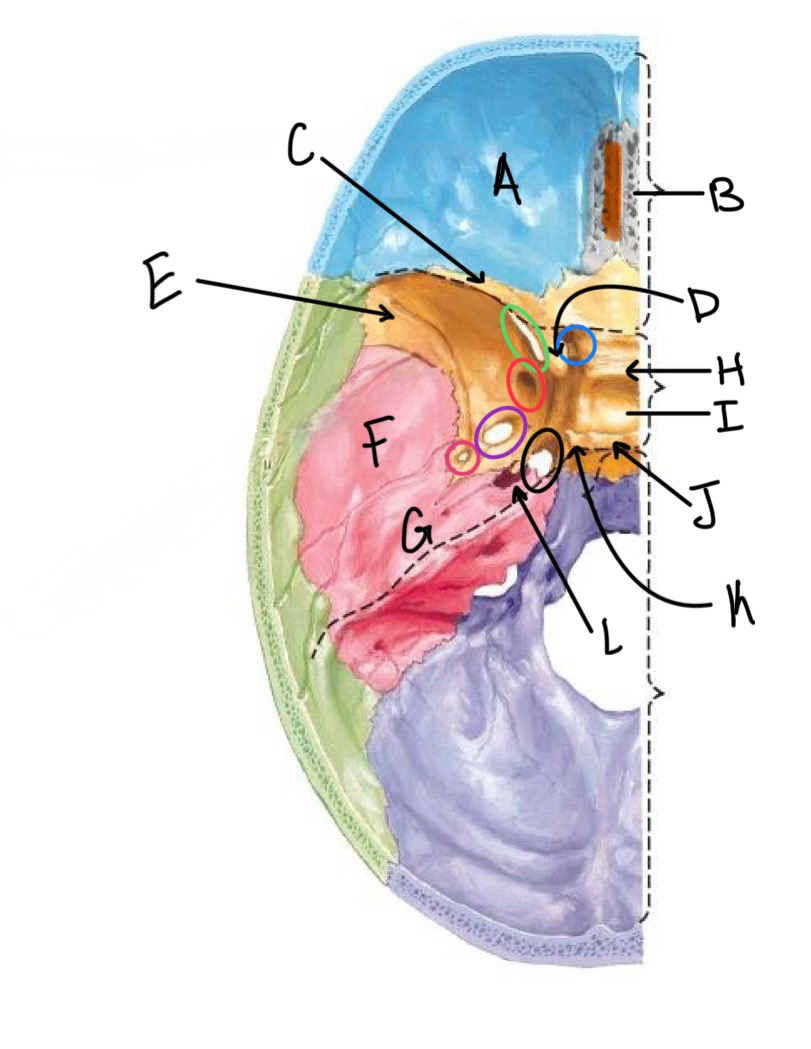
what structure is circled in green?
superior orbital fissure
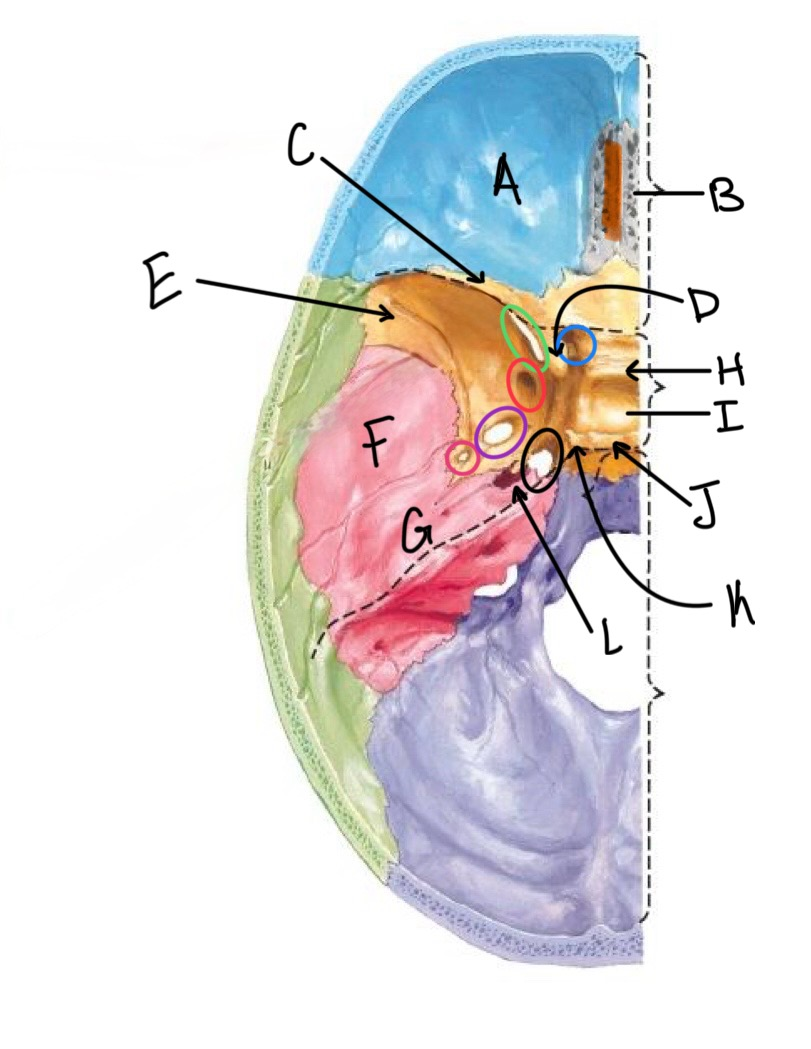
what structure is circled in red?
foramen rotundum
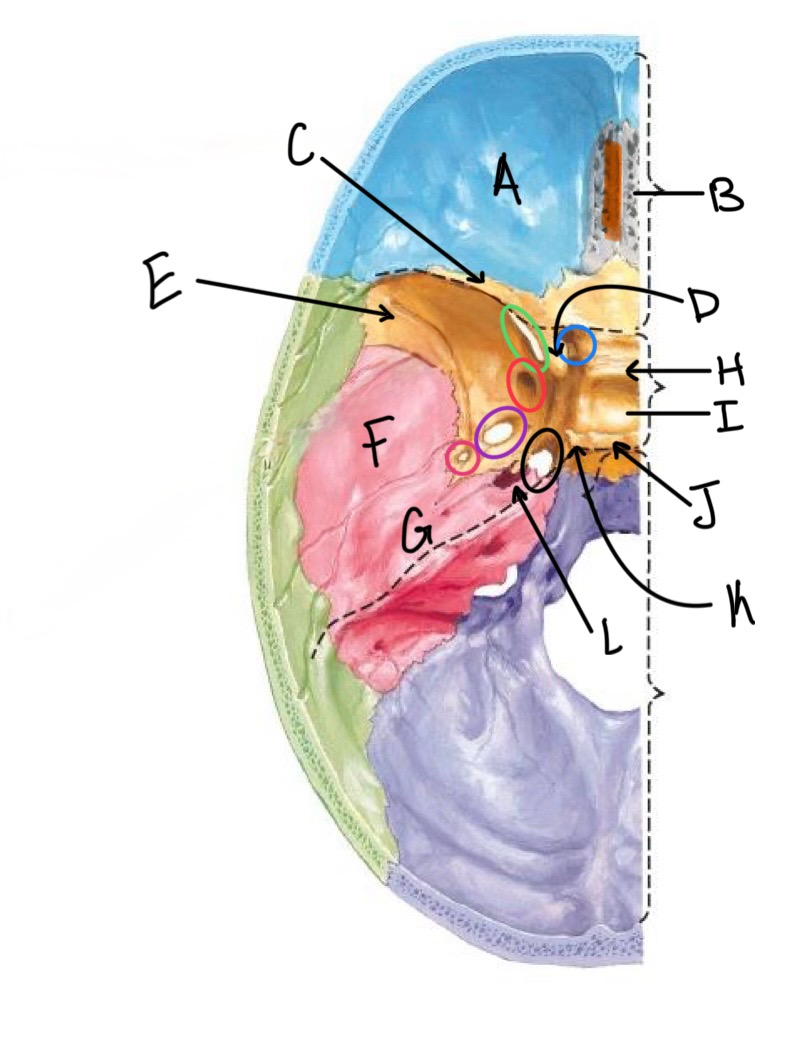
what structure is circled in purple?
foramen ovale
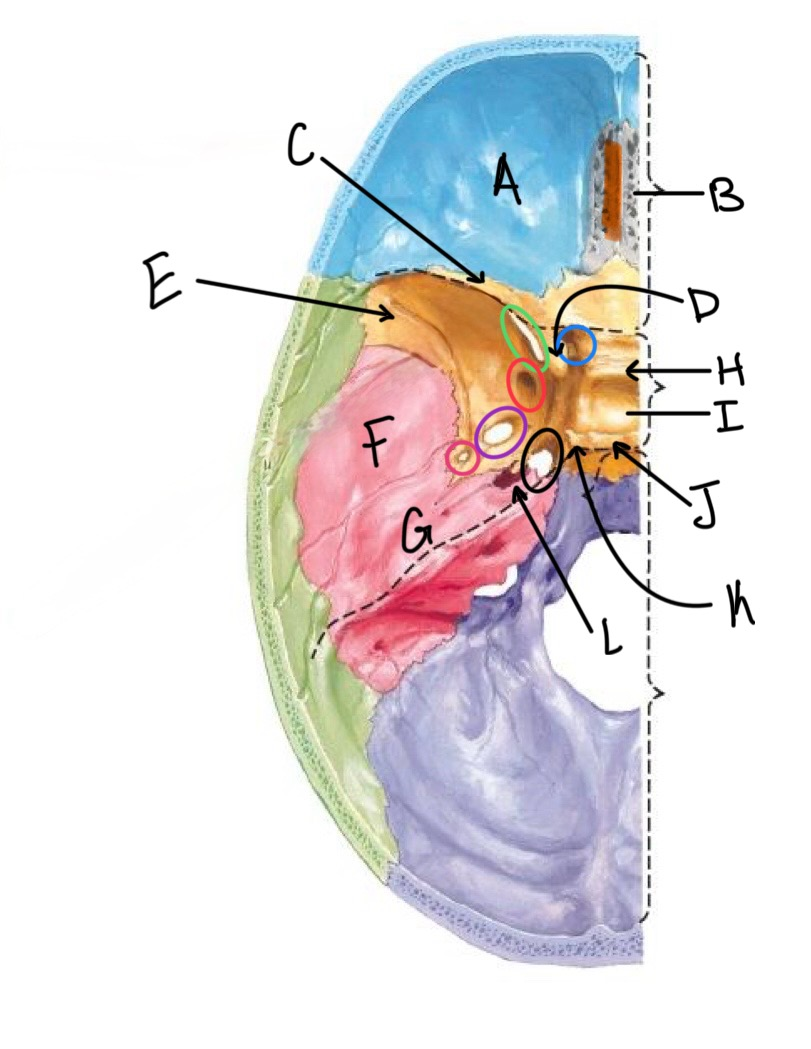
what structure is circled in pink?
foramen spinosum
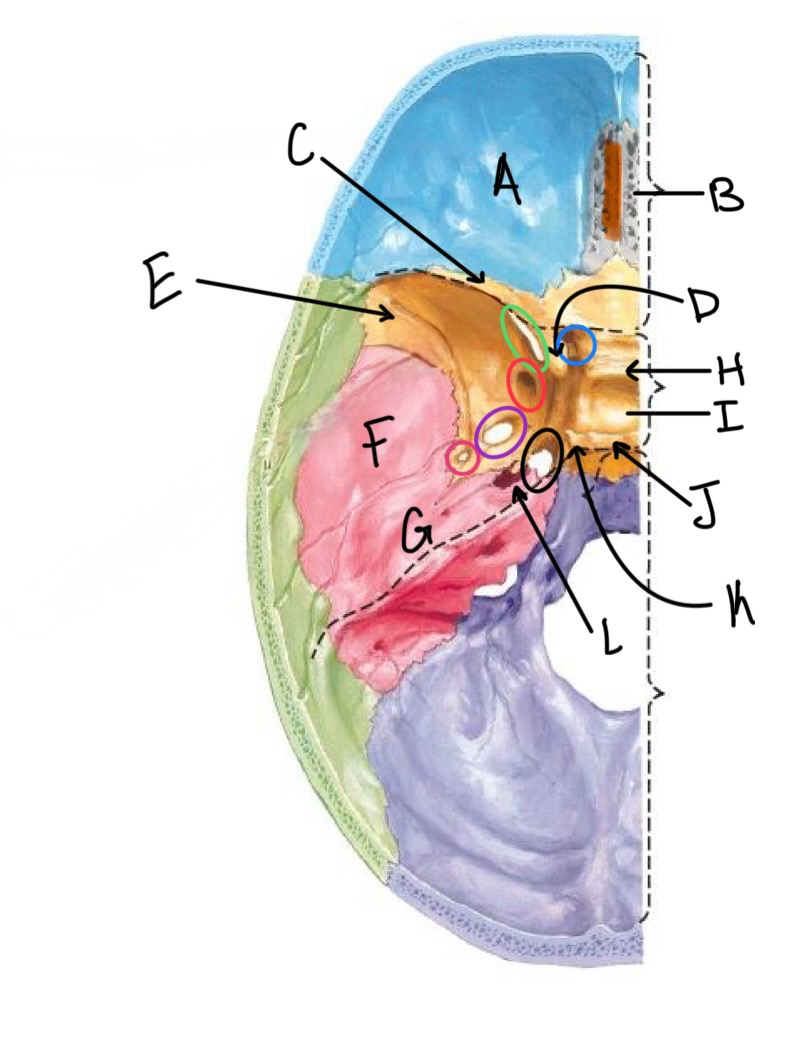
what structure is labeled K?
posterior clinoid process
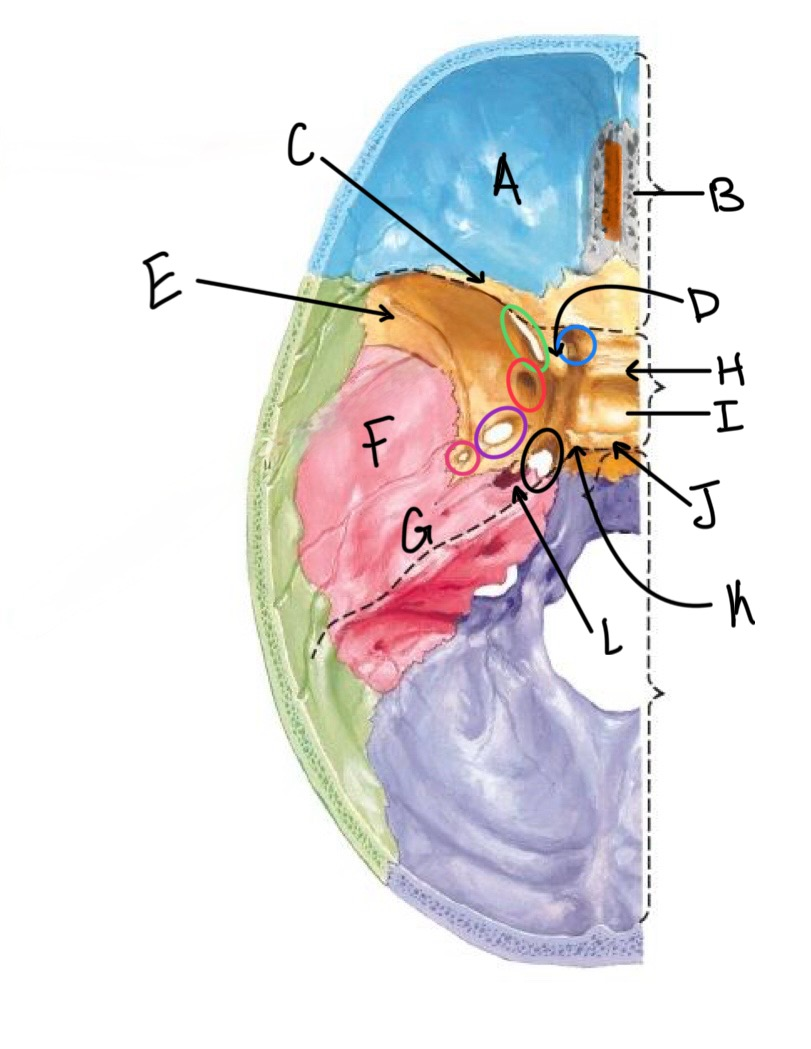
what structure is circled in black?
foramen lacerum
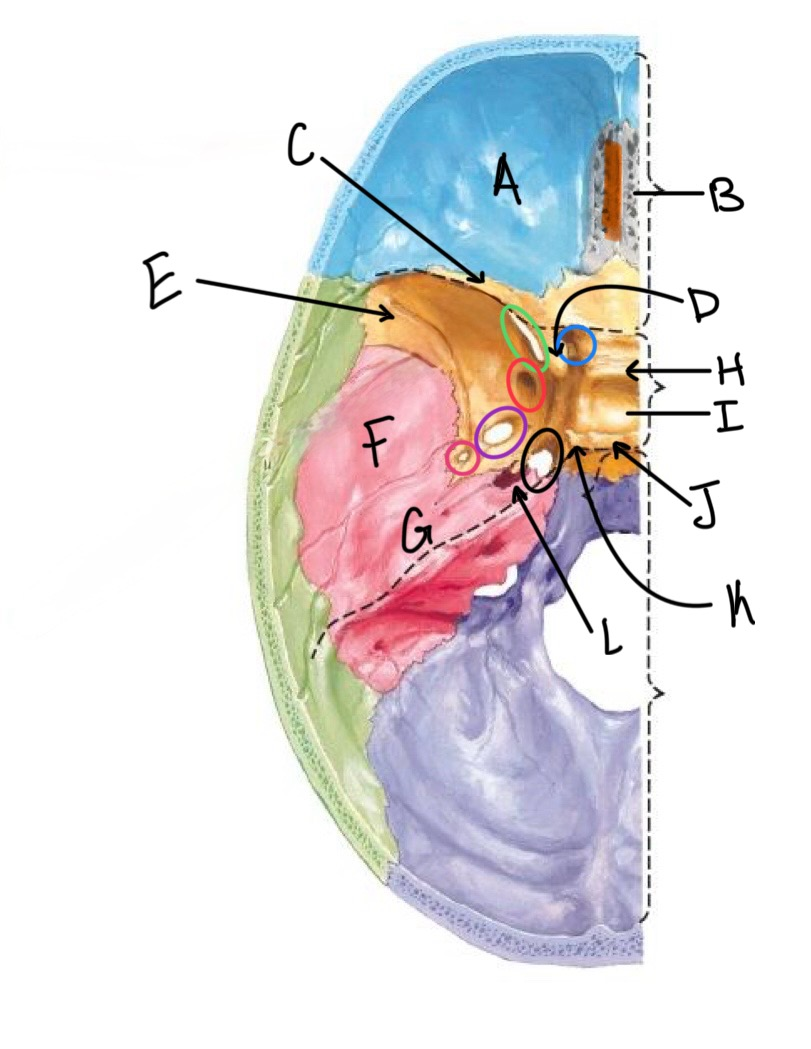
what structure is labeled L?
carotid canal
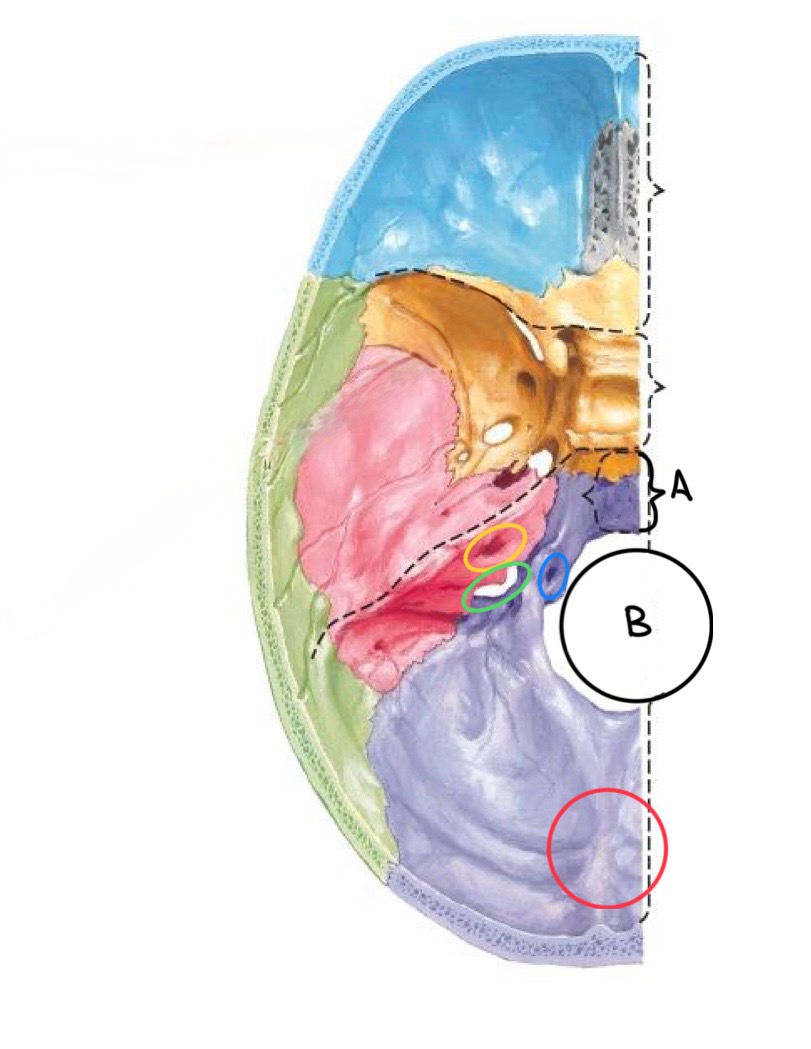
what structure is labeled A?
clivus
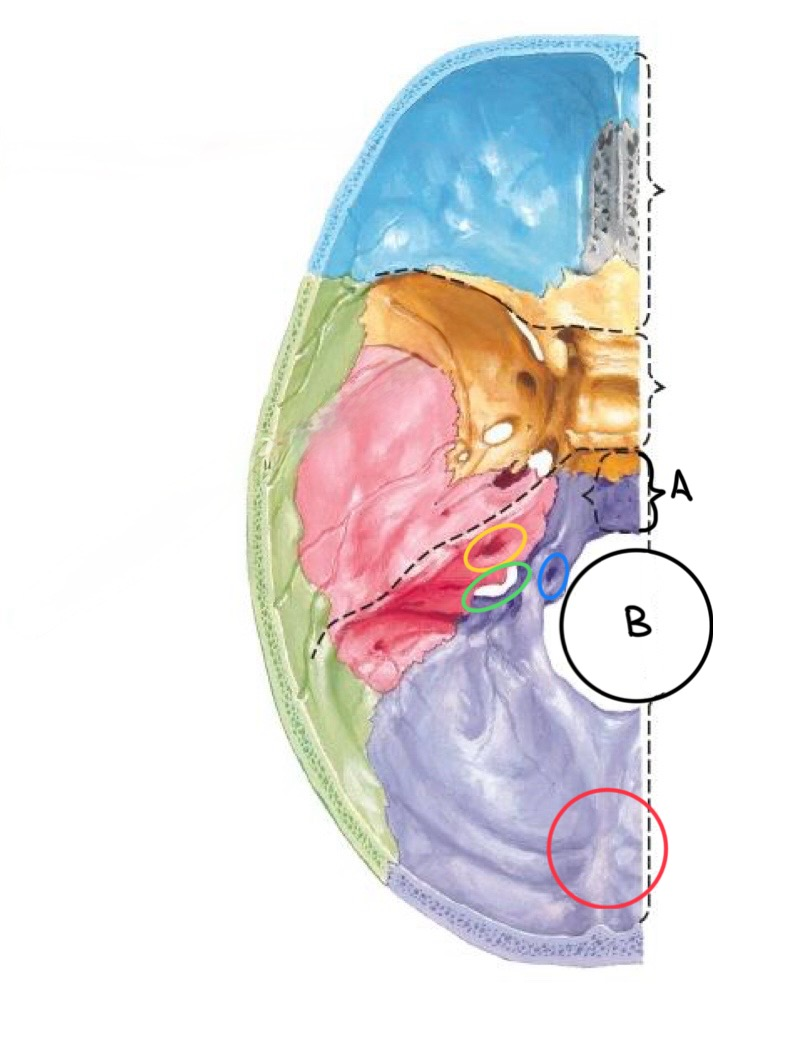
what structure is labeled B?
foramen magnum
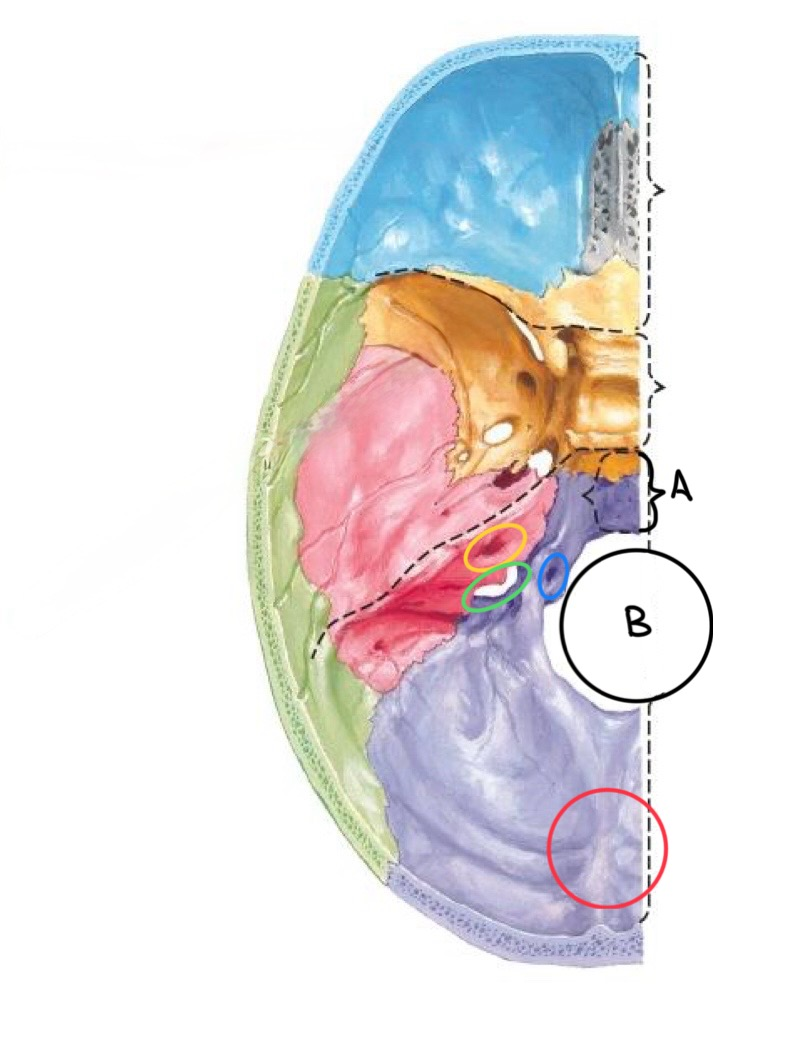
what structure is circled in blue?
hypoglossal canal
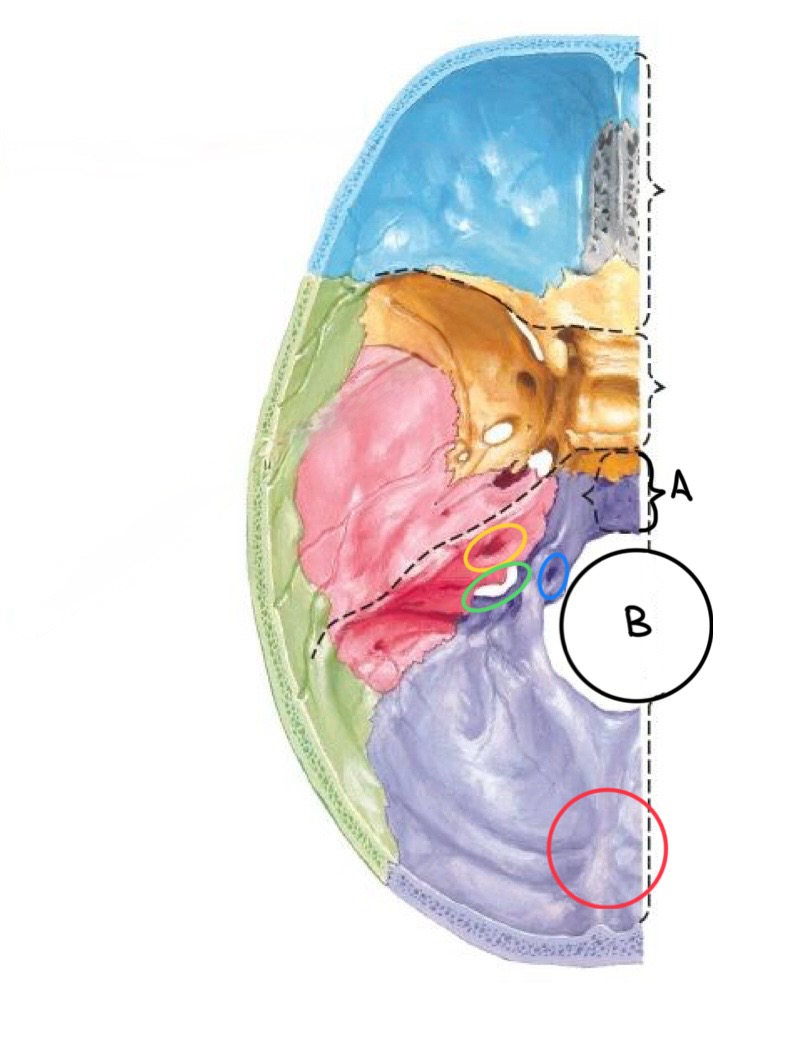
what structure is circled in yellow?
internal auditory meatus
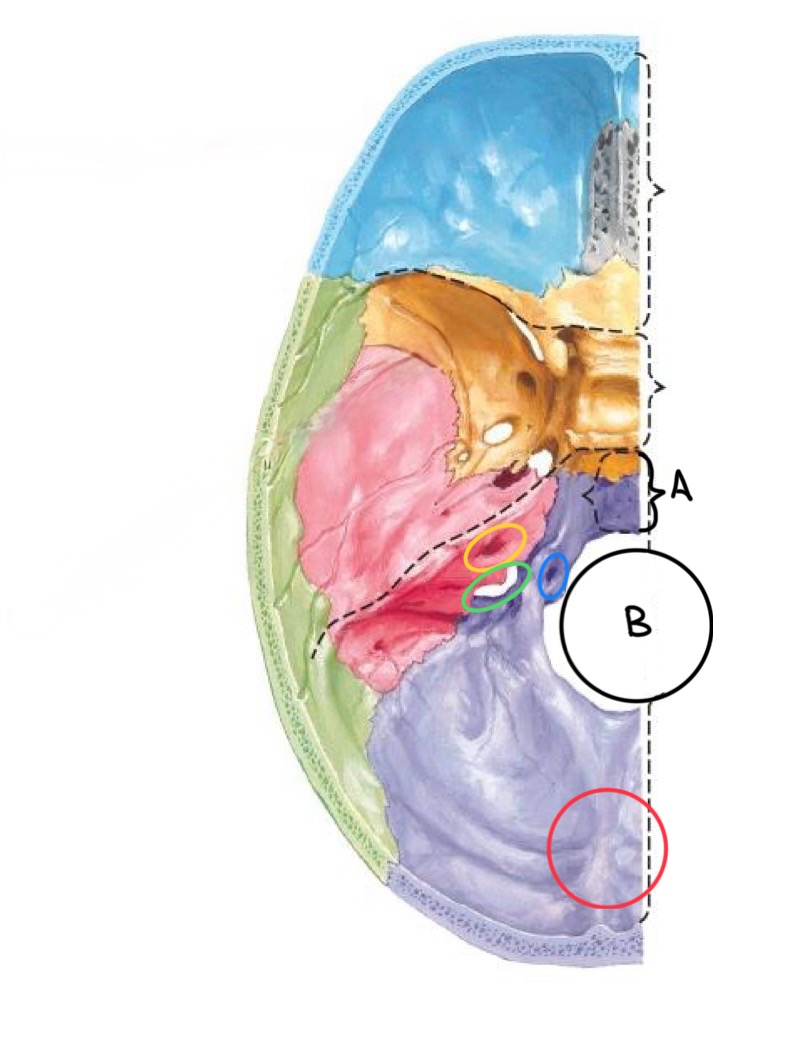
what structure is circled in green?
jugular foramen
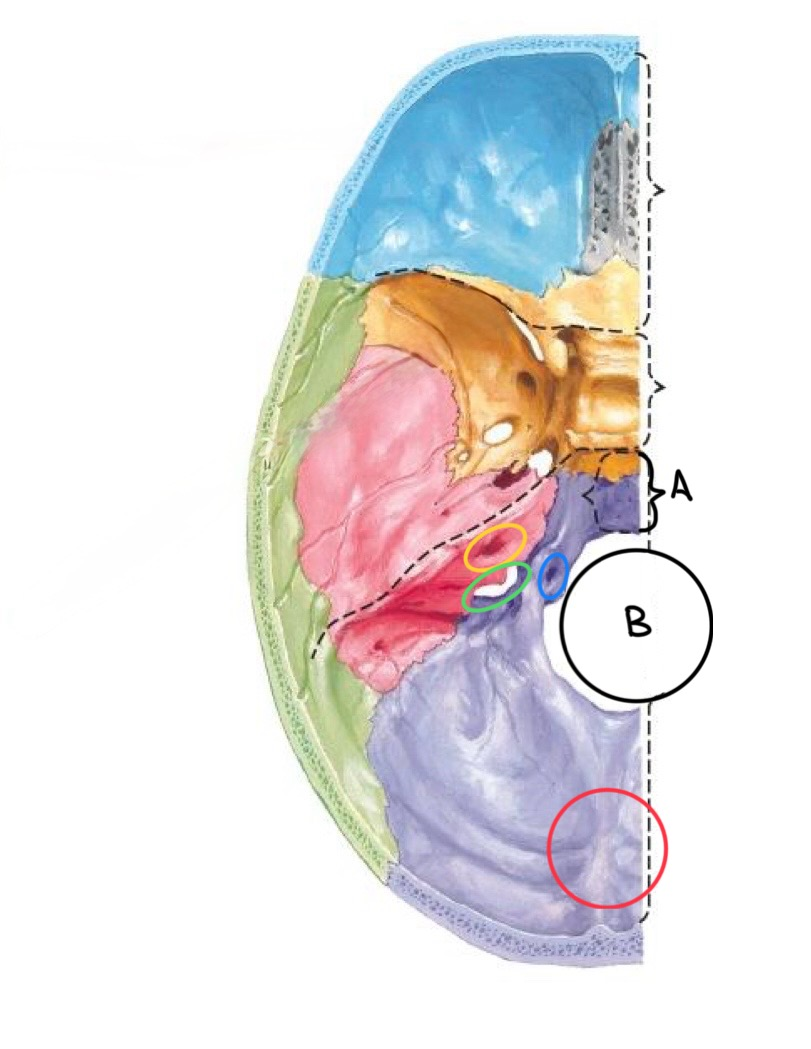
what structure is circled in red?
internal occipital protuberance
what structure is labeled A?
crista galli
what structure is circled in red?
sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
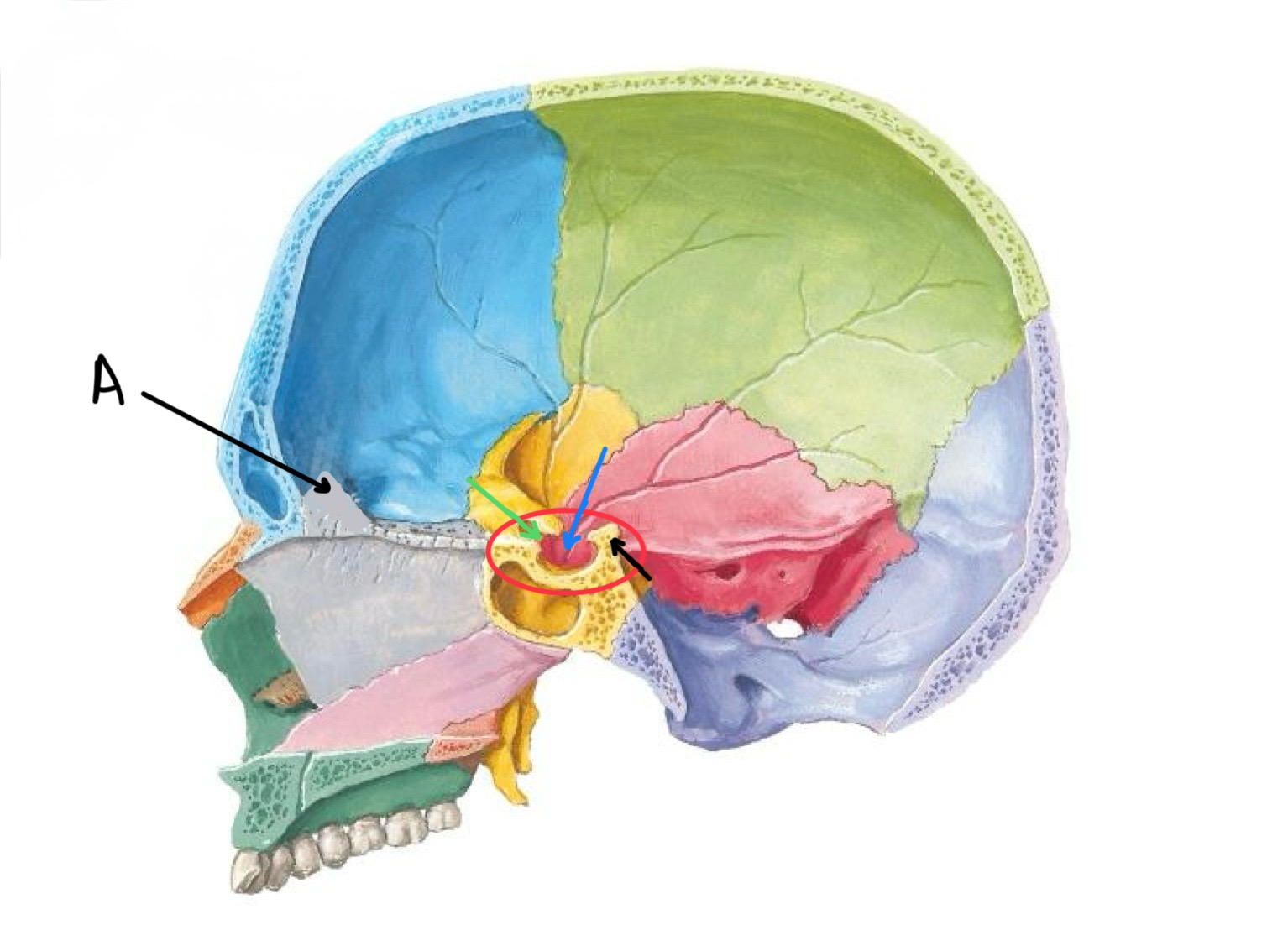
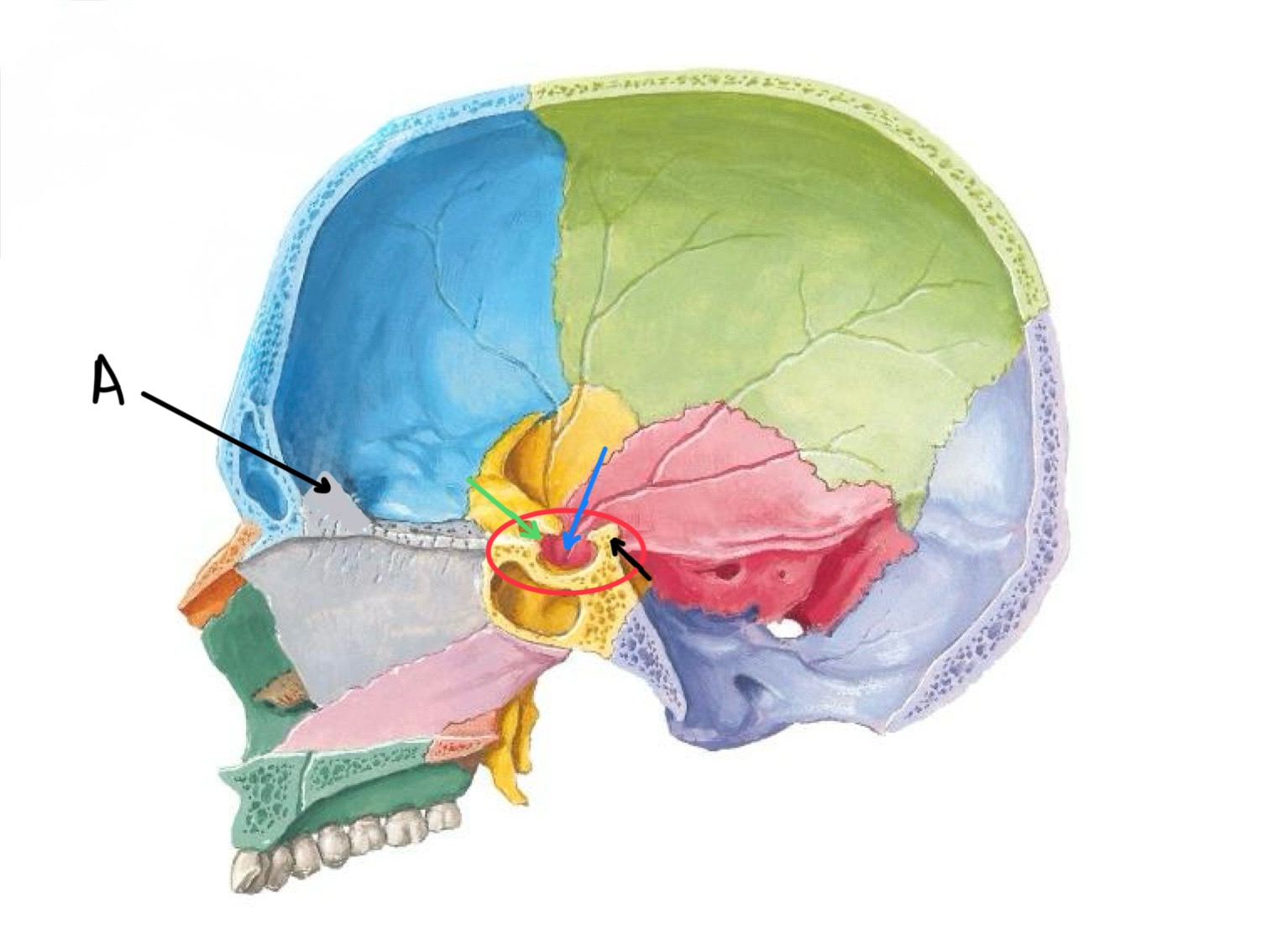
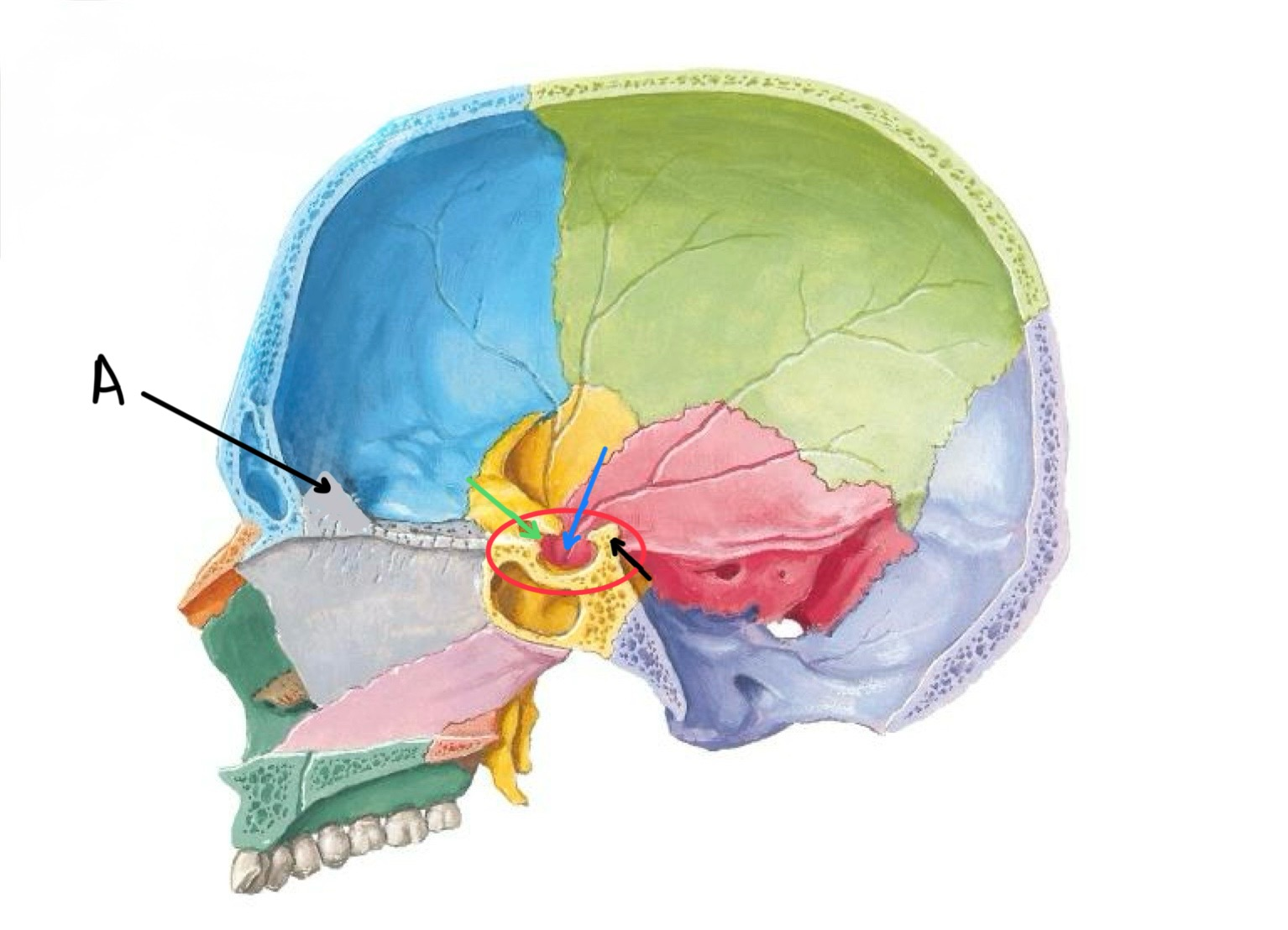
what structure is the black arrow pointing at?
dorsum sellae
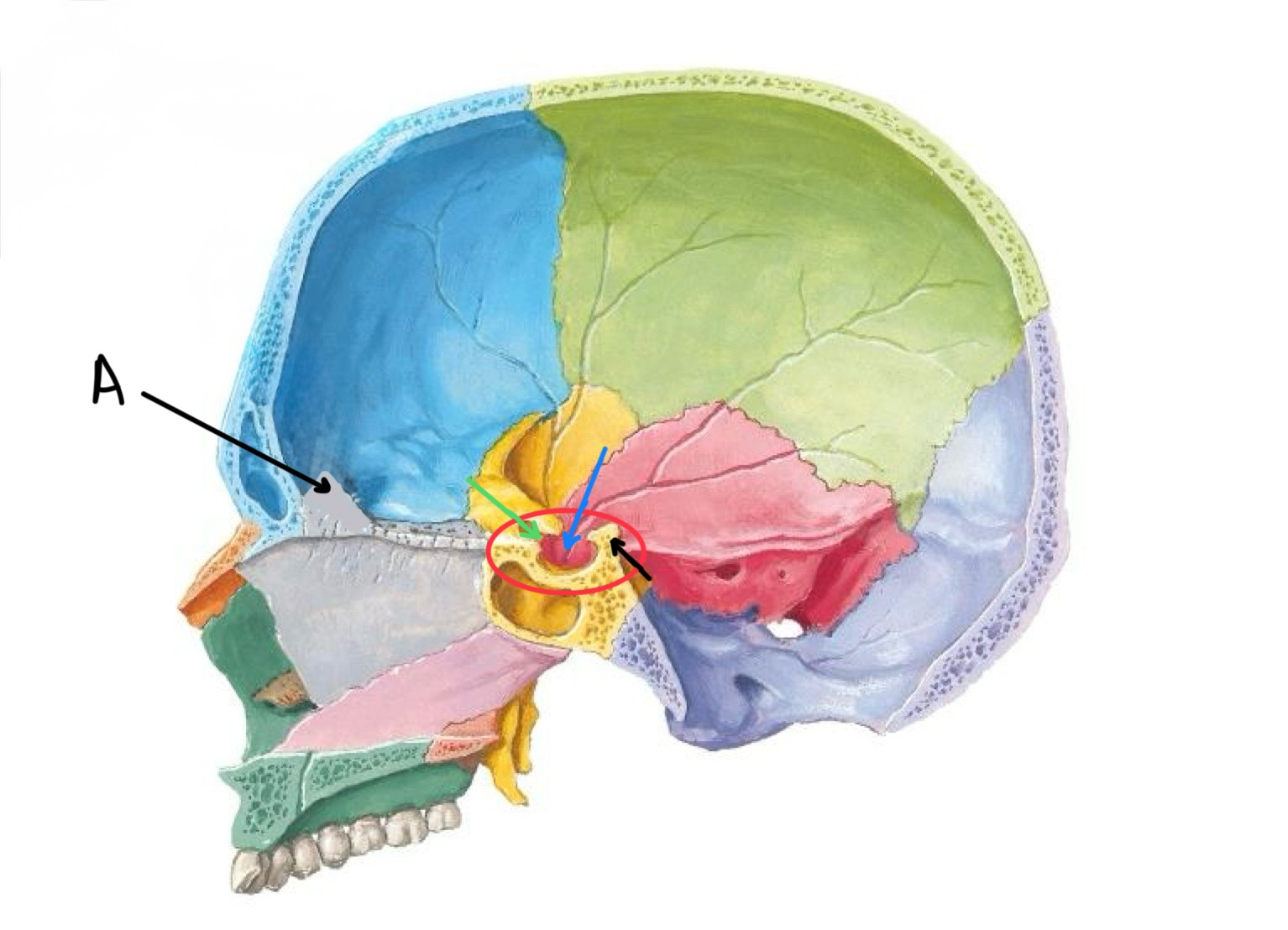
what structure is the blue arrow pointing at?
hypophyseal fossa
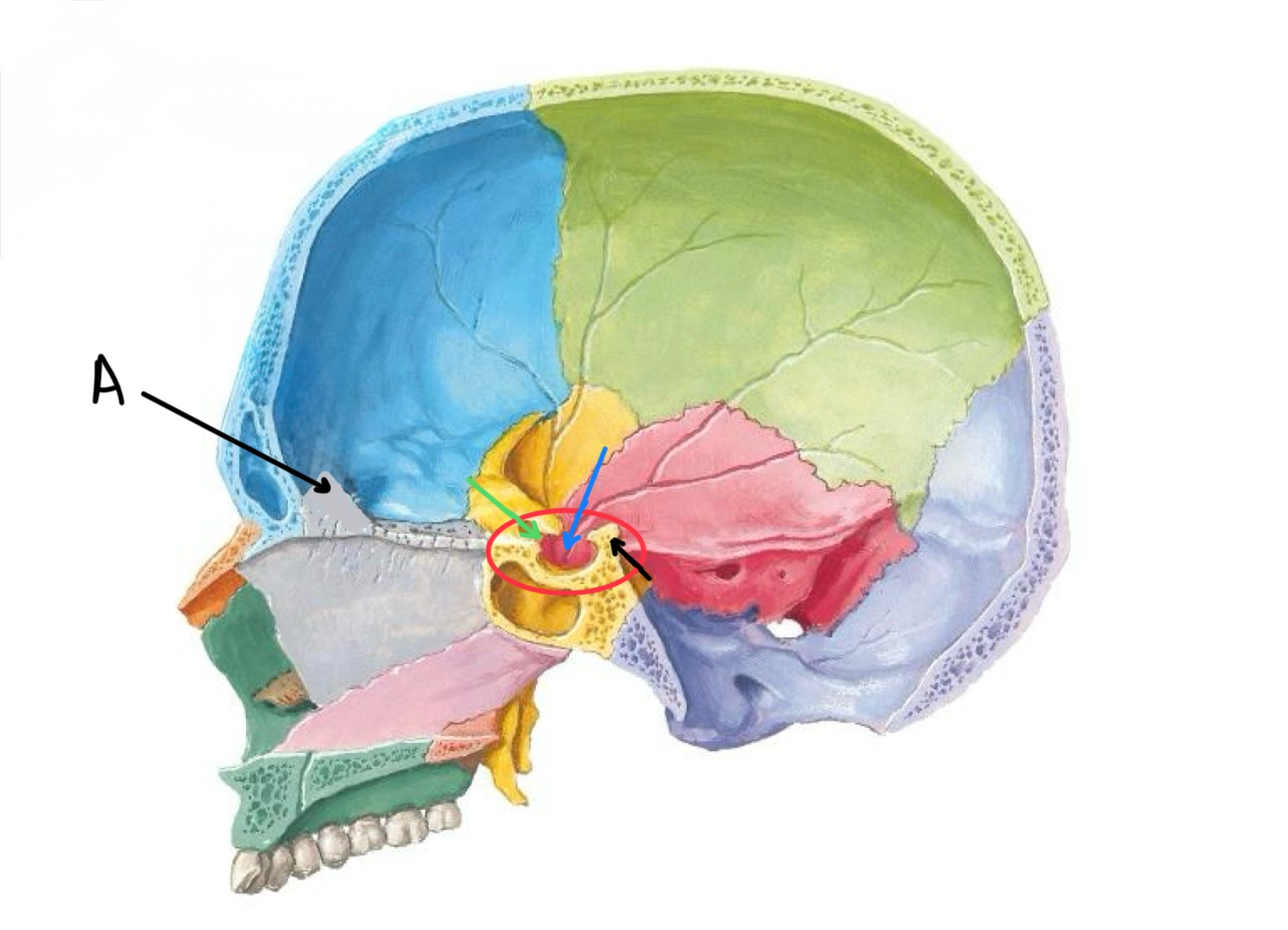
what structure is the green arrow pointing at?
tuberculum sellae
what structure is labeled B / highlighted green?
lesser wing of sphenoid
what structure is highlighted in blue?
cribriform plate
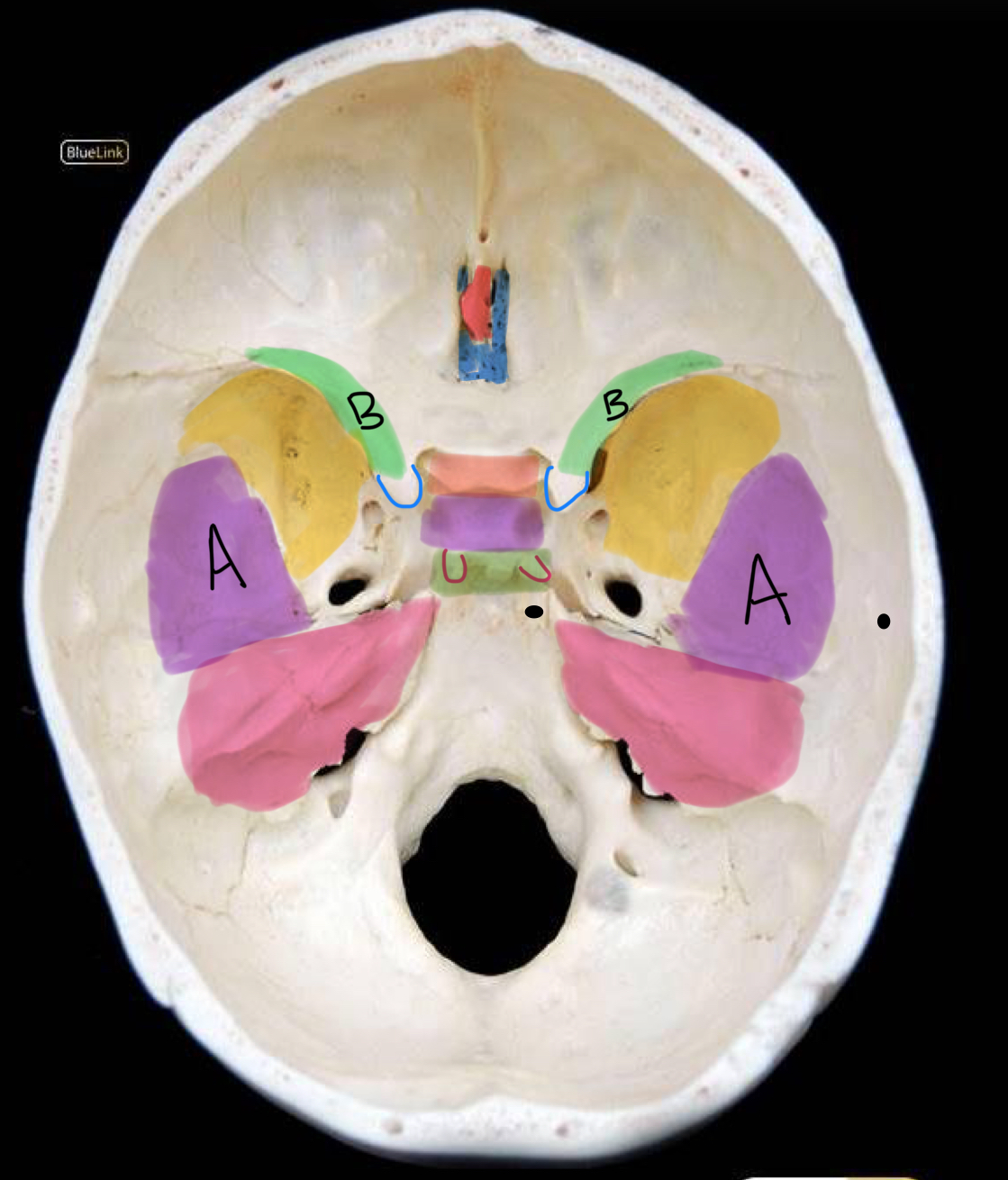
what structure is highlighted in yellow?
greater wing of sphenoid
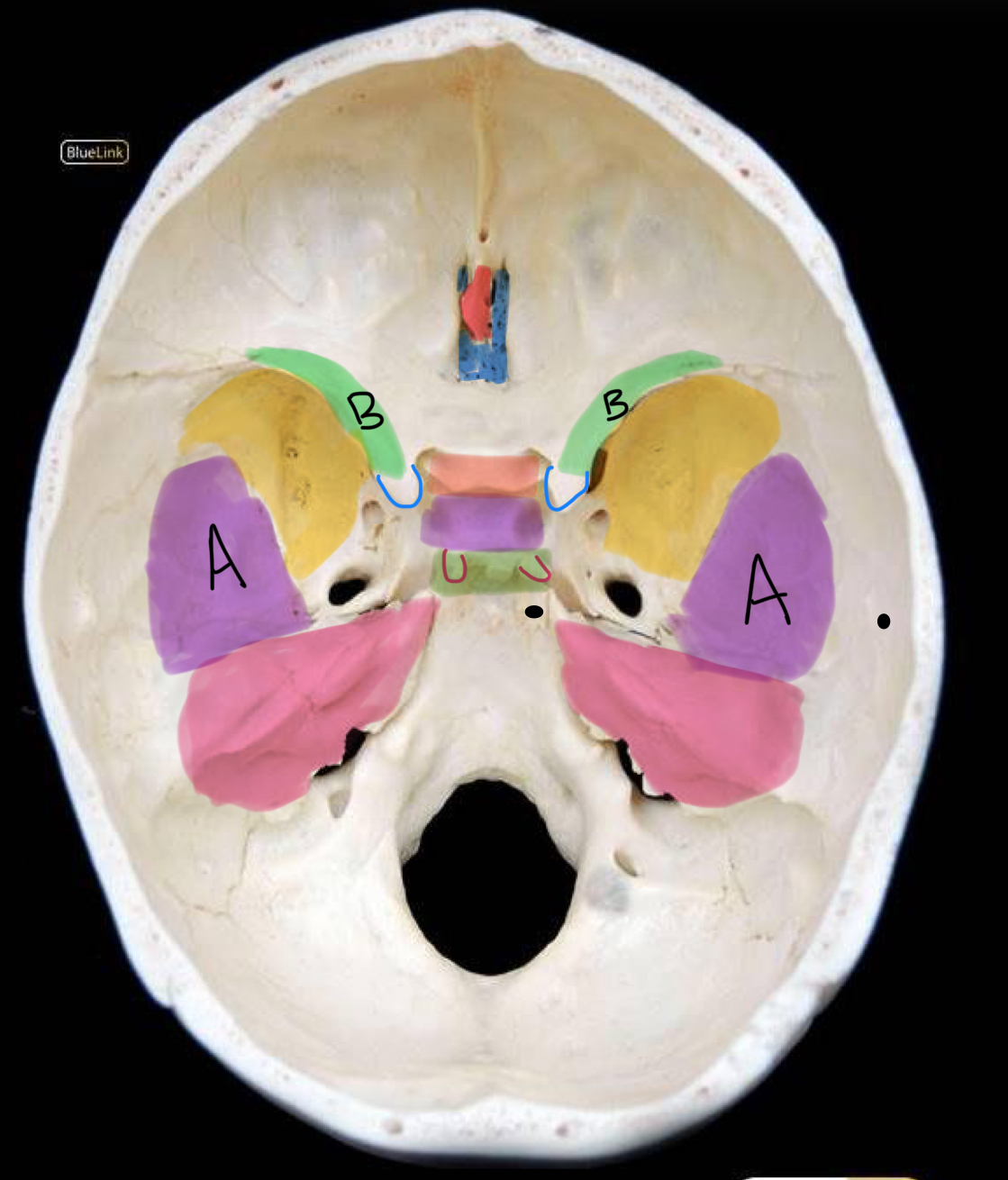
what structure is labeled A / highlighted purple?
squamous temporal bone
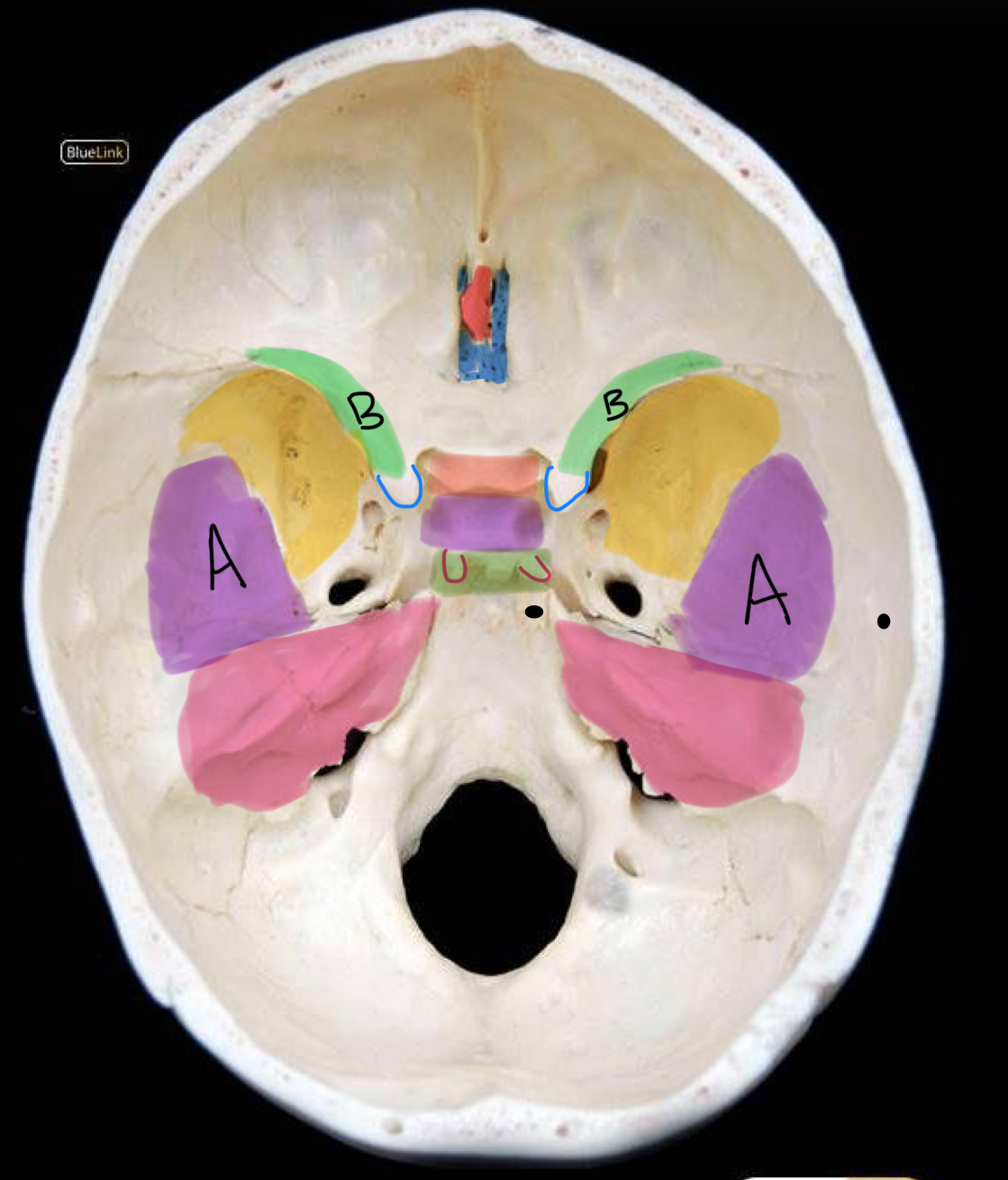
what structure is highlighted pink?
petrous temporal bone
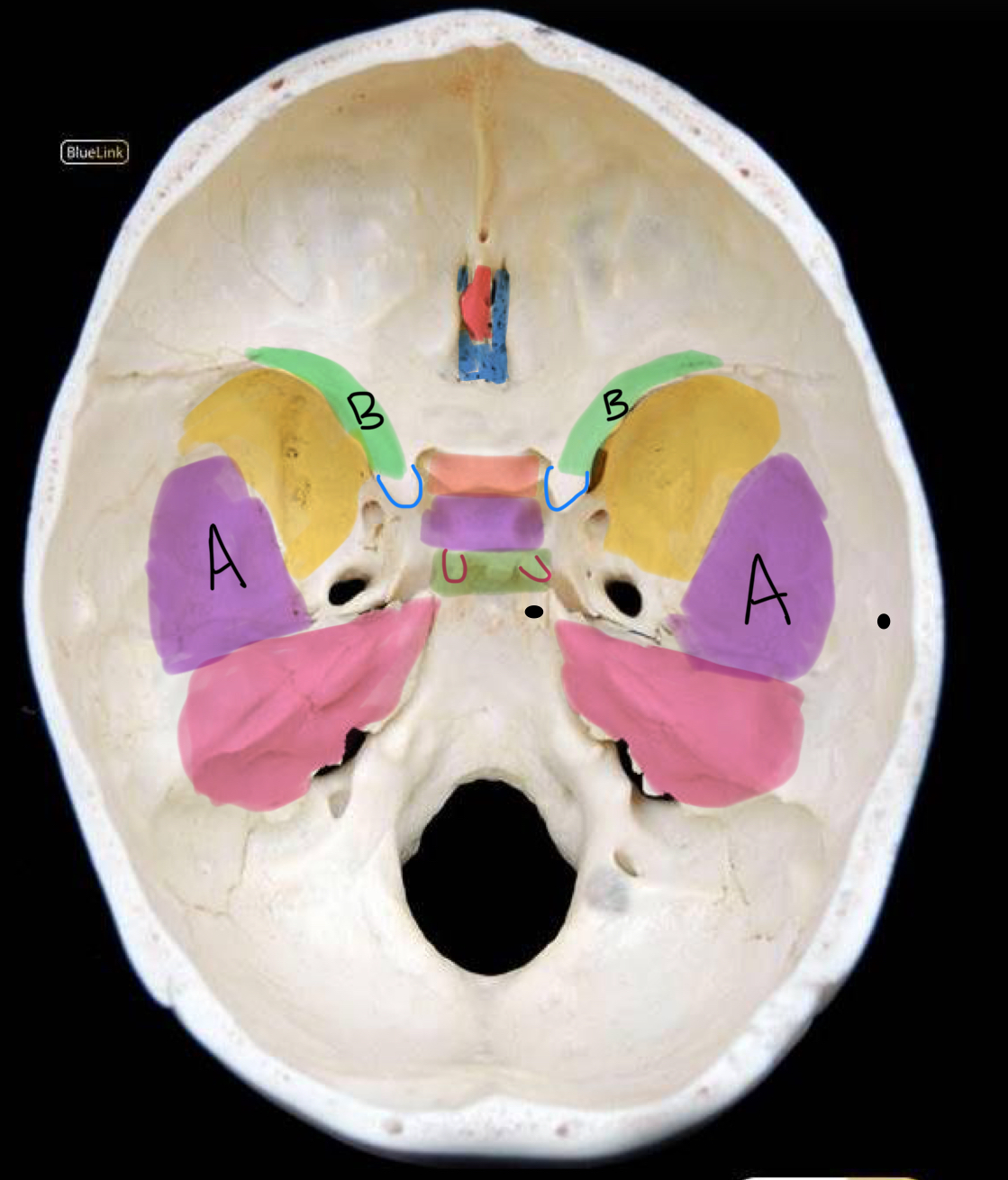
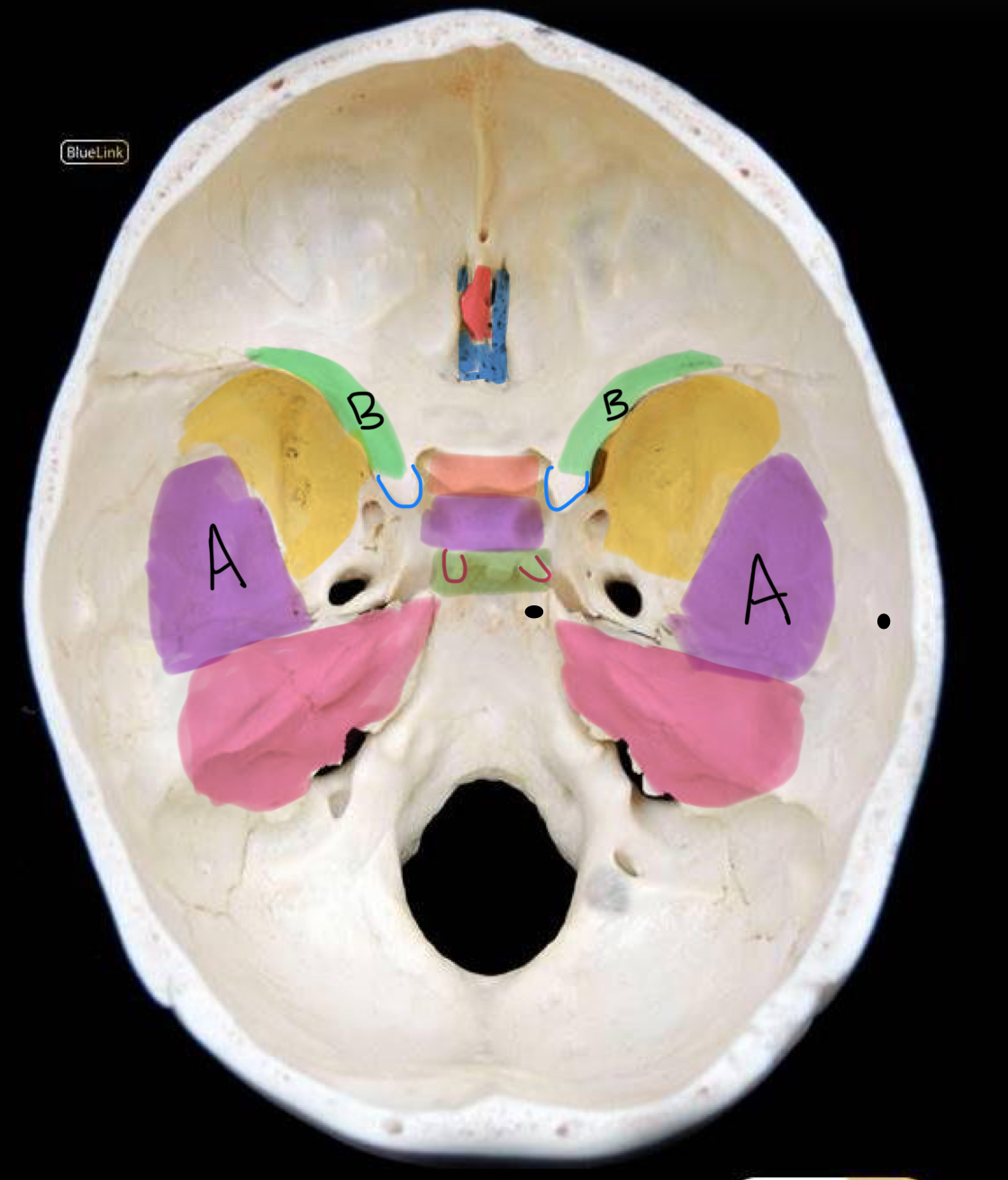
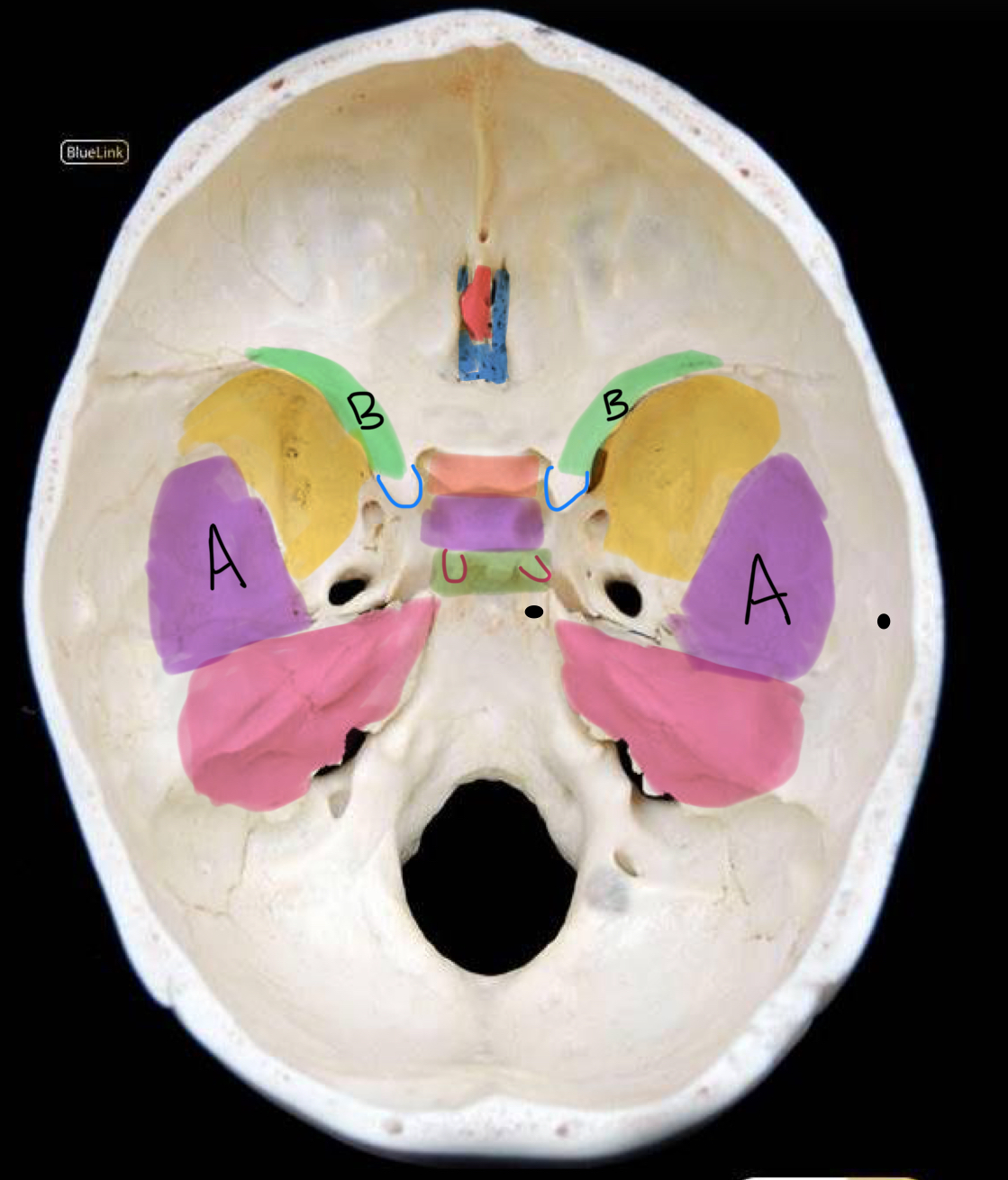
what structure is highlighted in red?
crista galli
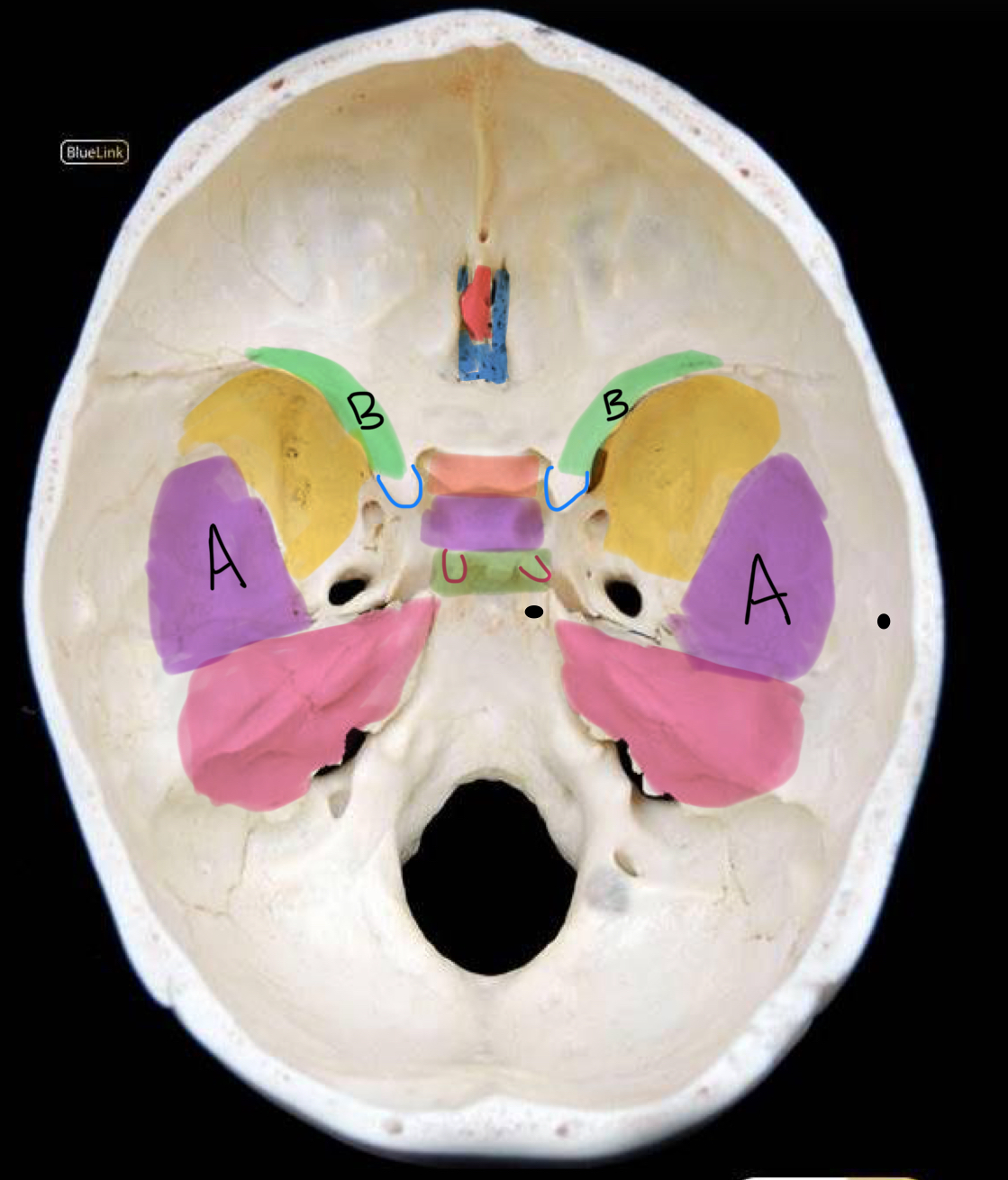
what structure is highlighted in coral?
tuberculum sellae
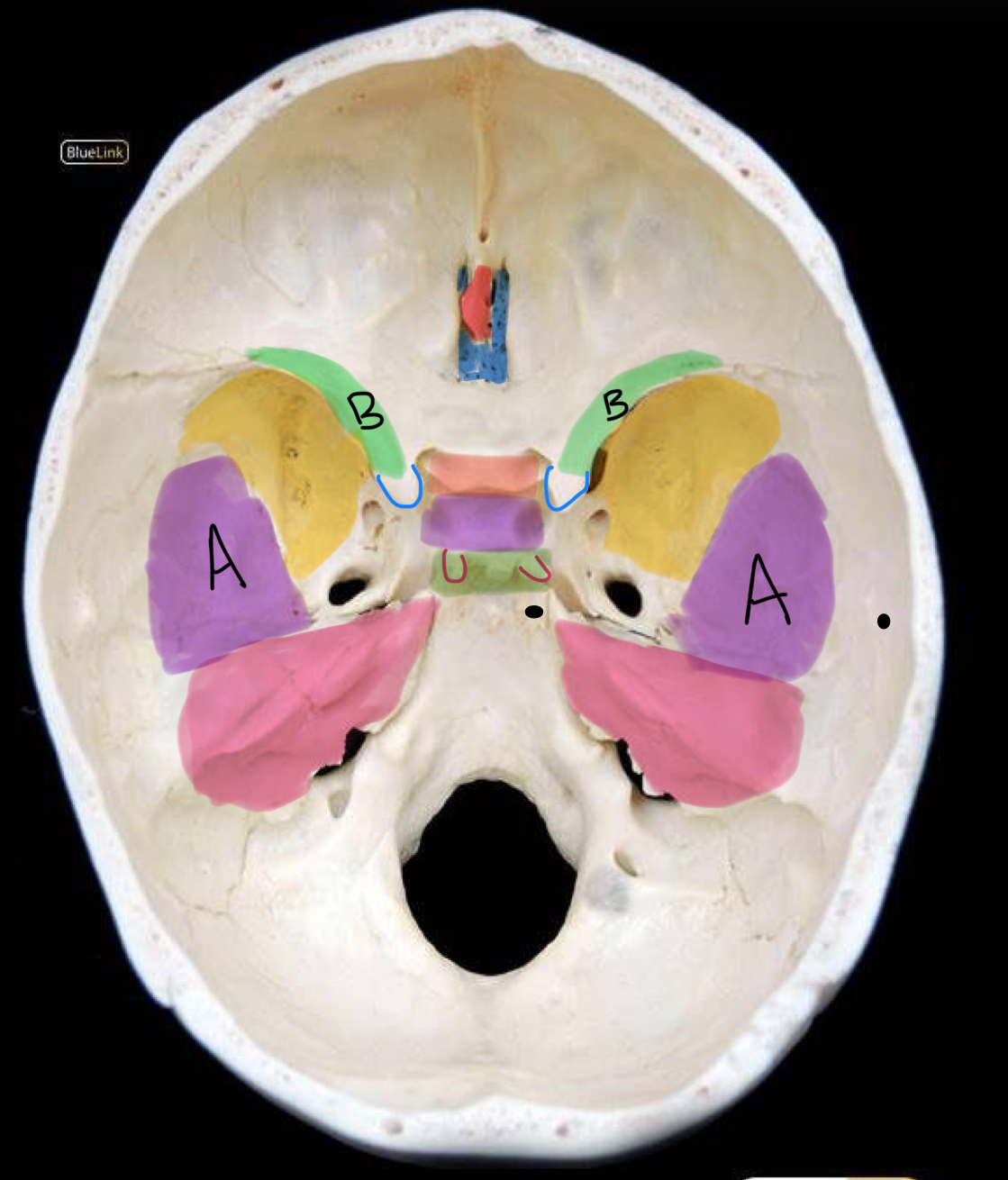
what structure is highlighted in purple (and not labeled A)?
hypophyseal fossa
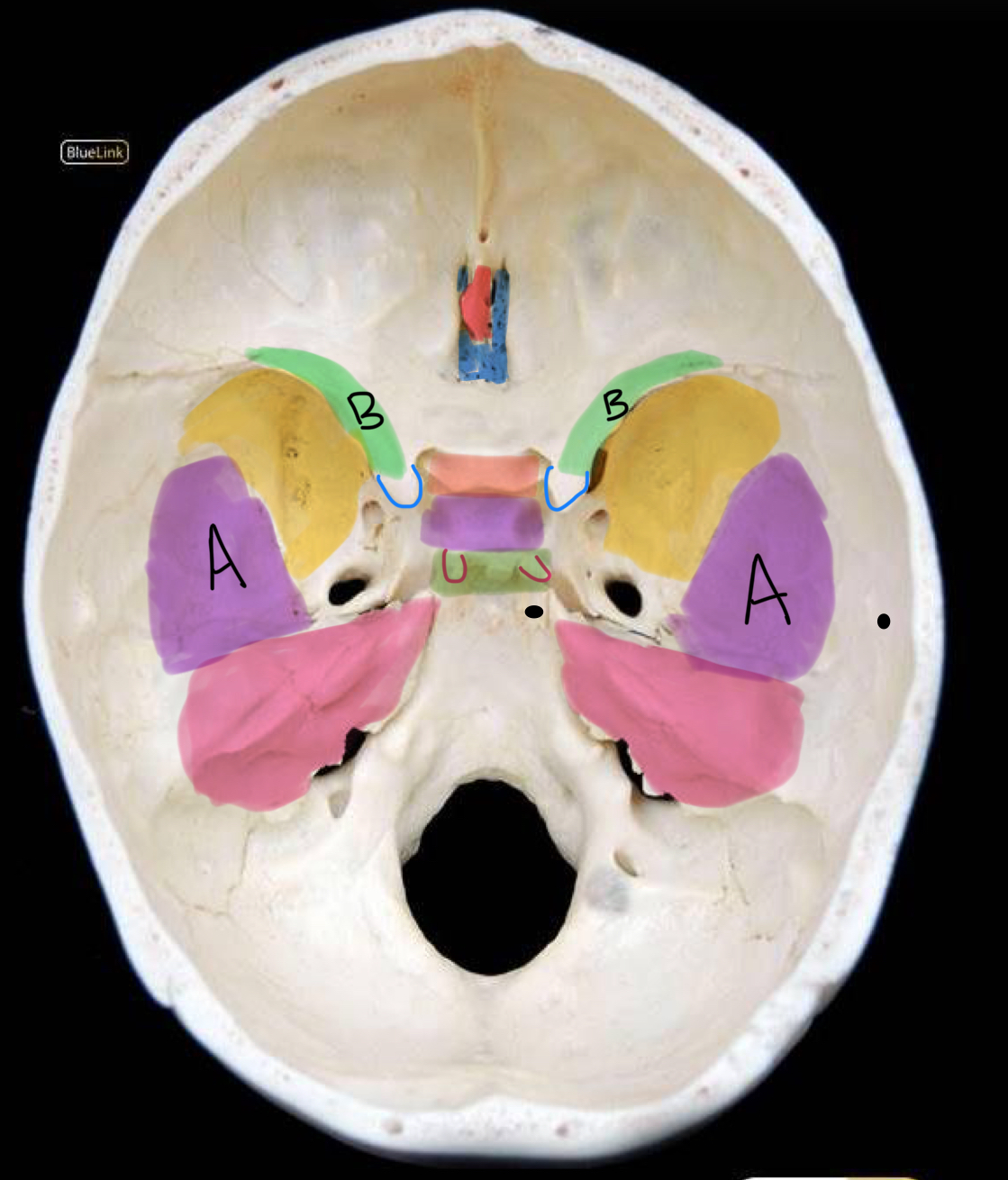
what structure is highlighted in green?
dorsum sellae
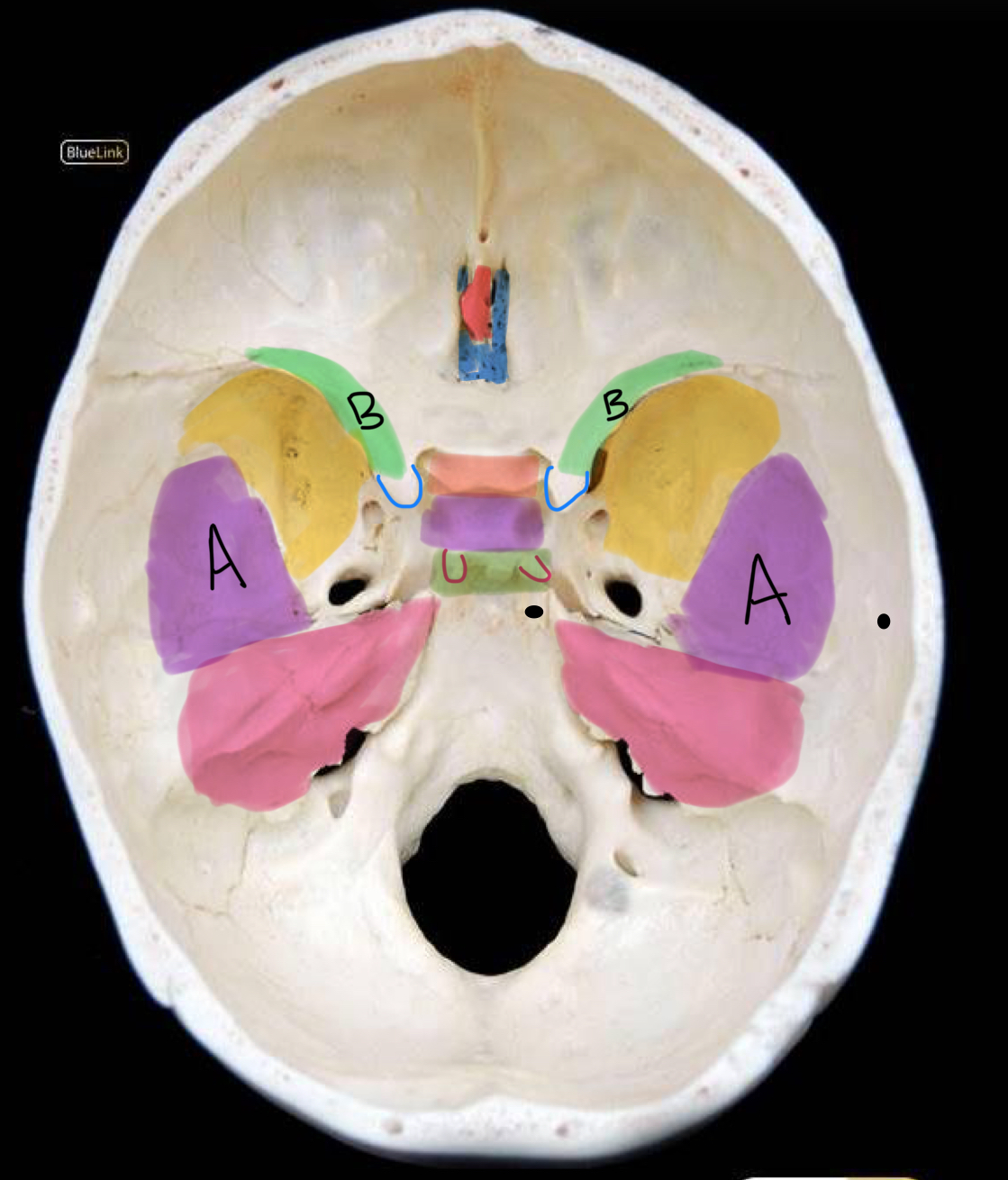
what structure is outlined in blue?
anterior clinoid process
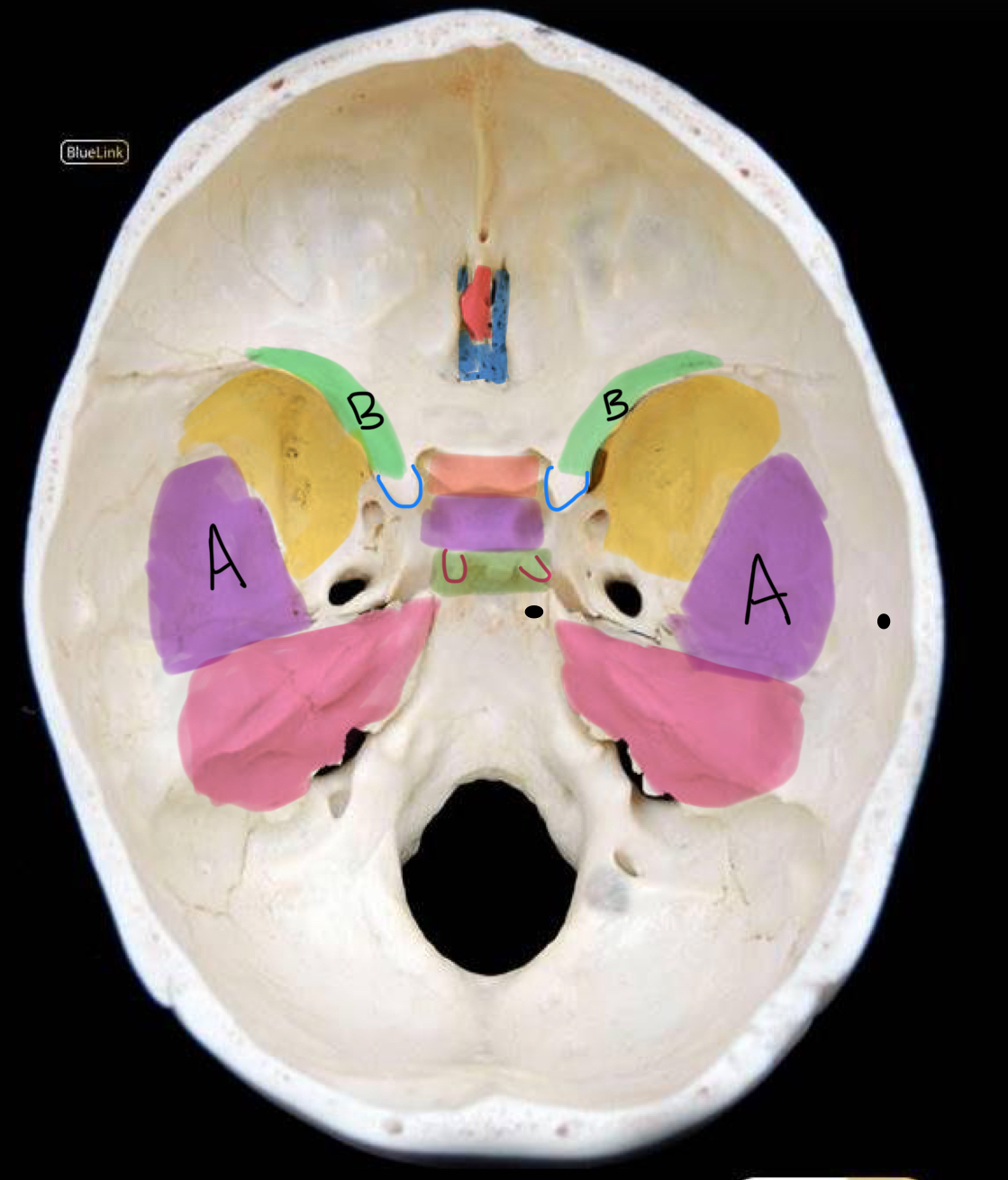
what structure is outlined in red?
posterior clinoid process
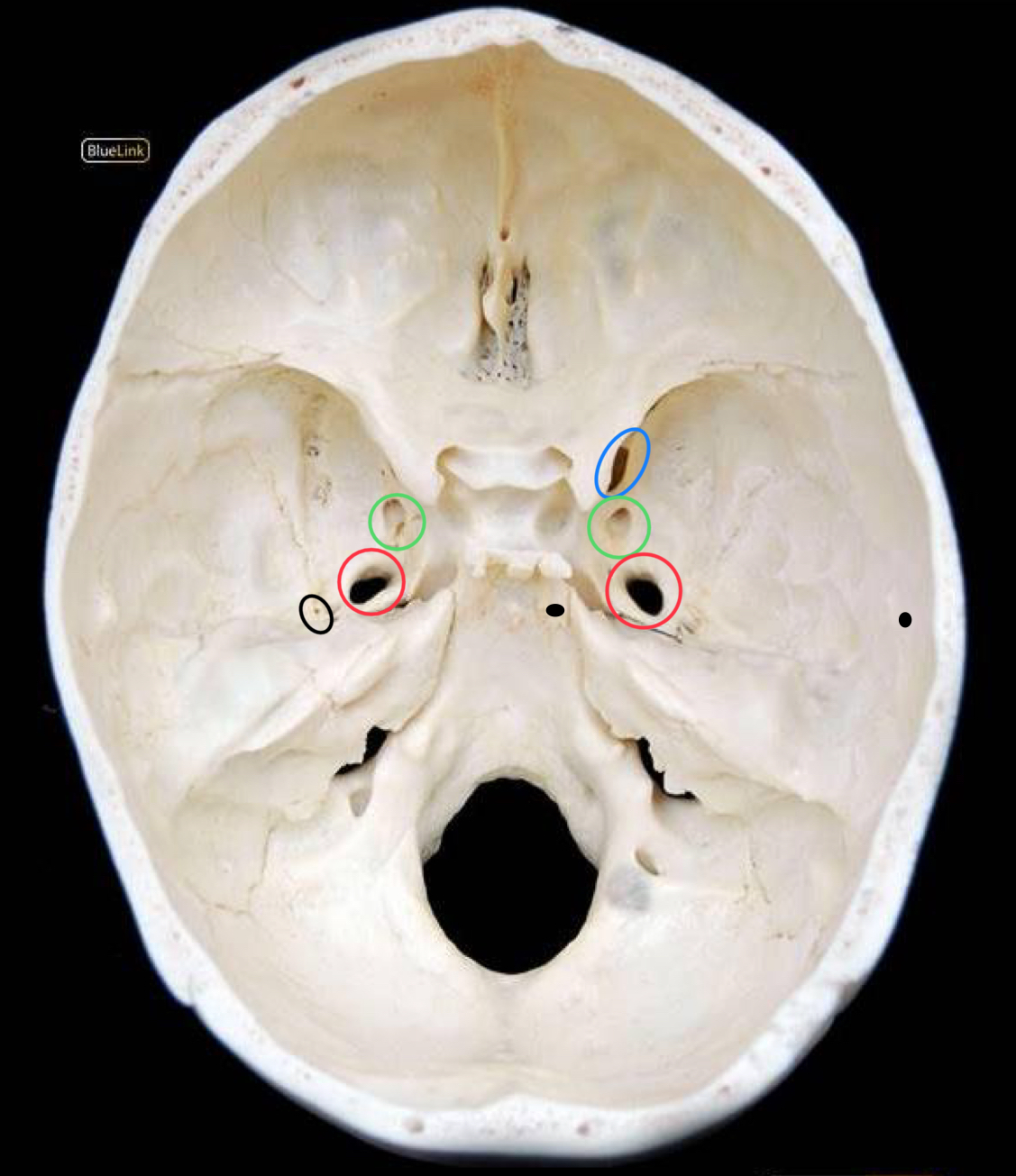
what structure is circled in blue?
superior orbital fissure
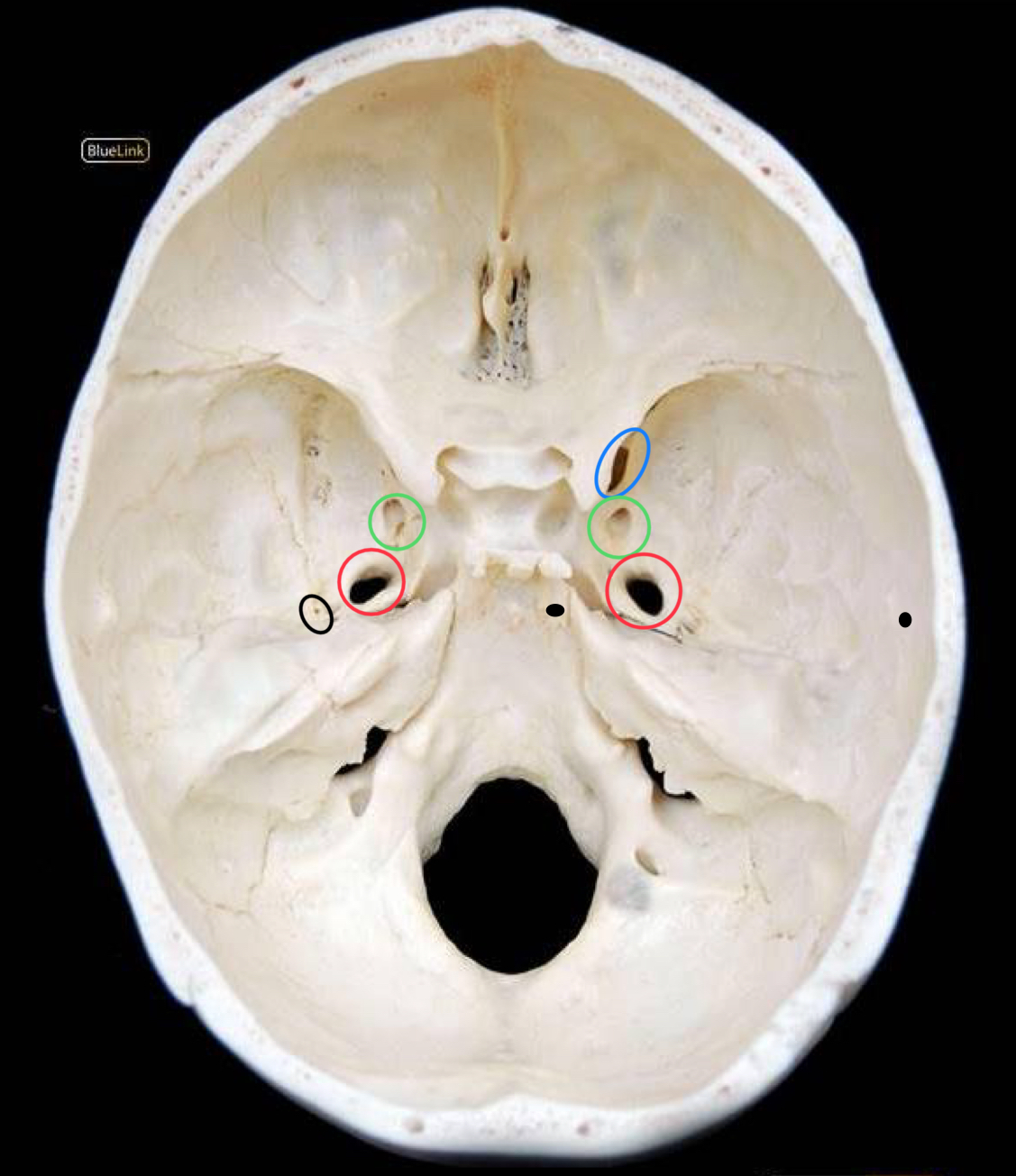
what structure is circled in green?
foramen rotundum
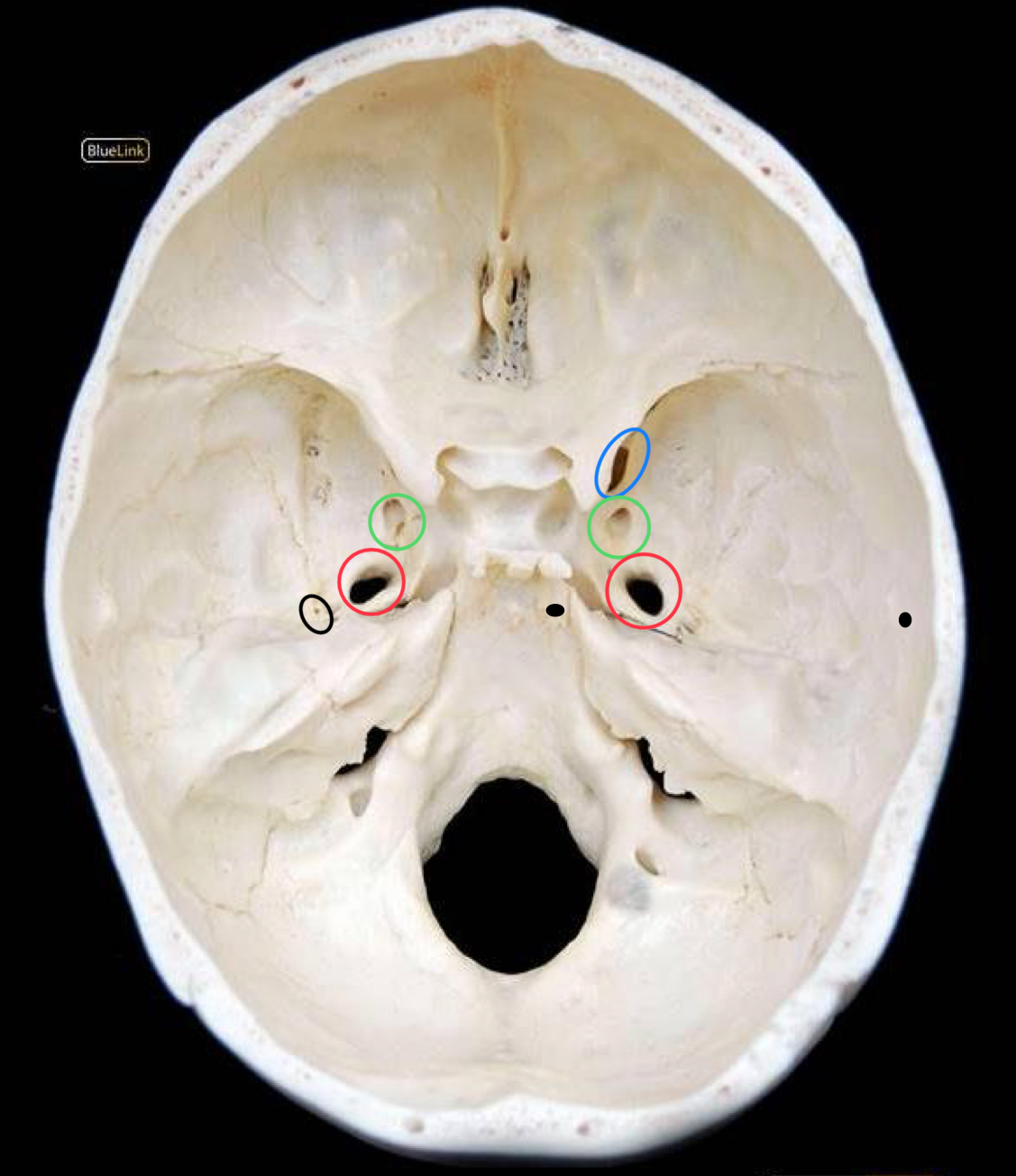
what structure is circled in red?
foramen ovale
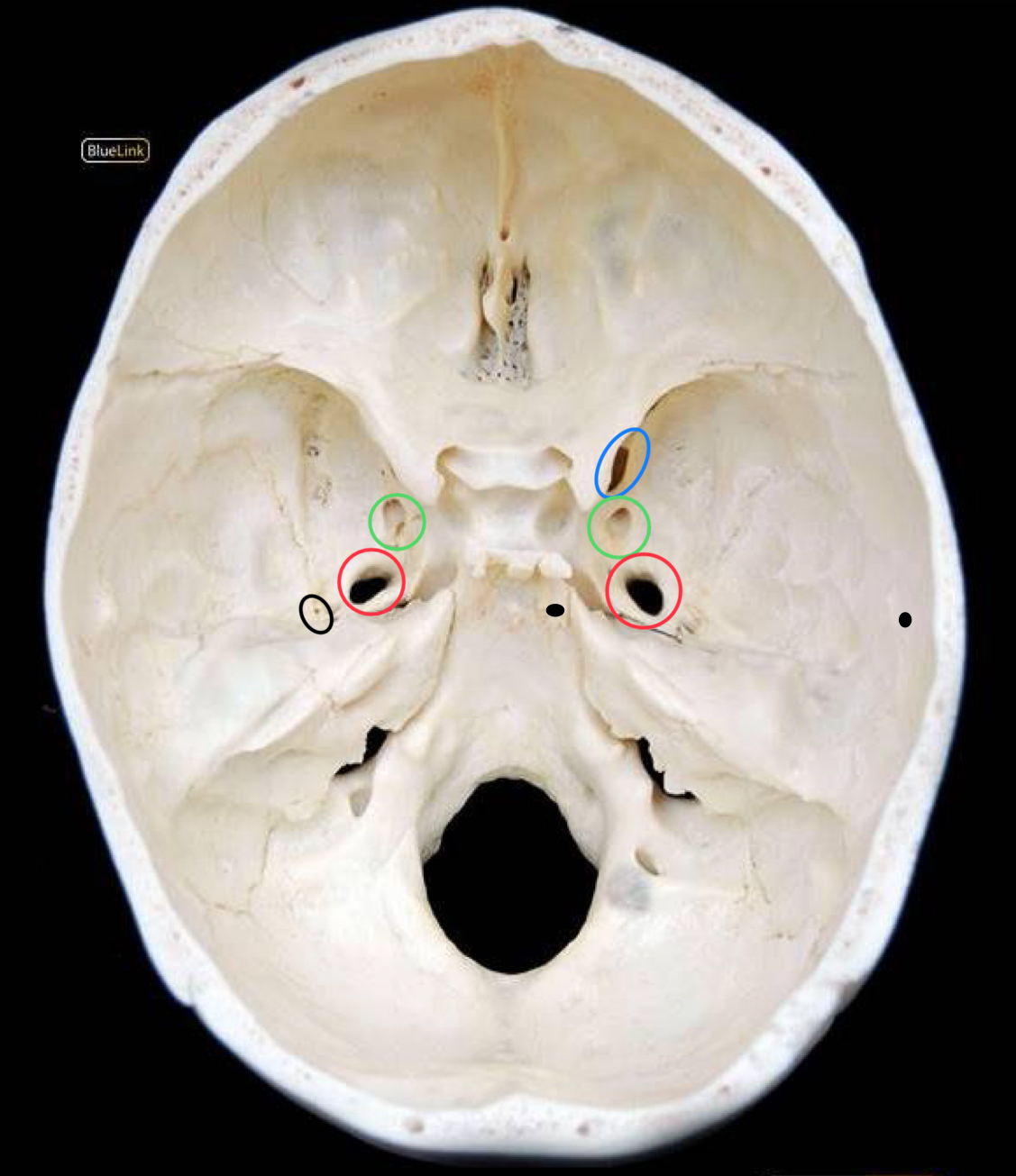
what structure is circled in black?
foramen spinosum
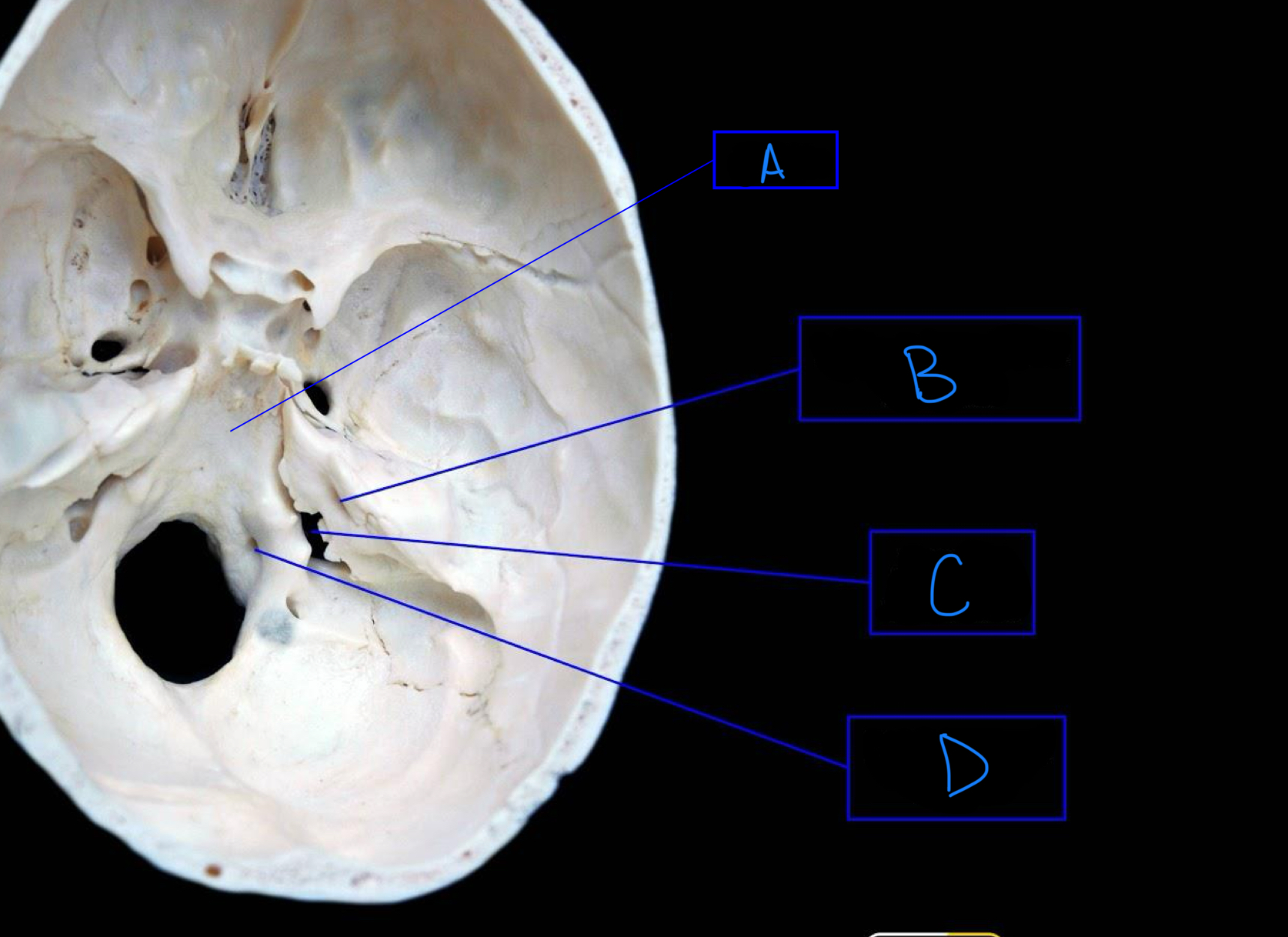
what structure is labeled A?
clivus