Autonomic nervous system
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
2 major subdivisions
-Sympathetic division
-Parasympathetic division
Sympathetic division
-Also called thoracolumbar division
-Most active during times of stress, exertion, or emergency
-"Fight or flight"
Parasympathetic division
-Also called craniosacral division (associated with cranial nerves and 3 sacral nerves
-Most active during resting conditions
-"Rest and digest"
Sympathetic division consists of:
-Preganglionic neurons in lateral gray horns between T1 and L2
-Neuronal cell bodies in ganglia near vertebral column
-> Sympathetic chain ganglia
-> Collateral ganglia/prevertebral ganglia
-Specialized neurons in the interior of the suprarenal gland
Suprarenal medullae
-Preganglionic fibers proceed to suprarenal medulla
-> Release neurotransmitters (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
Epinephrine
-Also called adrenaline
-Accounts for 75-80% of secretions from suprarenal medullae
Parasympathetic division
-Preganglionic neurons in brain stem and sacral segments
-Preganglionic neurons do not diverge as much
-Postganglionic neurons near the target organs or within target organ
Parasympathetic division- Preganglionic fibers leave the brain via:
Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons in:
-CN III (to intrinsic eye muscles, pupil, lens)
-CN VII (to tear glands and salivary glands)
-CN IX (to parotid salivary glands)
-CN X (to visceral organs of thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity)
Parasympathetic division- Preganglionic fibers leave the sacral region via:
-Lateral gray horns S2-4 (to visceral organs in inferior abdominopelvic cavity)
General functions of parasympathetic division
-Relaxation
-Food processing
-Energy absorption
Functions of autonomic nervous system
-Regulation (motor) of "visceral effectors" (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, adipose) thru stimulation of "visceral efferent (motor) fibers"
Dual intervention
-Many organs receive both SYMP and PARASYMP
-One will be excitatory and the other will inhibit activity
General organization of ANS
preganglionic neurons (from CNS) -> autonomic ganglia (excitatory synapse) -> postganglionic neuron (from ganglia) -> visceral effector (effect dependent on neurotransmitter released and specific receptors present)
Where do SYMP axons (fibers) travel before entering ganglion
Fibers travel out spinal nerve and branch into 'white rami communicantes' before entering ganglion
SYMP ganglion include:
-SYMP chain ganglion
-Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia-- celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric ganglia
-Adrenal medulla
What do SYMP preganglionic fibers release?
-Acetylcholine (ACh)
ACh
-Cholinergic fiber
-Excitatory response
What happens with SYMP postganglionic fibers?
-Postganglionic fibers synapse on visceral effector (target tissue)
-Then... norepinephrine is released (excitatory or inhibitory)
Norepinephrine
-Adrenergic
-Effects on target tissue is usually excitatory
....however the effect depends on the specific receptor present
Where do PARASYMP preganglionic fibers travel to?
Preganglionic fibers travel to "terminal ganglia" in or near visceral effectors
What do PARASYMP preganglionic fibers release?
ACh (excitatory response)
What do PARASYMP postganglionic fibers release?
ACh
-Effects depends on specific receptors present
PARASYMP response
-GI stimulation and enzyme secretion
-Decreased heart rate
-Decreased blood pressure
-Energy storage
-Nutrient uptake
-Pupil constriction
SYMP response
-Pupil dilation
-Increased heart rate and blood pressure
-Bronchodilation
-Vasodilation
-Release of epi and norepi from adrenal medulla
The post ganglionic response when ACh binds is:
Always excitatory
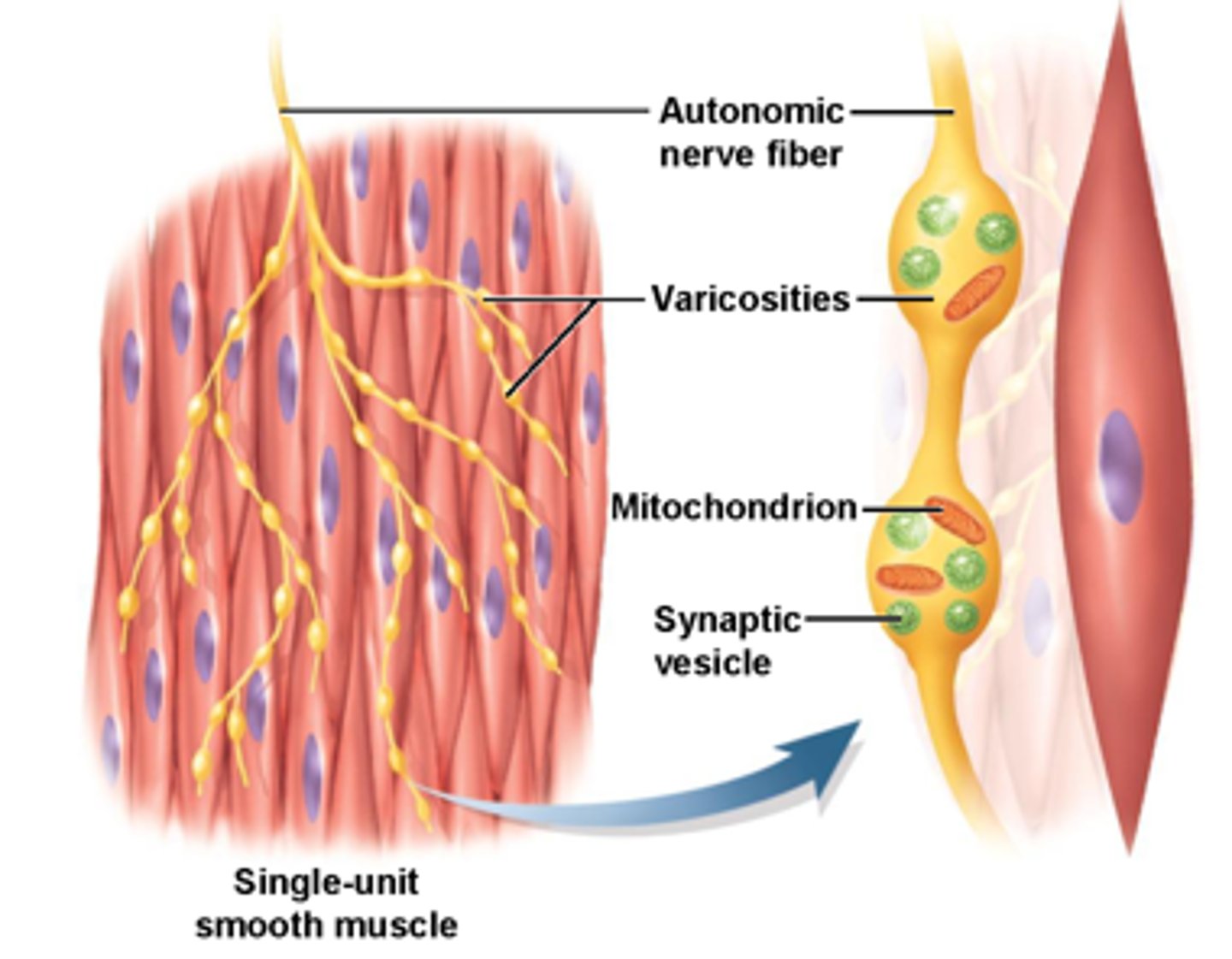
Variscosities is a feature of:
Sympathetic
-They are little teeny synaptic terminal chains