Biochemistry Chapter 3
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Proteins are constructed from a common set of what?
20 amino acids
Amino acids are joined in linear sequences through what type of bond linkage
An amide linkage, the peptide bond.
Proteins can be separated based on what?
Differences in their chemical and functional properties.
Amino acids sequences are a key resource to understanding what theory?
Evolutionary relationships
Proteins are what? Be specific.
Linear heteropolymers of alpha-amino acids
Amino acids have properties that are well suited to carry out a variety of biological functions such as what?
Capacity to polmerize
Useful acid-base properties
Varied physical properties
Varied chemical functionality
What is a protein complex?
More than one protein
What is the primary function of proteins?
Means by which the genetic information is expressed and propagated
What are the main biological functions of proteins? And what are some examples of proteins that serve these functions?
Catalysis
Enolase (Glycolytic pathway)
DNA polymerase (DNA replication)
Transport
Hemoglobin (O2 through blood)
Lactose permease (lactose across cell membrane)
Structure
Collagen (connective tissue)
Keratin (hair, nails, feathers, horns)
Motion
Myosin (muscle tissue)
Actin (muscle tissue, cell motility)
What dictates protein sequence?
DNA sequence
The alpha carbon of amino acids always has how many substituents? And is what shape?
Four and tetrahedral
What groups do all amino acids (except proline)?
Acidic carboxyl group on alpha carbon
Basic amino group on alpha carbon
Alpha hydrogen connect to the alpha carbon
R unique to each acid
What is the simplest amino acid?
Glycine, Gly, G
Amino acid residues in proteins are what type of stereoisomer?
L stereoisomer
D and L system specifies what?
Absolute configuration
What is another term for two possible stereoisomers?
Enantiomers
Are amino acids optically active?
Yes
How do you name an amino acid?
Start from the alpha carbon and go down the R-group.
Common amino acids can be placed in five basic groups based on their R substituents. What are those 5 groups and how many amino acids are in each group?
Nonpolar, aliphatic (7)
Aromatic (3)
Polar, uncharged (5)
Positively charged (3)
Negatively charged (2)
What amino acids make up the non-polar, aliphatic group? And what is characteristic properties of this group?
Glycine
Alanine
Proline
Valine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
They are unable to form hydrogen bonding
Hydrophobic effect stabilizes them
Most likely to be found in the center of a protein
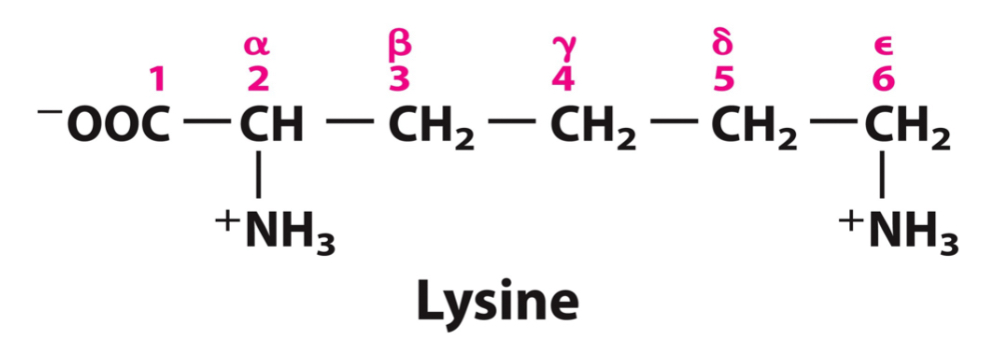
What amino acids make up the positively charged group? What are some important notes about this group?
Lysine
Arginine
Histidine
Structural formula shows predominate form at pH 7.0
Exception is His, shown uncharged however significant fraction is positively charged
Basic
What amino acids make up the negatively charged group? And what’s important to note?
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
Acidic (COOH) side chains
Net negative charge at pH 7.0
What amino acids make up the aromatic group? And what’s important to note?
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
R groups absorb UV light at 270-280nm
Can contribute to hydrophobic effect
What amino acids make up the polar uncharged group? And what’s important to note?
Serine
Threonine
Cysteine
Asparagine
Glutamine
R groups can form hydrogen bonds
Cysteine can form disulfide bonds
What 3 amino acids can be phosphorylated?
Tyrosine
Serine
Threonine
Which 3 amino acids are heterocyclic?
Tryptophan
Histidine
Proline
How do uncommon amino acids arise In proteins?
By post-translational modifications of proteins
Are uncommon amino acids found in ribosomes?
No, except for Selenocysteine
Are modifications of uncommon amino acids reversible and if so, why?
Yes, especially phosphorylation, they are important in regulation and signaling.
What are 3 times and examples of when modifications of common amino acids occur?
After protein synthesis (ex. 4-hydroxyproline in collagen and plant cell wall)
During protein synthesis (ex. pyrrolysine contributes to methane biosynthesis)
Modified transiently to change protein’s function (ex. phosphorylation)
What 3 properties make up amino acids?
Chirality (except glycine)
Light absorbance
Acidic/Basic
Uncommon amino acids are found often as what?
Free metabolites (ex. ornithine, intermediate in arginine biosynthesis)
Amino acids absorb what kind of light?
All amino acids absorb light in the infrared (IR) region. Only Phe, Tyr, and Trp absorb UV light.
What wavelength is used to quantify proteins?
280nm
What is a zwitterion and when does it occur?
Amino acid form as dipolar ion at a neutral pH with a net charge of zero.
Without an ionizable side chains what point in a titration is when a zwitterion forms? And what can be said about the amino acid property wise?
At the isoelectric point (pI) which is when the amino acid is least soluble in water and does not migrate in an electric field.
Amino acids contain how many ionizable protons each with their own pKa?
At least two
Amino acids without ionizable R chains can act as buffers in how many pH regimes?
2
What is the isoelectric point and how is it calculated?
The pI is the characteristic pH at which the net electric charge is ZERO. pI=1/2(pK1+pK2)
Amino acids with a single alpha NH2 group and a single alpha COOH group with an R groups that does NOT ionize have similar, if not identical pKa in what range for each group?
COOH = 1.8-2.4
NH3+ = 8.8-11.0
For triprotic acids (Asp, Glu, Arg, Lys, His) the pI is the average of which two pKa’s?
The two that dissociate the neutral species
Amino acids are amphoteric which means what?
They have both basic and acidic groups. Allows them to act as base or acid.
What type of product are peptides?
Small condensation products of amino acids.
How are peptides named?
From the amino terminus to the carboxyl terminus
What are some biological functions and examples of peptides?
Hormones and pheromones
Insulin (sugar)
Oxytocin (childbirth)
Neuropeptides
Substance P (pain mediator)
Antibiotics
Polymyxin B (Gram - bacteria)
Bacitracin (Gram + bacteria)
Protection (Toxins)
Amanitin (mushrooms)
Conotoxin (cone snails)
Chlorotoxin (scorpions)
What proteins comprised of?
Polypeptides (covalently linked amino acids) and possibly any of the following…
Cofactors
Functional non-amino acid component
Metal ions or organic molecules
Coenzymes
Organic cofactors
NAD+ or FAD
Prosthetic groups
Covalently attached cofactors
Heme in myoglobin
Other modifications
How can you estimate the number of amino acid residues in a molecule?
# of residues = molecular weight/110
What is the average molecular weight of a free amino acid? And the average of a bound amino acid?
~128 Free
~110 Bound (-18 for water removed in peptides bond)
What are the two primary methods for determining amino acid sequence of a protein? And how do they differ?
“Genomic” method
Sequence the gene
Sequence the mRNA
Biochemical method
Isolate protein to homogeneity
Then determine amino acid sequence using a direct chemical method
What was the first protein to be fully sequenced?
Insulin
What is the first set of steps in sequencing a protein?
Isolate and purify protein of choice
Reduce (break) disulfide bonds w/ reducing agent (ex. DTT)
Label amino-terminal residue with FDNB or other labeling agent
Determine number of peptides in the protein
What are the three common agents used for labeling amino acids?
Dabsyl chloride
Dansyl chloride
FDNB (1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene)
How does concentrated HCl affect peptides?
Hydrolyzes all the peptide bonds. Useless for further determination of protein sequence.
Sequencing beyond the first residue is done by a method called what? Briefly explain how and up to what length?
The method is called “Edman Degradation”.
It requires an isolated single polypeptide. Which is immobilized by its carboxyl-terminus to a solid support. A PITC reacts with the amino terminus to form a PTC adduct this is repeated for each residue in the chain.
This method can practically sequence ~50 residues.
Oxidation of disulfide bonds by which agents prevent the reformation of these bonds?
Performic acid
Carboxymethylation after reduction by DTT
Name 4 ways how permanently reducing disulfide bonds can help us resolve a protein?
Cleaving polypeptide chain
Sequencing the peptide
Determination of order of peptides
Locating disulfide bonds
Proteases are used to what?
Cleave proteins to smaller fragments.