Exam 3: Event-Related Potentials (ERPs) Method
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
How are ERPs derived?
EEG epochs (commonly 1 sec around the stimulus) are averaged in a manner that is time-locked to an event onset across many trials
ERPs: The basic principles of averaging
To extract small, consistent, brain signals that are time-locked to a specific event (like a stimulus presentation) from the much larger, random background electrical activity (noise) measured by the EEG
What is the basic experimental setup (how EEG is recorded and what is the role of stimulus markers)?
Stimuli (ie faces) are presented on the screen (or tones delivered via speakers) by a presentation computer. Stimulus markers are sent out at the same time to the EEG-recording computer. EEG signal is recorded continuously, but these markers (my marking the exact time when each stimulus was presented) make it possible to segment EEG data into epochs (ie 1 sec around the stimulus onset) for each chanel
EEG epochs (obtained for each condition and from each channel) are then averaged together to obtain ERPs. Most commonly, ERPs are averaged with respect to the stimulus onset for each type of interest (ie faces vs cars vs butterflies, etc)
What are EEG epochs?
A fixed-length segment (commonly 1 sec around the stimulus) extracted from a continuous recording, time-locked to an experimental event
What happens to the signal and what happens to the baseline noise as a result of averaging?
Oscillatory brain activity that we record with EEG is a mixture of both signal and noise
Averaging makes the signal stronger relative to the noise, while the noise is reduced
What does SNR refer to?
Signal-to-noise - expresses the relative strength of the signal (ERP after stimulus onset) compared to noise (baseline before stimulus onset)
How are the ERPs named/described?
ERP Nomenclature - ERP waveforms consist of voltage “bumps” (deflections) that are negative or positive in polarity and that appear at different latencies. ERP deflections are named based on their:
Polarity - make sure to look at how the y-axis is labeled
Negative deflections: N1, N2, N400
Positive deflections: P1, P3, or P300
Latency (in msec) after stimulus onset (N100, P300, N400)
Ordinal position (the first peak is P1, the first negative peak is N1, the second one is N2, etc)
ERPs are classified based on their:
Sensory modality (visual, auditory, somatosensory)
Latency
Early - peaking before 100ms primarily depend on the sensory features → low level sensory processing in sensory cortices
Late - peaking after 150 ms increased influence of cognitive processes (attention, meaning, etc)
What are the basic advantages/disadvantages of the scalp ERPs?
Advantages: excellent temporal resolution (they reflect postsynaptic potentials with perfect precision, ms by ms); we can examine how the brain processing unfolds in time (stages of processing)
Disadvantages: poor spatial resolution; cannot localize generators (can’t determine where they are coming from in the brain) based on the scalp ERPs
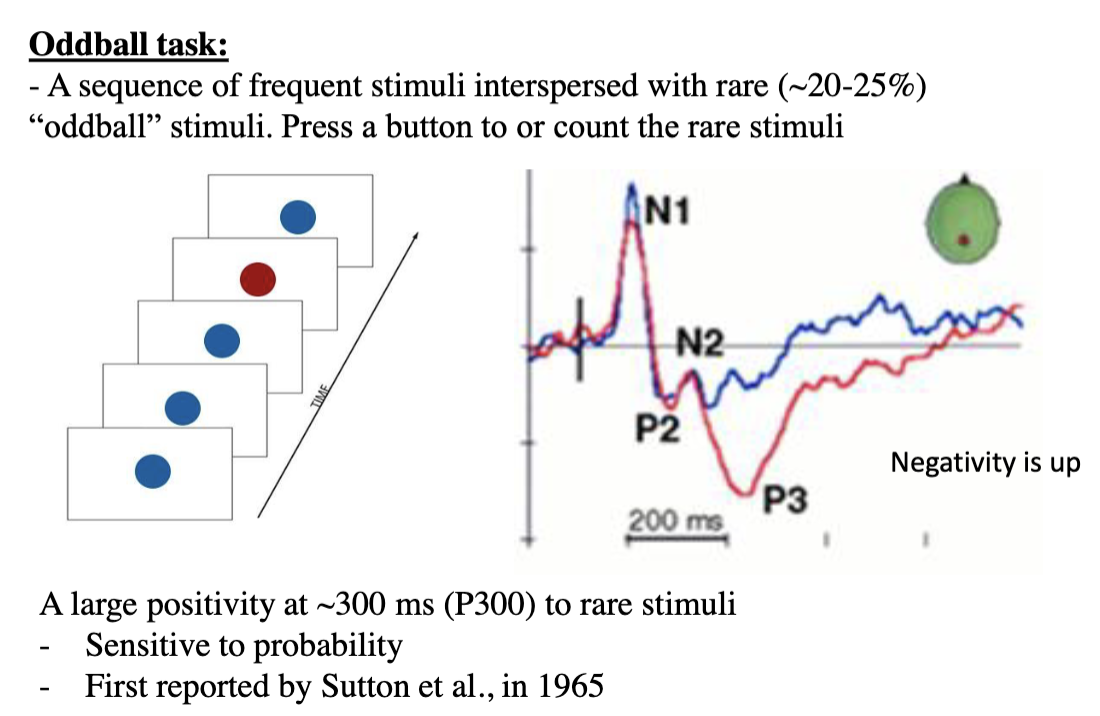
What are the basic parameters of the most common paradigms, such as: the oddball task & the semantic mismatch task
The oddball task - a sequence of frequent, repeating stimuli interspersed with occasional rare stimuli (~20-25%), which are perceived as oddballs (surprises) in the sequence; only the oddball stimuli evoke a large positivity (P3 or P300); frequent stimuli do not evoke the P300 because they are expected (only “oddball” stimuli elicit attention); N100 is a sensory deflection first evoked by a stimulus, and P300 is sensitive to probability attentional effects
Semantic mismatch task - presenting sentences that had congruent or incongruent endings (ie “I like my tea with sugar” vs “I like my tea with nails”); “nails” evoked a greater negativity (N400) peaking at approximately 400ms after word onset; N400 is sensitive to meaning and congruence with context
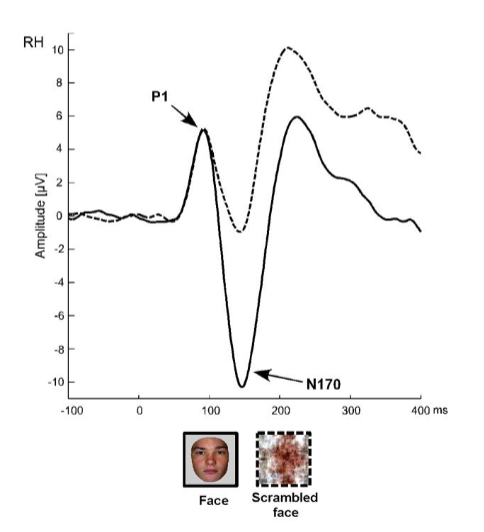
What is the earliest ERP deflection sensitive to faces?
The N170 is the earliest deflection that is larger for faces than for other visual objects (cars, butterflies, etc)
But the N170 to regular faces is smaller than to inverted or misaligned faces.
generated in the ventral temporal lobe → fusiform gyrus
What do the following ERP deflections mean?
P100
N170
N250
N400
The P100 (generated in the visual cortex) is NOT sensitive to faces
The N170 is the earliest deflection that is larger for faces than for other visual objects (cars, butterflies, etc)
But the N170 to regular faces is smaller than to inverted or misaligned faces.
The N250: the earliest index of memory engagement (it differentiates previously seen from novel faces)
It is often followed by the N400, which characterizes semantic processing and integration with the context, resulting in conscious recognition
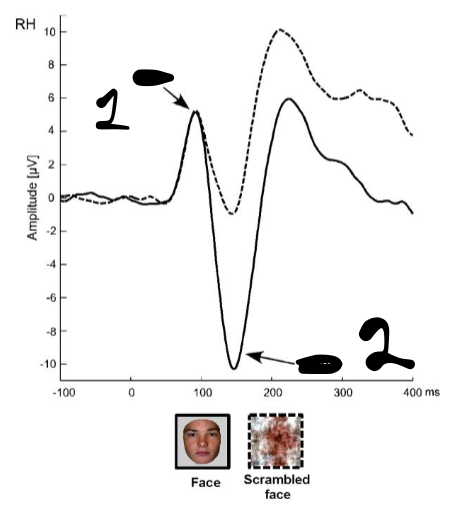
In the oddball task, label the ERPs
1: P1
2: N170