Chapter 13: Separation techniques and Mass Spectrometry
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
The stationary phase is
a solid (alumina or silica gel)
The mobile phase is
a liquid
Define retention time
the time required for an analyte to reach the detector after sample injection
Define Void/Dead Time
the time for the unretained species to reach the detector
Define Gradient Elution
a systematic increase in the composition of mobile phase mixture to achieve better separation
Define isocratic Elution
separation using a single mobile phase or a single composition of mixed solvent mobile phase,
What is the dead time for environmental pollutant separation in liquid chromatography?
A. retained pollutants time
B. mobile phase time
C. unretained pollutants
D. stationary phase time.
C
Separation of the pollutant analytes increases when
A. peaks overlapped
B. peak widths increase
C. band peak increase
D. peaks widths decrease
D
A Pollutant Analyte ‘A’ will elute first
A. if ‘A’ stays in the stational phase more.
B. if ‘A’ stays in the mobile phase more.
C. if ‘A’ interacts with more stational phase
D. if ‘A’ is hydrophobic
B
Which is not a part of HPLC instrument
A. Solvent delivery system
B. Detector
C. Ion source
D. High pressure column
C
Size-exclusion chromatography separate analytes based on
A. Charge
B. Hydrophobic interaction
C. Hydrophilic interaction
D. molecular size
D
Sulfonate used in
A. Normal phase
B. Reverse Phase
C. Ion-exchange
D. Size exclusion
C
Nonpolar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase used in
A. Normal phase
B. Ion-exchange
C. Reverse Phase
D. Size exclusion
C
Positively charges heavy metals can be separated by
A. Normal phase
B. Ion-exchange
C. Reverse Phase
D. Size exclusion
B
Mobile phases consist of buffers with increasing ionic strength
A. Normal phase
B. Ion-exchange
C. Reverse Phase
D. Size exclusion
B
Molecular weights of microplastic or formaldehyde-urea resin are determined by
A. Normal phase
B. Reverse Phase
C. Ion-exchange
D. Size exclusion
D
The most popular chromatography method is
A. Normal phase
B. Reverse Phase
C. Ion-exchange
D. Size exclusion
B
Which microplastic elutes the latest in Size-exclusion chromatography?
A. Large microplastic
B. Polar microplastic
C. Nonpolar microplastic
D. small microplastic
D
Which pesticide elutes the latest in reverse phase chromatography?
A. Large pesticide
B. Polar Pesticide
C. Nonpolar Pesticide
D. small pesticide
C
Which pesticide elutes the latest in normal phase chromatography?
A. Large pesticide
B. Polar Pesticide
C. Nonpolar Pesticide
D. small pesticide
B
The solvent delivery system is comprised of a ____ container(s), _____tubes, and ____.
solvent, connecting tubes, pumps
an environmental sample injection valve is a device that allows the _____and _____ injection of a sample into the column
accurate, reproducible
a high-pressure column is ?
analytical separation column containing the stationary phase
typical stationary phases are a _____ exchange (sulfonate) or ____ exchange (quaternary ammonium) groups bonded to polymeric or silica materials.
cationic, anionic
Mobile phases consist of buffers, often with increasing ionic strength, to force the ____ of analytes.
migration
common applications of ion-exchange chromatography (SEC) are the analysis of ions and biological component such as ____, ____, and ___.
charged pesticides, heavy metal oxides, and viral nucleotides
The function of a guard column is:
- ____ separation
- prevents ___ and ____ of analytical column
preparatory, clogging, damaging
Analytical column
- used for actual ____.
- it is ___ and ___ than the guard column
analyte separation
shorter and wider
what is a disadvantage of gradient elution?
longer analysis time
Gradient elution is useful for separation of analytes with wide differences in ___.
polarity
the larger the theoretical plate number, the ___ the peaks.
sharper
the ___ the theoretical plate number, the sharper the peaks.
larger
The smaller the particle size, the ___ the plate number and the better separation.
higher
the ___ the particle size, the higher the plate number and the better the separation. However, ___ pressure is required for the separation.
smaller, high
an efficient column produces ___ peaks and separates ______ in a given time.
sharp, many sample components
peaks tend to be Guassian and broaden with ___ .
retention time
the goal of HPLC analyses is the ________ in the sample from each other, usually for quantitative measurements.
separation of analytes
In electron ionization, the molecules are bombarded with fast moving electrons and converts the molecules into ___. Because the electrons are so energetic, the ionized species typically ___ upon bombardment with electrons. The fragmentation pattern can be used to elucidate the ____ of the molecules.
metal anions, fragmented, chemical structure
chemical ionization is widely used for ____, ____ or ____ organic compounds especially when coupled with gas chromatography.
low-mass, volatile, thermally stable
What mass spectrometry does?
A. Separate molecules
B. Identify molecules
C. Excite molecules
D. Vibrate Molecules
B
A
A

D

C

C
B
D
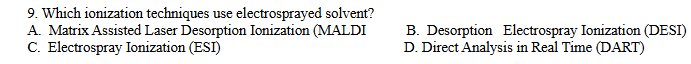
B
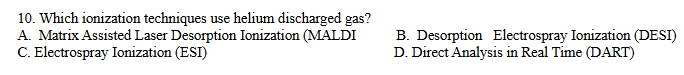
D
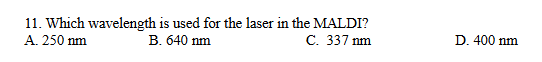
C
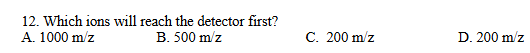
C
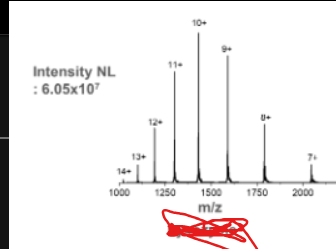
This is the mass spectrum for ____.
Lysozyme
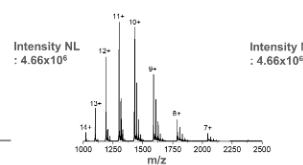
This is the mass spectrum for ____.
Lysozyme with Glyphosate
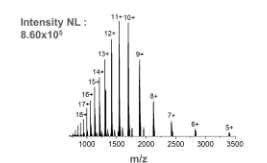
This is the mass spectrum for ____.
myoglobin in water
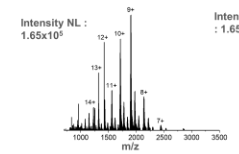
This is the mass spectrum for ____.
myoglobin with glyphosate
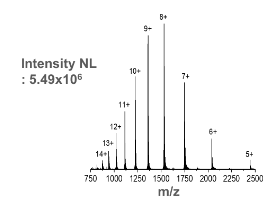
This is the mass spectrum for
Cytochrome C
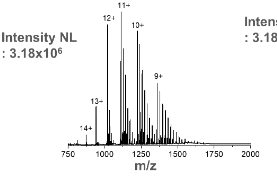
this is the mass spectrum for ____.
Cytochrome C with Glyphosate