HOSA: Nutrition Food-Related Illnesses, Intolerances, and Allergies (copy)
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
What are nutrients?
Chemical substances necessary for life.
Functions of Nutrients
Provide energy
Build and Repair body tissue
Regulate body processes (i.e circulation, respiration, digestion, and elimination)
What are the 6 classes of nutrients?
Carbohydrates (CHO)
Fats (lipids)
Proteins
Vitamins
Minerals
Water
True or false: No nutrient can work alone
True
Where are essential nutrients found?
Found only in foods
What is special about organic nutrients?
Must be broken down to be used by body (also contain carbon)
Inorganic Nutrients
Already in their smallest components
Which nutrients are organic?
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Vitamins
What nutrients are inorganic?
Water
Minerals
What is the function of Carbohydrates?
To provide energy
What is the function of fats?
To provide energy
What is the function of proteins?
To build and repair tissues and provide energy
What is the function of vitamins?
To regulate body processes
What is the function of minerals?
To regulate body processes
What is the function of Water?
To regulate body processes
Consider the following scenario:
A client is recovering from surgery at home. You ask what she has eaten during the last 24 hours. She answers:
Breakfast: two doughnuts, orange juice
Lunch: lettuce salad with oil and vinegar, soda
Snack: pretzels, soda
Dinner: spaghetti with tomato sauce, garlic bread, wine
What nutrients are missing in her diet? Why are these nutrients important for her?
Breakfast: Carbohydrates (sugar) and Vitamins
Lunch: Carbs (fiber and sugar) and fats
Dinner: Carbohydrates and alcohol
Nutrients she is getting:
Carbs
Fats
Vitamins
Minerals
MISSING:
Proteins and Water
SHE JUST HAD SURGERY!
Protein is needed to build and repair body tissues after surgery
Water is needed to prevent dehydration
What are characteristics of good nutritional status?
Alert expression
Shiny hair
Clear complexion
Good color
Bright, clear eyes
Pink, firm gums and well-developed teeth
Firm abdomen
Firm, well-developed muscles
Well-developed bone structure
Normal weight for height
Erect Posture
Emotional stability
Good stamina
Seldom ill
Healthy appetite
Healthy, normal sleep habits
Normal elimination
What are characteristics of poor nutritional status?
Apathy
Dull, lifeless hair
Greasy, blemished complexion
Poor color
Dull, red-rimmed eyes
Red, puffy, receding gums and missing or cavity-prone teeth
Swollen abdomen
Underdeveloped, flabby muscles
Bowed legs and "pigeon breast"
Overweight or underweight
Slumped posture
Easily irritated or depresses and poor attention span
Easily fatigued
Frequently ill
Excessive or poor appetite
Insomnia at night and fatigued during day
Constipation or diarrhea
What are two types of malnutrition?
Overnutrition- Excess energy or nutrient intake
Undernutrition- Deficient energy or nutrient intake
True or false- Undernutrition is a larger problem than overnutrition in the US.
False- Supersizing, fast-food industry contributes to OVERNUTRITION in the US.
What are the top 10 fattest cities in the US?
Miami, FL
Oklahoma City, OK
San Antonio, TX
Las Vegas, NV
New York, NY
Houston, TX
El Paso, TX
Jacksonville, FL
Charlotte, NC
Louisville-Jefferson, KY
What are the cumulative effects of excess nutrition?
Atherosclerosis
Obesity
Hypertension
diabetes
Gallbladder disease
Some cancers
What is atherosclerosis?
A disease of the arteries characterized by the deposition of plaques of fatty material on their inner walls. The build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in and on the artery walls.
What is hypertension?
High blood pressure
What is gallbladder disease?
See picture
What are the cumulative effects of deficient nutrition?
Iron deficiency
Beriberi
Scurvy
Obseomalacia
Osteoporosis
Rickets
Goiter
What is iron deficiency?
Low body stores of iron
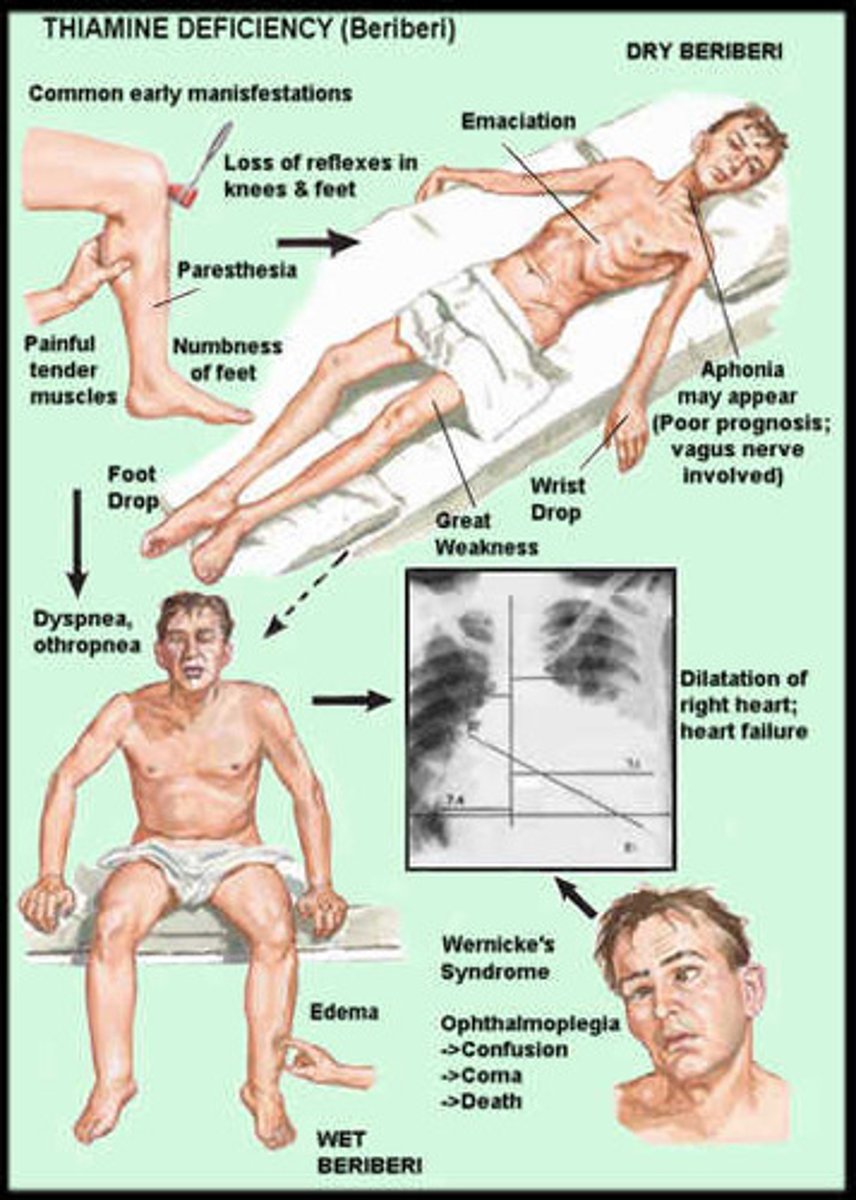
What is beriberi?
Deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1) resulting in muscle wasting and nerve damage
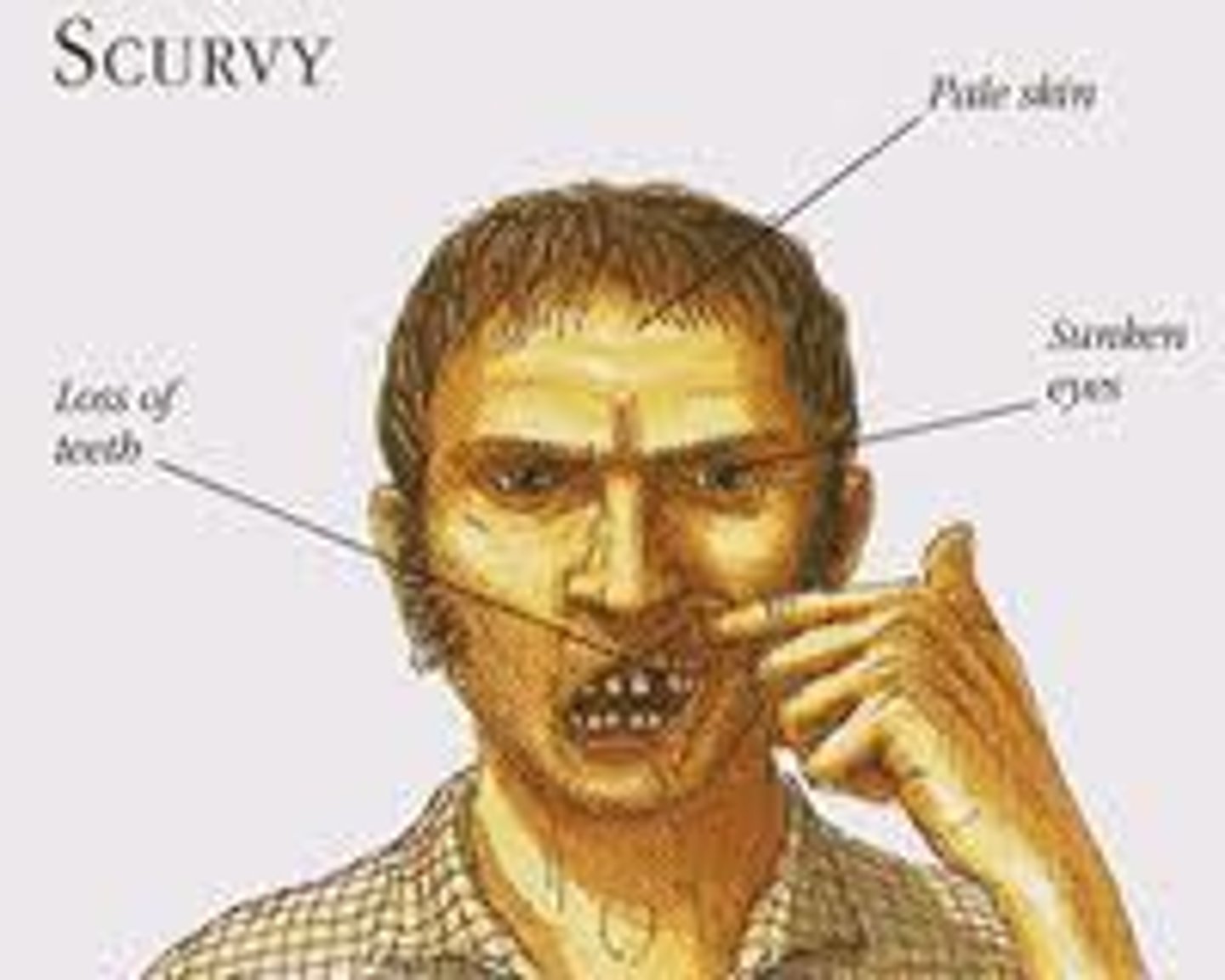
What is scurvy?
A disease caused by lack of vitamin C
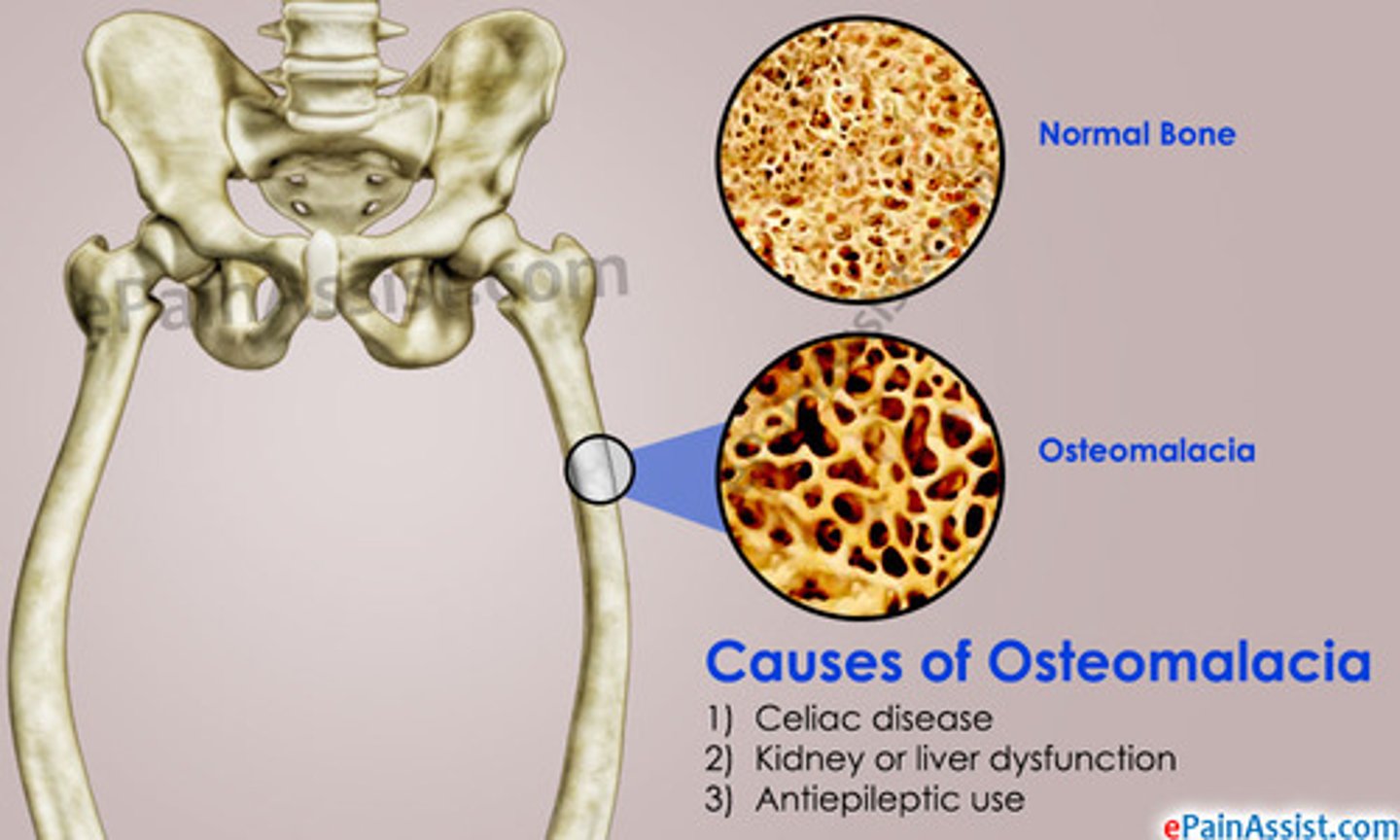
What is osteomalacia?
A rare condition of the adult bone associated with vitamin D deficiency, resulting in decalcification and softening of bone.
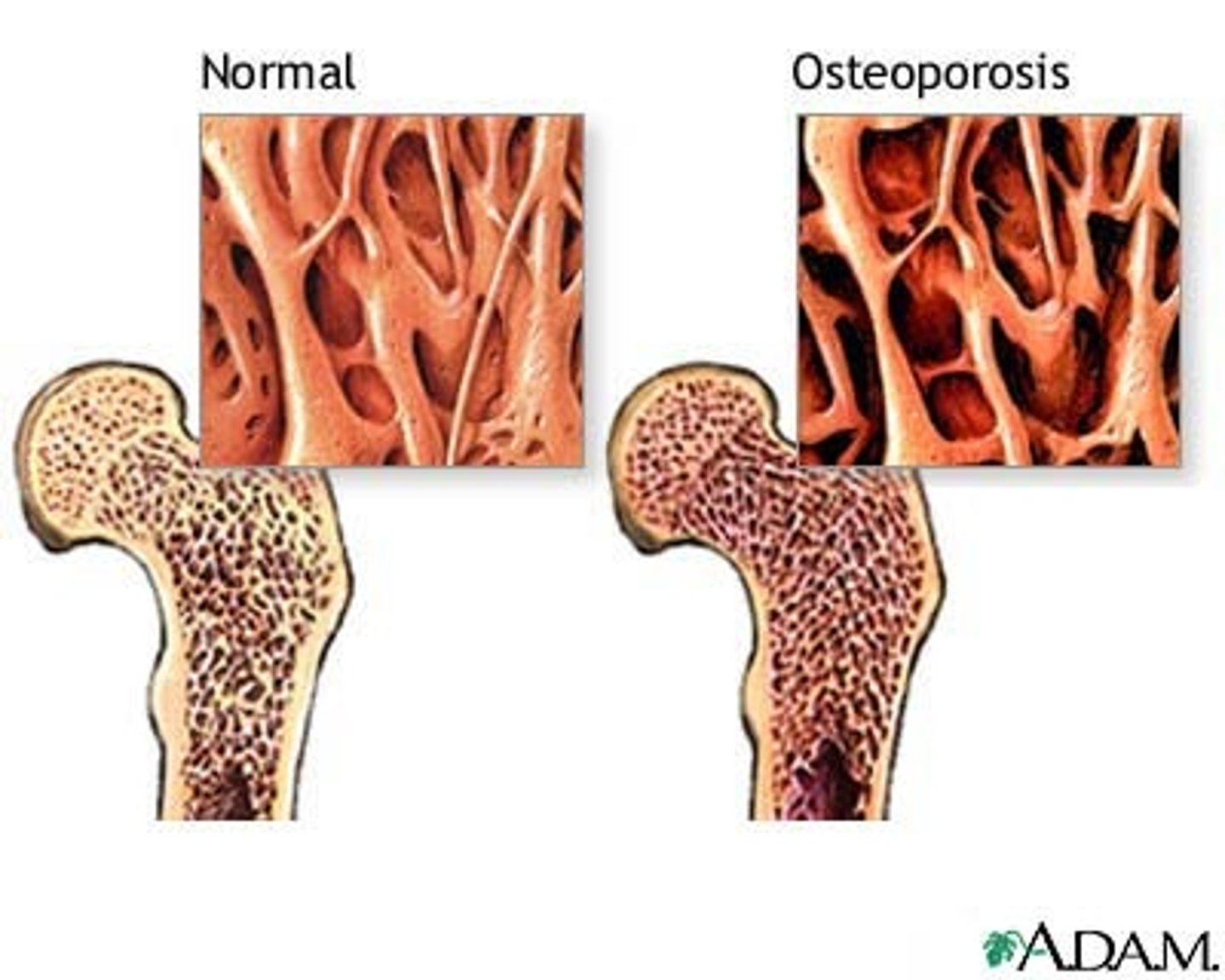
What is osteoporosis?
A medical condition in which the bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue, typically as a result of hormonal changes, or deficiency of calcium or vitamin D.
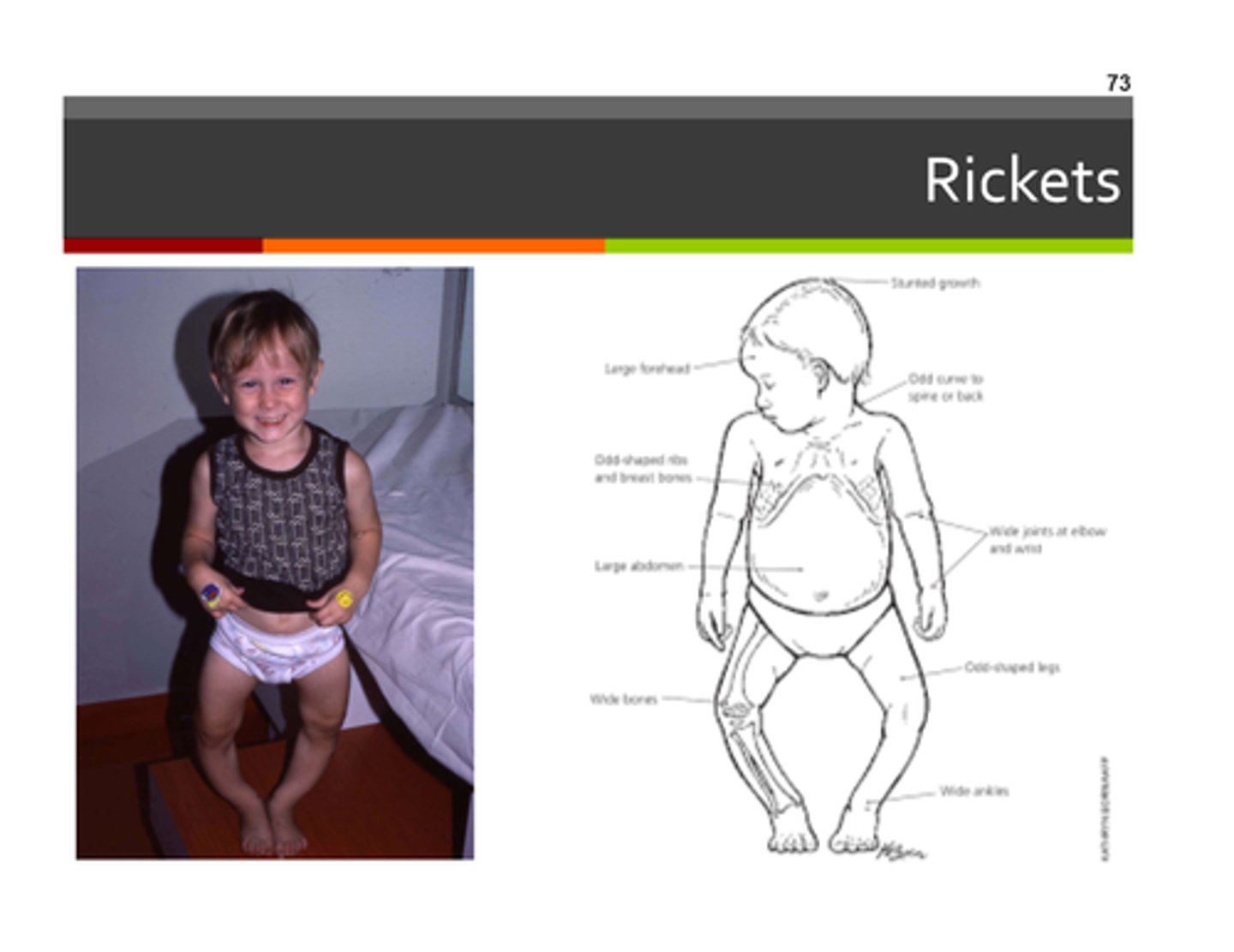
What is rickets?
Vitamin D deficiency in children
What is a goiter?
enlargement of the thyroid gland due to iodine deficiency

What is Primary nutrient deficiency?
Nutrient deficiency caused by inadequate dietary intake
What is secondary nutrient deficiency?
Nutrient deficiency due to causes other than dietary intake.
These include disorders that affect gastrointestinal function, wasting disorders and conditions that increase metabolic demands such as infections, hyperthyroidism, other endocrine disorders, burns, trauma, surgery, and other critical illnesses and conditions.
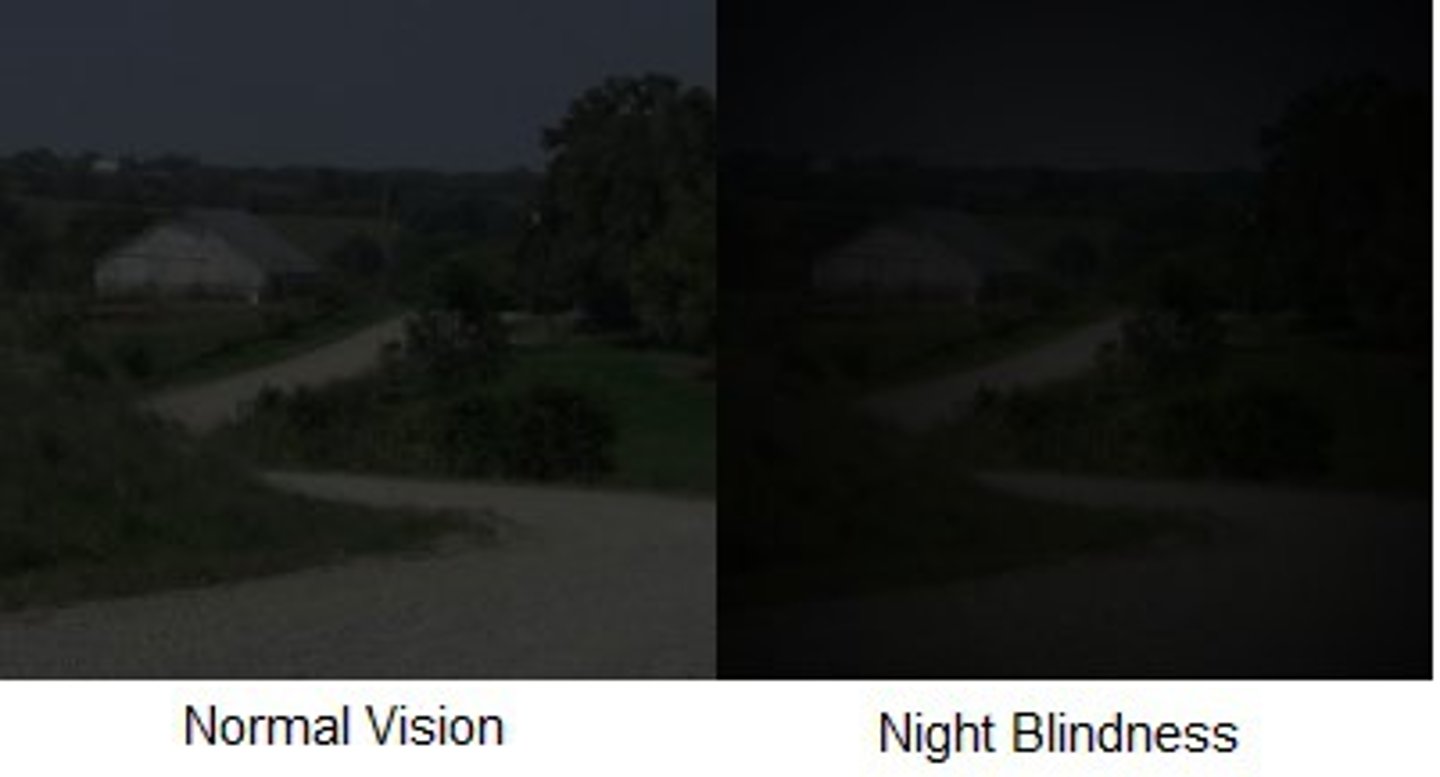
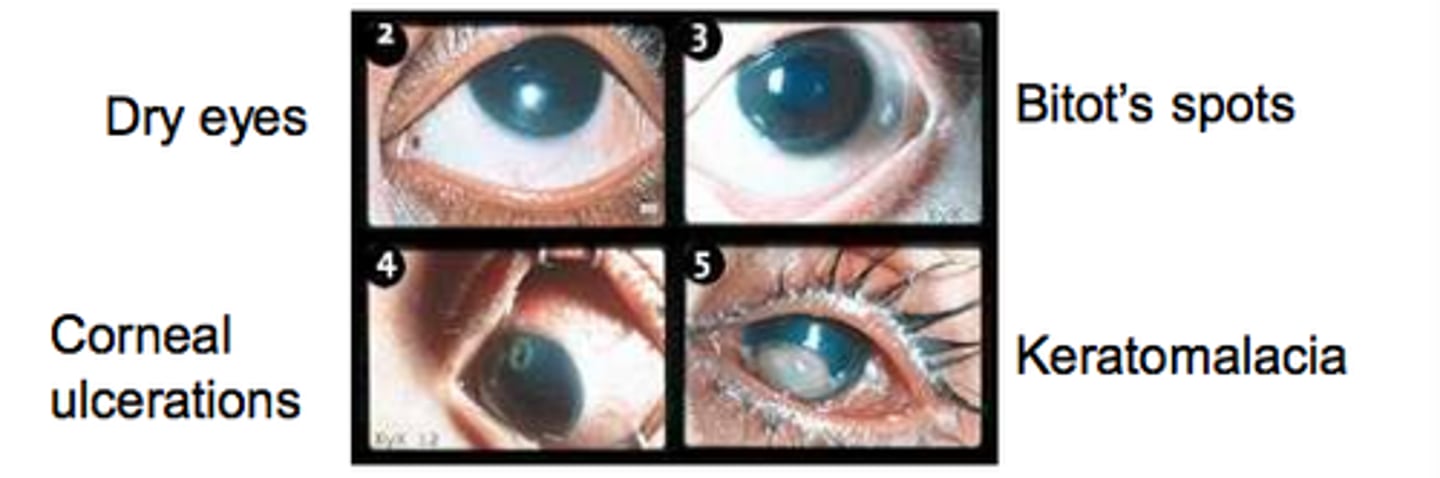
What is night blindness?
vitamin A deficiency disorder that results in loss of ability to see under low-light conditions

What is Kwashiorkor?
PROTEIN deficiency resulting from: MEAL //M - malnutrition; E - edema; A - anemia; L - liver (fatty change due to decrease apolipoprotein synthesis)
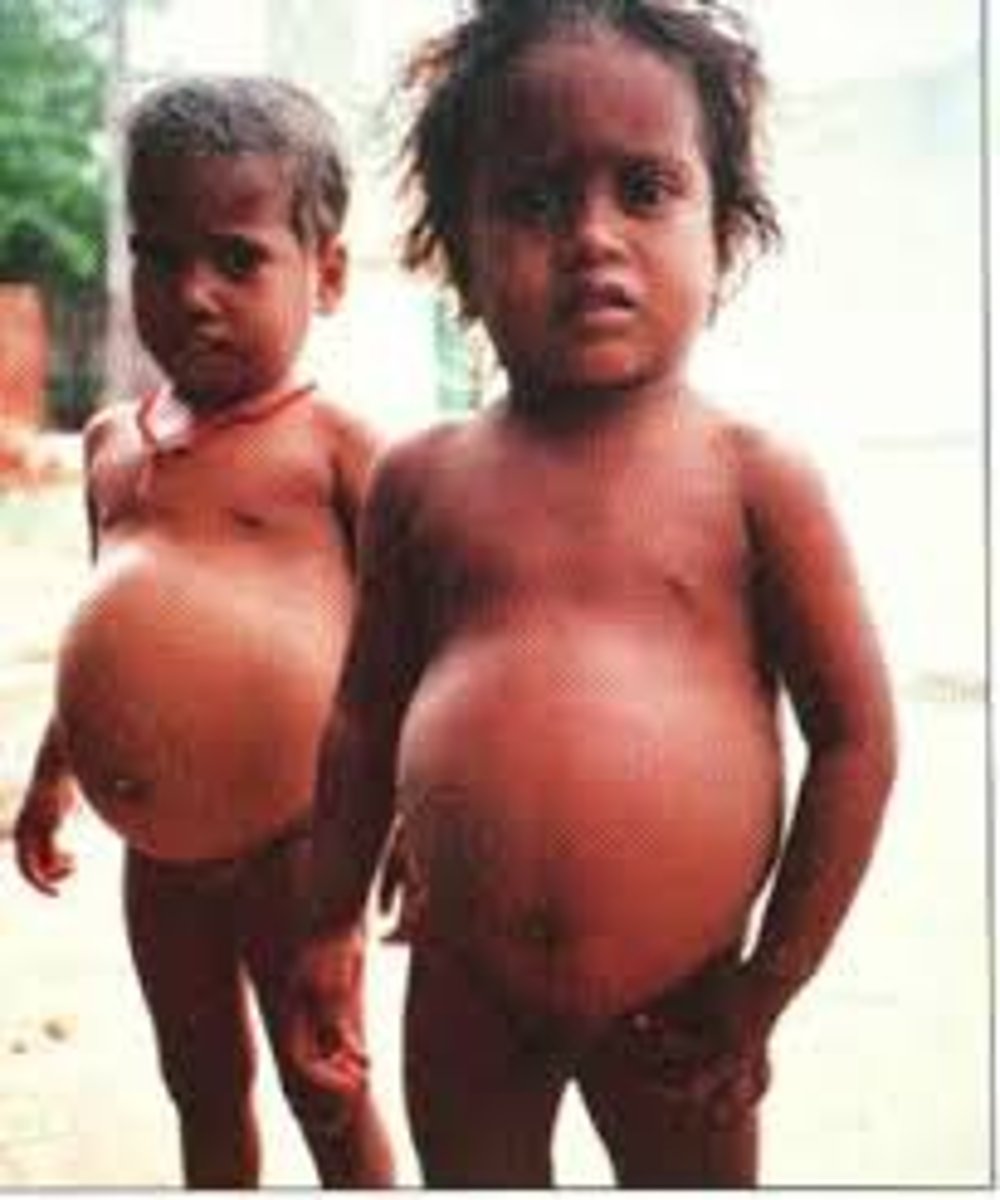
What is marasmus?
Starvation, skinny, calorie deficiency (All nutrients lacking)

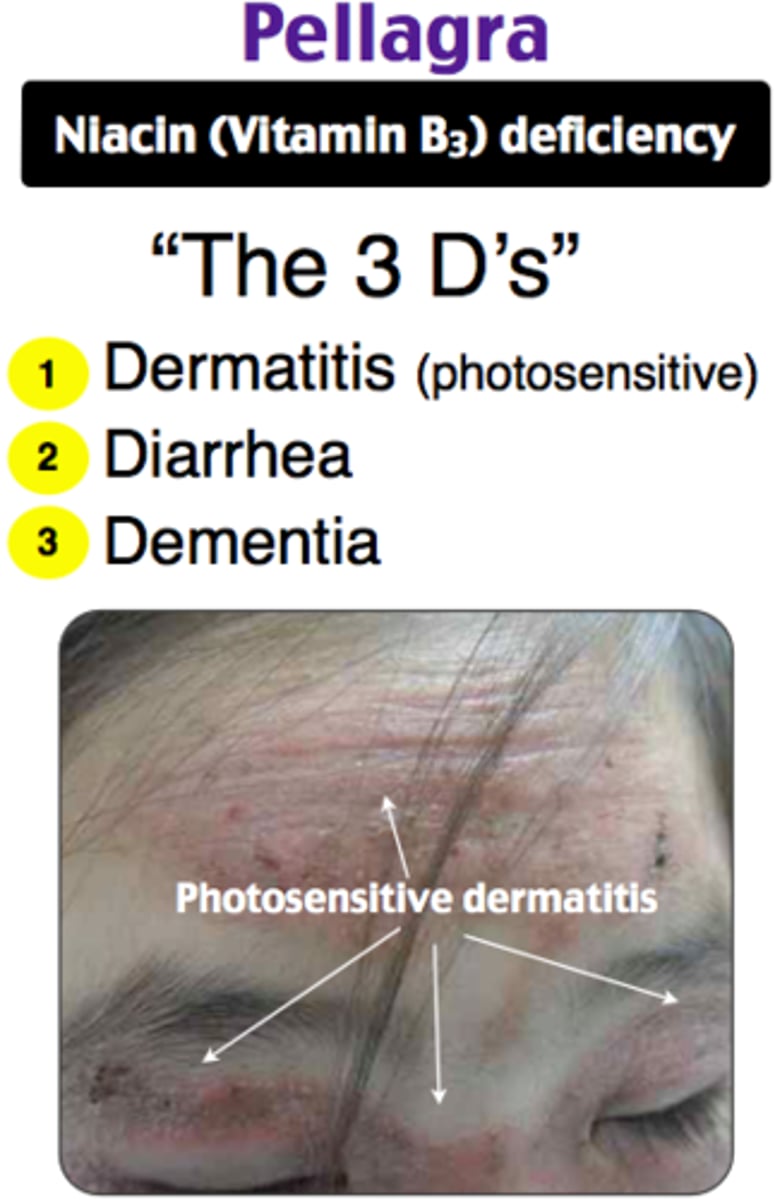
What is Pellagra?
condition that occurs due to dietary deficiency of niacin
- common if eating corn-based diet
- also seen in alcoholics,
Sx: 3Ds
- diarrhea
- dermatitis (present in sun-exposed areas)
- dementia
- death if untreated
What is xerophthalmia?
Dry eyes caused by vitamin A deficiency.
What are the 4 types of nutritional assessments?
Anthropocentric measurements
Clinical examination
Biochemical tests
Dietary and social history
What are Anthropocentric measurements?
Measures of
Height
Weight
Head,chest, and abdominal circumference (for children)
Upper arm measurement
Skinfold measurement with caliper
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with pallor, blue half-circles beneath eyes?
Possible deficiencies include
Iron
Copper
Zinc
B12
B6
Biotin
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with edema?
Protein deficiency
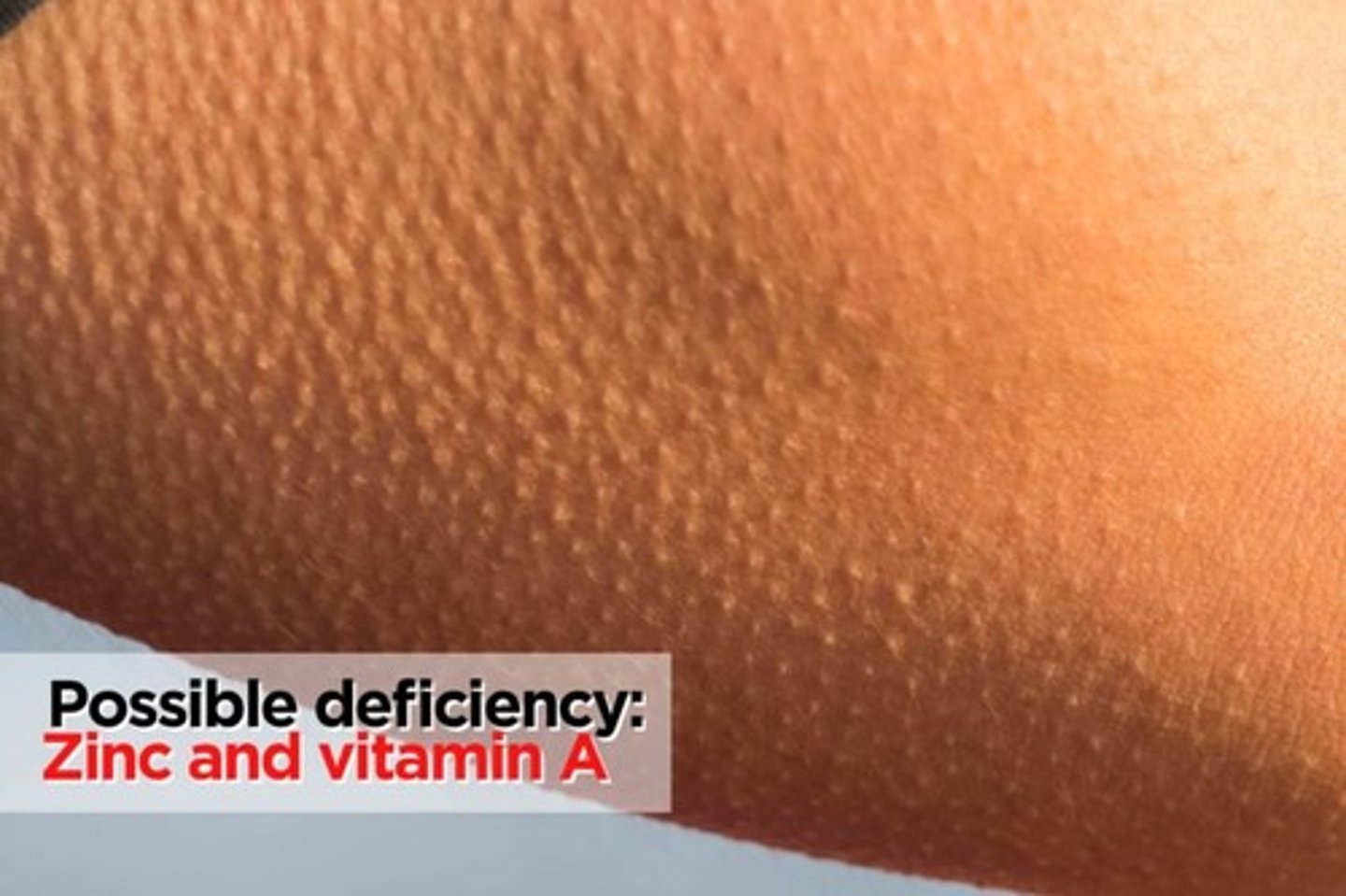
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with Bumpy "gooseflesh"
Vitamin A deficiency
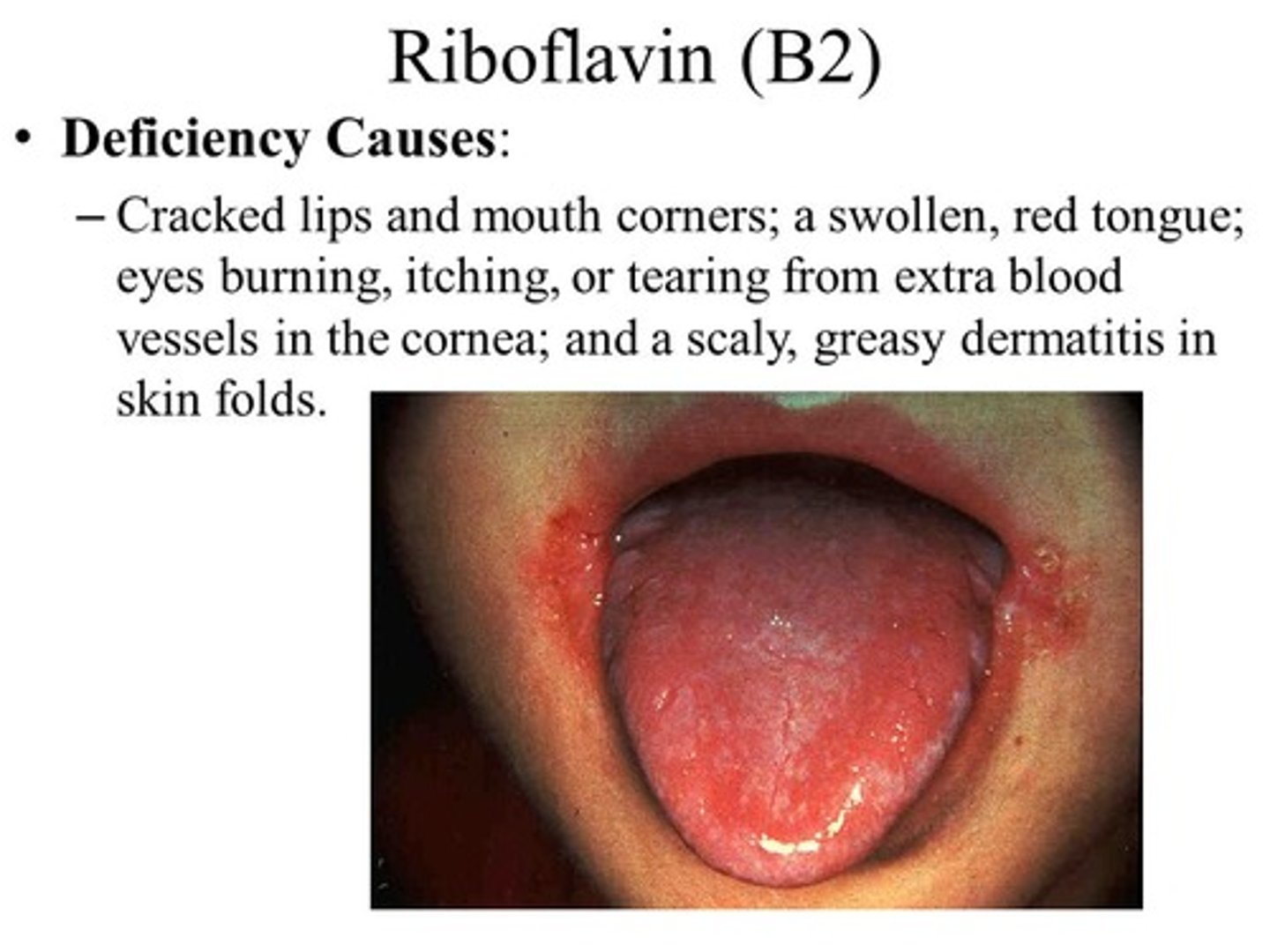
What is Riboflavin?
Vitamin B2
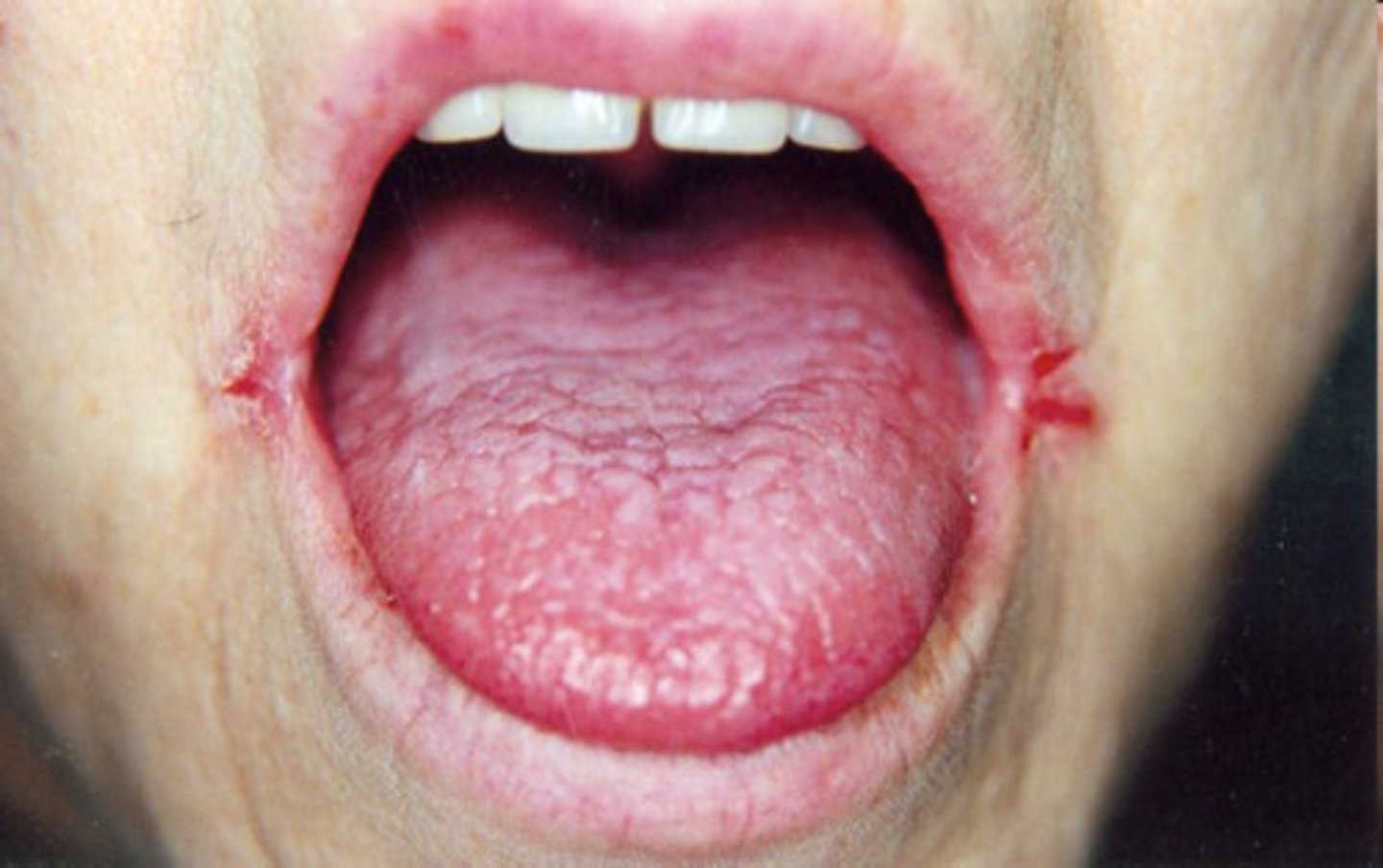
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with lesions at corner of mouth
Riboflavin deficiency
What is Folic Acid?
Vitamin B9

What is glossitis?
Inflammation of the tongue
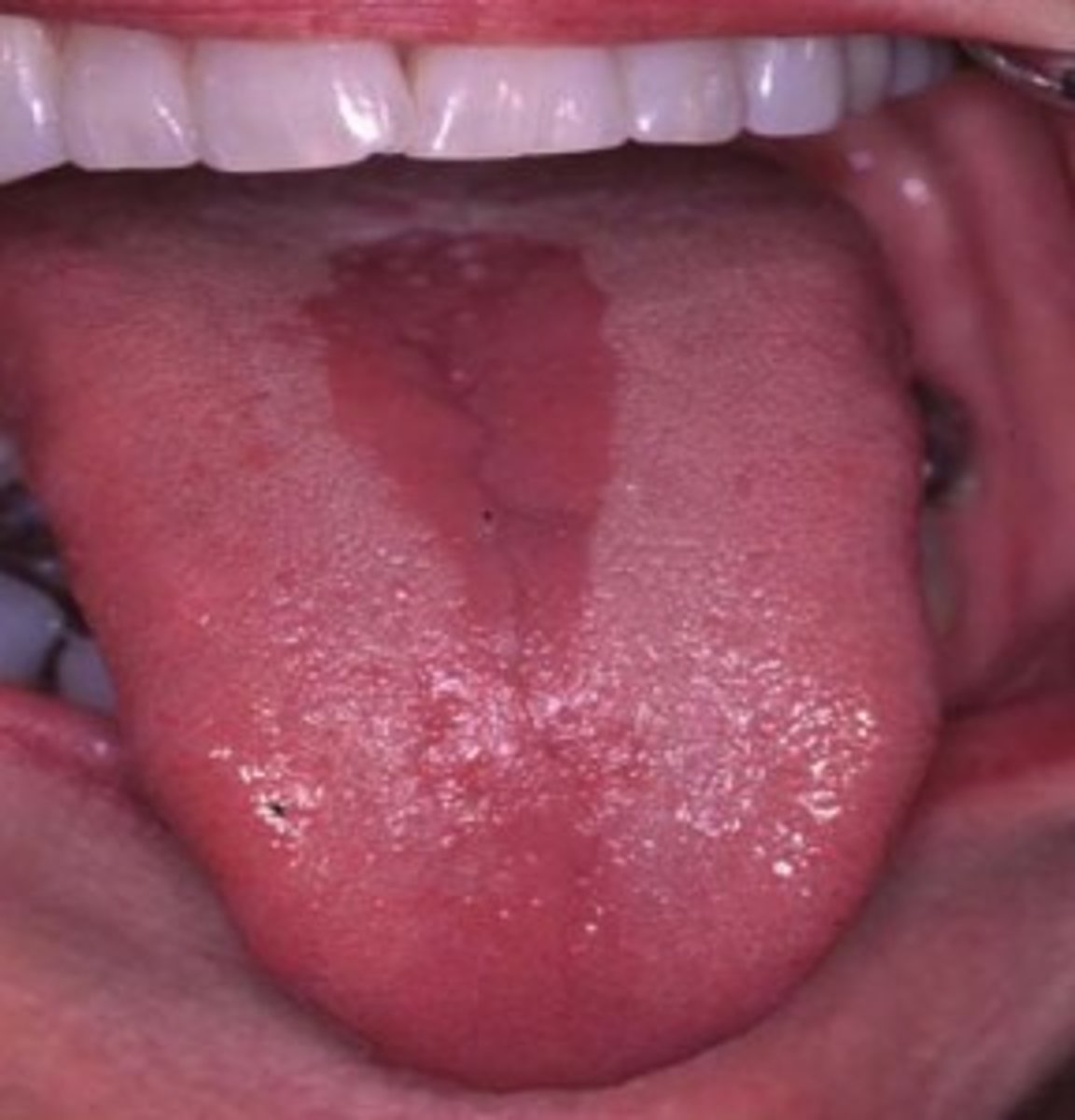
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with Glossitis?
Folic Acid deficiency
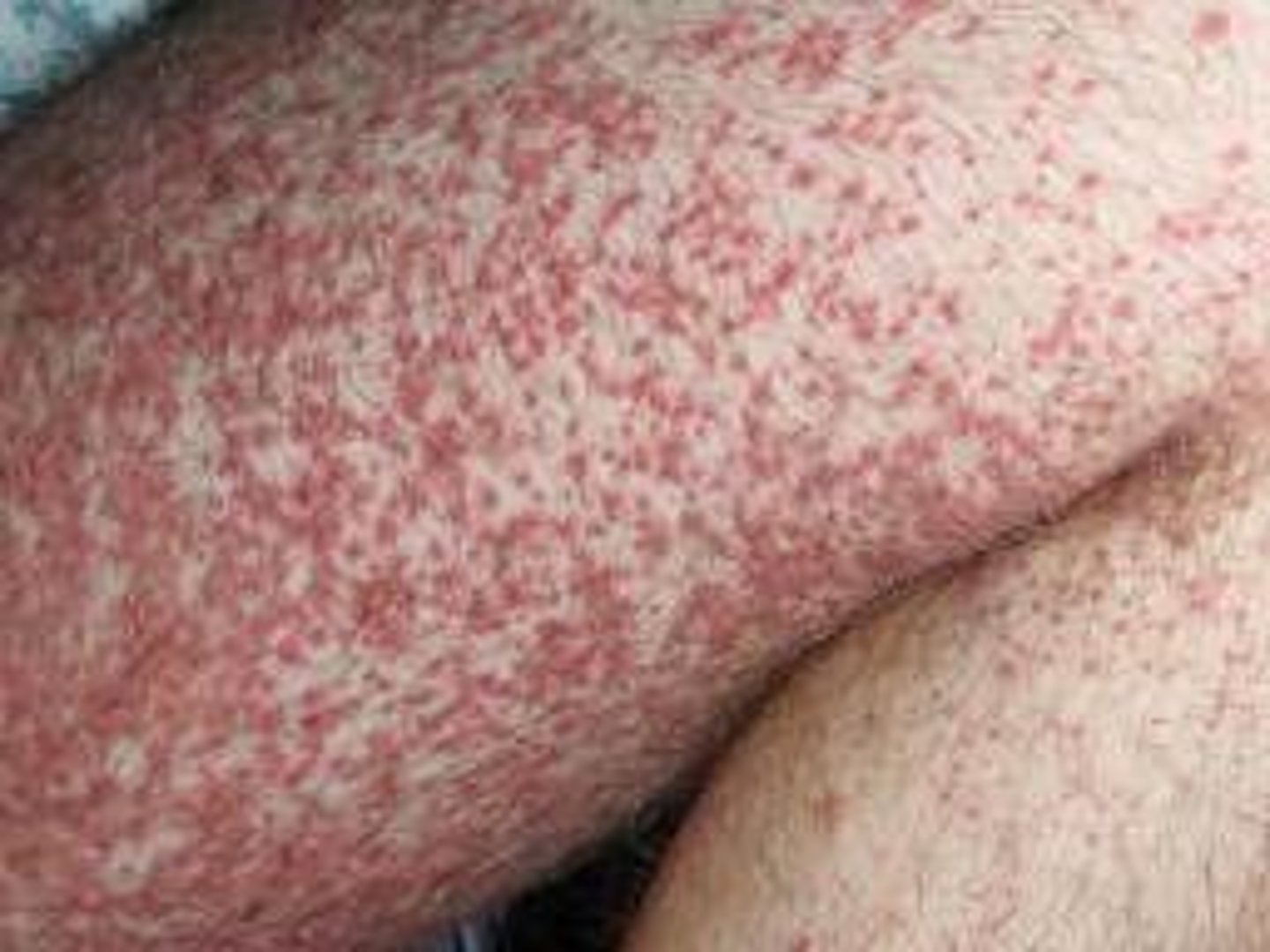
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with numerous black and blue spots and tiny, red pin-prick hemorrhages under skin?
Vitamin C deficiency
What is emaciation?
the state of being abnormally thin or weak
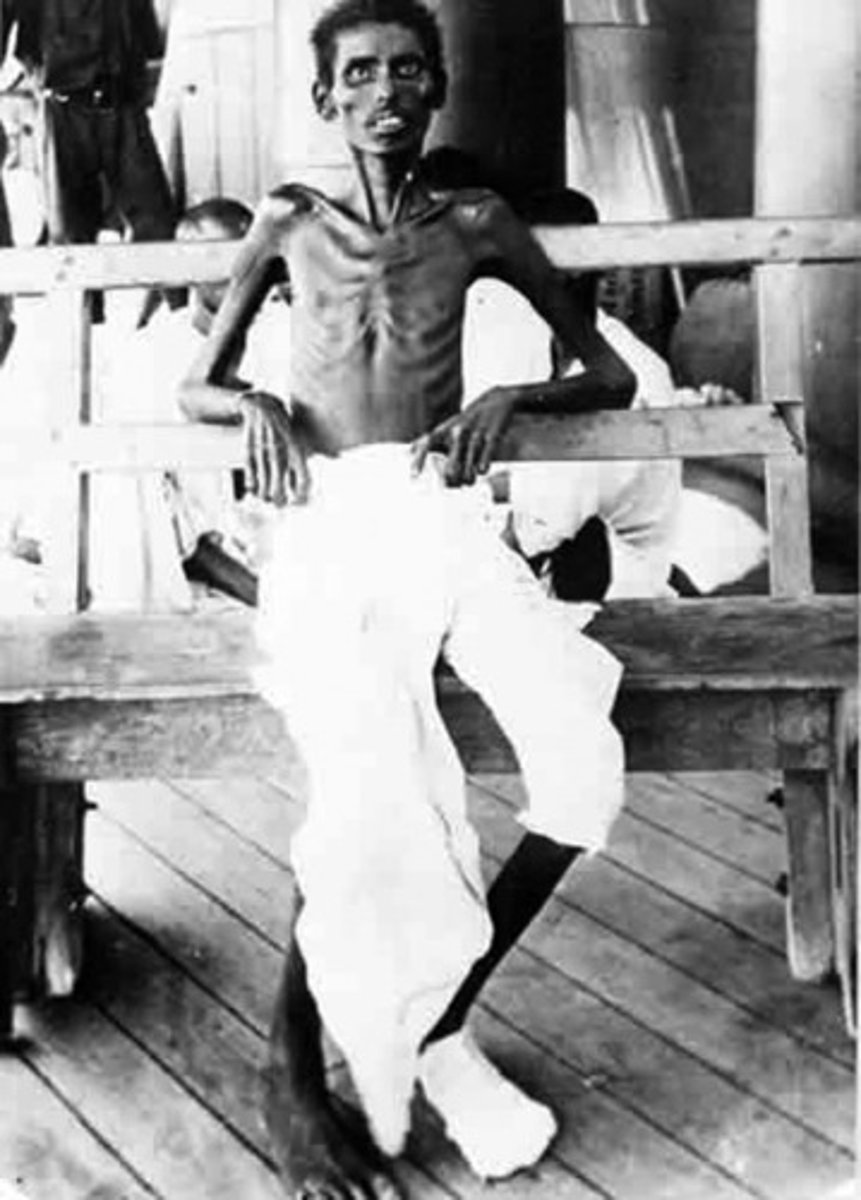

Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with emaciation?
Possible deficiencies include
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Calories
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with poorly shaped bones or teeth, or delayed appearance of teeth in children
Vitamin C deficiency
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with slow clotting time of blood?
Vitamin K deficiency
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with unusual nervousness, dermatitis, and diarrhea in same client
Niacin deficiency
What is Niacin?
Vitamin B3

What is tetany?
a condition marked by intermittent muscular spasms, caused by malfunction of the parathyroid glands and a consequent deficiency of calcium.
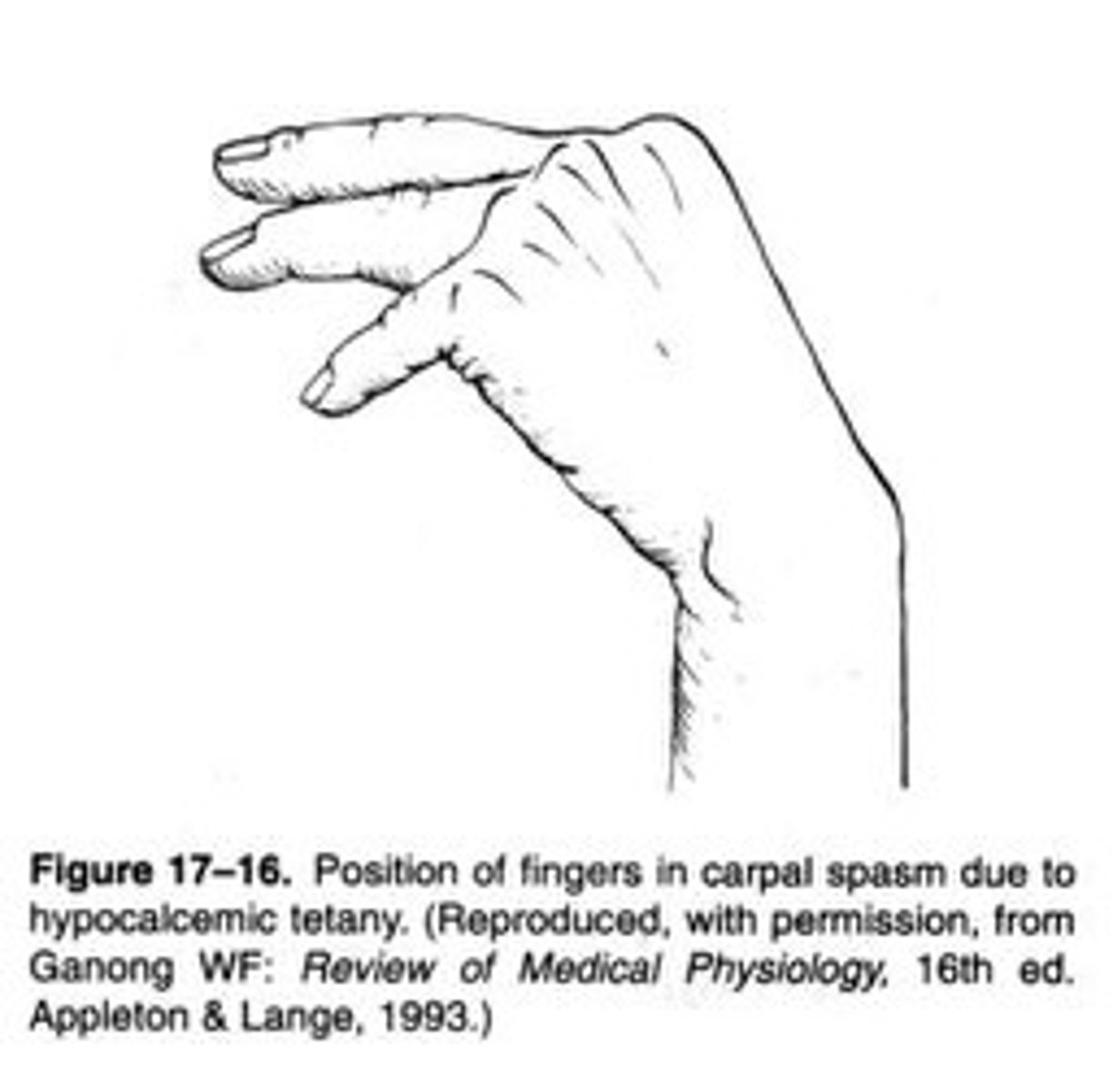
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with tetany?
Possible deficiencies include
Calcium
Potassium
Sodium
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with Goiter?
Iodine deficiency
What is eczema?
An inflammatory skin disorder usually involving only the epidermal layer of the skin
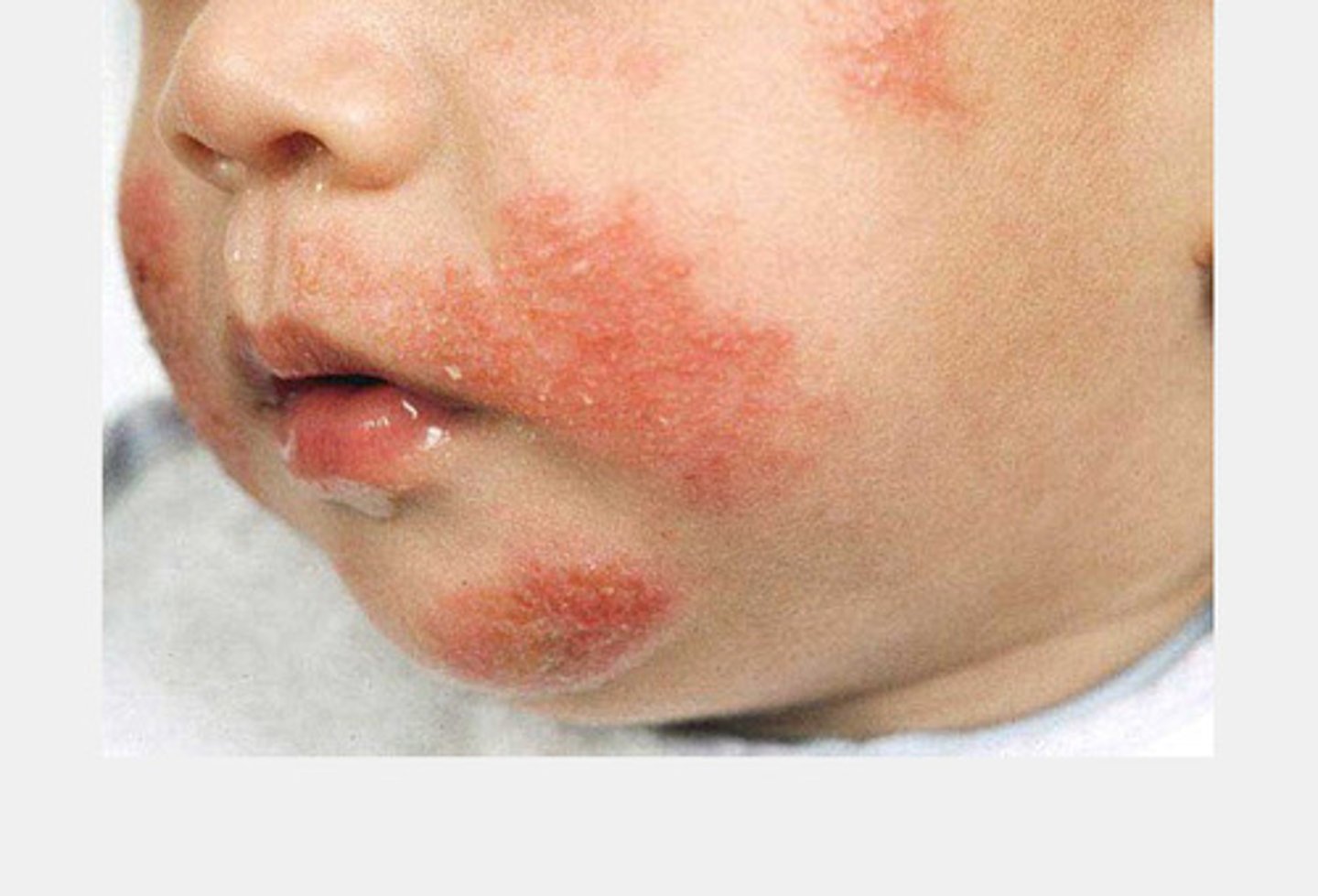
Clinical Signs: What deficiencies are associated with eczema?
Fat (lipid) deficiency
Biochemical tests: What does the serum albumin level measure?
Measures main protein in blood
Determines protein status
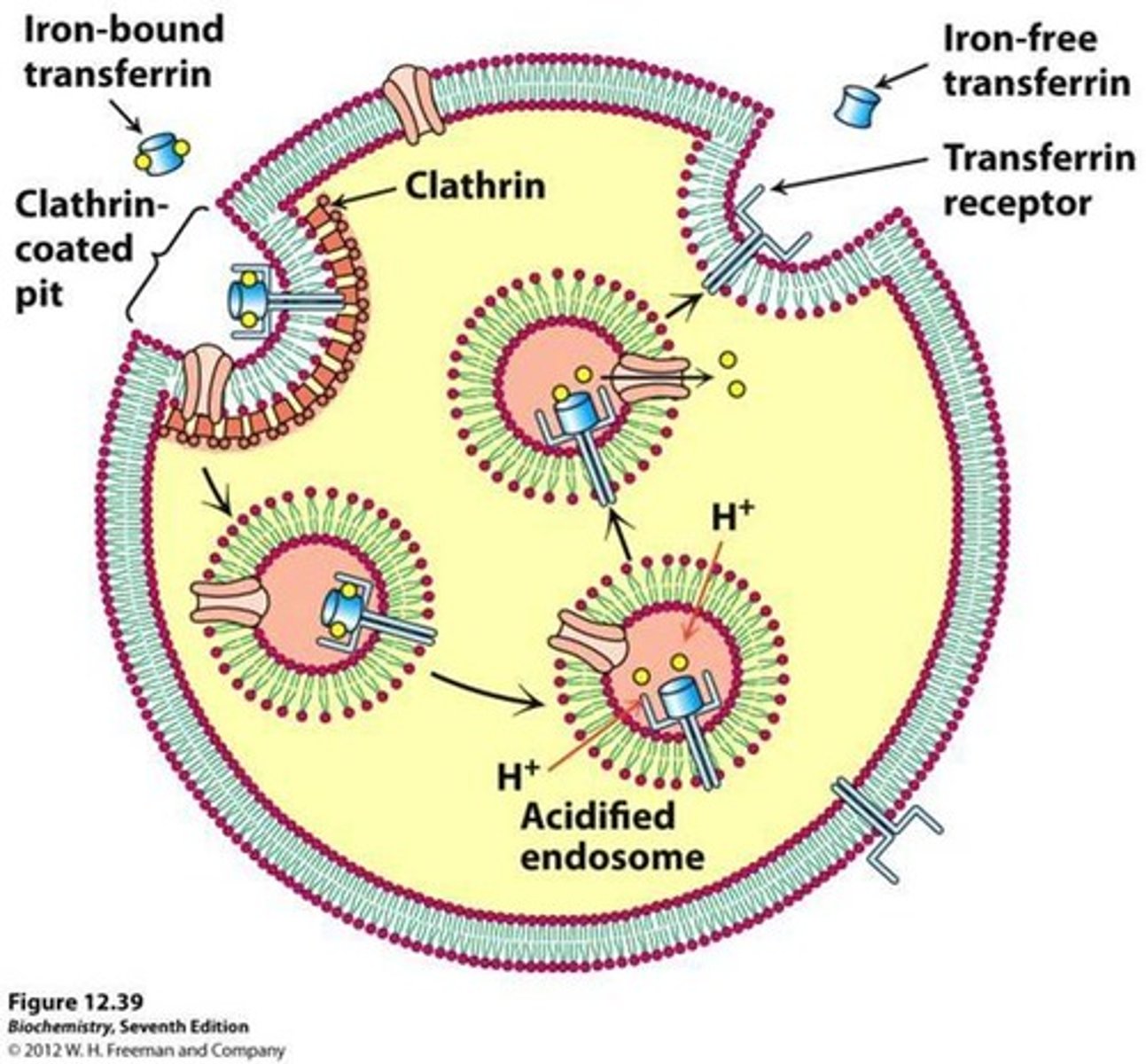
Biochemical tests: What does the serum transferrin level measure?
Indicates iron-carrying protein in blood
High indicates iron stores low
Low indicates body lacks protein
What is (blood) urea nitrogen (BUN)?
Level of nitrogenous waste in blood

Biochemical tests: What does Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) measure?
May indicate renal failure, insufficient renal blood supply, or blockage of urinary tract
What is creatinine?
Product of muscle breakdown, measurement of kidney function
Biochemical tests: What does Serum creatinine measure?
Indicates amount of creatinine in blood
Used to evaluate renal function
Biochemical tests: What does creatinine exertion test indicate?
Indicates amount of creatinine excreted in urine during 24-hour period
Used in estimating body muscle mass
Muscle mass depleted, as in malnutrition
Level will be low
What are some general biochemical tests done on a patient to determine their nutritional status?
Other tests include
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
Hematocrit (Hct)- the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood.
Red blood cells (RBCs)
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
Lipid Profile- High and low density lipoprotien and Serum triglycerides
Urinalysis
Dietary and Social History: What is done to evaluate food habits?
24-hour recall
Types, amounts, and preparation of all foods eaten in last 24 hours
Food diary
Written record of all food and drink ingested in specified period
Computer diet analysis
Determines nutrient deficiencies or toxicities
Dietary and Social History: What is done to evaluate social history of client?
Consideration of financial resources to do the following:
Obtain needed food
Properly store and cook food
Food-drug interactions that can lead to malnutrition
What is a balanced diet?
A diet that includes all essential nutrients in appropriate amounts and preserves and promotes good health.
How do you know you eat a balanced diet?
Meal planning
Tables provide Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)
Simple system
Dietary Guidelines for Americans developed by United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS)
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding nutrients?
Consume nutrient-dense foods to receive adequate nutrients within caloric needs.
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding weight management?
Balance calories consumed with calories expended
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding physical activity?
To prevent chronic diseases, manage body weight, prevent weight gain, and sustain weight loss
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding food groups?
Consume variety of fruits and vegetables
Consume half of grains from whole grains
Consume fish, nuts, and vegetable oils as sources of fats
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding fats?
Have total fat intake between 20 and 35 percent calories
Limit saturated fat and trans-fatty acids
Consume less than 300 milligram (mg) cholesterol per day
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding carbohydrates?
Consume fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Limit foods with added sugars
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding sodium and potassium?
Consume less than 2,300 mg sodium per day
People with high blood pressure should have less than 1,500 mg per day (African Americans, middle-aged adults, and older adults)
Consume 4,700 mg per day of potassium
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding Alcoholic beverages?
Limit to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men
What are some key recommendations listed in the dietary guidelines for Americans regarding food safety?
Wash hands when handling foods
Wash, store, cook, and chill foods properly
Avoid foods more likely to be contaminated
What did the Nutrition Labeling & Education Act (1990) do?
Required mandatory labeling for nearly all processed foods started in May 1994
What is the primary objective of food labeling?
To ensure labels on most foods provide consistent nutrition information
What are health claims?
They identify a food-health relationship. Health Claims describe an association between a food or dietary compound and a disease (prevention) or health condition.
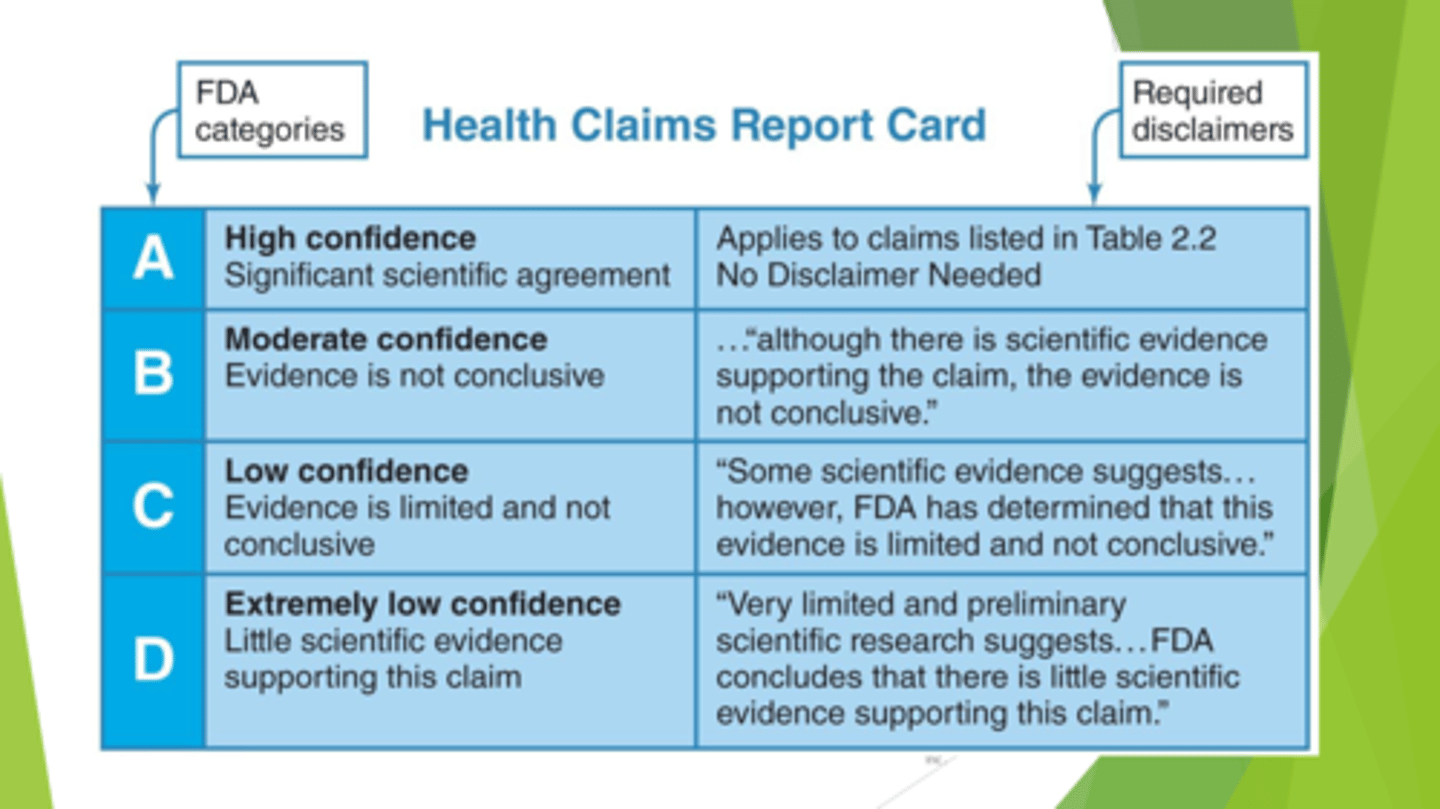
What does the Food and Drug Administration do?
Sets health claims allowed
Determines serving sizes
Standardizes descriptive terms
What nutrition facts are required on food labels?
Total calories
Calories from fat
Total fat
Saturated fat
Trans fat
Cholesterol
Sodium
Total Carbohydrates
Dietary fiber
Sugars
Protein
Vitamin A
Vitamin C
Calcium
Iron
What factors affect food habits?
Nationality, culture and religion all affect food habits.
Economic and social status may also contribute to food habits.
How can a health care professional gain knowledge regarding a client's dietary preferences?
Talking with clients and learning about their background helps health care professionals gain knowledge regarding food preferences
Why is it important for a health care professional to understand food patterns unique to different cultures?
By understanding food patterns unique to a client's culture, a health care professional can plan nourishing meals consisting of foods that appeal to the client.
Adjustments in diet can be made gradually and effectively
How has the Native American diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Influenced half of edible plants commonly eaten in U.S. today
E.g., corn, potatoes, squash, cranberries, pumpkins, peppers, beans, wild rice, sunflower seeds, sweet potatoes, avocados, papayas, cocoa beans
Influenced wild fruits, game, and fish
Prepared as soups and stews or dried
How has the U.S Southern- African American diet influenced what Americans eat today?
African-American influence
Popular foods:
Down-home breads, biscuits, greens, black-eye peas, okra, etc.
Soul foods
High in fat, sodium, and carbohydrates
May be deficient in iron, calcium, fiber, potassium, and vitamin C
How has the U.S Southern- French American diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Cajun and Creole cuisine are fusion of French and Spanish cooking
Popular foods:
Wild game, seafood, vegetables, herbs, rice, tomatoes, sausage, hot peppers, and crawfish
French-American influence
Lacking in fruits
Creole cooking adds rich sauces and calories
May be deficient in calcium, vitamin D, vitamin E and vitamin C
How has the Spanish- Mexican diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Combination of Spanish and Native Americans foods
Popular foods:
Beans, rice, tomatoes, onions, jalapenos, masa harina, corn tortilla stuffed with cheese, beef, and pork
Flan- Favorite dessert
Often lacking in vitamin C and green and yellow vegetables and fruits
Lactose intolerance common
How has the Spanish- Puerto Rican diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Influenced by Spanish, Africans, and Taino Indians
Popular foods:
Corn, wheat, seafood, beef, pork, rice, olive oil, chicken, pinto beans, and okra
Often use starchy vegetables and tropical fruits
Lacking in milk and non-starchy vegetables
How has the Mediterranean diet influenced what Americans eat today?
HEALTHIEST IN THE WORLD!
Italian influence
Popular foods:
Pastas, rice, beans, olives, fruits, vegetables, seafood, and cheese
Use olive oil
Eat small portions
Seldom eat beef
Eat main meal at lunch
Could benefit from increase in low-fat milk and meat
Greek influence
Popular foods:
Broccoli, cauliflower, wild greens, artichokes, fava beans, green beans, eggplants, legumes, olives, yogurt, and feta cheese
Includes fish, seafood, lamb, goat, and pork
Use bread as basis of meal
Use fruity olive oil as primary fat
Eat fruit for dessert
How has the Northern and Western European diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Have given U.S. "meat and potato" mentality
Lots of meat, poultry, or fish with small amounts of vegetable and starch
Essential to have sausages, blood sausage, head cheese, dark breads, and dairy
Could benefit from more fresh fruits and vegetables
How has the Central European diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Popular foods:
Pork, chicken, beef, sausages, fish and game, cabbage, carrots, turnips, potatoes, beans, lentils, and onions
Use eggs and dairy products abundantly
Consume spatzle, dark breads, and muesli
Could benefit from limiting number of eggs, using fat-free or low-fat dairy products, and adding fresh fruits and vegetables
How has the Middle Eastern diet influenced what Americans eat today?
Popular foods:
Lamb, pita and flatbread, sourdough, legumes, and dairy
Use dates, figs, pistachios, and fresh fruits for snacks and desserts
Adding fresh fruits and vegetables would increase vitamins, minerals, and fiber