Clinical Reasoning and Reflective Practice (NURS2205)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering clinical reasoning concepts, reflective practice, nursing diagnoses, and related frameworks from the notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Clinical Reasoning
The collection and processing of data to identify problems and plan goals and actions for safe, effective patient care; relies on critical thinking and is not strictly linear.
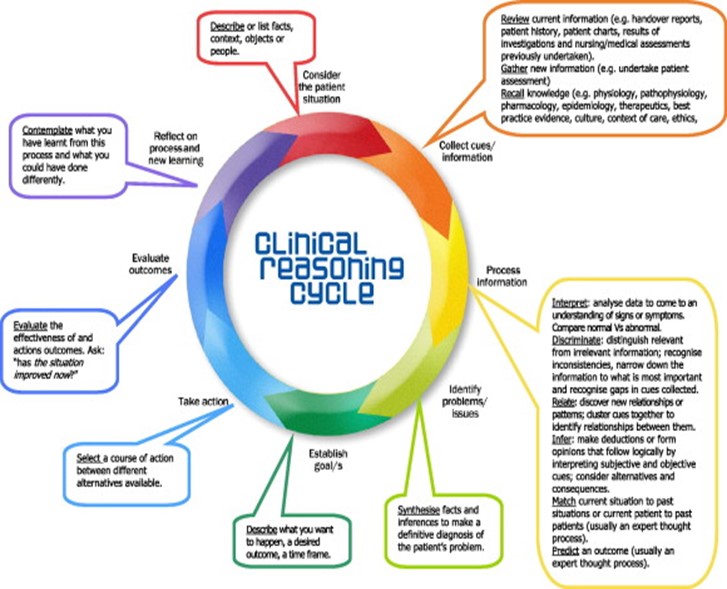
Clinical Reasoning Cycle (CRC)
A cyclical framework for nursing practice: gather cues, process information, identify problems, establish goals, take action, evaluate outcomes, and reflect to guide patient care.
Critical Thinking
Deliberate, systematic, logical thinking that questions bias and assumptions; includes interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and self-regulation.
Reflective Practice
A deliberate process of reflecting on experience to improve knowledge, skills, and professional judgment.
Gibbs Reflective Cycle
A six-step model (Description, Feelings, Evaluation, Analysis, Conclusion, Action Plan) for structured reflection on practice.
AEB (As Evidenced By)
Evidence or manifestations that support a nursing diagnosis.
RT (Related To)
Etiology linking the problem to its cause in a nursing diagnosis.
Three-Part Nursing Diagnosis
Problem/Diagnostic Label linked to Etiology and supported by Signs/Symptoms (evidence).
Two-Part Nursing Diagnosis (Risk)
A risk diagnosis: problem + etiology, with evidence (AEB) indicating likelihood rather than current problem.
Nursing Diagnosis
A clinical judgment about a client’s response to actual or potential health problems, guiding care planning and interventions.
Impaired Physical Mobility
A nursing diagnosis referring to limited ability to move due to muscle or control impairment.
Impaired Myocardial Tissue Perfusion
Nursing diagnosis indicating reduced coronary blood flow causing chest pain or risk of myocardial injury.
Excess Fluid Volume
Nursing diagnosis indicating fluid overload due to compromised cardiac function, evidenced by edema and distended neck veins.
ABC Framework
Priority framework: Airway, Breathing, Circulation; highest priority for life-threatening problems.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Ordering of needs from physiological first to self‑actualisation, guiding prioritisation of nursing care.
Failure to Rescue
When failure to recognize and respond to patient deterioration leads to adverse outcomes.
Subjective Data
Information provided by the patient (perceptions, feelings, reports).
Objective Data
Observed or measured information (vital signs, examination findings).
Pitting Edema
Edema that leaves a depression (pit) when pressed, indicating fluid overload.
Right-Sided Heart Failure
Heart failure with edema, distended neck veins, and elevated right atrial pressure; often with peripheral signs.
Left-Sided Heart Failure
Heart failure with pulmonary signs such as dyspnea and crackles; left ventricular dysfunction predominant.
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing; a potential nursing problem.
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Neurodegenerative disorder with tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and gait disturbance.
Dyskinesia
Involuntary movements often a side effect of PD medications.
Atrial Fibrillation
An irregular heart rhythm that can reduce cardiac output and increase stroke risk.
AEB and RT connectors
'AEB' means As Evidenced By; 'RT' means Related To; they link signs/symptoms to etiology in nursing diagnoses.