Module 8 Flashcards
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Common routes of virus entry into human host
Respiratory
GI
genitourinaryconjunctiva
skin
Types of Viral Infections
Localized infection
Disseminated infection
Systemic infection
Localized infection
Replication at primary site of infection that spreads to adjacent cells
Disseminated infection
Virus breaches physical and immunological barriers and extends beyond primary site of infection → migrates through blood and capillaries
Systemic infection
Virus that affects many organs/systems
Virus Transmission: Aerosols
Droplets (ie. sneeze/cough, saliva) - Flu, Covid, Rhinovirus
Virus Transmission: Fecal-Oral
Diarrhea/Vomiting associated with gastroenteritis - often transmitted from contaminated food or water (ie. shellfish)
rotavirus, norovirus, hepatitis A and E
Virus Transmission: Skin Lesions
virus replicates and releases within skin lesion
Herpes
Virus Transmission: Blood
Viral exposure from contaminated blood, infected fluid, sexual activity, childbirth
HIV, Hep B/C
Virus Transmission: Body Fluids
Semen
HIV, CMV, Hep B
Breast Milk
CMV
Urine
Hantaviruses
Immunopathology
The study of the immune response's role in the pathogenesis of diseases
often occurs when cytokine stimulate T cells that cause lesions of host tissue
Two major types of parasites that affect humans
Plasmodium
Causes Malaria - Th1
Leishmania
Causes Leishmaniasis - Th2
Mechanism of killing parasites
Normally:
Parasite can be killed by macrophages or neutrophils
If parasite persists:
monocytes are recruited to the Leishmania lesion via CC-chemokine receptor 2
monocytes are great at killing Leishmania parasites
monocytes differentiate into dendritic cells, migrate to lymph nodes, and synth IL-12 to promote differentiation of TH1 cells
TH1 cells migrate to skin and eliminate parasites by inducing nitric oxide
Th1 Cells
cell mediated T cells
develop following infections by intracellular bacteria and some viruses
stimulate cellular immune response (T cells) and activate macrophages
Stimulate B cells to produce IgM and IgG
Th2 Cells
humoral mediated (B cell)
predominate in response to infestations by GI parasites, nematodes, and helminths
stimulates humoral immune reponse = B cell proliferation
induces antibody production (IL-4)
Mechanism of if a lesion will occur
Parasite enters the skin
complement system, innate immune sys, macrophages, leukocytes
If above fails to kill parasites:
monocytes differentiate into;
dendritic cells → stimulate production of Th1 and Th2
macrophages - M1 or M2
Th1 can stimulate production of M1 = killing of parasite
Th2 stimulates M2 production = immunopathology and lesion formation
Treg is a regulatory T cell that amplifies this response in lesion formation
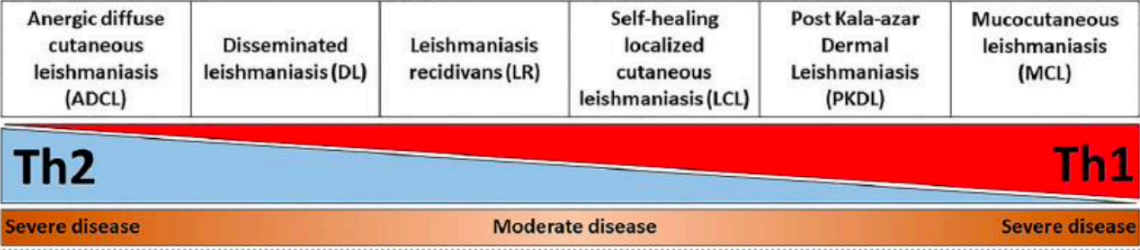
Anergic Diffuse Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (ADCL)
A form of leishmaniasis characterized by widespread skin lesions
occurs when Th2 cells are predominant over Th1 cells
Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis (MCL)
Lesions characterized by a chronic and hyperactive inflammatory immune response
predominant Th1 over Th2
IFN-gamma and TNF stimulate Th1 and cytotoxic CD8+ for tissue destruction
Polarization of Th1 and Th2
Extreme levels of either Th1 or 2 causes severe disease
Types of Vaccines
Live attenuated or inactivated virus vaccine
Subunit vaccine
Recombinant virus vaccine
mRNA/DNA vaccine
Live attenuated or inactivated virus vaccine
highly immunogenic
reversion to virulence
can be dangerous for immunosuppressed people
ex,, MMR, polio, yellow fever, chicken pox
Subunit vaccine
safe
poorly immunogenic → requires adjuvant
can self assemble into virus-like particles
ex,, HepB, HPV, pertussis, meningicoccal, shingles, covid (novavax)
Recombinant virus vaccine
strong cellular immune response
pre-existing immunity to vector reduces vaccine efficacy
ex,, covid (astra zeneca), ebola, flu
mRNA /DNA vaccine
easily produced
high efficacy
poor durability of immunity
ex,, covid (moderna, pfizer)
Three sites of vaccine activation
Muscle/skin
infiltration of pro-inflammatory cells
takes up antigen and adjuvant
migrates to lymph nodes for immune response
Lymph nodes
vaccine delivered directly to where immunity is generated
activates T and B cells
Blood
antibodies administered (humoral immunity) or effector T cells delivered (cell-mediated immunity)
Action of antibodies
Neutralizing: block pathogen binding/entry into host cells
Opsonization: mark pathogens for destruction by immune cells (phagocytosis, complement system)
Action of memory B cells
rapidly produce antibodies
Effector and Memory T cells
produce antiviral cytokines
can directly kill infected cells
can be circulating or tissue resident
Challenges in vaccine development
Potency, quality, durability
vulnerable populations
vaccine stability
Reason for adjuvants
increase peak immune response and durability
Types of carrier adjuvants
aluminum salts
emulsions
liposomes
Types of immunostimulatory adjuvants
Natural organic extracts
pathogen products
Steps of Vaccine testing
preclinical trials - animals and human tissue models
clinical trials
Phase I - Safety, dose range, side effects
Phase II - Immunogenicity, number of doses, side effects
Phase III - Random clinical trial, effectiveness, protection against disease, side effects
Phase IV - monitoring long-term effects and safety after approval
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
is a dsDNA virus and member of herpesvirus family
Symptoms: fever, sweats, tiredness, uneasiness, sore threat, joint/muscle pain, low appetite, weight loss, mouth ulcers
generally does not cause severe issue in healthy people
At Risk: pregnant and immunocompromised
Prevention: protected sex, not sharing personal items (toothbrush)
Diagnosis: blood test
Complications: vision loss, encephalitis, seizures, pneumonia,
Treatment:
prophylaxis with (val)ganciclovir for 3-12 months after organ transplant
pre-emptive approach - viral load monitoring, treat with valganciclovir if viral load is detecable
treat with (val)ganciclovir if affected with CMV
(val)ganciclovir
Drug class: nucleoside analogue
Mechanism of action: stops viral DNA elongation
Use: against CMV, HSV, EBV, VZV, HBV
Prodrug: valganciclovir → becomes ganciclovir
Treatment: 900mg or 5 mg/kg 2x daily for 14-21 days
prophylaxis 900mg or 5 mg/kg once daily
drug should be adjusted based on renal clearance
DDIs: nephrotoxic
Adverse reactions: diarrhea, leukopenia, nausea, anemia, headache, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain, lower appetite, kidney problem
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
dsDNA virus and member of herpesvirus family
Symptoms - ulcers around mouth and genitals
Prevention - avoid contact with infected regions, no sharing personal items
Diagnosis - PCR
Complications - encephalitis (neonates), meningitis (adults)
Treatments - acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir
DDIs - nephrotoxic and immunosuppressive drugs
Adverse reactions - diarrhea, leukopenia, nausea, anemia, headache, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain, lower appetite, kidney problem
(Val)aciclovir
Drug class: nucleoside analogue
Mechanism of action: stops DNA viral replication
Use: HSV, VZV
Prodrug: valaciclovir → aciclovir
Treatment: 400-800 mg oral or 5-10 mg/kg IV every 8 hr for 5-14 days
Prophylaxis: 400-800mg oral 2x daily
Monitor clearance and adjust dose
Hepatitis B
circular partial-dsDNA virus - part of Hepdnavirus family
8 known genotype of HepB: A-H
present in blood, tissue fluids, saliva, semen
considered a non-curable disease
Label the parts of HBV
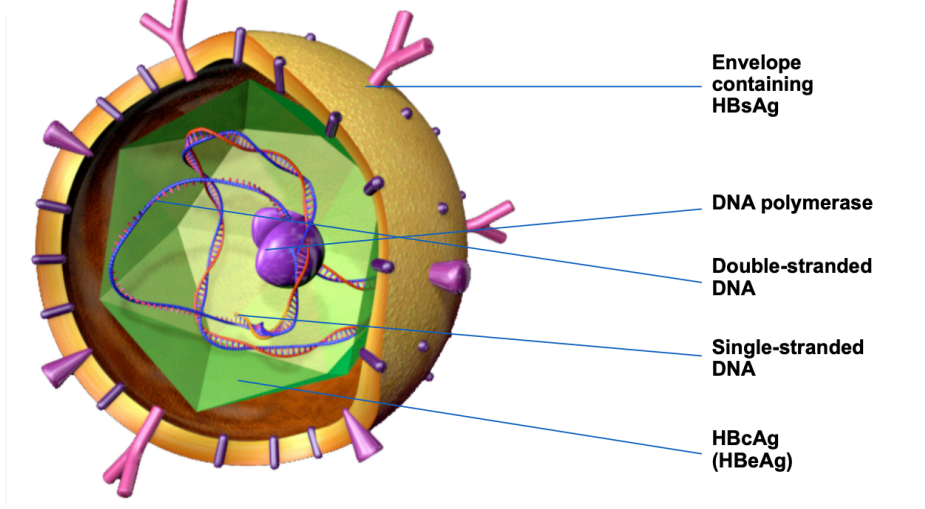
What part of HBV is tested for
HBsAG - serum testing from blood
core antigen cannot be directly tested
Epidemiology of HBV
~1% of australian pop
>290 million ppl worldwide - migrants/refugees = 95% of cases
Concentration of HBV in body fluids
HIGH: blood, serum, exudate
MODERATE: semen, vaginal, saliva
LOW: urine, feces, sweat, tears, breast milk
Transmission HBV
birth or childhood (most common)
needles
sexual contact
Chronic HepB can lead to
Liver cirrhosis (30%), liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma (53%), death
Treatment of HepB
Supportive care - provide fluids, diet, remove alcohol
Medicine - 3 dose vaccine series
Liver transplantation - last resort
Oral treatment - entecavir or tenofovir → well-tolerated but lasts for only one year
Subcutaneous injection - Peginterferon alpha-2a → lasts forever but has many adverse side effects
Phases of HBV infection
Immune tolerance
ALT (alanine aminotransferase - keep inflammatory enzyme in liver) = low
HBV DNA = high
HBeAg = positive
Immune Clearance
ALT fluctuates
HBV DNA fluctuates opposite to ALT
Immune Control
Low ALT
Low HBV DNA
HBeAg = positive
Low viraemia
Immune escape
can become viraemic at times
Possible Outcomes in HBV infection
Clinical Illness: <5yrs = <10%, >5yrs = 30-50%
Acute case fatality rate: 0.5-1%
Chronic infection rate: <5yrs = 30-90%, >5yrs 2-10%
Premature mortality from liver disease: 15-25%
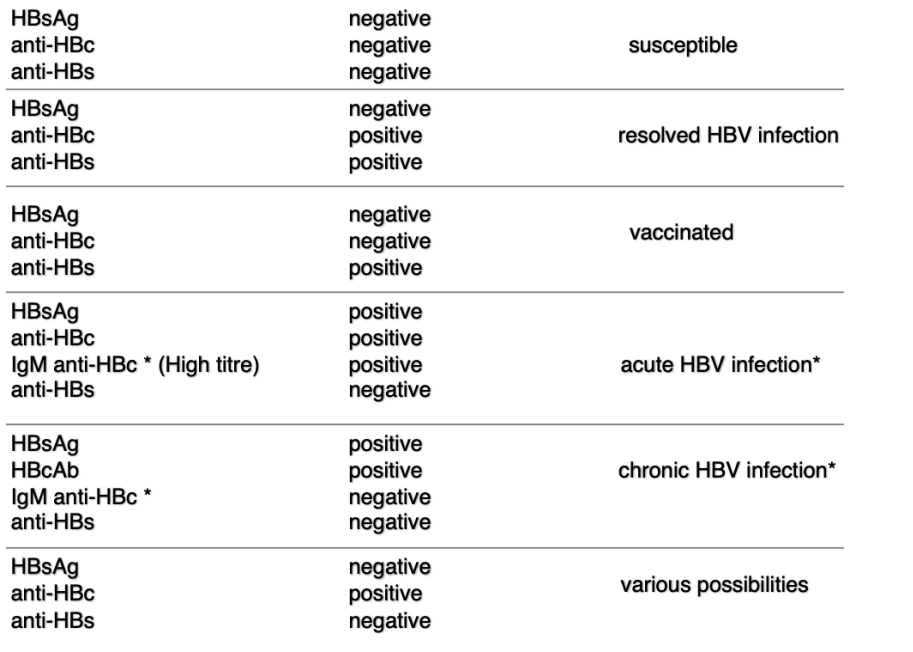
Interpretations of HBV serology
Hep B surface antigen (HBsAg)
Presence: HBsAg is present during acute and chronic HepB
is a protein on the surface of HepB
can be detected in blood during active infection
is earliest marker of infection
Hepatitis B core Antigen (HBcAg)
Present during acute phase of HepB infection - not typically detectable during chronic infection
is an internal antigen of HepB virus
not directly detectable during acute phase
detected by measuring HepB core antibodies
Hepatitis B surface Antibody (HBsAb)
present after recovery from acute HepB infection or after vaccination
antibody produced by immune system in respone to HepB surface antigen
Hepatitis B e Antigen (HBeAg)
typically present during acute and early chronic phases of HepB infection
indicates active viral replication and high likelihood of transmission
cannot be detected bc antigen is not on surface
Hepatitis B core Antibody (HBcAB)
appears during acute phase of HepB infection and persists during chronic infection
detectable in blood and is a marker of prior HepB exposure
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
enveloped positive-strand RNA virus - part of hepacivirus genus of flaviviridae family
curable disease but no vaccine exists
7 major genotypes (1-7)
rapid replication bc RNA polymerase does not require proof-reading
weakens T cell response
Pathogenesis of HCV
Liver injury is caused by the virus suppressing the immune response (NOT the virus attacking hepatocytes itself) - via release of cytokines and chemokines that lead to inflammation and fibrosis of liver
Symptoms of HCV
loss of appetite, fatigue, nausea, rash, pain, fever, jaundice, mood swings, liver damage
Transmission of HCV
oral exposure
needles
blood transfusions
mother-child
Diagnosis of HCV
Serology and PCR testing for viral RNA
PCR ensures no false positive bc antibodies exists even when infection resolves
Clinical features of HCV
incubation period: 6-7 wks
Acute infection illness = <20%
Acute infection fatality = very low
Chronic infection = 60-90%
Cirrhosis = 5-20%
Mortality from chronic infection = 3%
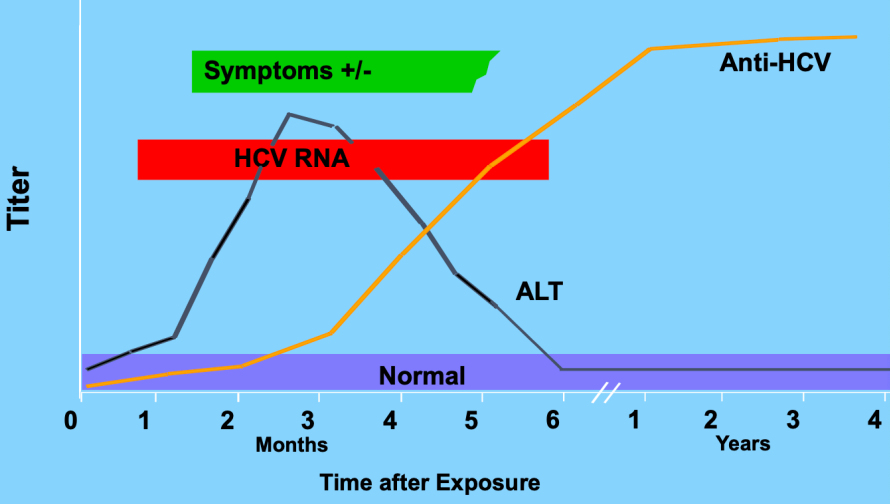
Acute HepC infection
Serum HCV RNA detectable around 3 months post infection
50-70% antibodies detectable right at symptoms
90% detectable after 3 months
can be severe, but rarely liver failure
symptoms uncommon
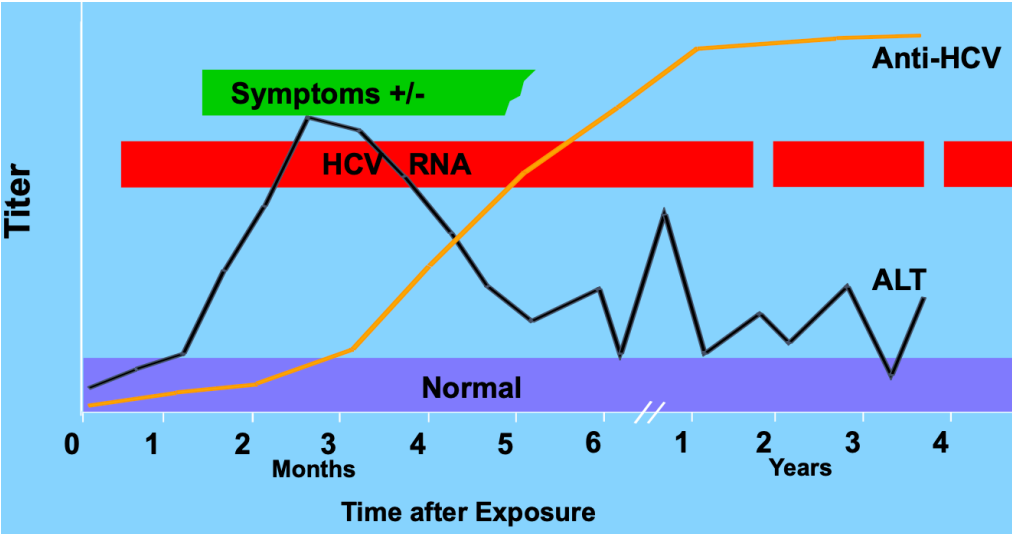
Chronic HepC infection
Leads to:
liver cirrhosis
liver failure
hepatocellular carcinoma death
~30% of HCV resolves on its own (better chances: younger, female, genetics [IL-28B polymorphism])
~70% of HCV becomes chronic
Treatment of HCV
goal =
achieve sustained virological response (no virus detected)
prevent/delay cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
improve outcomes of liver transplant
Treatment:
antivirals
protease inhibitors
polymerase inhibitors
=works in 95% of patients
Testing for Cirrhosis
Blood test, APRI score, and hepascore
Liver biopsy
Transient elastography
mechanical pulse that assesses fibrosis
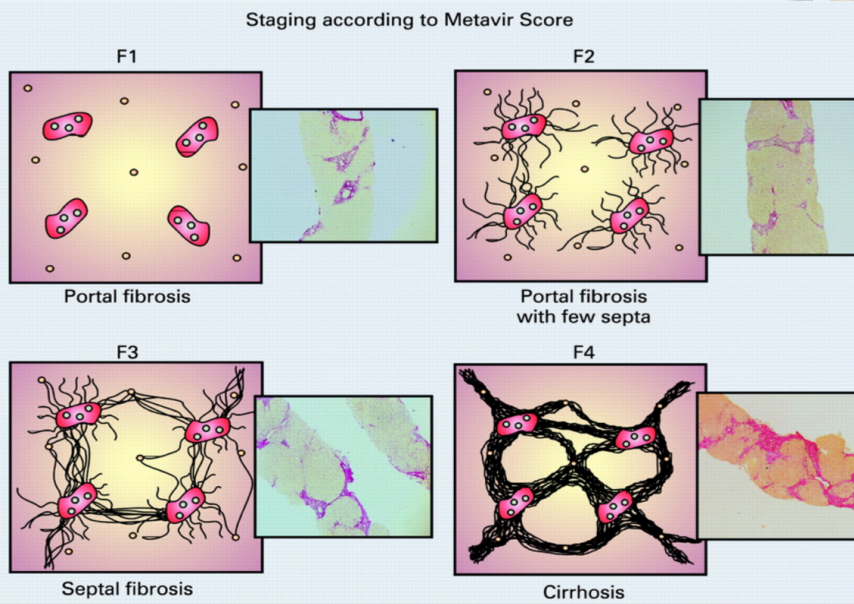
Liver Biopsy F scores
F1: portal fibrosis
F2: portal fibrosis with few septa
F3: Septal Fibrosis
F4: Cirrhosis
Pattern of acute HCV
Pattern of Acute → Chronic HCV
Hepatitis D virus
defective single-stranded RNA virus
requires HBV infection to form envelope made of HBsAg
only ppl with HBV can get HDV
no vaccine
Modes of HDV Transmission
injections
sexual contact
Prevention of HDV (and associated HBV)
Coinfection (getting HBV and HDV at the same time): treat HBV with vaccine to prevent onset of HDV
Superinfection (getting HDV after chronic HBV): no specific vaccine exists - educate patient on risk prevention
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
retrovirus (in lentivirus group) containing single stranded RNA
integrates in host cell genome = permanent
infects CD4+ T cells (mainly), macrophages, monocytes
Quiescent T cells
Form reservoirs for HIV but not actually producing HIV - can be activated to produce lots of HIV
Features of HIV
RNA (for replication)
Reverse transcriptase (RNA → DNA)
Integrase (viral integration into host genome)
Protease (new virus formation)
Types of HIV
HIV1 and HIV2
HIV1 is responsible for most global infections - most common cause of AIDS
HIV2 is mostly confined to west africa
High risk groups for HIV
female sex workers
men who have sex with men
injections
truckers
migrant labourers
Transmission of HIV
sexual contact
mother-child
contact with infected blood
Preventing HIV
If HIV-negative: use HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) prior to exposure
If HIV-positive: HIV treatment to achieve undetectable viral load
involves combo of 3-4 antiretroviral (ARV) drugs
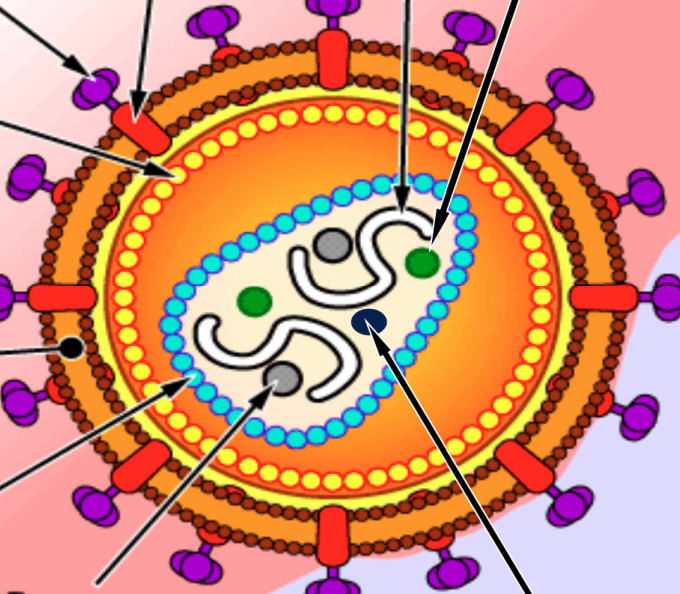
Label the HIV virus
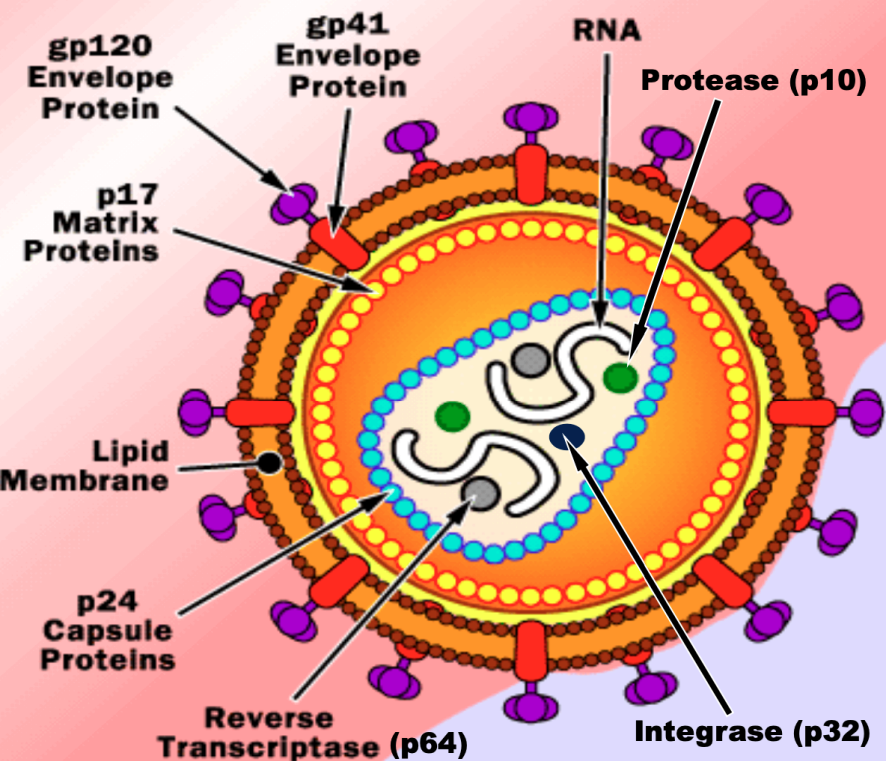
Important structures of HIV virus
Reverse transcriptase (p64): converts RNA to DNA
Integrase (p32): integration of virus into host genome
Protease (p10): cleaves viral proteins to make viruses viable
GP120,41 (glycoprotein): helps the virus attach to host cells
HP41 (glycoprotein): for entry in host cell
Lipid Bilayer: increases vulnerability of human cell to HIV - bc lipid bilayer matches that of human cells
P24 (protein): capsule protein — is first to show up in antigen testing
HIV Life cycle
HIV fuses into the phospholipid bilayer of a normal cell
GP120 and GP41 attach to CR5 receptors on the human cell
people w/o this receptor are resistant to HIV this way
Inside cell, reverse transcriptase converts HIV RNA into dsDNA
Virus integrates with cell, DNA is duplicated and becomes prominent DNA of host cell
Once new DNA is established, HIV buds from cell to find new host cell to infect
When does HIV integration occur after infection?
72 hours - HIV is preventable if treated before this
Pathogenesis of HIV Infection
Dendritic cells at HIV entry site capture virus
migrates virus to lymph nodes and delivers them to CD4+ T cells
Virus replicates in lymph node and enters blood = viremia
Triggers adaptive immune system
Antibodies try to control replication - HIV replicates slowly but this leads to progressive loss of T cells
Virus destroys lymphoid tissue and deplete CD4+ T cells = host susceptible to other pathogens
Course of untreated HIV infection
CD4+ T cell Count
Viral Load
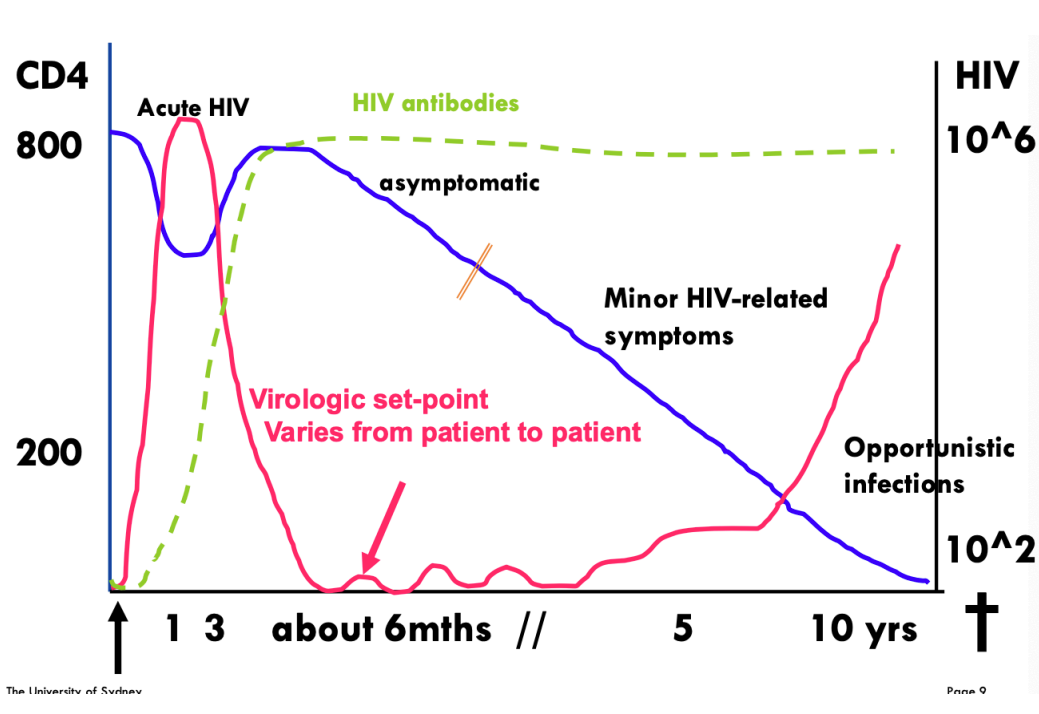
Phases of HIV
Acute Phase (rise in HIV viral load, decrease in CD4+ T cells)
Chronic Phase (clinical latency)
Final Phase (AIDS)
Death
First 2 weeks of HIV
Decline in CD4 and rapid rise in viral load
Symptoms
rash, fever, chills headache, sore throat
fatigue
swollen lymph nodes
sweats
loss of appetite
muscle aches
diarrhea
ulcers
6-9 Months into HIV infection
Stable viral load (patient is usually asymptomatic)
Gradual decline in CD4 count, gradual increase in Viral Load
Opportunistic infections occur due to weakened immune sys. (CD4 <200 cells/ul)
Candida, CMV, etc.
10-12 Years into HIV infection
Untreated patients die from opportunistic infections
Virus vs. Retrovirus
Difference in replication pattern
most viruses replicate using their own DNA/RNA
retroviruses convert their RNA into DNA before entering host and then integrate into host cell genome
Retroviruses are usually permanent — viruses can eventually be cleared by host immune sys after acute infection
Potential Opportunistic Infections: CD4 <200 cells/ul
Candidiasis
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP)
Toxoplasmosis
Potential Opportunistic Infections: CD4 <100 cells/ul
Cryptococcosis
Cryptosporidiosis
Potential Opportunistic Infections: CD4 <50 cells/ul
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
Cytomegalovirus
Microsporidiosis
Cerebral Lymphoma
Potential Opportunistic Infections: Any CD4 count
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Potential Opportunistic Infections: Exotic and Rare
Multicentric Castleman’s Disease
Penicilliosis
Histoplasmosis
Bartonellosis
Rhodococcus
Skin and Oral Conditions by CD4 count: >500 cells/ul
seroconversion rash
seborrheic dermatitis
psoriasis
tinea
anychomycosis
Skin and Oral Conditions by CD4 count: 200-500 cells/ul
oral candidiasis
OHL
herpes zoster
herpes simplex
psoriasis
warts
aychomycosis
xerosis
Skin and Oral Conditions by CD4 count: <200 cells/ul
Disseminated HSV
folliculitis
molluscum contagiosum
kaposi sarcoma
penicilliosis
bacillary angiomatosis
CMV
ulcers
scabies
Kaposi Sarcoma (KS)
AIDS defining virus
caused by herpesvirus-8 (HHV8) when HIV destroys immune sys
formation of tumors in endothelium characterized by abnormal angiogenesis, inflammation and proliferation
causes skin lesions (macules, papules, nodules, plaque) — pink, purple, or brown
HIV diagnostic test
Screening test
ELISA
detects all infected individuals and true negatives (no infection)
Confirmation test
higher specificity
Western Blot
identify true positives and false positives from ELISA
Goals of Antiretroviral Therapy
Virology control
Immunological recovery
Maintain future options for ARV therapy
Minimize side effects
Prevent onward transmission
Antiretroviral regime
Consists of two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) and one active drug that is either:
integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)
non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI)
protease inhibitor (PI) with pharmacokinetic enhancer
Example of NRTI drugs
abacavir
lamivudine
emtricitabine
stavudine
zidovudine
didanosine
tenofovir